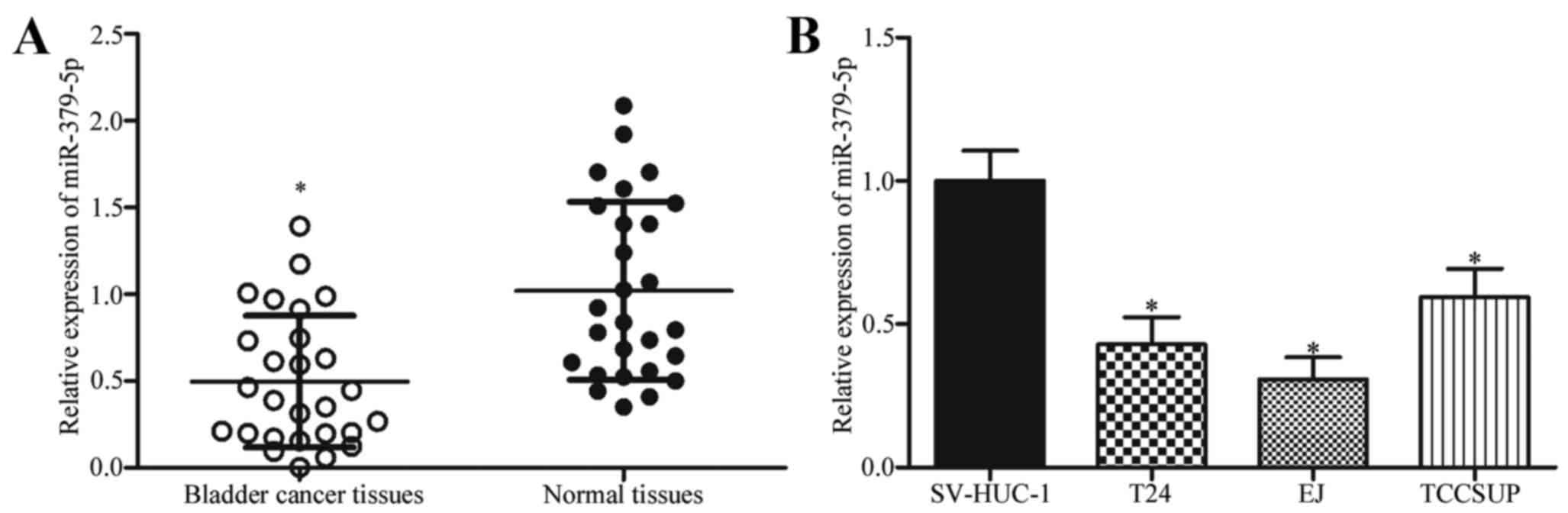
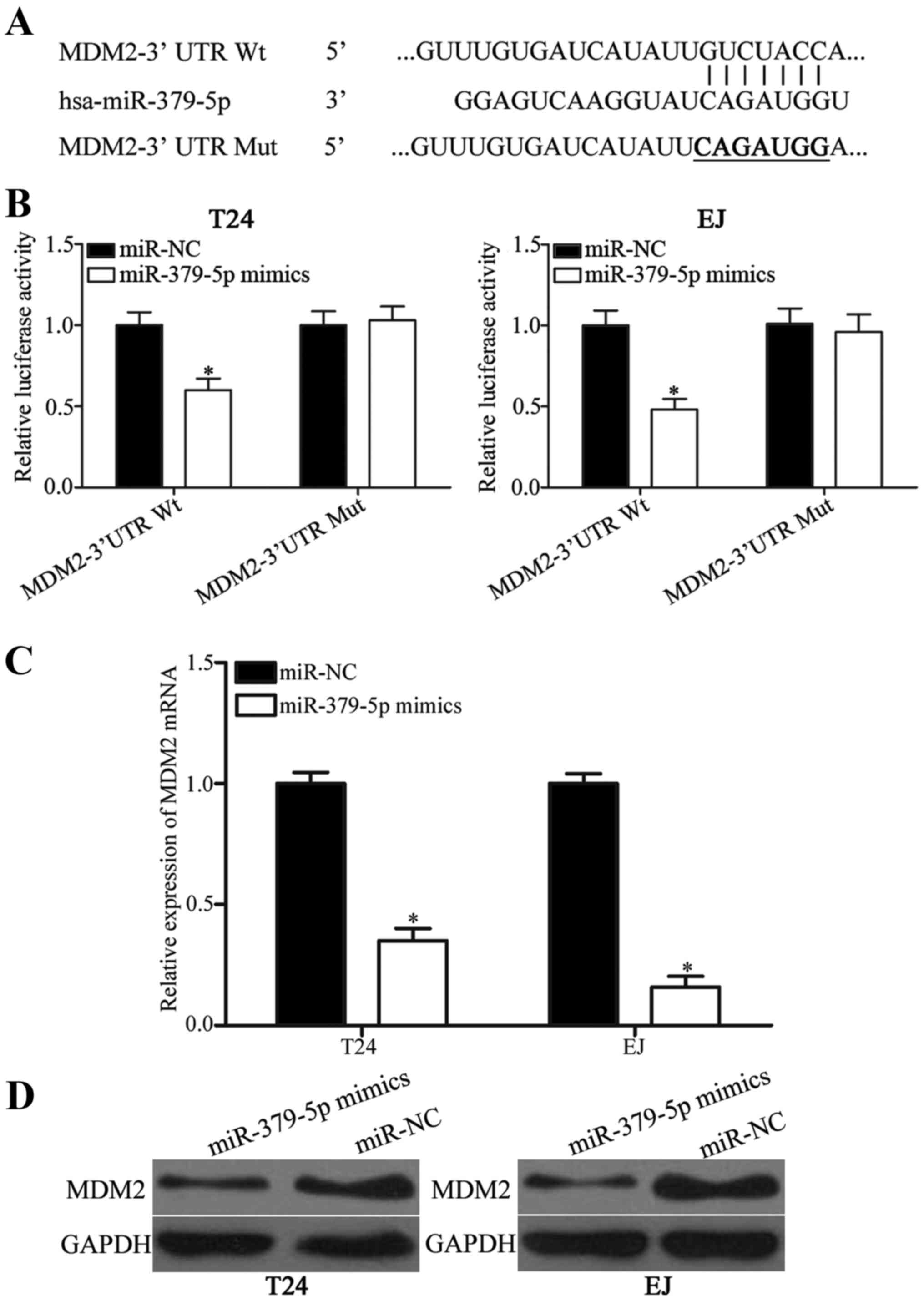
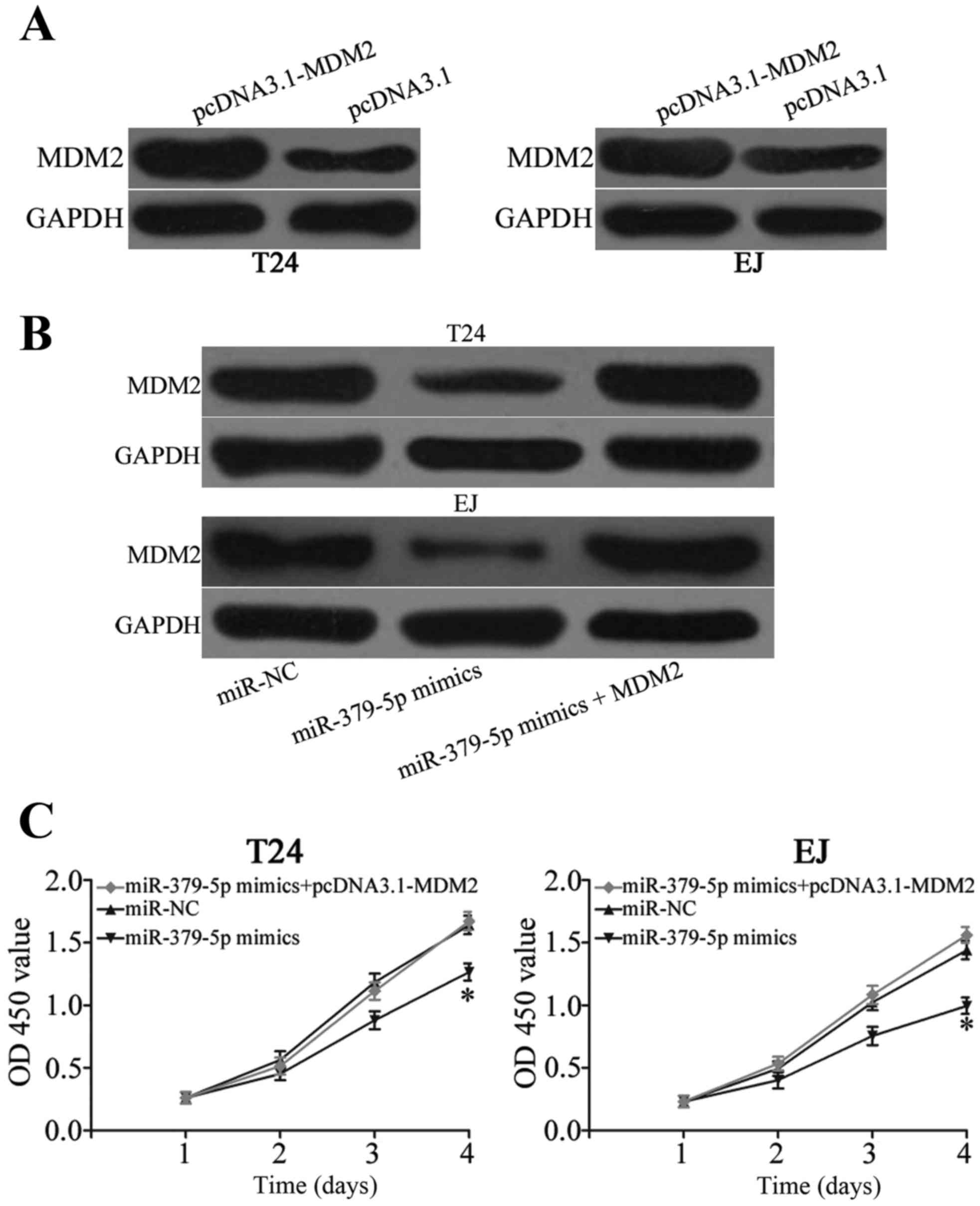
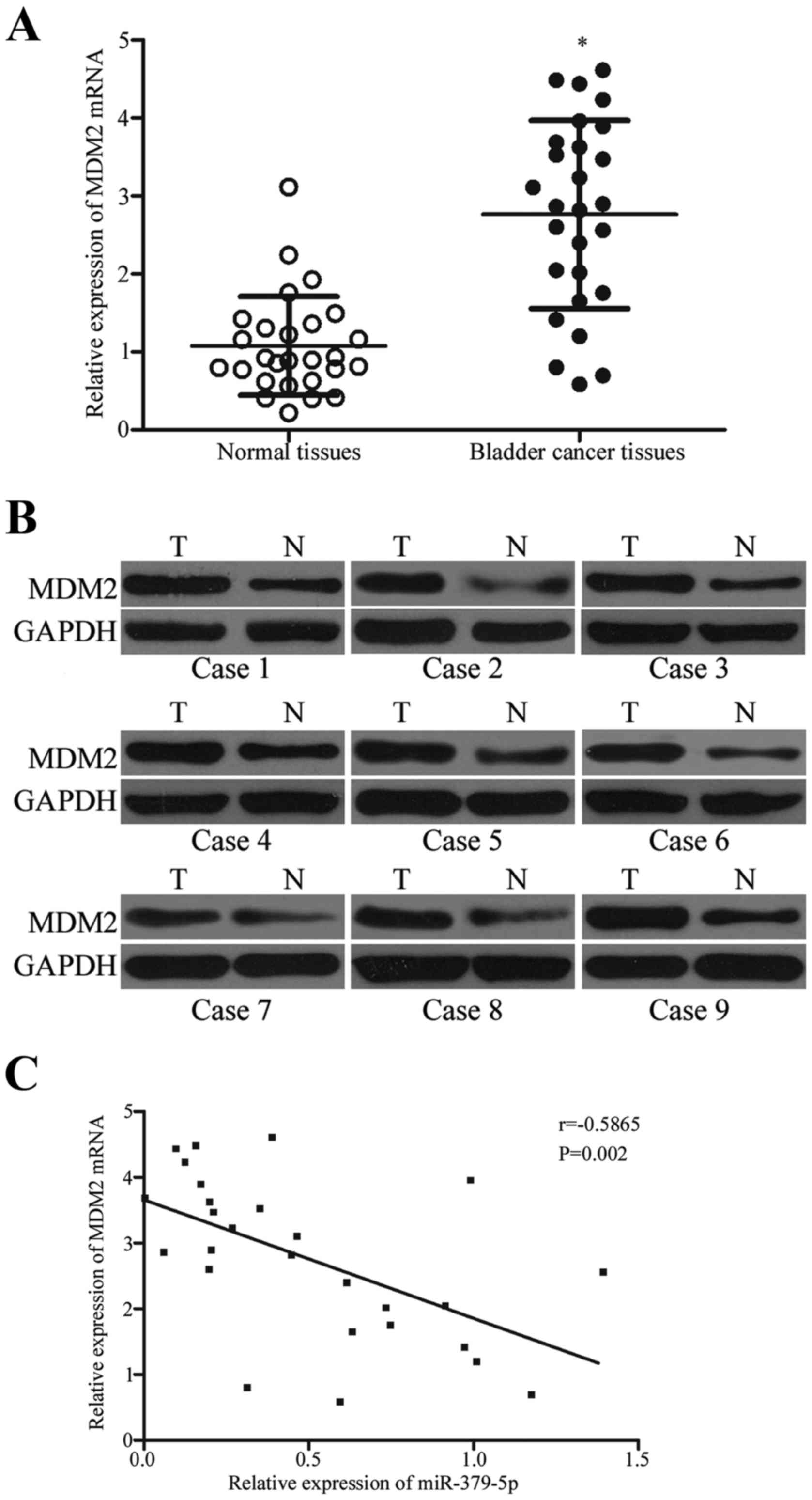
|
1
|
Zhang Y, Sun Y, Chen T, Hu H, Xie W, Qiao
Z, Ding N, Xie L, Li S, Wang W, et al: Genetic variations
rs11892031 and rs401681 are associated with bladder cancer risk in
a Chinese population. Int J Mol Sci. 15:19330–19341. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Knowles MA: Molecular pathogenesis of
bladder cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 13:287–297. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Scélo G and Brennan P: The epidemiology of
bladder and kidney cancer. Nat Clin Pract Urol. 4:205–217. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu D, Zhou Y, Pan H, Zhou J, Fan Y and Qu
P: microRNA-99a inhibiting cell proliferation, migration and
invasion by targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 in
bladder cancer. Oncol Lett. 7:1219–1224. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim WJ and Bae SC: Molecular biomarkers in
urothelial bladder cancer. Cancer Sci. 99:646–652. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ambros V: MicroRNA pathways in flies and
worms: Growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell. 113:673–676.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu W, Sun M, Zou GM and Chen J: MicroRNA
and cancer: Current status and prospective. Int J Cancer.
120:953–960. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nelson KM and Weiss GJ: MicroRNAs and
cancer: Past, present, and potential future. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:3655–3660. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Garzon R, Fabbri M, Cimmino A, Calin GA
and Croce CM: MicroRNA expression and function in cancer. Trends
Mol Med. 12:580–587. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Alvarez-Garcia I and Miska EA: MicroRNA
functions in animal development and human disease. Development.
132:4653–4662. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tana C, Giamberardino MA and Cipollone F:
microRNA profiling in atherosclerosis, diabetes and migraine. Ann
Med. 49:93–105. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Piletič K and Kunej T: MicroRNA epigenetic
signatures in human disease. Arch Toxicol. 90:2405–2419. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shang Y, Zang A, Li J, Jia Y, Li X, Zhang
L, Huo R, Yang J, Feng J, Ge K, et al: MicroRNA-383 is a tumor
suppressor and potential prognostic biomarker in human non-small
cell lung caner. Biomed Pharmacother. 83:1175–1181. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Khan S, Brougham CL, Ryan J, Sahrudin A,
O'Neill G, Wall D, Curran C, Newell J, Kerin MJ and Dwyer RM:
miR-379 regulates cyclin B1 expression and is decreased in breast
cancer. PLoS One. 8:e687532013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen JS, Li HS, Huang JQ, Dong SH, Huang
ZJ, Yi W, Zhan GF, Feng JT, Sun JC and Huang XH: MicroRNA-379-5p
inhibits tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting FAK/AKT
signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 375:73–83.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen JS, Huang JQ, Dong SH and Huang XH:
Effects of microRNA-379-5p on proliferation, migration and invasion
of hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.
96:1450–1453. 2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhong XY, Yu JH, Zhang WG, Wang ZD, Dong
Q, Tai S, Cui YF and Li H: MicroRNA-421 functions as an oncogenic
miRNA in biliary tract cancer through down-regulating farnesoid X
receptor expression. Gene. 493:44–51. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu D, Niu X, Pan H, Zhou Y, Qu P and Zhou
J: MicroRNA-335 is downregulated in bladder cancer and inhibits
cell growth, migration and invasion via targeting ROCK1. Mol Med
Rep. 13:4379–4385. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang X, Liu Y, Liu X, Yang J, Teng G,
Zhang L and Zhou C: MiR-124 inhibits cell proliferation, migration
and invasion by directly targeting SOX9 in lung adenocarcinoma.
Oncol Rep. 35:3115–3121. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Baker M: RNA interference: MicroRNAs as
biomarkers. Nature. 464:12272010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gururajan M, Josson S, Chu GC, Lu CL, Lu
YT, Haga CL, Zhau HE, Liu C, Lichterman J, Duan P, et al: miR-154*
and miR-379 in the DLK1-DIO3 microRNA mega-cluster regulate
epithelial to mesenchymal transition and bone metastasis of
prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 20:6559–6569. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Osada H and Takahashi T: MicroRNAs in
biological processes and carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 28:2–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pichiorri F, Suh SS, Rocci A, De Luca L,
Taccioli C, Santhanam R, Zhou W, Benson DM Jr, Hofmainster C, Alder
H, et al: Downregulation of p53-inducible microRNAs 192, 194, and
215 impairs the p53/MDM2 autoregulatory loop in multiple myeloma
development. Cancer Cell. 18:349–351. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Marchetti A, Buttitta F, Girlando S, Palma
P Dalla, Pellegrini S, Fina P, Doglioni C, Bevilacqua G and
Barbareschi M: mdm2 gene alterations and mdm2 protein expression in
breast carcinomas. J Pathol. 175:31–38. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Marchetti A, Buttitta F, Pellegrini S,
Merlo G, Chella A, Angeletti CA and Bevilacqua G: mdm2 gene
amplification and overexpression in non-small cell lung carcinomas
with accumulation of the p53 protein in the absence of p53 gene
mutations. Diagn Mol Pathol. 4:93–97. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang C, Liu J, Wang X, Wu R, Lin M,
Laddha SV, Yang Q, Chan CS and Feng Z: MicroRNA-339-5p inhibits
colorectal tumorigenesis through regulation of the MDM2/p53
signaling. Oncotarget. 5:9106–9117. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Riou G, Barrois M, Prost S, Terrier MJ,
Theodore C and Levine AJ: The p53 and mdm-2 genes in human
testicular germ-cell tumors. Mol Carcinog. 12:124–131. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lianes P, Orlow I, Zhang ZF, Oliva MR,
Sarkis AS, Reuter VE and Cordon-Cardo C: Altered patterns of MDM2
and TP53 expression in human bladder cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
86:1325–1330. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tuna B, Yörükoğlu K, Tüzel E, Güray M,
Mungan U and Kirkali Z: Expression of p53 and mdm2 and their
significance in recurrence of superficial bladder cancer. Pathol
Res Pract. 199:323–328. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schmitz-Dräger BJ, Kushima M, Goebell P,
Jax TW, Gerharz CD, Bültel H, Schulz WA, Ebert T and Ackermann R:
p53 and MDM2 in the development and progression of bladder cancer.
Eur Urol. 32:487–493. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shiina H, Igawa M, Shigeno K, Yamasaki Y,
Urakami S, Yoneda T, Wada Y, Honda S and Nagasaki M: Clinical
significance of mdm2 and p53 expression in bladder cancer. A
comparison with cell proliferation and apoptosis. Oncology.
56:239–247. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|