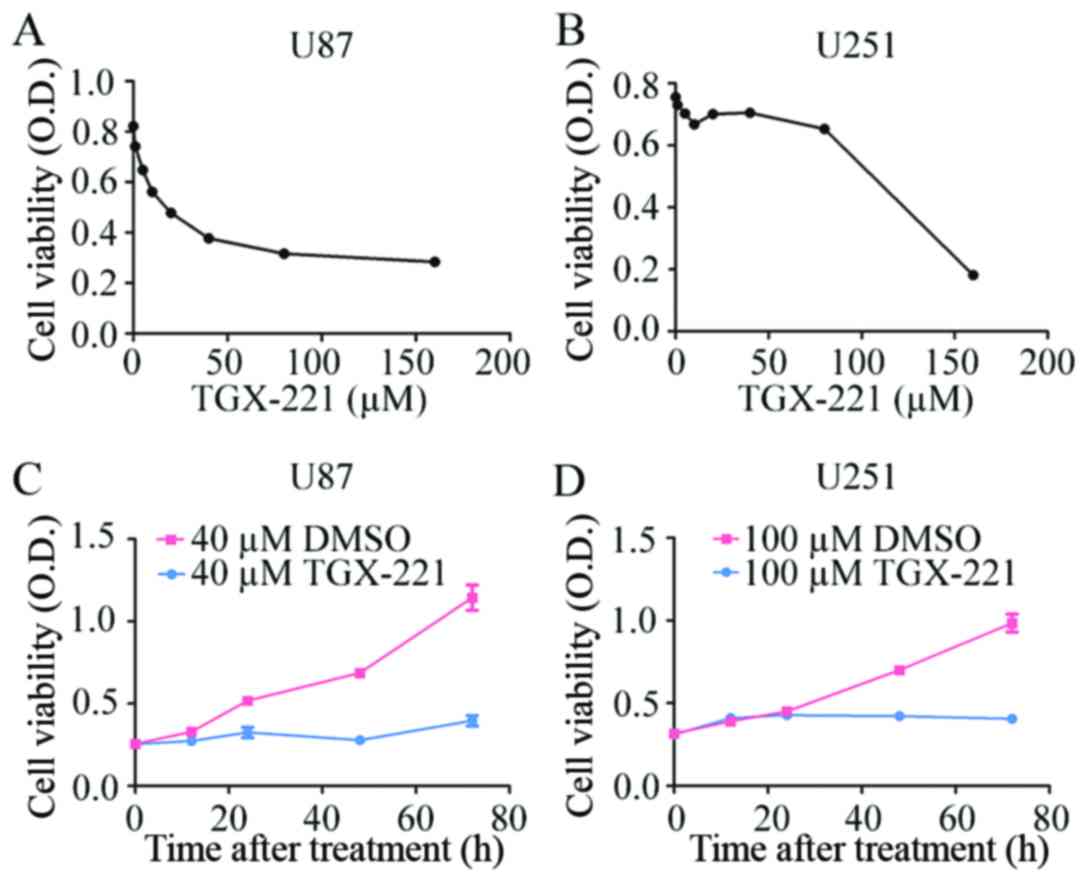
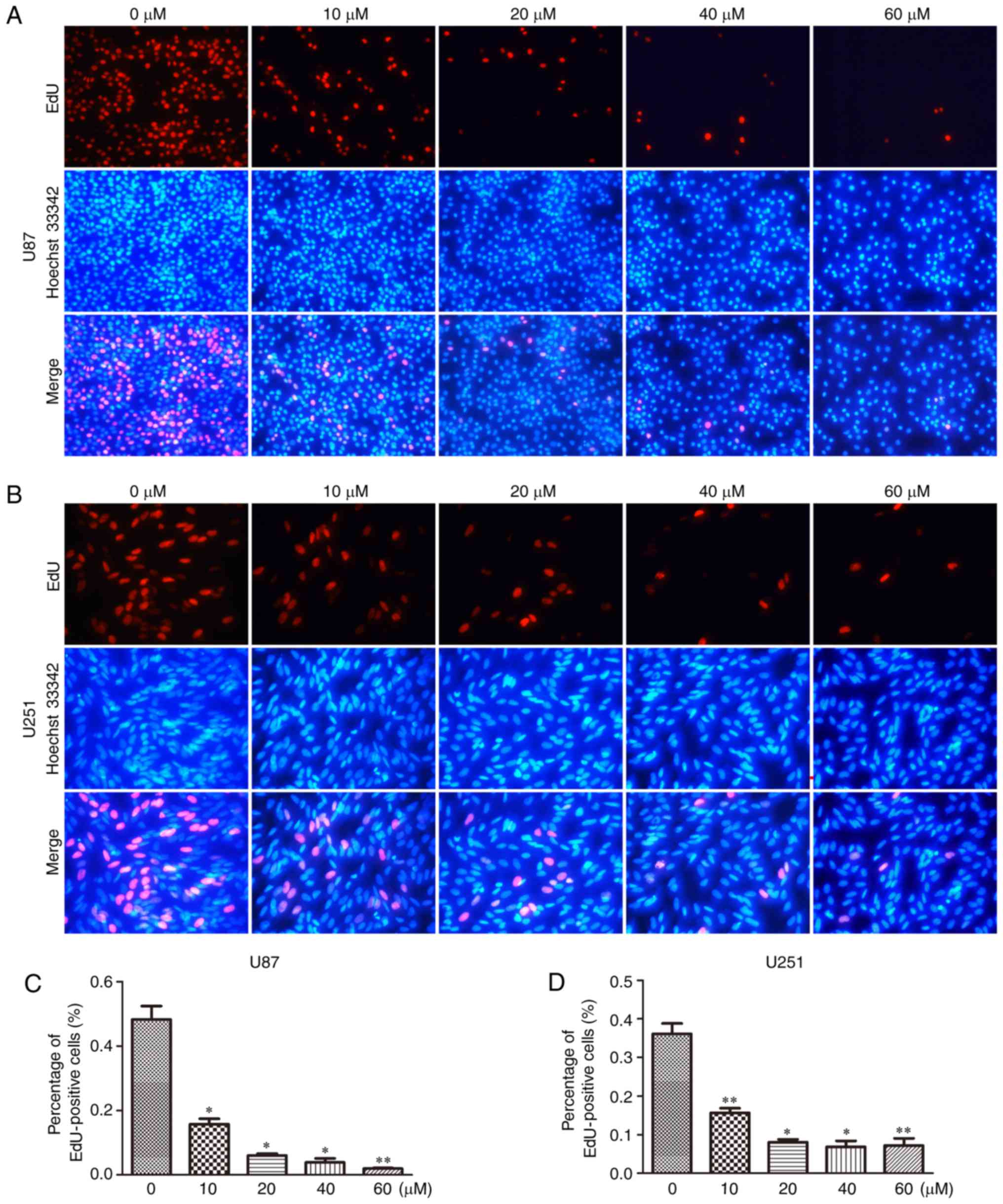
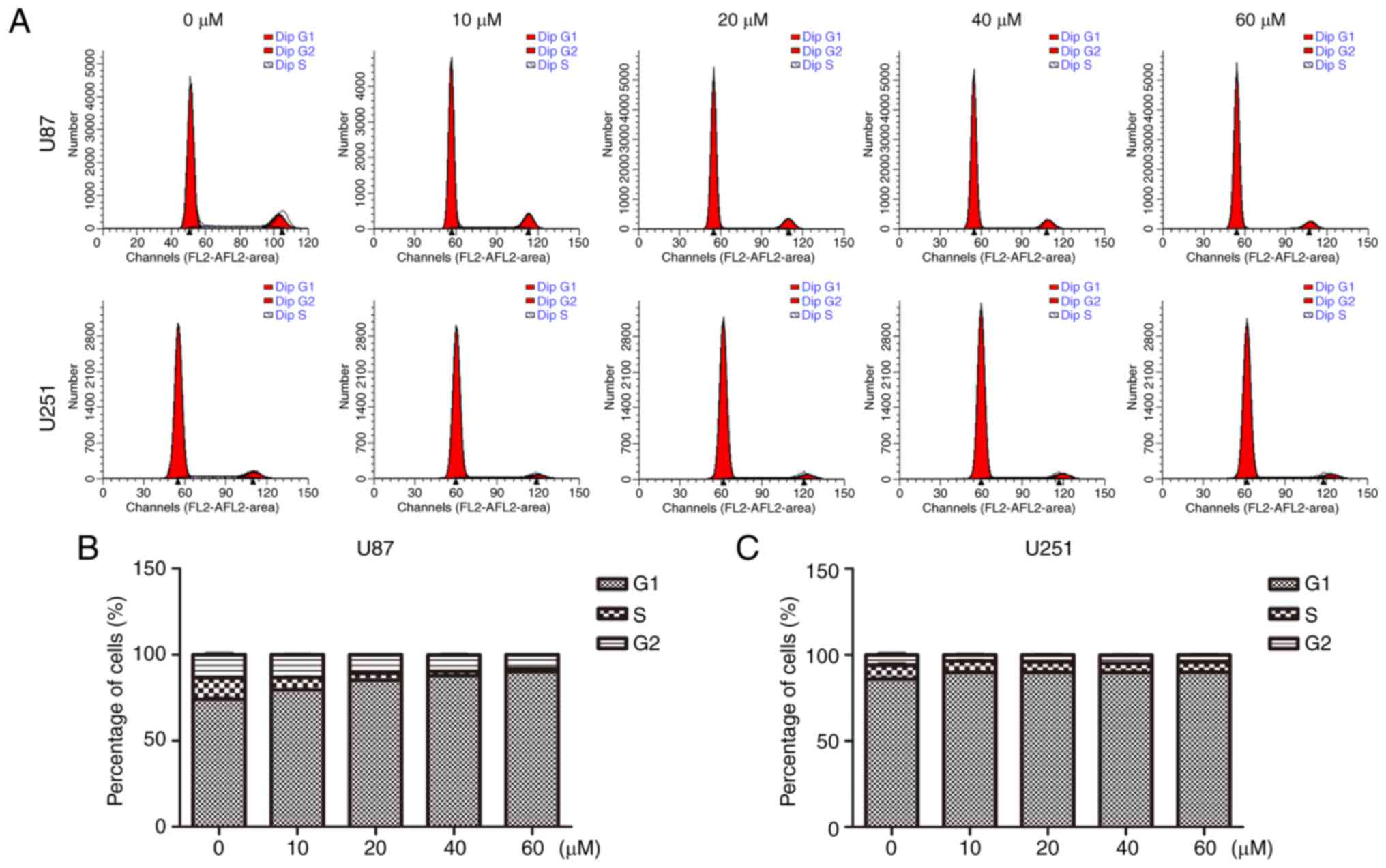
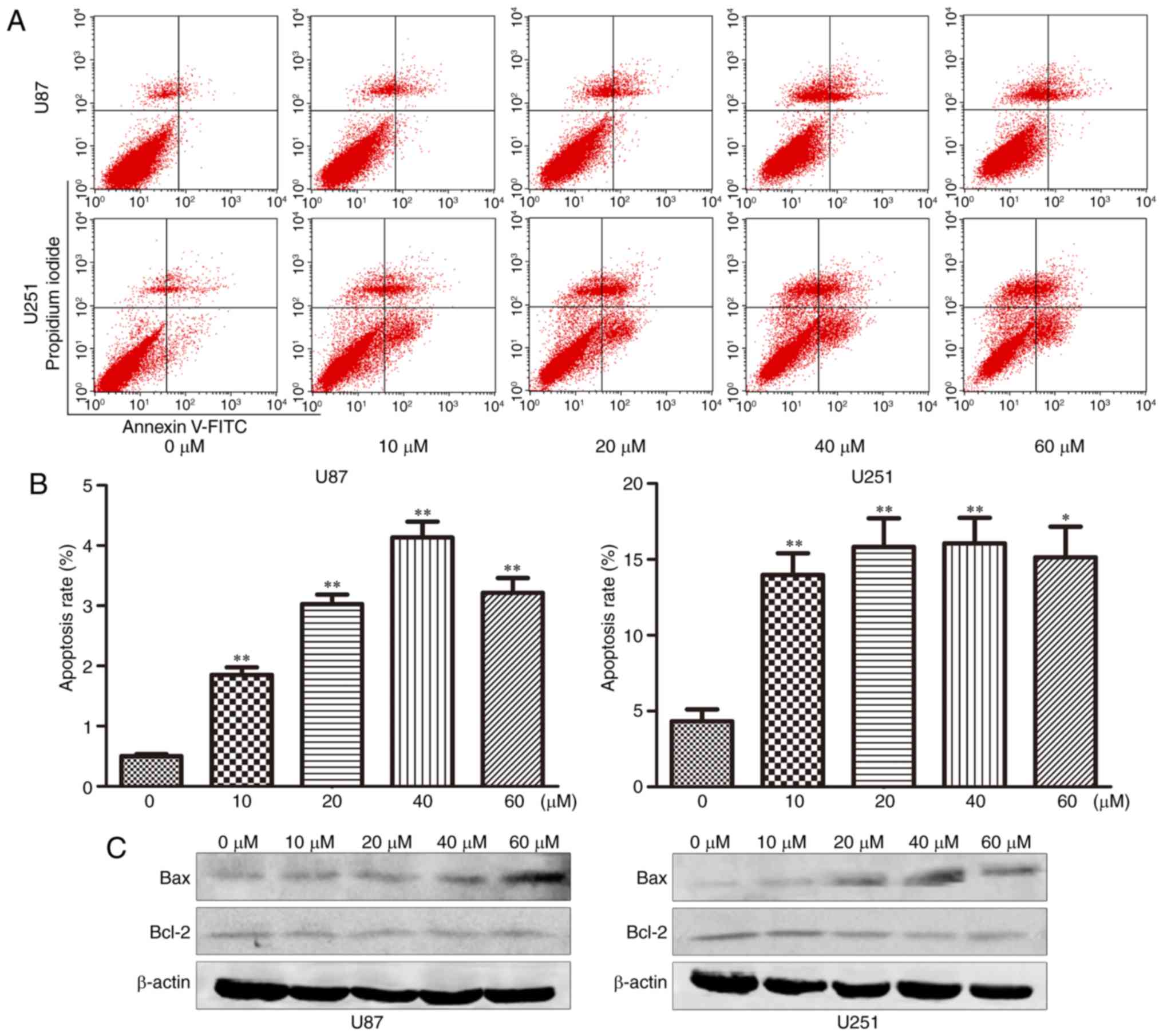
|
1
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Davis FG, McCarthy BJ, Freels S, Kupelian
V and Bondy ML: The conditional probability of survival of patients
with primary malignant brain tumors: Surveillance, epidemiology,
and end results (SEER) data. Cancer. 85:485–491. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Farah P, Ondracek
A, Chen Y, Wolinsky Y, Stroup NE, Kruchko C and Barnholtz-Sloan JS:
CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central nervous system
tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2006–2010. Neuro Oncol. 15
Suppl 2:ii1–ii56. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vanhaesebroeck B, Stephens L and Hawkins
P: PI3K signalling: The path to discovery and understanding. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:195–203. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kang S, Denley A, Vanhaesebroeck B and
Vogt PK: Oncogenic transformation induced by the p110beta, -gamma,
and -delta isoforms of class I phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 103:pp. 1289–1294. 2006; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen H, Mei L, Zhou L, Shen X, Guo C,
Zheng Y, Zhu H, Zhu Y and Huang L: PTEN restoration and PIK3CB
knockdown synergistically suppress glioblastoma growth in vitro and
in xenografts. J Neurooncol. 104:155–167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Edgar KA, Wallin JJ, Berry M, Lee LB,
Prior WW, Sampath D, Friedman LS and Belvin M: Isoform-specific
phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors exert distinct effects in
solid tumors. Cancer Res. 70:1164–1172. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu Q, Youn H, Tang J, Tawfik O, Dennis K,
Terranova PF, Du J, Raynal P, Thrasher JB and Li B:
Phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase p85alpha and p110beta are essential
for androgen receptor transactivation and tumor progression in
prostate cancers. Oncogene. 27:4569–4579. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen R, Zhao Y, Huang Y, Yang Q, Zeng X,
Jiang W, Liu J, Thrasher JB, Forrest ML and Li B: Nanomicellar
TGX221 blocks xenograft tumor growth of prostate cancer in nude
mice. Prostate. 75:593–602. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee SH, Poulogiannis G, Pyne S, Jia S, Zou
L, Signoretti S, Loda M, Cantley LC and Roberts TM: A
constitutively activated form of the p110beta isoform of PI3-kinase
induces prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia in mice. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 107:pp. 11002–11007. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jia S, Liu Z, Zhang S, Liu P, Zhang L, Lee
SH, Zhang J, Signoretti S, Loda M, Roberts TM, et al: Essential
roles of PI(3)K-p110beta in cell growth, metabolism and
tumorigenesis. Nature. 454:776–779. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang X, Chen S, Asara JM and Balk SP:
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway activation in phosphate and
tensin homolog (PTEN)-deficient prostate cancer cells is
independent of receptor tyrosine kinases and mediated by the
p110beta and p110delta catalytic subunits. J Biol Chem.
285:14980–14989. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fruman DA, Meyers RE and Cantley LC:
Phosphoinositide kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 67:481–507. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wee S, Lengauer C and Wiederschain D:
Class IA phosphoinositide 3-kinase isoforms and human
tumorigenesis: Implications for cancer drug discovery and
development. Curr Opin Oncol. 20:77–82. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shayesteh L, Lu Y, Kuo WL, Baldocchi R,
Godfrey T, Collins C, Pinkel D, Powell B, Mills GB and Gray JW:
PIK3CA is implicated as an oncogene in ovarian cancer. Nat Genet.
21:99–102. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ma YY, Wei SJ, Lin YC, Lung JC, Chang TC,
Whang-Peng J, Liu JM, Yang DM, Yang WK and Shen CY: PIK3CA as an
oncogene in cervical cancer. Oncogene. 19:2739–2744. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, Silliman N,
Ptak J, Szabo S, Yan H, Gazdar A, Powell SM, Riggins GJ, et al:
High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers.
Science. 304:5542004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Campbell IG, Russell SE, Choong DY,
Montgomery KG, Ciavarella ML, Hooi CS, Cristiano BE, Pearson RB and
Phillips WA: Mutation of the PIK3CA gene in ovarian and breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 64:7678–7681. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu G, Mambo E, Guo Z, Hu S, Huang X,
Gollin SM, Trink B, Ladenson PW, Sidransky D and Xing M: Uncommon
mutation, but common amplifications, of the PIK3CA gene in thyroid
tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 90:4688–4693. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Phillips WA, Russell SE, Ciavarella ML,
Choong DY, Montgomery KG, Smith K, Pearson RB, Thomas RJ and
Campbell IG: Mutation analysis of PIK3CA and PIK3CB in esophageal
cancer and Barrett's esophagus. Int J Cancer. 118:2644–2646. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pu P, Kang C, Zhang Z, Liu X and Jiang H:
Downregulation of PIK3CB by siRNA suppresses malignant glioma cell
growth in vitro and in vivo. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 5:271–280.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
An HJ, Cho NH, Yang HS, Kwak KB, Kim NK,
Oh DY, Lee SW, Kim HO and Koh JJ: Targeted RNA interference of
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase p110-beta induces apoptosis and
proliferation arrest in endometrial carcinoma cells. J Pathol.
212:161–169. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oda K, Okada J, Timmerman L,
Rodriguez-Viciana P, Stokoe D, Shoji K, Taketani Y, Kuramoto H,
Knight ZA, Shokat KM, et al: PIK3CA cooperates with other
phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase pathway mutations to effect
oncogenic transformation. Cancer Res. 68:8127–8136. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wee S, Wiederschain D, Maira SM, Loo A,
Miller C, deBeaumont R, Stegmeier F, Yao YM and Lengauer C:
PTEN-deficient cancers depend on PIK3CB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:pp. 13057–13062. 2008; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jackson SP, Schoenwaelder SM, Goncalves I,
Nesbitt WS, Yap CL, Wright CE, Kenche V, Anderson KE, Dopheide SM,
Yuan Y, et al: PI 3-kinase p110β: A new target for antithrombotic
therapy. Nat Med. 11:507–514. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin H, Erhard K, Hardwicke MA, Luengo JI,
Mack JF, McSurdy-Freed J, Plant R, Raha K, Rominger CM, Sanchez RM,
et al: Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of
imidazo[1,2-a]pyrimidin-5(1H)-ones as a novel series of beta
isoform selective phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors. Bioorg
Med Chem Lett. 22:2230–2234. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Luo J, Manning BD and Cantley LC:
Targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway in human cancer: Rationale and
promise. Cancer Cell. 4:257–262. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sturgeon SA, Jones C, Angus JA and Wright
CE: Advantages of a selective beta-isoform phosphoinositide
3-kinase antagonist, an anti-thrombotic agent devoid of other
cardiovascular actions in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 587:209–215.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bird JE, Smith PL, Bostwick JS, Shipkova P
and Schumacher WA: Bleeding response induced by anti-thrombotic
doses of a phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-β inhibitor in mice.
Thromb Res. 127:560–564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Garcia A, Kim S, Bhavaraju K,
Schoenwaelder SM and Kunapuli SP: Role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase
β in platelet aggregation and thromboxane A2 generation
mediated by Gi signalling pathways. Biochem J.
429:369–377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Roche S, Downward J, Raynal P and
Courtneidge SA: A function for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase beta
(p85alpha-p110beta) in fibroblasts during mitogenesis: Requirement
for insulin- and lysophosphatidic acid-mediated signal
transduction. Mol Cell Biol. 18:7119–7129. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hooshmand-Rad R, Hájková L, Klint P,
Karlsson R, Vanhaesebroeck B, Claesson-Welsh L and Heldin CH: The
PI 3-kinase isoforms p110(alpha) and p110(beta) have differential
roles in PDGF- and insulin-mediated signaling. J Cell Sci. 113(Pt
2): 1–214. 2000.
|
|
34
|
Asano T, Kanda A, Katagiri H, Nawano M,
Ogihara T, Inukai K, Anai M, Fukushima Y, Yazaki Y, Kikuchi M, et
al: p110beta is up-regulated during differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells
and contributes to the highly insulin-responsive glucose transport
activity. J Biol Chem. 275:17671–17676. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kubo H, Hazeki K, Takasuga S and Hazeki O:
Specific role for p85/p110beta in GTP-binding-protein-mediated
activation of Akt. Biochem J. 392:607–614. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kurosu H, Maehama T, Okada T, Yamamoto T,
Hoshino S, Fukui Y, Ui M, Hazeki O and Katada T: Heterodimeric
phosphoinositide 3-kinase consisting of p85 and p110beta is
synergistically activated by the betagamma subunits of G proteins
and phosphotyrosyl peptide. J Biol Chem. 272:24252–24256. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|