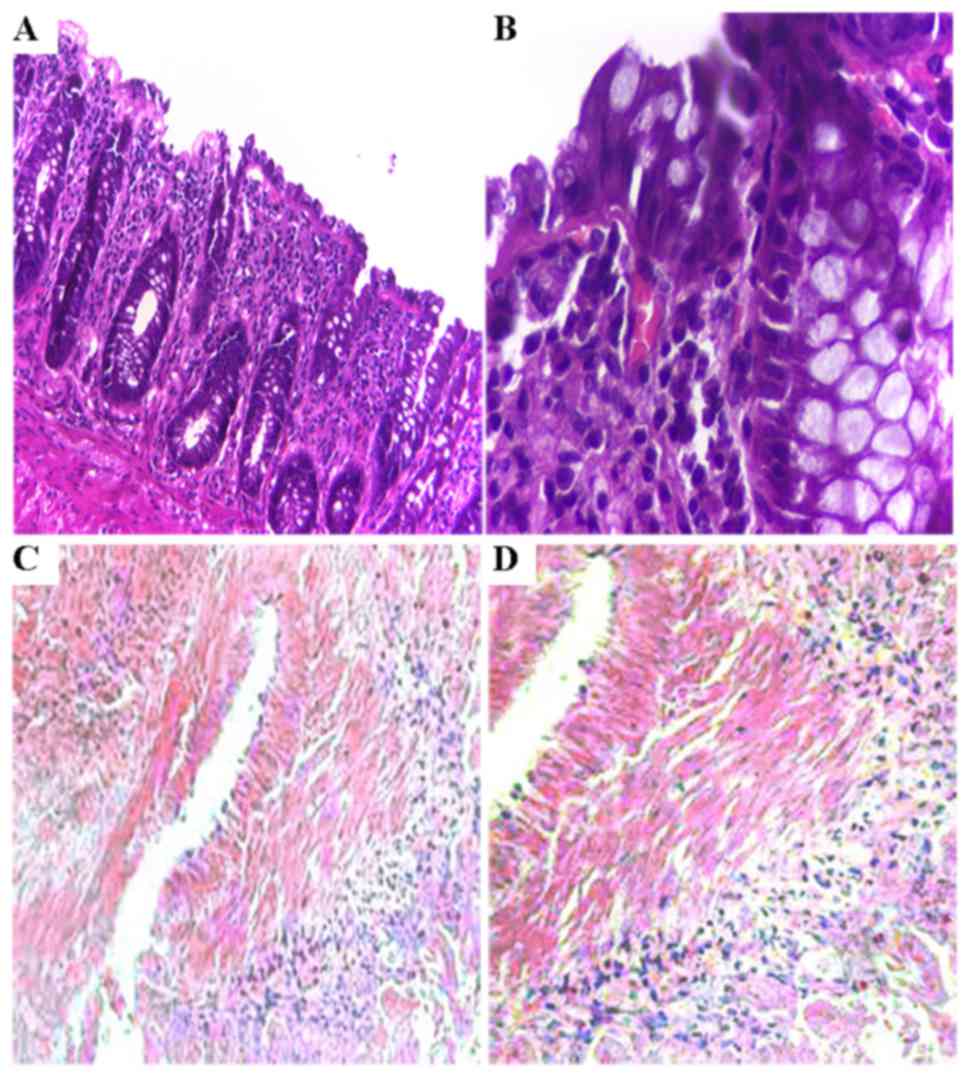
|
1
|
Tenesa A and Dunlop MG: New insights into
the aetiology of colorectal cancer from genome-wide association
studies. Nat Rev Genet. 10:353–358. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Friess H, Langrehr JM, Oettle H, Raedle J,
Niedergethmann M, Dittrich C, Hossfeld DK, Stöger H, Neyns B,
Herzog P, et al: A randomized multi-center phase II trial of the
angiogenesis inhibitor cilengitide (EMD 121974) and gemcitabine
compared with gemcitabine alone in advanced unresectable pancreatic
cancer. BMC Cancer. 6:2852006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Philip PA, Benedetti J, Corless CL, Wong
R, O'Reilly EM, Flynn PJ, Rowland KM, Atkins JN, Mirtsching BC,
Rivkin SE, et al: Phase III study comparing gemcitabine plus
cetuximab versus gemcitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic
adenocarcinoma: Southwest Oncology Group-directed intergroup trial
S0205. J Clin Oncol. 28:3605–3610. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
van Kampen JG, Marijnissen-van Zanten MA,
Simmer F, van der Graaf WT, Ligtenberg MJ and Nagtegaal ID:
Epigenetic targeting in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Treat Rev.
40:656–664. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Garagnani P, Pirazzini C and Franceschi C:
Colorectal cancer microenvironment: Among nutrition, gut
microbiota, inflammation and epigenetics. Curr Pharm Des.
19:765–778. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Postovit LM, Seftor EA, Seftor RE and
Hendrix MJ: Influence of the microenvironment on melanoma cell fate
determination and phenotype. Cancer Res. 66:7833–7836. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Adjei IM and Blanka S: Modulation of the
tumor microenvironment for cancer treatment: A biomaterials
approach. J Funct Biomater. 6:81–103. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shi X and Wang X: The role of MTDH/AEG-1
in the progression of cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:4795–4807.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma H, Xu H and Qin J: Biomimetic tumor
microenvironment on a microfluidic platform. Biomicrofluidics.
7:115012013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schmaus A, Bauer J and Sleeman JP: Sugars
in the microenvironment: The sticky problem of HA turnover in
tumors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 33:1059–1079. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zu X, Zhang Q, Cao R, Liu J, Zhong J, Wen
G and Cao D: Transforming growth factor-β signaling in tumor
initiation, progression and therapy in breast cancer: An update.
Cell Tissue Res. 347:73–84. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Neuzillet C, Tijeras-Raballand A, Cohen R,
Cros J, Faivre S, Raymond E and de Gramont A: Targeting the TGFβ
pathway for cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 147:22–31. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ohshio Y, Teramoto K, Hashimoto M,
Kitamura S, Hanaoka J and Kontani K: Inhibition of transforming
growth factor-β release from tumor cells reduces their motility
associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Rep.
30:1000–1006. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mao Y, Keller ET, Garfield DH, Shen K and
Wang J: Stromal cells in tumor microenvironment and breast cancer.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 32:303–315. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Quante M, Varga J, Wang TC and Greten FR:
The gastrointestinal tumor microenvironment. Gastroenterology.
145:63–78. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee JY, Jeong W, Lim W, Lim CH, Bae SM,
Kim J, Bazer FW and Song G: Hypermethylation and
post-transcriptional regulation of DNA methyltransferases in the
ovarian carcinomas of the laying hen. PLoS One. 8:e616582013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xue G, Ren Z, Chen Y, Zhu J, Du Y, Pan D,
Li X and Hu B: A feedback regulation between miR-145 and DNA
methyltransferase 3b in prostate cancer cell and their responses to
irradiation. Cancer Lett. 361:121–127. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mendell JT: MicroRNAs: Critical regulators
of development, cellular physiology and malignancy. Cell Cycle.
4:1179–1184. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vaiopoulos AG, Athanasoula KCh and
Papavassiliou AG: NF-κB in colorectal cancer. J Mol Med.
91:1029–1037. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hamidi T, Singh AK and Chen T: Genetic
alterations of DNA methylation machinery in human diseases.
Epigenomics. 7:247–265. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cea M, Cagnetta A, Gobbi M, Patrone F,
Richardson PG, Hideshima T and Anderson KC: New insights into the
treatment of multiple myeloma with histone deacetylase inhibitors.
Curr Pharm Des. 19:734–744. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Andreoli F, Barbosa AJ, Parenti MD and Del
Rio A: Modulation of epigenetic targets for anticancer therapy:
Clinicopathological relevance, structural data and drug discovery
perspectives. Curr Pharm Des. 19:578–613. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Esteller M: Epigenetics in cancer. N Engl
J Med. 358:1148–1159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Laird PW: The power and the promise of DNA
methylation markers. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:253–266. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Markowitz SD and Bertagnolli MM: Molecular
origins of cancer: Molecular basis of colorectal cancer. N Engl J
Med. 361:2449–2460. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu Q and Ni X: ROS-mediated DNA
methylation pattern alterations in carcinogenesis. Curr Drug
Targets. 16:13–19. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Luczak MW and Jagodziński PP: The role of
DNA methylation in cancer development. Folia Histochem Cytobiol.
44:143–154. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pastuszak-Lewandoska D, Kordiak J,
Migdalska-Sęk M, Czarnecka KH, Antczak A, Górski P, Nawrot E,
Kiszałkiewicz JM, Domańska D and Brzeziańska-Lasota E: Quantitative
analysis of mRNA expression levels and DNA methylation profiles of
three neighboring genes: FUS1NPRL2/G21 and RASSF1A in non-small
cell lung cancer patients. Respir Res. 16:762015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Garzon R, Fabbri M, Cimmino A, Calin GA
and Croce CM: MicroRNA expression and function in cancer. Trends
Mol Med. 12:580–587. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xiong Y, Fang JH, Yun JP, Yang J, Zhang Y,
Jia WH and Zhuang SM: Effects of microRNA-29 on apoptosis,
tumorigenicity, and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 51:836–845. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fabbri M, Garzon R, Cimmino A, Liu Z,
Zanesi N, Callegari E, Liu S, Alder H, Costinean S,
Fernandez-Cymering C, et al: MicroRNA-29 family reverts aberrant
methylation in lung cancer by targeting DNA methyltransferases 3A
and 3B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:15805–15810. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu H, Cheung IY, Guo HF and Cheung NK:
MicroRNA miR-29 modulates expression of immunoinhibitory molecule
B7-H3: Potential implications for immune based therapy of human
solid tumors. Cancer Res. 69:6275–6281. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ji W, Yang L, Yuan J, Yang L, Zhang M, Qi
D, Duan X, Xuan A, Zhang W, Lu J, et al: MicroRNA-152 targets DNA
methyltransferase 1 in NiS-transformed cells via a feedback
mechanism. Carcinogenesis. 34:446–453. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Langhe R, Norris L, Saadeh FA,
Blackshields G, Varley R, Harrison A, Gleeson N, Spillane C, Martin
C, O'Donnell DM, et al: A novel serum microRNA panel to
discriminate benign from malignant ovarian disease. Cancer Lett.
356:628–636. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pinto R, De Summa S, Danza K, Popescu O,
Paradiso A, Micale L, Merla G, Palumbo O, Carella M and Tommasi S:
MicroRNA expression profiling in male and female familial breast
cancer. Br J Cancer. 111:2361–2368. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Omrane I and Benammar-Elgaaied A: The
immune microenvironment of the colorectal tumor: Involvement of
immunity genes and microRNAs belonging to the TH17 pathway. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1856:28–38. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Slaby O, Svoboda M, Michalek J and Vyzula
R: MicroRNAs in colorectal cancer: Translation of molecular biology
into clinical application. Mol Cancer. 8:1022009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen C, Yu Z, Li Y, Fichna J and Storr M:
Effects of berberine in the gastrointestinal tract - a review of
actions and therapeutic implications. Am J Chin Med. 42:1053–1070.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang L, Cao H, Lu N, Liu L, Wang B, Hu T,
Israel DA, Peek RM Jr, Polk DB and Yan F: Berberine inhibits
proliferation and down-regulates epidermal growth factor receptor
through activation of Cbl in colon tumor cells. PLoS One.
8:e566662013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Park JJ, Seo SM, Kim EJ, Lee YJ, Ko YG, Ha
J and Lee M: Berberine inhibits human colon cancer cell migration
via AMP-activated protein kinase-mediated downregulation of
integrin β1 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 426:461–467.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Murthy KN Chidambara, Jayaprakasha GK and
Patil BS: The natural alkaloid berberine targets multiple pathways
to induce cell death in cultured human colon cancer cells. Eur J
Pharmacol. 688:14–21. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kan SF, Yu CH, Pu HF, Hsu JM, Chen MJ and
Wang PS: Anti-proliferative effects of evodiamine on human prostate
cancer cell lines DU145 and PC3. J Cell Biochem. 101:44–56. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kobayashi Y: The nociceptive and
anti-nociceptive effects of evodiamine from fruits of Evodia
rutaecarpa in mice. Planta Med. 69:425–428. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chien CC, Wu MS, Shen SC, Ko CH, Chen CH,
Yang LL and Chen YC: Activation of JNK contributes to
evodiamine-induced apoptosis and G2/M arrest in human colorectal
carcinoma cells: A structure-activity study of evodiamine. PLoS
One. 9:e997292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|