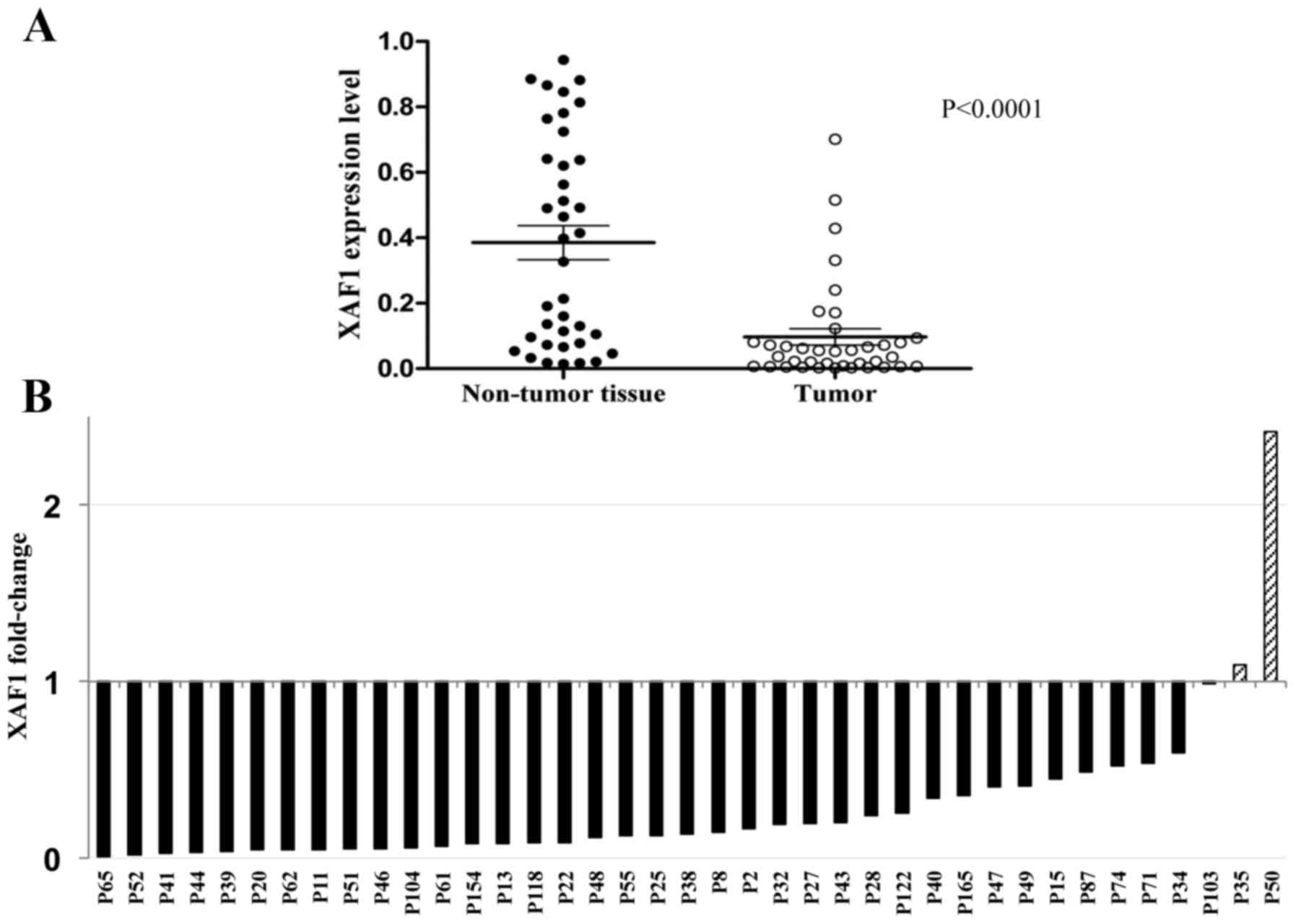
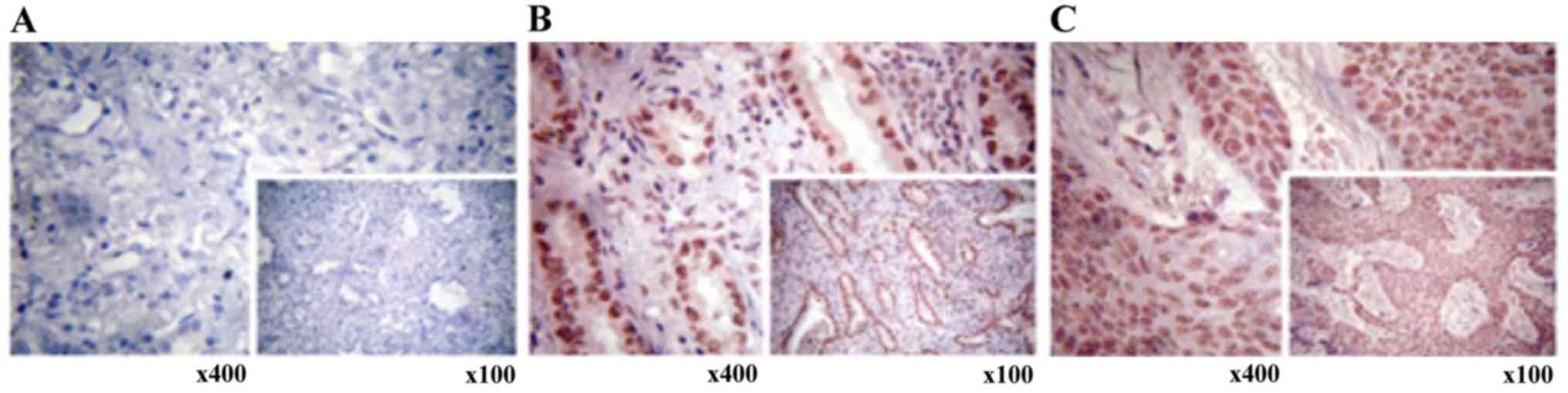
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M,
Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and
Bray F: GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality
Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11 (Internet). International Agency
for Research on Cancer. Lyon, France: 2013 http://globocan.iarc.frJanuary 23–2015.
|
|
2
|
Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern D, Read
W, Tierney R, Vlahiotis A, Spitznagel EL and Piccirillo J: Changing
epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over
the last 30 years: Analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and
end results database. J Clin Oncol. 24:4539–4544. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Holcik M, Gibson H and Korneluk RG: XIAP:
Apoptotic brake and promising therapeutic target. Apoptosis.
6:253–261. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liston P, Fong WG, Kelly NL, Toji S,
Miyazaki T, Conte D, Tamai K, Craig CG, McBurney MW and Korneluk
RG: Identification of XAF1 as an antagonist of XIAP anti-caspase
activity. Nat Cell Biol. 3:128–133. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Arora V, Cheung HH, Plenchette S, Micali
OC, Liston P and Korneluk RG: Degradation of survivin by the
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP)-XAF1 complex. J Biol Chem.
282:26202–26209. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xia Y, Novak R, Lewis J, Duckett CS and
Phillips AC: Xaf1 can cooperate with TNFalpha in the induction of
apoptosis, independently of interaction with XIAP. Mol Cell
Biochem. 286:67–76. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Straszewski-Chavez SL, Visintin IP,
Karassina N, Los G, Liston P, Halaban R, Fadiel A and Mor G: XAF1
mediates tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis and X-linked
inhibitor of apoptosis cleavage by acting through the mitochondrial
pathway. J Biol Chem. 282:13059–13072. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee MG, Huh JS, Chung SK, Lee JH, Byun DS,
Ryu BK, Kang MJ, Chae KS, Lee SJ, Lee CH, et al: Promoter CpG
hypermethylation and downregulation of XAF1 expression in human
urogenital malignancies: Implication for attenuated p53 response to
apoptotic stresses. Oncogene. 25:5807–5822. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zou B, Chim CS, Pang R, Zeng H, Dai Y,
Zhang R, Lam CS, Tan VP, Hung IF, Lan HY, et al: XIAP-associated
factor 1 (XAF1), a novel target of p53, enhances p53-mediated
apoptosis via post-translational modification. Mol Carcinog.
51:422–432. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang J, Gu Q, Li M, Zhang W, Yang M, Zou
B, Chan S, Qiao L, Jiang B, Tu S, et al: Identification of XAF1 as
a novel cell cycle regulator through modulating G2/M checkpoint and
interaction with checkpoint kinase 1 in gastrointestinal cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 30:1507–1516. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sun PH, Zhu LM, Qiao MM, Zhang YP, Jiang
SH, Wu YL and Tu SP: The XAF1 tumor suppressor induces autophagic
cell death via upregulation of Beclin-1 and inhibition of Akt
pathway. Cancer Lett. 310:170–180. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu LM, Shi DM, Dai Q, Cheng XJ, Yao WY,
Sun PH, Ding Y, Qiao MM, Wu YL, Jiang SH, et al: Tumor suppressor
XAF1 induces apoptosis, inhibits angiogenesis and inhibits tumor
growth in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 5:5403–5415. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Byun DS, Cho K, Ryu BK, Lee MG, Kang MJ,
Kim HR and Chi SG: Hypermethylation of XIAP-associated factor 1, a
putative tumor suppressor gene from the 17p13.2 locus, in human
gastric adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 63:7068–7075. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chung SK, Lee MG, Ryu BK, Lee JH, Han J,
Byun DS, Chae KS, Lee KY, Jang JY, Kim HJ, et al: Frequent
alteration of XAF1 in human colorectal cancers: Implication for
tumor cell resistance to apoptotic stresses. Gastroenterology.
132:2459–2477. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shibata T, Noguchi T, Takeno S, Gabbert
HE, Ramp U and Kawahara K: Disturbed XIAP and XAF1 expression
balance is an independent prognostic factor in gastric
adenocarcinomas. Ann Surg Oncol. 15:3579–3587. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang F, Wu LM, Zhou L, Chen QX, Xie HY,
Feng XW and Zheng SS: Predictive value of expression and promoter
hypermethylation of XAF1 in hepatitis B virus-associated
hepatocellular carcinoma treated with transplantation. Ann Surg
Oncol. 15:3494–3502. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sakemi R, Yano H, Ogasawara S, Akiba J,
Nakashima O, Fukahori S, Sata M and Kojiro M: X-linked inhibitor of
apoptosis (XIAP) and XIAP-associated factor-1 expressions and their
relationship to apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma and
non-cancerous liver tissues. Oncol Rep. 18:65–70. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pinho MB, Costas F, Sellos J, Dienstmann
R, Andrade PB, Herchenhorn D, Peixoto FA, Santos VO, Small IA,
Guimarães DP, et al: XAF1 mRNA expression improves progression-free
and overall survival for patients with advanced bladder cancer
treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Urol Oncol. 27:382–390.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang J, Yao WY, Zhu Q, Tu SP, Yuan F,
Wang HF, Zhang YP and Yuan YZ: XAF1 as a prognostic biomarker and
therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci. 101:559–567.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen YB, Shu J, Yang WT, Shi L, Guo XF,
Wang FG and Qian YY: XAF1 as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic
target in squamous cell lung cancer. Chin Med J. 124:3238–3243.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kempkensteffen C, Hinz S, Jäger T, Weikert
S, Krause H, Schostak M, Christoph F, Strenziok R, Miller K and
Schrader M: Expression levels of the IAP antagonists XAF1,
Smac/DIABLO and HtrA2 in testicular germ cell tumours. Aktuelle
Urol. 39:436–441. 2008.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ling ZQ, Lv P, Lu XX, Yu JL, Han J, Ying
LS, Zhu X, Zhu WY, Fang XH, Wang S, et al: Circulating methylated
XAF1 DNA indicates poor prognosis for gastric cancer. PLoS One.
8:e671952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fang X, Liu Z, Fan Y, Zheng C, Nilson S,
Egevad L, Ekman P and Xu D: Switch to full-length of XAF1 mRNA
expression in prostate cancer cells by the DNA methylation
inhibitor. Int J Cancer. 118:2485–2489. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zou B, Chim CS, Zeng H, Leung SY, Yang Y,
Tu SP, Lin MC, Wang J, He H, Jiang SH, et al: Correlation between
the single-site CpG methylation and expression silencing of the
XAF1 gene in human gastric and colon cancers. Gastroenterology.
131:1835–1843. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dai C, Whitesell L, Rogers AB and
Lindquist S: Heat shock factor 1 is a powerful multifaceted
modifier of carcinogenesis. Cell. 130:1005–1018. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang J, He H, Yu L, Xia HH, Lin MC, Gu Q,
Li M, Zou B, An X, Jiang B, et al: HSF1 down-regulates XAF1 through
transcriptional regulation. J Biol Chem. 281:2451–2459. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Logan IR, McNeill HV, Cook S, Lu X, Meek
DW, Fuller-Pace FV, Lunec J and Robson CN: Heat shock factor-1
modulates p53 activity in the transcriptional response to DNA
damage. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:2962–2973. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang W, Guo Z, Jiang B, Niu L, Xia G,
Wang X, Cheng T, Zhang Y and Wang J: Identification of a functional
p53 responsive element within the promoter of XAF1 gene in
gastrointestinal cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 36:1031–1037.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tu SP, Liston P, Cui JT, Lin MC, Jiang XH,
Yang Y, Gu Q, Jiang SH, Lum CT, Kung HF, et al: Restoration of XAF1
expression induces apoptosis and inhibits tumor growth in gastric
cancer. Int J Cancer. 125:688–697. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Augello C, Caruso L, Maggioni M, Donadon
M, Montorsi M, Santambrogio R, Torzilli G, Vaira V, Pellegrini C,
Roncalli M, et al: Inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs)
expression and their prognostic significance in hepatocellular
carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 9:1252009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kempkensteffen C, Fritzsche FR, Johannsen
M, Weikert S, Hinz S, Dietel M, Riener MO, Moch H, Jung K, Krause
H, et al: Down-regulation of the pro-apoptotic XIAP associated
factor-1 (XAF1) during progression of clear-cell renal cancer. BMC
Cancer. 9:2762009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Y, Mao H, Hao Q, Wang Y, Yang Y, Shen
L, Huang S and Liu P: Association of expression of XIAP-associated
factor 1 (XAF1) with clinicopathologic factors, overall survival,
microvessel density and cisplatin-resistance in ovarian cancer.
Regul Pept. 178:36–42. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Christians ES, Yan LJ and Benjamin I: Heat
shock factor 1 and heat shock proteins: Critical partners in
protection against acute cell injury. Crit Care Med. 30 Suppl
1:S43–S50. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Westerheide SD and Morimoto RI: Heat shock
response modulators as therapeutic tools for diseases of protein
conformation. J Biol Chem. 280:33097–33100. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Santagata S, Hu R, Lin NU, Mendillo ML,
Collins LC, Hankinson SE, Schnitt SJ, Whitesell L, Tamimi RM,
Lindquist S, et al: High levels of nuclear heat-shock factor 1
(HSF1) are associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:18378–18383. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li T, Chen CL, Wang JD, Cui SD, Cui DY and
Guo W: Expression of heat-shock transcription factor 1 and X-linked
inhibitor of apoptosis protein-associated factor-1 in
gastrointestinal cancer. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 28:487–490.
2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Vihervaara A and Sistonen L: HSF1 at a
glance. J Cell Sci. 127:261–266. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Santagata S, Mendillo ML, Tang YC,
Subramanian A, Perley CC, Roche SP, Wong B, Narayan R, Kwon H,
Koeva M, et al: Tight coordination of protein translation and HSF1
activation supports the anabolic malignant state. Science.
341:12383032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee MG, Han J, Jeong SI, Her NG, Lee JH,
Ha TK, Kang MJ, Ryu BK and Chi SG: XAF1 directs apoptotic switch of
p53 signaling through activation of HIPK2 and ZNF313. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 111:15532–15537. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Toh CK, Gao F, Lim WT, Leong SS, Fong KW,
Yap SP, Hsu AA, Eng P, Koong HN, Thirugnanam A, et al:
Never-smokers with lung cancer: Epidemiologic evidence of a
distinct disease entity. J Clin Oncol. 24:2245–2251. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Govindan R, Ding L, Griffith M,
Subramanian J, Dees ND, Kanchi KL, Maher CA, Fulton R, Fulton L,
Wallis J, et al: Genomic landscape of non-small cell lung cancer in
smokers and never-smokers. Cell. 150:1121–1134. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gou LY, Niu FY, Wu YL and Zhong WZ:
Differences in driver genes between smoking-related and
non-smoking-related lung cancer in the Chinese population. Cancer.
121 Suppl 17:S3069–S3079. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|