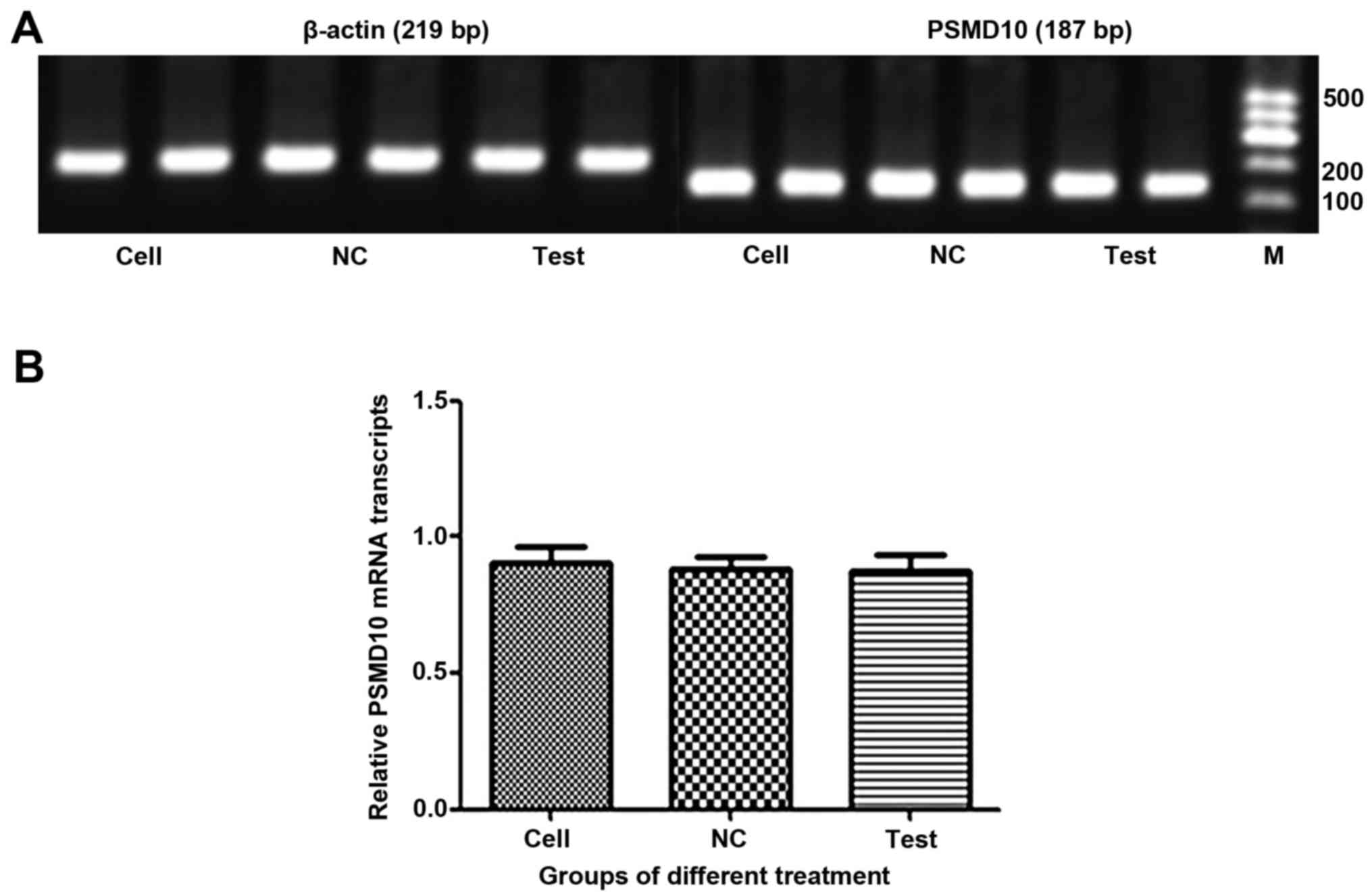
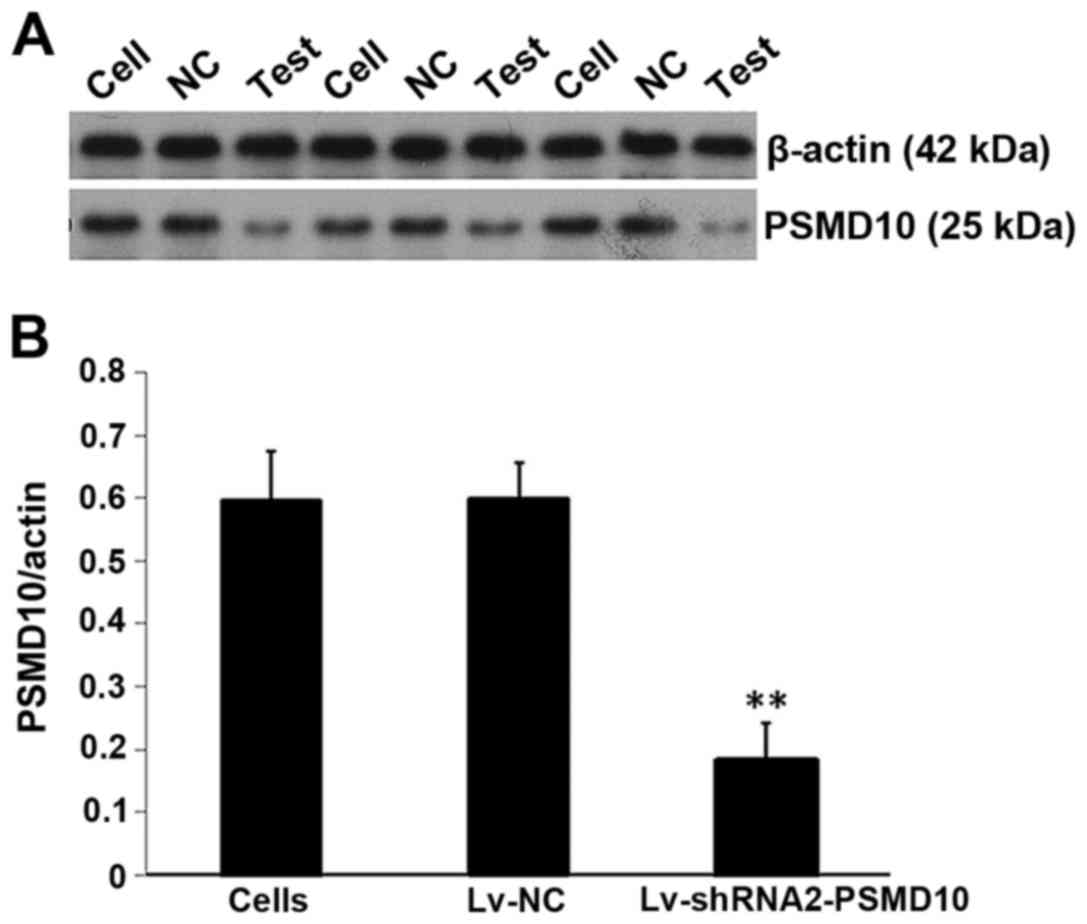
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
National Cancer Institute SEER database:
Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. 2014.(cited
June 30). http://seer.cancer.gov/
|
|
3
|
Becker N: Epidemiology of multiple
myeloma. Multiple Myeloma: Recent Results in Cancer Research.
Moehler T and Goldschmid H: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany:
Springer-Verlag; pp. 25–35. 2011, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bergsagel PL: Epidemiology, etiology, and
molecularpathogenesis. Multiple Myeloma. Richardson PG and Anderson
KC: London, Chicago: Remedica Publi-shing; pp. 1–24. 2004
|
|
5
|
Liu Y, Xu J, Jiang M, Ni L, Chen Y and
Ling Y: Association between functional PSMD10 Rs111638916 variant
regulated by MiR-505 and gastric cancer risk in a Chinese
population. Cell Physiol Biochem. 37:1010–1017. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Uddin MH, Choi MH, Kim WH, Jang JJ and
Hong ST: Involvement of PSMD10, CDK4, and tumor suppressors in
development of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma of Syrian Golden
Hamsters induced by Clonorchis sinensis and
N-nitrosodimethylamine. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 9:e00040082015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li J, Tian F, Li D, Chen J, Jiang P, Zheng
S, Li X and Wang S: MiR-605 represses PSMD10/Gankyrin and inhibits
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell progression. FEBS Lett.
588:3491–3500. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen BF, Suen YK, Gu S, Li L and Chan WY:
A miR-199a/miR-214 self-regulatory network via PSMD10, TP53 and
DNMT1 in testicular germ cell tumor. Sci Rep. 4:64132014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Luo T, Fu J, Xu A, Su B, Ren Y, Li N, Zhu
J, Zhao X, Dai R, Cao J, et al: PSMD10/gankyrin induces autophagy
to promote tumor progression through cytoplasmic interaction with
ATG7 and nuclear transactivation of ATG7 expression. Autophagy.
12:1355–1371. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu T, Tao Y, Yang M, Chen P, Gao X, Zhang
Y, Zhang T, Chen Z, Hou J, Zhang Y, et al: Profiling human protein
degradome delineates cellular responses to proteasomal inhibition
and reveals a feedback mechanism in regulating proteasome
homeostasis. Cell Res. 24:1214–1230. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tomko RJ Jr, Funakoshi M, Schneider K,
Wang J and Hochstrasser M: Heterohexameric ring arrangement of the
eukaryotic proteasomal ATPases: Implications for proteasome
structure and assembly. Mol Cell. 38:393–403. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Higashitsuji H, Itoh K, Nagao T, Dawson S,
Nonoguchi K, Kido T, Mayer RJ, Arii S and Fujita J: Reduced
stability of retinoblastoma protein by gankyrin, an oncogenic
ankyrin-repeat protein overexpressed in hepatomas. Nat Med.
6:96–99. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Higashitsuji H, Higashitsuji H, Itoh K,
Sakurai T, Nagao T, Sumitomo Y, Masuda T, Dawson S, Shimada Y,
Mayer RJ, et al: The oncoprotein gankyrin binds to MDM2/HDM2,
enhancing ubiquitylation and degradation of p53. Cancer Cell.
8:75–87. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bai Z, Tai Y, Li W, Zhen C, Gu W, Jian Z,
Wang Q, Lin JE, Zhao Q, Gong W, et al: Gankyrin activates IL-8 to
promote hepatic metastasis of colorectal cancer. Cancer Res.
73:4548–4558. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhen C, Chen L, Zhao Q, Liang B, Gu YX,
Bai ZF, Wang K, Xu X, Han QY, Fang DF, et al: Gankyrin promotes
breast cancer cell metastasis by regulating Rac1 activity.
Oncogene. 32:3452–3460. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Meng Y, He L, Guo X, Tang S, Zhao X, Du R,
Jin J, Bi Q, Li H, Nie Y, et al: Gankyrin promotes the
proliferation of human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 297:9–17.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Misiewicz-Krzeminska I, Sarasquete ME,
Quwaider D, Krzeminski P, Ticona FV, Paíno T, Delgado M, Aires A,
Ocio EM, García-Sanz R, et al: Restoration of microRNA-214
expression reduces growth of myeloma cells through positive
regulation of P53 and inhibition of DNA replication. Haematologica.
98:640–648. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W,
Yalcin A, Weber K and Tuschl T: Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs
mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature.
411:494–498. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Karagiannis TC and El-Osta A: siRNAs:
Mechanism of RNA interference, in vivo and potential clinical
applications. Cancer Biol Ther. 3:1069–1074. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R and Agami R: A
system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian
cells. Science. 296:550–553. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Paddison PJ, Caudy AA, Bernstein E, Hannon
GJ and Conklin DS: Short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) induce
sequence-specific silencing in mammalian cells. Genes Dev.
16:948–958. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Reynolds A, Leake D, Boese Q, Scaringe S,
Marshall WS and Khvorova A: Rational siRNA design for RNA
interference. Nat Biotechnol. 22:326–330. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Barøy T, Sørensen K, Lindeberg MM and
Frengen E: shRNA expression constructs designed directly from siRNA
oligonucleotide sequences. Mol Biotechnol. 45:116–120. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kumar SK, Rajkumar SV, Dispenzieri A, Lacy
MQ, Hayman SR, Buadi FK, Zeldenrust SR, Dingli D, Russell SJ, Lust
JA, et al: Improved survival in multiple myeloma and the impact of
novel therapies. Blood. 111:2516–2520. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rovira M, Rosinol L, Martinez C,
Fernández-Avilés F and Blade J: Is there a curative potential of
autologous stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma? Long-term
results from a single-centre series. Bone Marrow Transplant.
42:S147(abstract P592). 2009.
|
|
26
|
Gahrton G, Svensson H, Cavo M, Apperly J,
Bacigalupo A, Björkstrand B, Bladé J, Cornelissen J, de Laurenzi A,
Facon T, et al: European Group for Blood and Marrow
Transplantation: Progress in allogenic bone marrow and peripheral
blood stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma: A comparison
between transplants performed 1983–93 and 1994–98 at European Group
for Blood and Marrow Transplantation centres. Br J Haematol.
113:209–216. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kyle RA and Rajkumar SV: Multiple myeloma.
Blood. 111:2962–2972. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Adams J: The proteasome: A suitable
antineoplastic target. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:349–360. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bianchi G, Oliva L, Cascio P, Pengo N,
Fontana F, Cerruti F, Orsi A, Pasqualetto E, Mezghrani A, Calbi V,
et al: The proteasome load versus capacity balance determines
apoptotic sensitivity of multiple myeloma cells to proteasome
inhibition. Blood. 113:3040–3049. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Meister S, Schubert U, Neubert K, Herrmann
K, Burger R, Gramatzki M, Hahn S, Schreiber S, Wilhelm S, Herrmann
M, et al: Extensive immunoglobulin production sensitizes myeloma
cells for proteasome inhibition. Cancer Res. 67:1783–1792. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ortiz-Navarrete V, Seelig A, Gernold M,
Frentzel S, Kloetzel PM and Hämmerling GJ: Subunit of the 20S
proteasome (multicatalytic proteinase) encoded by the major
histocompatibility complex. Nature. 353:662–664. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rivett AJ, Bose S, Brooks P and Broadfoot
KI: Regulation of proteasome complexes by gamma-interferon and
phosphorylation. Biochimie. 83:363–366. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Niewerth D, Jansen G, Assaraf YG, Zweegman
S, Kaspers GJ and Cloos J: Molecular basis of resistance to
proteasome inhibitors in hematological malignancies. Drug Resist
Updat. 18:18–35. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Agarwal AK, Xing C, DeMartino GN, Mizrachi
D, Hernandez MD, Sousa AB, de Martínez Villarreal L, dos Santos HG
and Garg A: PSMB8 encoding the β5i proteasome subunit is
mutated in joint contractures, muscle atrophy, microcytic anemia,
and panniculitis-induced lipodystrophy syndrome. Am J Hum Genet.
87:866–872. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kincaid EZ, Che JW, York I, Escobar H,
Reyes-Vargas E, Delgado JC, Welsh RM, Karow ML, Murphy AJ,
Valenzuela DM, et al: Mice completely lacking immunoproteasomes
show major changes in antigen presentation. Nat Immunol.
13:129–135. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chondrogianni N, Stratford FLL, Trougakos
IP, Friguet B, Rivett AJ and Gonos ES: Central role of the
proteasome in senescence and survival of human fibroblasts:
Induction of a senescence-like phenotype upon its inhibition and
resistance to stress upon its activation. J Biol Chem.
278:28026–28037. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chondrogianni N, Tzavelas C, Pemberton AJ,
Nezis IP, Rivett AJ and Gonos ES: Overexpression of proteasome
beta5 assembled subunit increases the amount of proteasome and
confers ameliorated response to oxidative stress and higher
survival rates. J Biol Chem. 280:11840–11850. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Franke NE, Niewerth D, Assaraf YG, van
Meerloo J, Vojtekova K, van Zantwijk CH, Zweegman S, Chan ET, Kirk
CJ, Geerke DP, et al: Impaired bortezomib binding to mutant β5
subunit of the proteasome is the underlying basis for bortezomib
resistance in leukemia cells. Leukemia. 26:757–768. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Blackburn C, Gigstad KM, Hales P, Garcia
K, Jones M, Bruzzese FJ, Barrett C, Liu JX, Soucy TA, Sappal DS, et
al: Characterization of a new series of non-covalent proteasome
inhibitors with exquisite potency and selectivity for the 20S
beta5-subunit. Biochem J. 430:461–476. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rückrich T, Kraus M, Gogel J, Beck A, Ovaa
H, Verdoes M, Overkleeft HS, Kalbacher H and Driessen C:
Characterization of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in
bortezomib-adapted cells. Leukemia. 23:1098–1105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Niewerth D, Franke NE, Jansen G, Assaraf
YG, van Meerloo J, Kirk CJ, Degenhardt J, Anderl J, Schimmer AD,
Zweegman S, et al: Higher ratio immune versus constitutive
proteasome level as novel indicator of sensitivity of pediatric
acute leukemia cells to proteasome inhibitors. Haematologica.
98:1896–1904. 2013.b. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Heckmann D, Laufs S, Maier P, Zucknick M,
Giordano FA, Veldwijk MR, Eckstein V, Wenz F, Zeller WJ, Fruehauf
S, et al: A lentiviral CXCR4 overexpression and knockdown model in
colorectal cancer cell lines reveals plerixafor-dependent
suppression of SDF-1α-induced migration and invasion. Onkologie.
34:502–508. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Christoph T, Bahrenberg G, De Vry J,
Englberger W, Erdmann VA, Frech M, Kögel B, Röhl T, Schiene K,
Schröder W, et al: Investigation of TRPV1 loss-of-function
phenotypes in transgenic shRNA expressing and knockout mice. Mol
Cell Neurosci. 37:579–589. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sacca R, Engle SJ, Qin W, Stock JL and
McNeish JD: Genetically engineered mouse models in drug discovery
research. Methods Mol Biol. 602:37–54. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lozano G and Zambetti GP: Gankyrin: An
intriguing name for a novel regulator of p53 and RB. Cancer Cell.
8:3–4. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Umemura A, Itoh Y, Itoh K, Yamaguchi K,
Nakajima T, Higashitsuji H, Onoue H, Fukumoto M, Okanoue T and
Fujita J: Association of gankyrin protein expression with early
clinical stages and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5
expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
47:493–502. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ooi MG, Hayden PJ, Kotoula V, McMillin DW,
Charalambous E, Daskalaki E, Raje NS, Munshi NC, Chauhan D,
Hideshima T, et al: Interactions of the Hdm2/p53 and proteasome
pathways may enhance the antitumor activity of bortezomib. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:7153–7160. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|