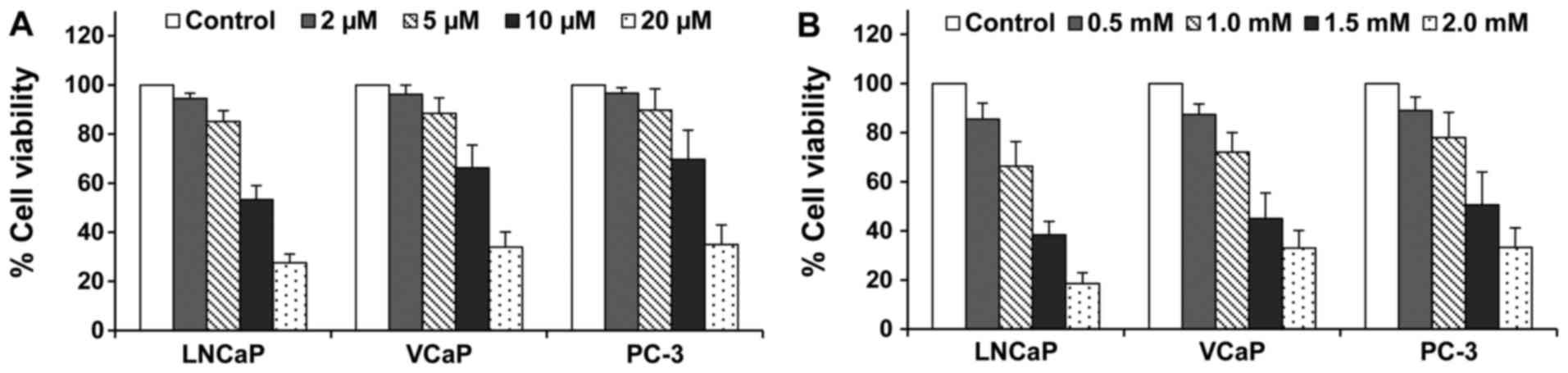
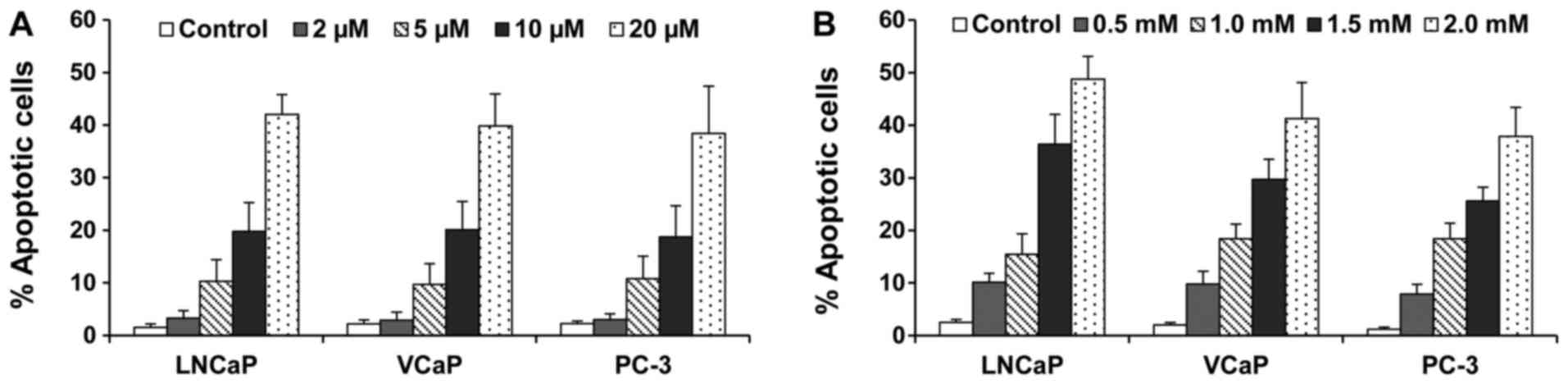
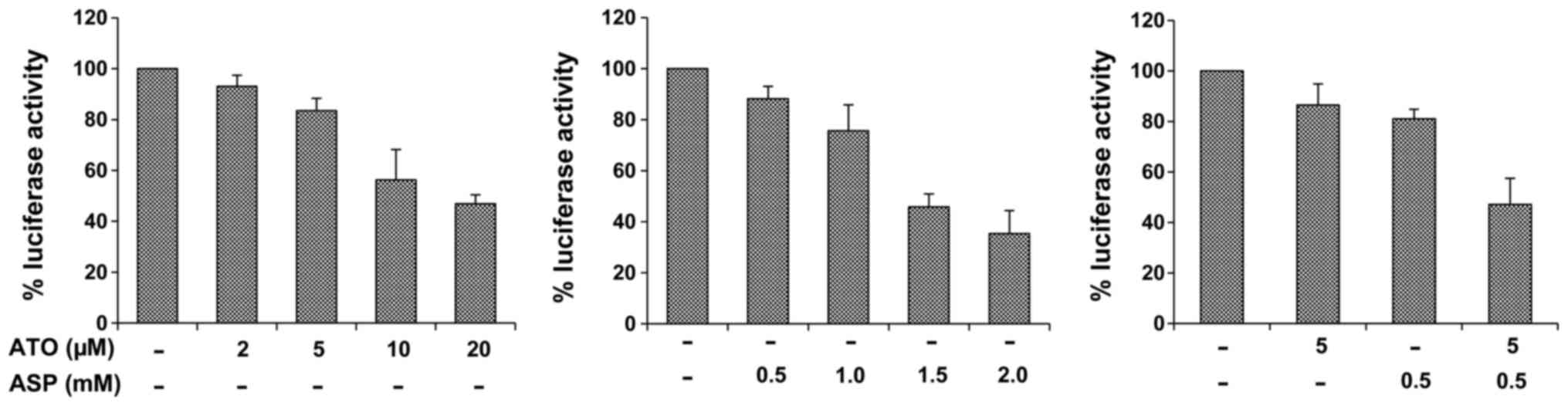
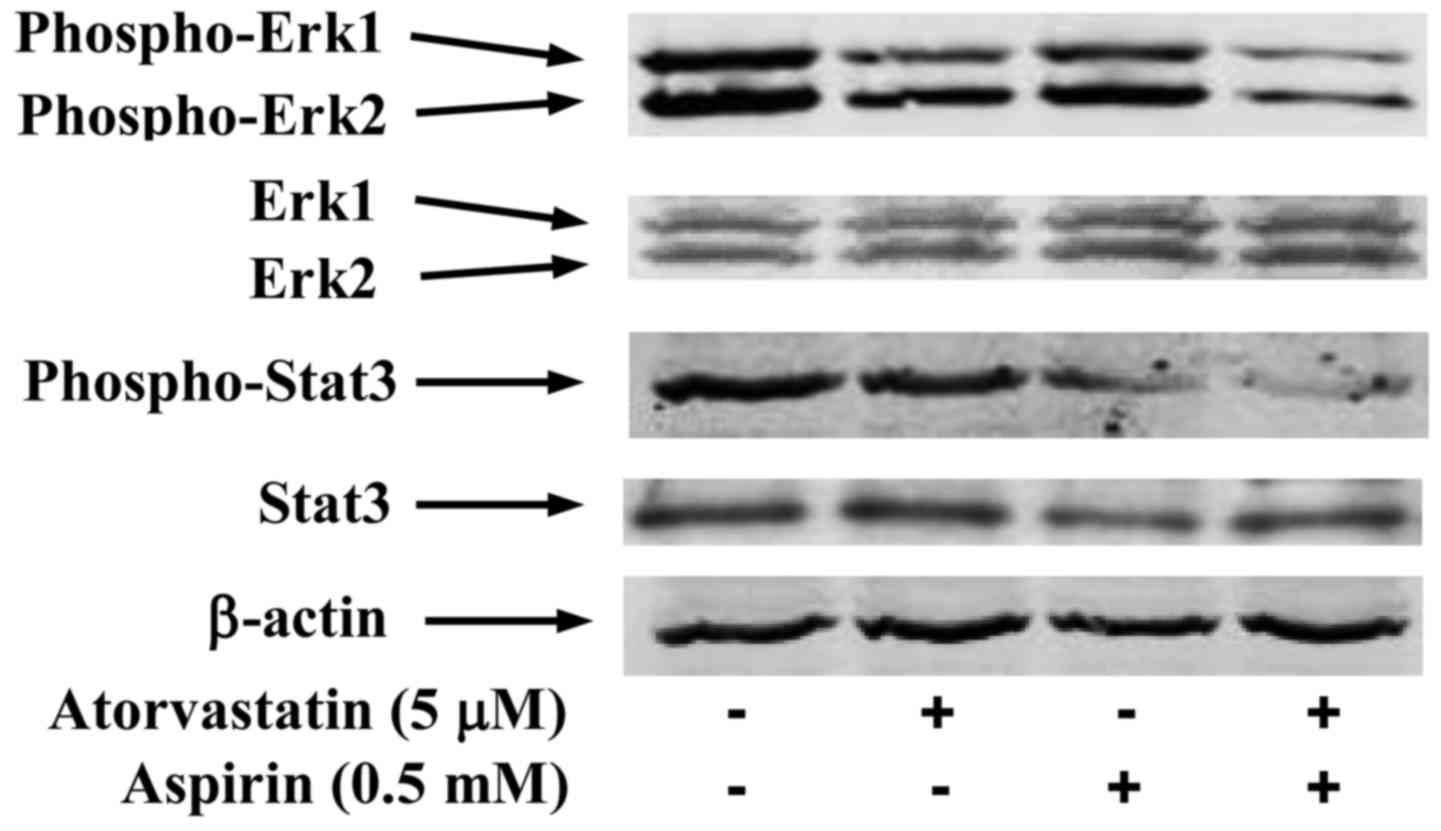
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sweeney CJ, Chen YH, Carducci M, Liu G,
Jarrard DF, Eisenberger M, Wong YN, Hahn N, Kohli M, Cooney MM, et
al: Chemohormonal therapy in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate
cancer. N Engl J Med. 373:737–746. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Malhotra HS and Goa KL: Atorvastatin: An
updated review of its pharmacological properties and use in
dyslipidaemia. Drugs. 61:1835–1881. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jacobs EJ, Rodriguez C, Bain EB, Wang Y,
Thun MJ and Calle EE: Cholesterol-lowering drugs and advanced
prostate cancer incidence in a large U.S. cohort. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 16:2213–2217. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Flick ED, Habel LA, Chan KA, Van Den Eeden
SK, Quinn VP, Haque R, Orav EJ, Seeger JD, Sadler MC, Quesenberry
CP Jr, et al: Statin use and risk of prostate cancer in the
California Men's Health Study cohort. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 16:2218–2225. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Murtola TJ, Tammela TL, Lahtela J and
Auvinen A: Cholesterol-lowering drugs and prostate cancer risk: A
population-based case-control study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 16:2226–2232. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Platz EA, Leitzmann MF, Visvanathan K,
Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC and Giovannucci E: Statin drugs
and risk of advanced prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
98:1819–1825. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cyrus-David MS, Weinberg A, Thompson T and
Kadmon D: The effect of statins on serum prostate specific antigen
levels in a cohort of airline pilots: A preliminary report. J Urol.
173:1923–1925. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Anai S, Tanaka M, Shiverick KT, Kim W,
Takada S, Boehlein S, Goodison S, Mizokami A and Rosser CJ:
Increased expression of cyclooxygenase-2 correlates with resistance
to radiation in human prostate adenocarcinoma cells. J Urol.
177:1913–1917. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Khor LY, Bae K, Pollack A, Hammond ME,
Grignon DJ, Venkatesan VM, Rosenthal SA, Ritter MA, Sandler HM,
Hanks GE, et al: COX-2 expression predicts prostate-cancer outcome:
Analysis of data from the RTOG 92-02 trial. Lancet Oncol.
8:912–920. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Richardsen E, Uglehus RD, Due J, Busch C
and Busund LT: COX-2 is overexpressed in primary prostate cancer
with metastatic potential and may predict survival. A comparison
study between COX-2, TGF-beta, IL-10 and Ki67. Cancer Epidemiol.
34:316–322. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ceylan Y, Lekili M, Muezzinoglu T, Nese N
and Isisag A: Predictive value of cyclooxygenase-2 over expression
for identifying prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia
in prostate biopsy specimens. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 68:255–262.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zheng X, Cui XX, Gao Z, Zhao Y, Lin Y,
Shih WJ, Huang MT, Liu Y, Rabson A, Reddy B, et al: Atorvastatin
and celecoxib in combination inhibits the progression of
androgen-dependent LNCaP xenograft prostate tumors to androgen
independence. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 3:114–124. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zheng X, Cui XX, Avila GE, Huang MT, Liu
Y, Patel J, Kong AN, Paulino R, Shih WJ, Lin Y, et al: Atorvastatin
and celecoxib inhibit prostate PC-3 tumors in immunodeficient mice.
Clin Cancer Res. 13:5480–5487. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen J, Shen P, Zhang XC, Zhao MD, Zhang
XG and Yang L: Efficacy and safety profile of celecoxib for
treating advanced cancers: A meta-analysis of 11 randomized
clinical trials. Clin Ther. 36:1253–1263. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Patel MI, Subbaramaiah K, Du B, Chang M,
Yang P, Newman RA, Cordon-Cardo C, Thaler HT and Dannenberg AJ:
Celecoxib inhibits prostate cancer growth: Evidence of a
cyclooxygenase-2-independent mechanism. Clin Cancer Res.
11:1999–2007. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kashiwagi E, Shiota M, Yokomizo A,
Inokuchi J, Uchiumi T and Naito S: EP2 signaling mediates
suppressive effects of celecoxib on androgen receptor expression
and cell proliferation in prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer
Prostatic Dis. 17:10–17. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pruthi RS, Derksen JE, Moore D, Carson CC,
Grigson G, Watkins C and Wallen E: Phase II trial of celecoxib in
prostate-specific antigen recurrent prostate cancer after
definitive radiation therapy or radical prostatectomy. Clin Cancer
Res. 12:2172–2177. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Murad AS, Down L, Smith G Davey, Donovan
JL, Lane J Athene, Hamdy FC, Neal DE and Martin RM: Associations of
aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug and paracetamol use
with PSA-detected prostate cancer: Findings from a large,
population-based, case-control study (the ProtecT study). Int J
Cancer. 128:1442–1448. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu X, Plummer SJ, Nock NL, Casey G and
Witte JS: Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and decreased risk of
advanced prostate cancer: Modification by lymphotoxin alpha. Am J
Epidemiol. 164:984–989. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dasgupta K, Di Cesar D, Ghosn J, Rajan R,
Mahmud S and Rahme E: Association between nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs and prostate cancer occurrence. Cancer J.
12:130–135. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu Y, Chen JQ, Xie L, Wang J, Li T, He Y,
Gao Y, Qin X and Li S: Effect of aspirin and other non-steroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs on prostate cancer incidence and mortality:
A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 12:552014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choe KS, Cowan JE, Chan JM, Carroll PR,
D'Amico AV and Liauw SL: Aspirin use and the risk of prostate
cancer mortality in men treated with prostatectomy or radiotherapy.
J Clin Oncol. 30:3540–3544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Choe KS, Correa D, Jani AB and Liauw SL:
The use of anticoagulants improves biochemical control of localized
prostate cancer treated with radiotherapy. Cancer. 116:1820–1826.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jacobs EJ, Newton CC, Stevens VL, Campbell
PT, Freedland SJ and Gapstur SM: Daily aspirin use and prostate
cancer-specific mortality in a large cohort of men with
nonmetastatic prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 32:3716–3722. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang H, Cui XX, Chen S, Goodin S, Liu Y,
He Y, Li D, Wang H, Van Doren J, Dipaola RS, et al: Combination of
Lipitor and Celebrex inhibits prostate cancer VCaP cells in vitro
and in vivo. Anticancer Res. 34:3357–3363. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang H, He Y, Cui XX, Goodin S, Wang H,
Du ZY, Li D, Zhang K, Kong AN Tony, DiPaola RS, et al: Potent
inhibitory effect of δ-tocopherol on prostate cancer cells cultured
in vitro and grown as xenograft tumors in vivo. J Agric Food Chem.
62:10752–10758. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wei X, Zhou D, Wang H, Ding N, Cui XX,
Wang H, Verano M, Zhang K, Conney AH, Zheng X, et al: Effects of
pyridine analogs of curcumin on growth, apoptosis and NF-κB
activity in prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Anticancer Res.
33:1343–1350. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ding N, Cui XX, Gao Z, Huang H, Wei X, Du
Z, Lin Y, Shih WJ, Rabson AB, Conney AH, et al: A triple
combination of atorvastatin, celecoxib and tipifarnib strongly
inhibits pancreatic cancer cells and xenograft pancreatic tumors.
Int J Oncol. 44:2139–2145. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang TB, Yan Y, Guo ZF, Zhang XL, Liu H,
Geng J, Yao XD and Zheng JH: Aspirin use and the risk of prostate
cancer: A meta-analysis of 24 epidemiologic studies. Int Urol
Nephrol. 46:1715–1728. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vane JR and Botting RM: The mechanism of
action of aspirin. Thromb Res. 110:255–258. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yoshimura R, Matsuyama M, Kawahito Y,
Takemoto Y, Tsuchida K, Kuratsukuri K, Segawa Y, Shinnka T, Sano H
and Nakatani T: The effects of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors on
urological cancer cells. Int J Mol Med. 13:789–793. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Michalik L, Desvergne B and Wahli W:
Peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptors and cancers: Complex
stories. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:61–70. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Farnier M and Davignon J: Current and
future treatment of hyperlipidemia: The role of statins. Am J
Cardiol. 82:3J–10J. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
McFarlane SI, Muniyappa R, Francisco R and
Sowers JR: Clinical review 145: Pleiotropic effects of statins:
lipid reduction and beyond. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 87:1451–1458.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Goldstein JL and Brown MS: Regulation of
the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 343:425–430. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pruitt K and Der CJ: Ras and Rho
regulation of the cell cycle and oncogenesis. Cancer Lett.
171:1–10. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Olivan M, Rigau M, Colás E, Garcia M,
Montes M, Sequeiros T, Regis L, Celma A, Planas J, Placer J, et al:
Simultaneous treatment with statins and aspirin reduces the risk of
prostate cancer detection and tumorigenic properties in prostate
cancer cell lines. Biomed Res Int. 2015:7621782015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Stark LA, Reid K, Sansom OJ, Din FV,
Guichard S, Mayer I, Jodrell DI, Clarke AR and Dunlop MG: Aspirin
activates the NF-kappaB signalling pathway and induces apoptosis in
intestinal neoplasia in two in vivo models of human colorectal
cancer. Carcinogenesis. 28:968–976. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|