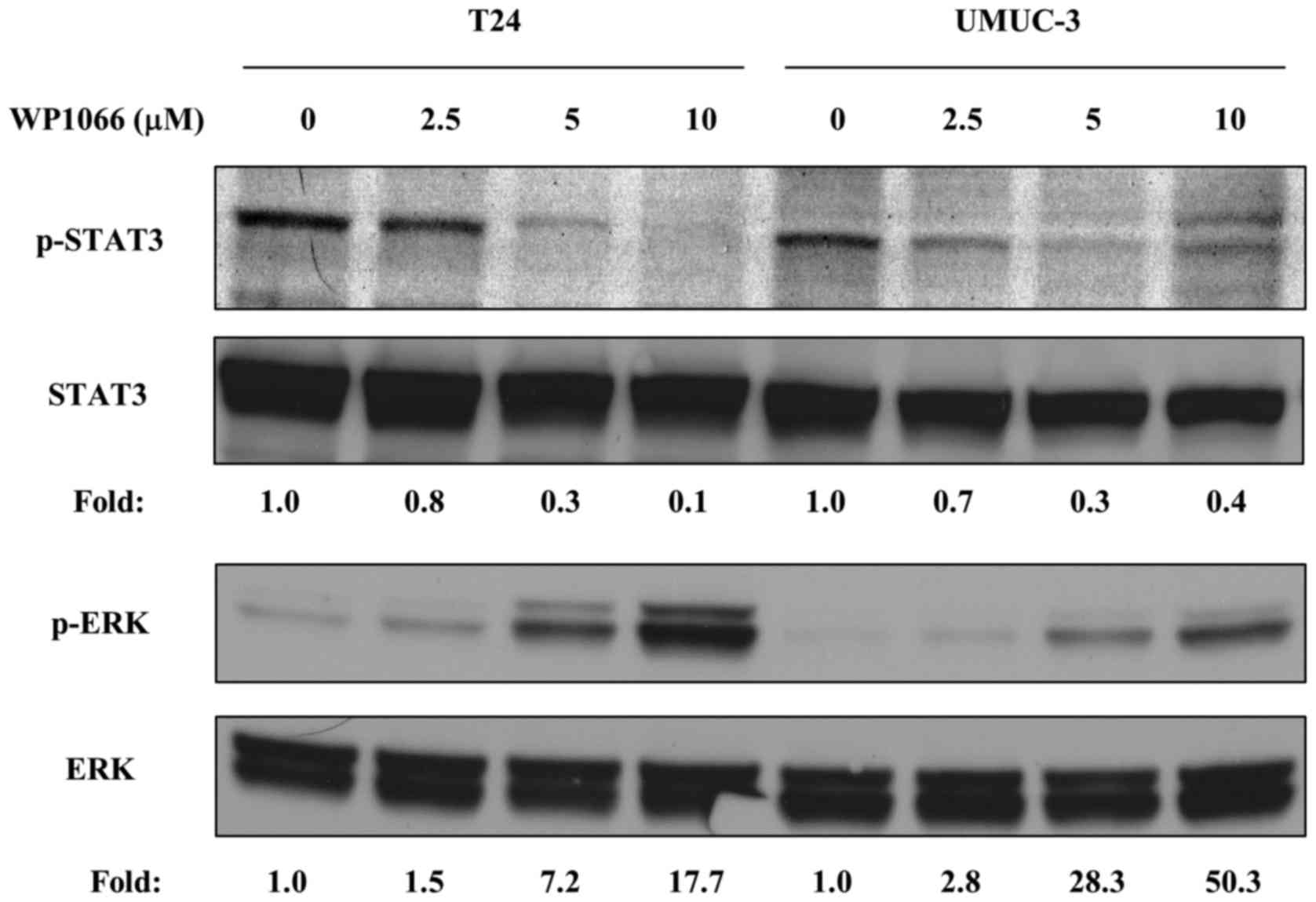
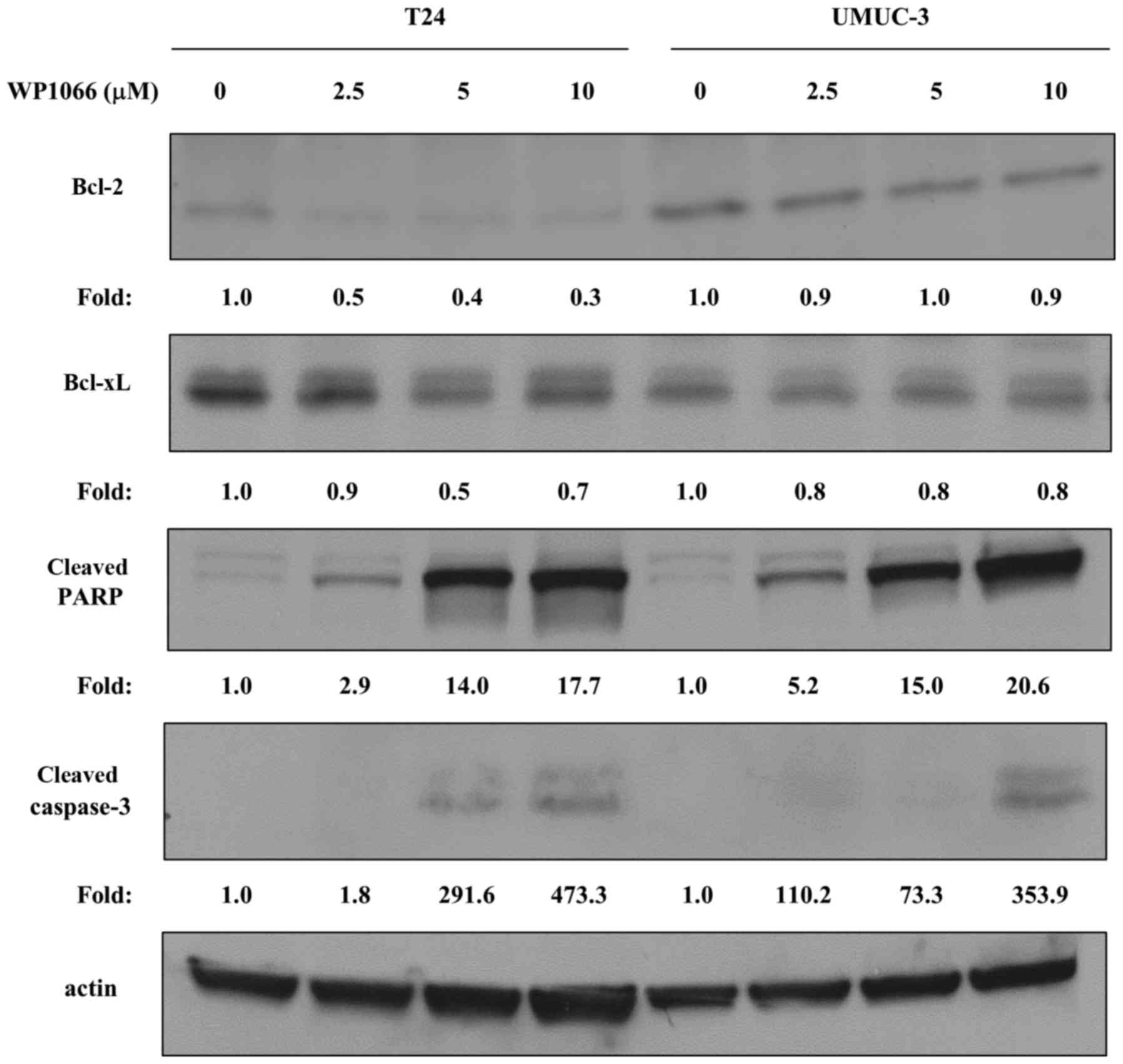
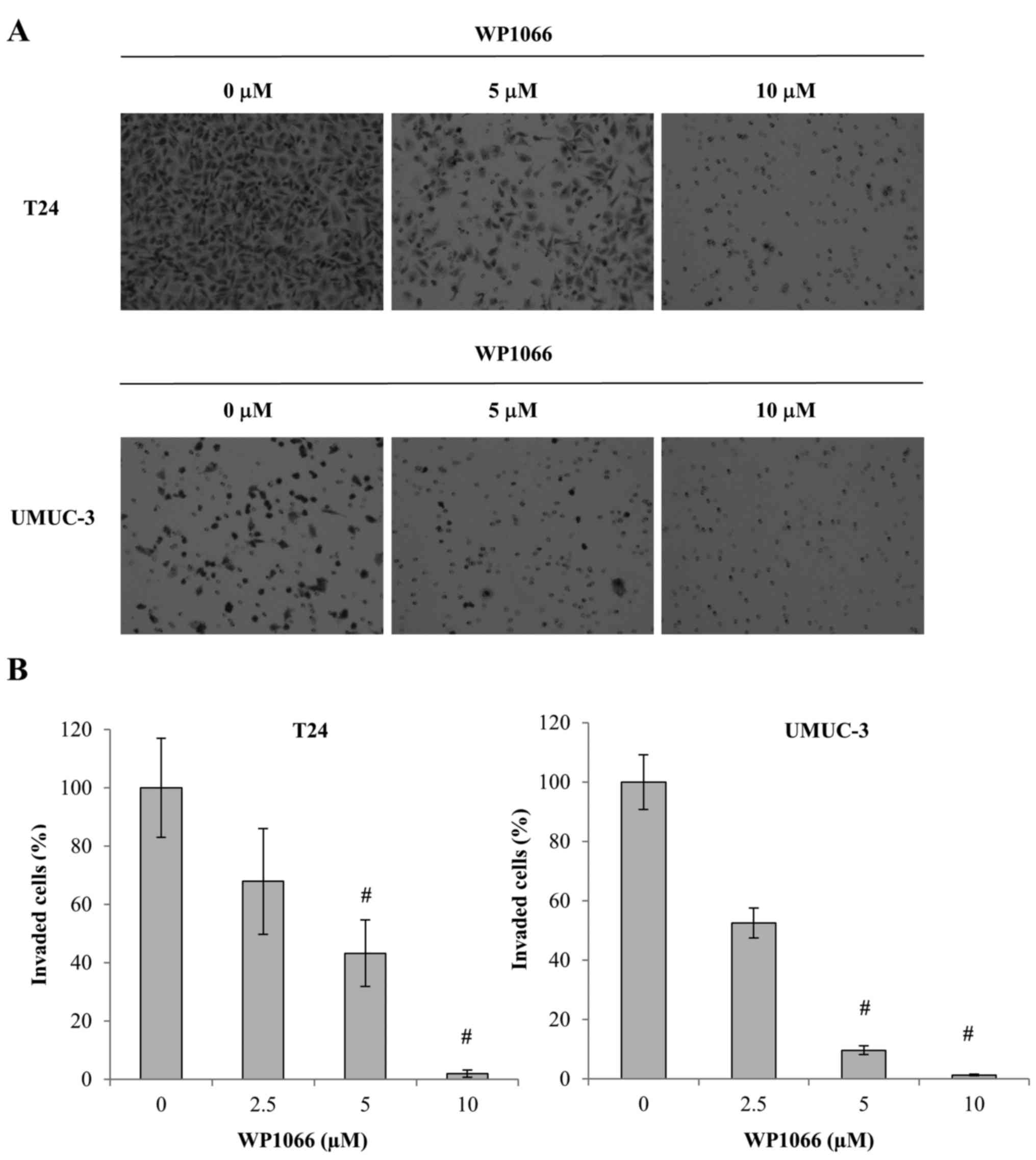
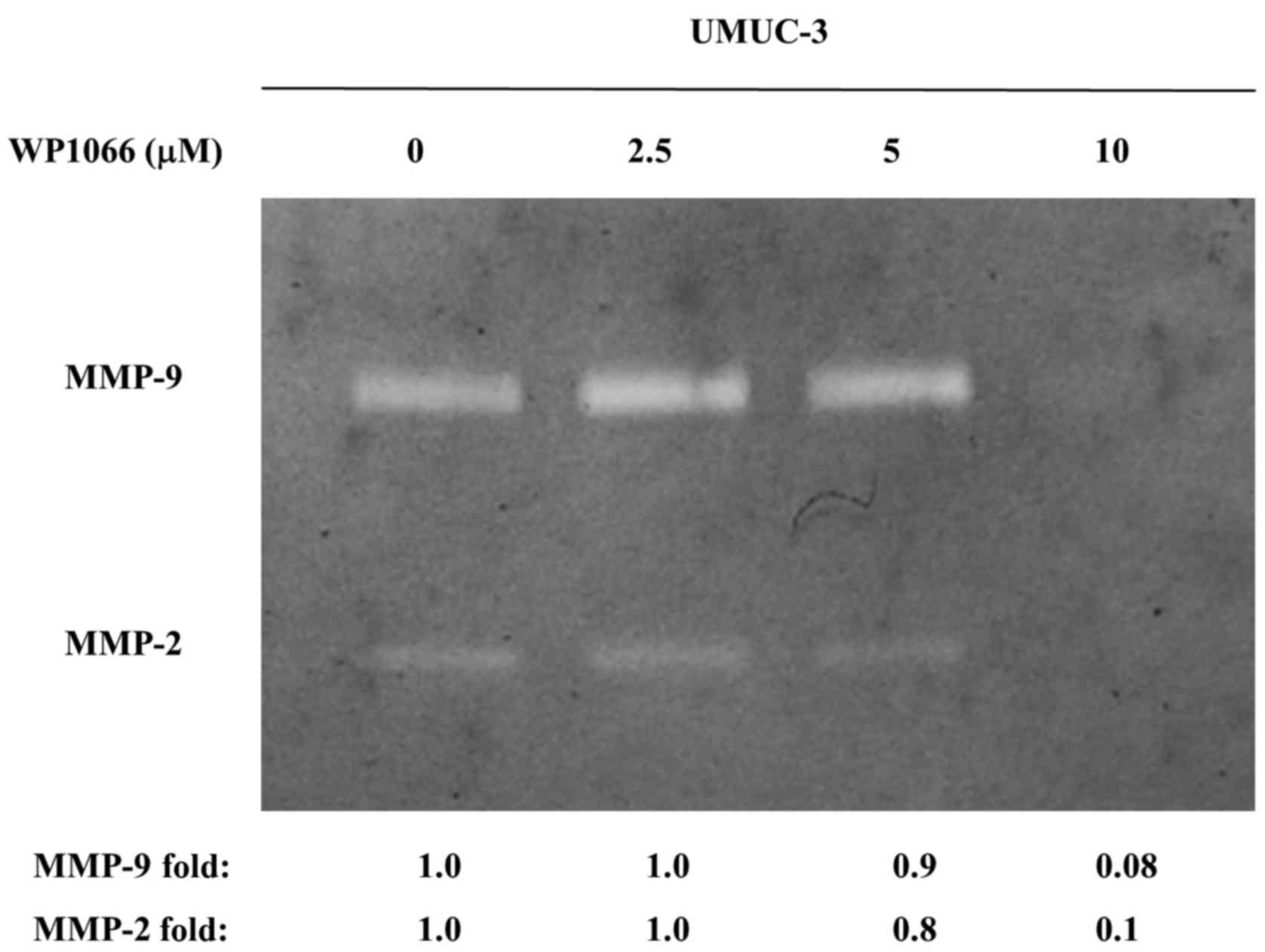
|
1
|
Ploussard G, Shariat SF, Dragomir A, Kluth
LA, Xylinas E, Masson-Lecomte A, Rieken M, Rink M, Matsumoto K,
Kikuchi E, et al: Conditional survival after radical cystectomy for
bladder cancer: Evidence for a patient changing risk profile over
time. Eur Urol. 66:361–370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rosenberg JE, Carroll PR and Small EJ:
Update on chemotherapy for advanced bladder cancer. J Urol.
174:14–20. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
von der Maase H, Sengelov L, Roberts JT,
Ricci S, Dogliotti L, Oliver T, Moore MJ, Zimmermann A and Arning
M: Long-term survival results of a randomized trial comparing
gemcitabine plus cisplatin, with methotrexate, vinblastine,
doxorubicin, plus cisplatin in patients with bladder cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 23:4602–4608. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
van Kessel KE, Zuiverloon TC, Alberts AR,
Boormans JL and Zwarthoff EC: Targeted therapies in bladder cancer:
An overview of in vivo research. Nat Rev Urol. 12:681–694. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schindler C and Darnell JE Jr:
Transcriptional responses to polypeptide ligands: The JAK-STAT
pathway. Annu Rev Biochem. 64:621–651. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Akira S, Nishio Y, Inoue M, Wang XJ, Wei
S, Matsusaka T, Yoshida K, Sudo T, Naruto M and Kishimoto T:
Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3
p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated
signaling pathway. Cell. 77:63–71. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu H, Lee H, Herrmann A, Buettner R and
Jove R: Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: New and unexpected
biological functions. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:736–746. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bruserud Ø, Nepstad I, Hauge M, Hatfield
KJ and Reikvam H: STAT3 as a possible therapeutic target in human
malignancies: Lessons from acute myeloid leukemia. Expert Rev
Hematol. 8:29–41. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Horiguchi A, Oya M, Shimada T, Uchida A,
Marumo K and Murai M: Activation of signal transducer and activator
of transcription 3 in renal cell carcinoma: A study of incidence
and its association with pathological features and clinical
outcome. J Urol. 168:762–765. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim HS, Park YH, Lee J, Ahn JS, Kim J,
Shim YM, Kim JH, Park K, Han J and Ahn MJ: Clinical impact of
phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3,
epidermal growth factor receptor, p53, and vascular endothelial
growth factor receptor 1 expression in resected adenocarcinoma of
lung using tissue microarray. Cancer. 116:676–685. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Masuda M, Suzui M, Yasumatu R, Nakashima
T, Kuratomi Y, Azuma K, Tomita K, Komiyama S and Weinstein IB:
Constitutive activation of signal transducers and activators of
transcription 3 correlates with cyclin D1 overexpression and may
provide a novel prognostic marker in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 62:3351–3355. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Takemoto S, Ushijima K, Kawano K,
Yamaguchi T, Terada A, Fujiyoshi N, Nishio S, Tsuda N, Ijichi M,
Kakuma T, et al: Expression of activated signal transducer and
activator of transcription-3 predicts poor prognosis in cervical
squamous-cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 101:967–972. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen CL, Cen L, Kohout J, Hutzen B, Chan
C, Hsieh FC, Loy A, Huang V, Cheng G and Lin J: Signal transducer
and activator of transcription 3 activation is associated with
bladder cancer cell growth and survival. Mol Cancer. 7:782008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ho PL, Lay EJ, Jian W, Parra D and Chan
KS: Stat3 activation in urothelial stem cells leads to direct
progression to invasive bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 72:3135–3142.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun Y, Cheng MK, Griffiths TR, Mellon JK,
Kai B, Kriajevska M and Manson MM: Inhibition of STAT signalling in
bladder cancer by diindolylmethane: Relevance to cell adhesion,
migration and proliferation. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 13:57–68.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang N, Duan WD, Leng JJ, Zhou L, Wang X,
Xu YZ, Wang XD, Zhang AQ and Dong JH: STAT3 regulates the migration
and invasion of a stem-like subpopulation through microRNA-21 and
multiple targets in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
33:1493–1498. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schneider CA, Rasband WS and Eliceiri KW:
NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods.
9:671–675. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Horiguchi A and Asano T, Kuroda K, Sato A,
Asakuma J, Ito K, Hayakawa M, Sumitomo M and Asano T: STAT3
inhibitor WP1066 as a novel therapeutic agent for renal cell
carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 102:1592–1599. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Iwamaru A, Szymanski S, Iwado E, Aoki H,
Yokoyama T, Fokt I, Hess K, Conrad C, Madden T, Sawaya R, et al: A
novel inhibitor of the STAT3 pathway induces apoptosis in malignant
glioma cells both in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 26:2435–2444.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Horiguchi A, Asano T, Asano T, Ito K,
Sumitomo M and Hayakawa M: Pharmacological inhibitor of fatty acid
synthase suppresses growth and invasiveness of renal cancer cells.
J Urol. 180:729–736. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Horiguchi A, Oya M, Marumo K and Murai M:
STAT3, but not ERKs, mediates the IL-6-induced proliferation of
renal cancer cells, ACHN and 769P. Kidney Int. 61:926–938. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bhattacharya S, Ray RM and Johnson LR:
STAT3-mediated transcription of Bcl-2, Mcl-1 and c-IAP2 prevents
apoptosis in polyamine-depleted cells. Biochem J. 392:335–344.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chang Q, Bournazou E, Sansone P, Berishaj
M, Gao SP, Daly L, Wels J, Theilen T, Granitto S, Zhang X, et al:
The IL-6/JAK/Stat3 feed-forward loop drives tumorigenesis and
metastasis. Neoplasia. 15:848–862. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou X, Ren Y, Liu A, Han L, Zhang K, Li
S, Li P, Li P, Kang C, Wang X, et al: STAT3 inhibitor WP1066
attenuates miRNA-21 to suppress human oral squamous cell carcinoma
growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep. 31:2173–2180.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang X, Sun Y, Pireddu R, Yang H, Urlam
MK, Lawrence HR, Guida WC, Lawrence NJ and Sebti SM: A novel
inhibitor of STAT3 homodimerization selectively suppresses STAT3
activity and malignant transformation. Cancer Res. 73:1922–1933.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Degoricija M, Situm M, Korać J, Miljković
A, Matić K, Paradžik M, Marinović Terzić I, Jerončić A, Tomić S and
Terzić J: High NF-κB and STAT3 activity in human urothelial
carcinoma: A pilot study. World J Urol. 32:1469–1475. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen RJ, Ho YS, Guo HR and Wang YJ: Rapid
activation of Stat3 and ERK1/2 by nicotine modulates cell
proliferation in human bladder cancer cells. Toxicol Sci.
104:283–293. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sai K, Wang S, Balasubramaniyan V, Conrad
C, Lang FF, Aldape K, Szymanski S, Fokt I, Dasgupta A, Madden T, et
al: Induction of cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in glioblastoma
stem-like cells by WP1193, a novel small molecule inhibitor of the
JAK2/STAT3 pathway. J Neurooncol. 107:487–501. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Judd LM, Menheniott TR, Ling H, Jackson
CB, Howlett M, Kalantzis A, Priebe W and Giraud AS: Inhibition of
the JAK2/STAT3 pathway reduces gastric cancer growth in vitro and
in vivo. PLoS One. 9:e959932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Monami G, Gonzalez EM, Hellman M, Gomella
LG, Baffa R, Iozzo RV and Morrione A: Proepithelin promotes
migration and invasion of 5637 bladder cancer cells through the
activation of ERK1/2 and the formation of a paxillin/FAK/ERK
complex. Cancer Res. 66:7103–7110. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Itoh M, Murata T, Suzuki T, Shindoh M,
Nakajima K, Imai K and Yoshida K: Requirement of STAT3 activation
for maximal collagenase-1c (MMP-1) induction by epidermal growth
factor and malignant characteristics in T24 bladder cancer cells.
Oncogene. 25:1195–1204. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Han Z, Hong Z, Gao Q, Chen C, Hao Z, Ji T,
Hu W, Yan Y, Feng J, Liao S, et al: A potent oncolytic adenovirus
selectively blocks the STAT3 signaling pathway and potentiates
cisplatin antitumor activity in ovarian cancer. Hum Gene Ther.
23:32–45. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou X, Ren Y, Liu A, Jin R, Jiang Q,
Huang Y, Kong L, Wang X and Zhang L: WP1066 sensitizes oral
squamous cell carcinoma cells to cisplatin by targeting
STAT3/miR-21 axis. Sci Rep. 4:74612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mooso BA, Vinall RL, Mudryj M, Yap SA,
deVere White RW and Ghosh PM: The role of EGFR family inhibitors in
muscle invasive bladder cancer: A review of clinical data and
molecular evidence. J Urol. 193:19–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sen M, Joyce S, Panahandeh M, Li C, Thomas
SM, Maxwell J, Wang L, Gooding WE, Johnson DE and Grandis JR:
Targeting Stat3 abrogates EGFR inhibitor resistance in cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 18:4986–4996. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|