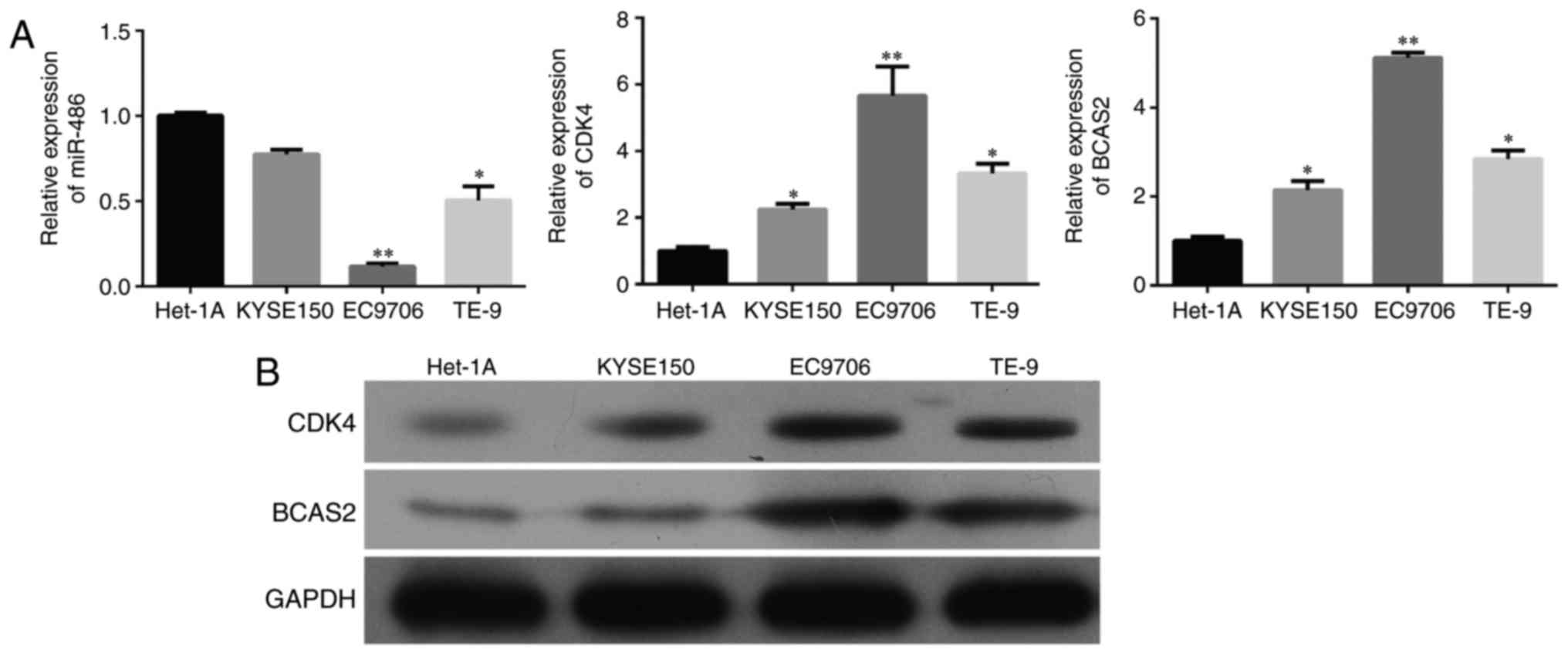
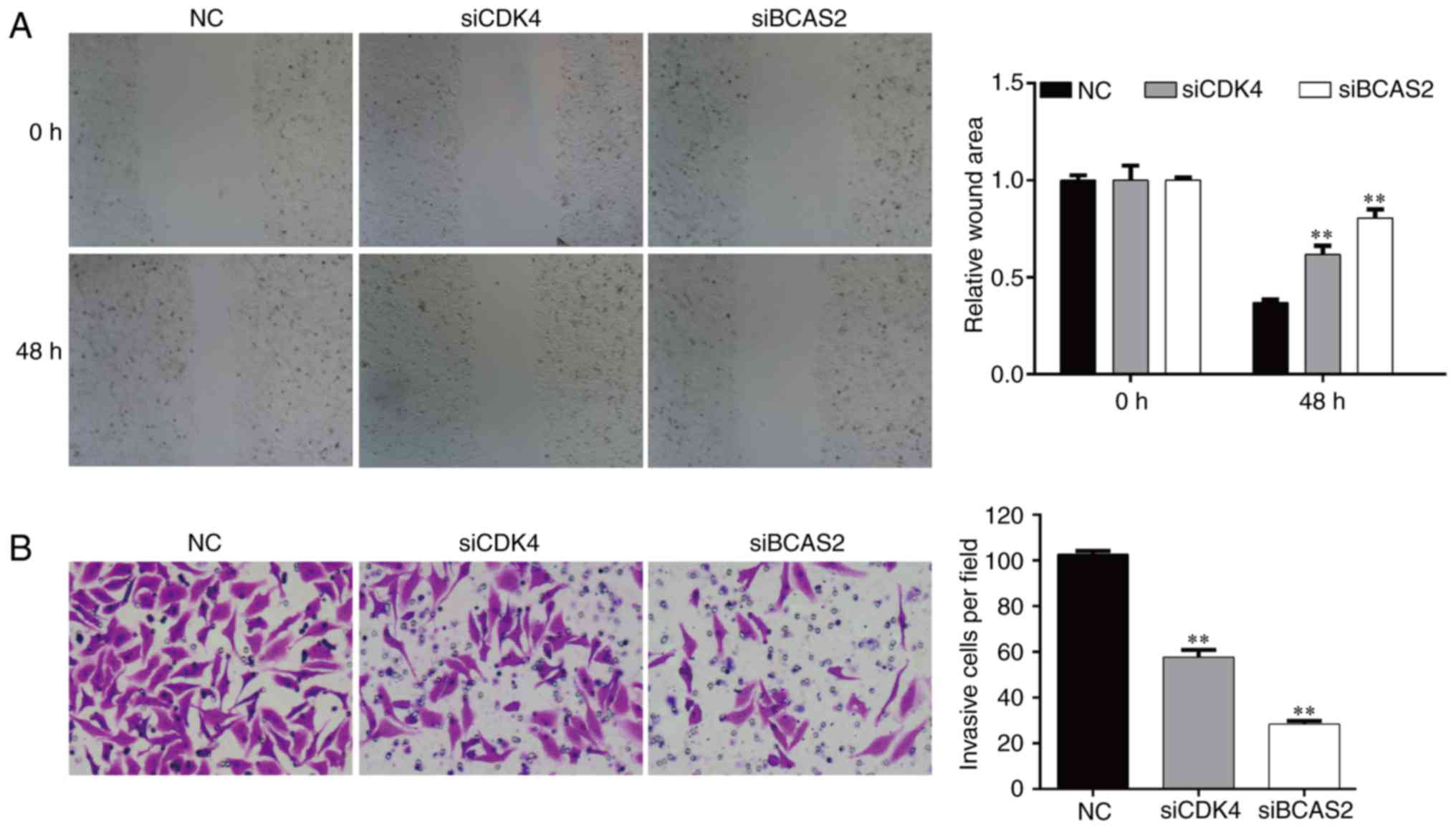
|
1
|
Beral V and Peto R: UK cancer survival
statistics. BMJ. 341(aug11 1): c41122010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Layke JC and Lopez PP: Esophageal cancer:
A review and update. Am Fam Physician. 73:2187–2194.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wu J, Wu X, Liang W, Chen C, Zheng L and
An H: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of chemokine
receptor CXCR4 overexpression in patients with esophageal cancer: A
meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 35:3709–3715. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gao YF, Yuan F, Liu J, Li LP, He YC, Gao
RJ, Cai YD and Jiang Y: Identification of new candidate Genes and
chemicals related to esophageal cancer using a hybrid interaction
network of chemicals and proteins. PLoS One. 10:e01294742015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
van Hagen P, Hulshof MC, van Lanschot JJ,
Steyerberg EW, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Wijnhoven BP, Richel DJ,
Nieuwenhuijzen GA, Hospers GA, Bonenkamp JJ, et al CROSS Group, :
Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer.
N Engl J Med. 366:2074–2084. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ming Z, Jiang D, Hu Q, Li X, Huang J, Xu
Y, Liu Y, Xu C, Hua X and Hou Y: Diagnostic application of PIK3CA
mutation analysis in Chinese esophageal cancer patients. Diagn
Pathol. 9:1532014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Agarwal D, Pineda S, Michailidou K,
Herranz J, Pita G, Moreno LT, Alonso MR, Dennis J, Wang Q, Bolla
MK, et al kConFab Investigators; Australian Ovarian Cancer Study
Group, ; GENICA Network; TNBCC, : FGF receptor genes and breast
cancer susceptibility: Results from the Breast Cancer Association
Consortium. Br J Cancer. 110:1088–1100. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hollstein MC, Metcalf RA, Welsh JA,
Montesano R and Harris CC: Frequent mutation of the p53 gene in
human esophageal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 87:pp. 9958–9961.
1990; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao H, Zheng L, Li X and Wang L: FasL
gene −844T/C mutation of esophageal cancer in South China and its
clinical significance. Sci Rep. 4:38662014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meng XR, Lu P, Mei JZ, Liu GJ and Fan QX:
Expression analysis of miRNA and target mRNAs in esophageal cancer.
Braz J Med Biol Res. 47:811–817. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Berezikov E, Guryev V, van de Belt J,
Wienholds E, Plasterk RH and Cuppen E: Phylogenetic shadowing and
computational identification of human microRNA genes. Cell.
120:21–24. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zamore PD and Haley B: Ribo-gnome: The big
world of small RNAs. Science. 309:1519–1524. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pillai RS: MicroRNA function: Multiple
mechanisms for a tiny RNA? RNA. 11:1753–1761. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen CZ, Li L, Lodish HF and Bartel DP:
MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science.
303:83–86. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hiyoshi Y, Kamohara H, Karashima R, Sato
N, Imamura Y, Nagai Y, Yoshida N, Toyama E, Hayashi N, Watanabe M,
et al: MicroRNA-21 regulates the proliferation and invasion in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1915–1922.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Feber A, Xi L, Luketich JD, Pennathur A,
Landreneau RJ, Wu M, Swanson SJ, Godfrey TE and Litle VR: MicroRNA
expression profiles of esophageal cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
135:255–260, discussion 260. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li B, Xu WW, Han L, Chan KT, Tsao SW, Lee
NPY, Law S, Xu LY, Li EM, Chan KW, et al: MicroRNA-377 suppresses
initiation and progression of esophageal cancer by inhibiting CD133
and VEGF. Oncogene. 36:3986–4000. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gao X, Wang X, Cai K, Wang W, Ju Q, Yang
X, Wang H and Wu H: MicroRNA-127 is a tumor suppressor in human
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through the regulation of
oncogene FMNL3. Eur J Pharmacol. 791:603–610. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fu H, Tie Y, Xu C, Zhang Z, Zhu J, Shi Y,
Jiang H, Sun Z and Zheng X: Identification of human fetal liver
miRNAs by a novel method. FEBS Lett. 579:3849–3854. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miya K, Shimojima K, Sugawara M, Shimada
S, Tsuri H, Harai-Tanaka T, Nakaoka S, Kanegane H, Miyawaki T and
Yamamoto T: A de novo interstitial deletion of 8p11.2 including
ANK1 identified in a patient with spherocytosis, psychomotor
developmental delay, and distinctive facial features. Gene.
506:146–149. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Oh HK, Tan AL, Das K, Ooi CH, Deng NT, Tan
IB, Beillard E, Lee J, Ramnarayanan K, Rha SY, et al: Genomic loss
of miR-486 regulates tumor progression and the OLFM4 antiapoptotic
factor in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 17:2657–2667. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Goto K, Oue N, Shinmei S, Sentani K,
Sakamoto N, Naito Y, Hayashi T, Teishima J, Matsubara A and Yasui
W: Expression of miR-486 is a potential prognostic factor after
nephrectomy in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Mol Clin Oncol.
1:235–240. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang XP, Hou J, Shen XY, Huang CY, Zhang
XH, Xie YA and Luo XL: MicroRNA-486-5p, which is downregulated in
hepatocellular carcinoma, suppresses tumor growth by targeting
PIK3R1. FEBS J. 282:579–594. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang J, Tian X, Han R, Zhang X, Wang X,
Shen H, Xue L, Liu Y, Yan X, Shen J, et al: Downregulation of
miR-486-5p contributes to tumor progression and metastasis by
targeting protumorigenic ARHGAP5 in lung cancer. Oncogene.
33:1181–1189. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang G, Liu Z, Cui G, Wang X and Yang Z:
MicroRNA-486-5p targeting PIM-1 suppresses cell proliferation in
breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 35:11137–11145. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yi Y, Lu X, Chen J, Jiao C, Zhong J, Song
Z, Yu X and Lin B: Downregulated miR-486-5p acts as a tumor
suppressor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Ther Med.
12:3411–3416. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Allum W.H..et al: Guidelines for the
management of oesophageal and gastric cancer. Gut. 2011.60(11):
1449–72. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Trichopoulos D: The unequal burden of
cancer. BMJ. 320:3212000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Parkin DM, Bray FI and Devesa SS: Cancer
burden in the year 2000. The global picture. Eur J Cancer. 37 Suppl
8:S4–S66. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mandard AM, Hainaut P and Hollstein M:
Genetic steps in the development of squamous cell carcinoma of the
esophagus. Mutat Res. 462:335–342. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zen K and Zhang CY: Circulating microRNAs:
A novel class of biomarkers to diagnose and monitor human cancers.
Med Res Rev. 32:326–348. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Guo J, Wang M and Liu X: MicroRNA-195
suppresses tumor cell proliferation and metastasis by directly
targeting BCOX1 in prostate carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
34:912015.https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-015-0209-7
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kawano M, Tanaka K, Itonaga I, Ikeda S,
Iwasaki T and Tsumura H: microRNA-93 promotes cell proliferation
via targeting of PTEN in osteosarcoma cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
34:762015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Esteller M: Non-coding RNAs in human
disease. Nat Rev Genet. 12:861–874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shao Y, Shen YQ, Li YL, Liang C, Zhang BJ,
Lu SD, He YY, Wang P, Sun QL, Jin YX, et al: Direct repression of
the oncogene CDK4 by the tumor suppressor miR-486-5p in non-small
cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 7:34011–34021. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Weinberg RA: The retinoblastoma protein
and cell cycle control. Cell. 81:323–330. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Meyerson M and Harlow E: Identification of
G1 kinase activity for cdk6, a novel cyclin D partner. Mol Cell
Biol. 14:2077–2086. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Matsushime H, Ewen ME, Strom DK, Kato JY,
Hanks SK, Roussel MF and Sherr CJ: Identification and properties of
an atypical catalytic subunit (p34PSK-J3/cdk4) for mammalian D type
G1 cyclins. Cell. 71:323–334. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kato J, Matsushime H, Hiebert SW, Ewen ME
and Sherr CJ: Direct binding of cyclin D to the retinoblastoma gene
product (pRb) and pRb phosphorylation by the cyclin D-dependent
kinase CDK4. Genes Dev. 7:331–342. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bates S, Bonetta L, MacAllan D, Parry D,
Holder A, Dickson C and Peters G: CDK6 (PLSTIRE) and CDK4 (PSK-J3)
are a distinct subset of the cyclin-dependent kinases that
associate with cyclin D1. Oncogene. 9:71–79. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Botz J, Zerfass-Thome K, Spitkovsky D,
Delius H, Vogt B, Eilers M, Hatzigeorgiou A and Jansen-Dürr P: Cell
cycle regulation of the murine cyclin E gene depends on an E2F
binding site in the promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 16:3401–3409. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM: CDK inhibitors:
Positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes
Dev. 13:1501–1512. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Neumann B, Walter T, Hériché JK,
Bulkescher J, Erfle H, Conrad C, Rogers P, Poser I, Held M, Liebel
U, et al: Phenotypic profiling of the human genome by time-lapse
microscopy reveals cell division genes. Nature. 464:721–727. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Song EJ, Werner SL, Neubauer J, Stegmeier
F, Aspden J, Rio D, Harper JW, Elledge SJ, Kirschner MW and Rape M:
The Prp19 complex and the Usp4Sart3 deubiquitinating enzyme control
reversible ubiquitination at the spliceosome. Genes Dev.
24:1434–1447. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kittler R, Surendranath V, Heninger AK,
Slabicki M, Theis M, Putz G, Franke K, Caldarelli A, Grabner H,
Kozak K, et al: Genome-wide resources of endoribonuclease-prepared
short interfering RNAs for specific loss-of-function studies. Nat
Methods. 4:337–344. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kuo PC, Tsao YP, Chang HW, Chen PH, Huang
CW, Lin ST, Weng YT, Tsai TC, Shieh SY and Chen SL: Breast cancer
amplified sequence 2, a novel negative regulator of the p53 tumor
suppressor. Cancer Res. 69:8877–8885. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|