|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ma M, Zhao LM, Yang XX, Shan YN, Cui WX,
Chen L and Shan BE: p-Hydroxylcinnamaldehyde induces the
differentiation of oesophageal carcinoma cells via the
cAMP-RhoA-MAPK signalling pathway. Sci Rep. 6:313152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bertolini G, Roz L, Perego P, Tortoreto M,
Fontanella E, Gatti L, Pratesi G, Fabbri A, Andriani F, Tinelli S,
et al: Highly tumorigenic lung cancer CD133+ cells display
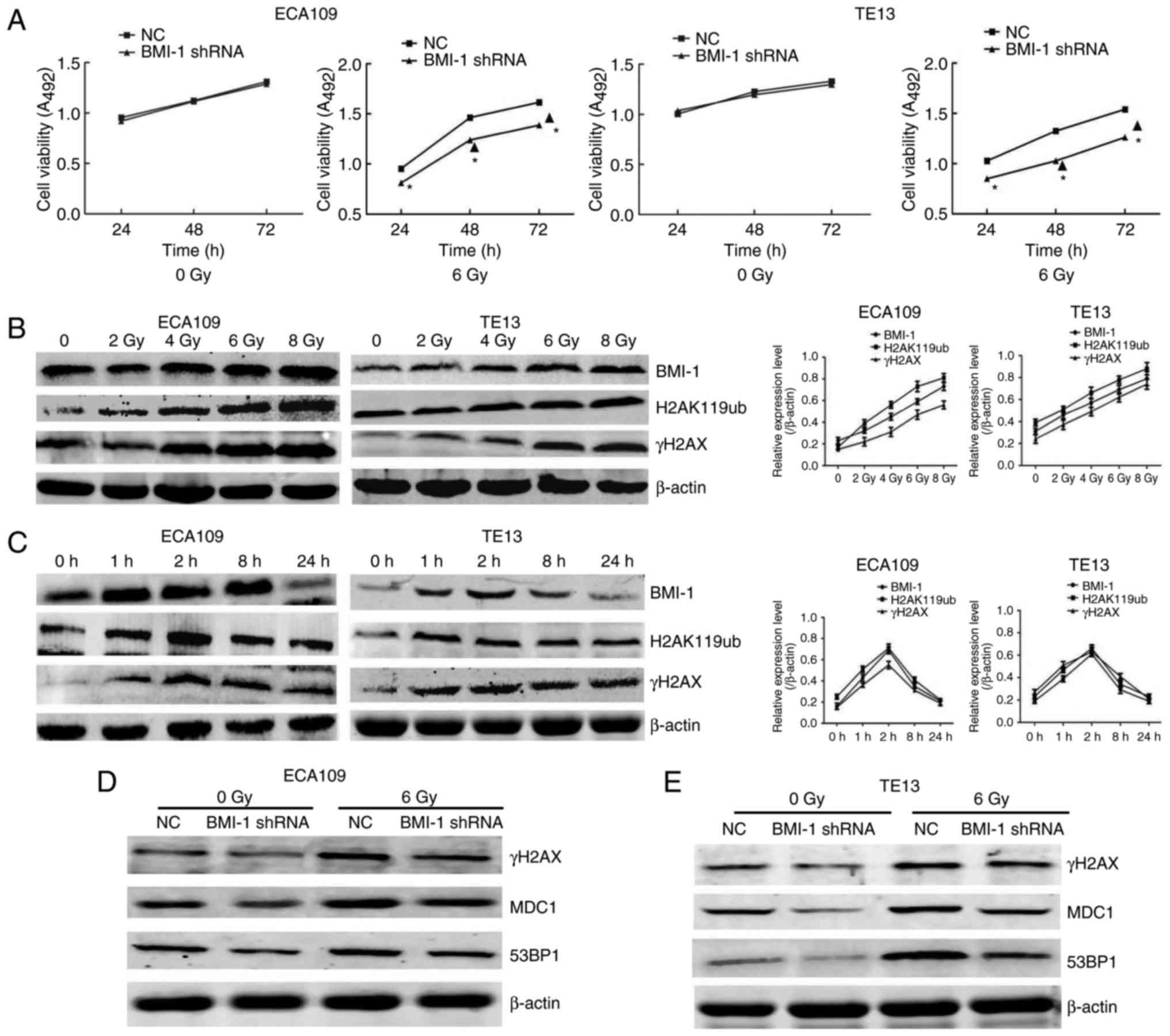
stem-like features and are spared by cisplatin treatment. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:pp. 16281–16286. 2009; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
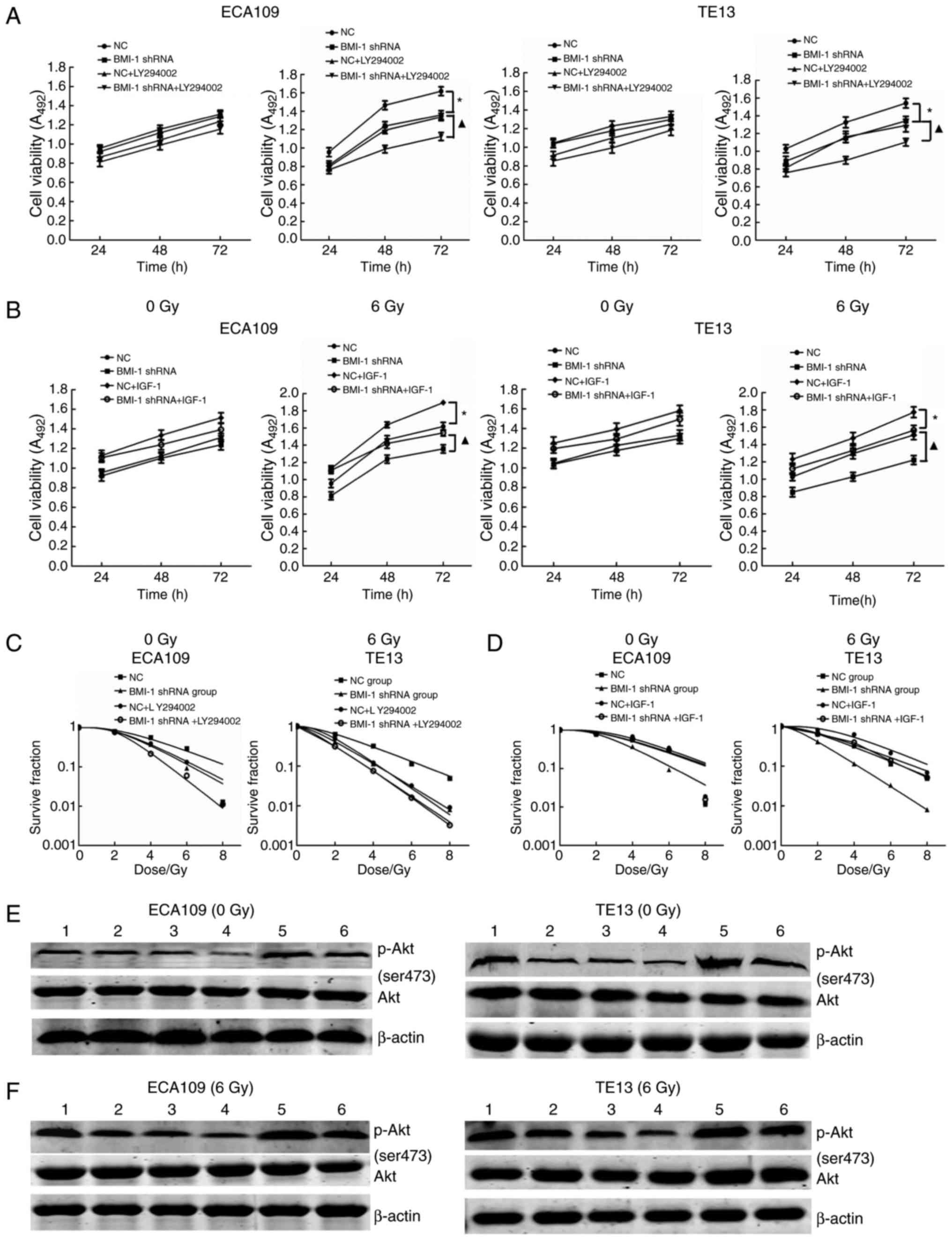
|
|
4
|
Zhao JX and Xie XL: Regulation of gene
expression in laryngeal carcinama by microRNAs. Int J Pathol Clin
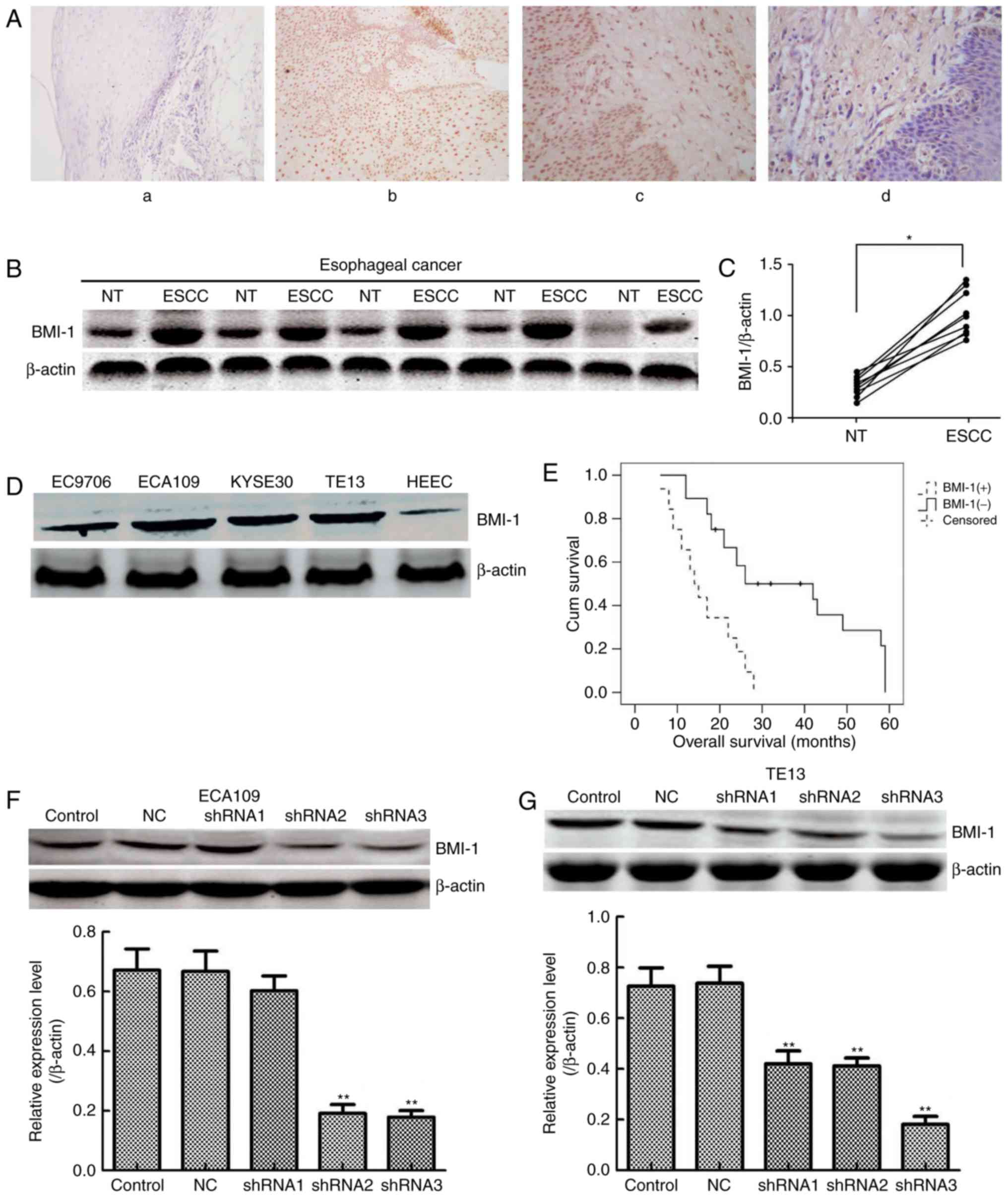
Med. 32:222–225. 2012.
|
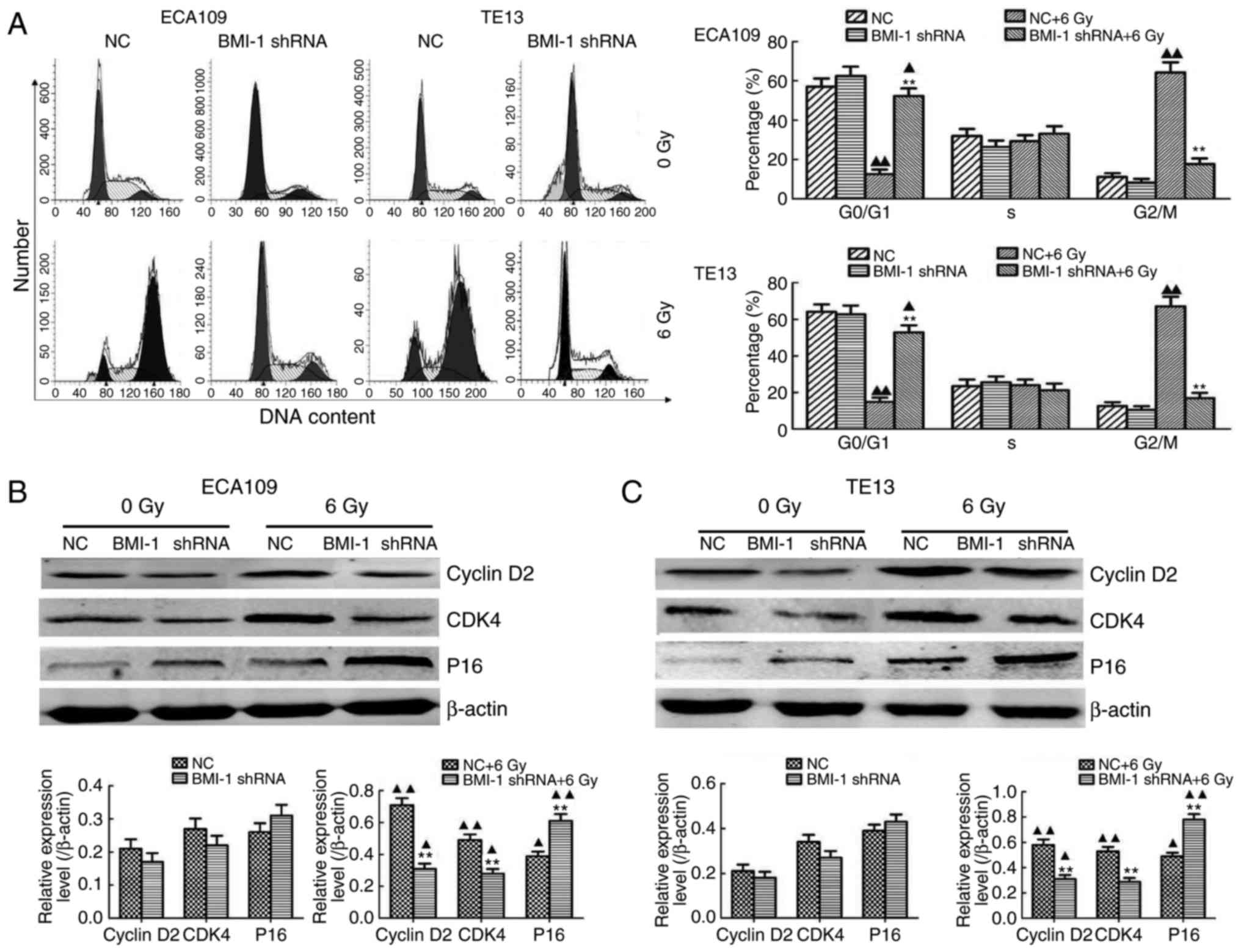
|
5
|
Nacerddine K, Beaudry JB, Ginjala V,
Westerman B, Mattiroli F, Song JY, van der Poel H, Ponz OB,
Pritchard C, Cornelissen-Steijger P, et al: Akt-mediated
phosphorylation of Bmi1 modulates its oncogenic potential, E3
ligase activity, and DNA damage repair activity in mouse prostate
cancer. J Clin Invest. 122:1920–1932. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ruan ZP, Xu R, Lv Y, Tian T, Wang WJ, Guo
H and Nan KJ: Bmi1 knockdown inhibits hepatocarcinogenesis. Int J
Oncol. 42:261–268. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Song W, Tao K, Li H, Jin C, Song Z, Li J,
Shi H, Li X, Dang Z and Dou K: Bmi-1 is related to proliferation,
survival and poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci.
101:1754–1760. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bosch A, Panoutsopoulou K, Corominas JM,
Gimeno R, Moreno-Bueno G, Martín-Caballero J, Morales S, Lobato T,
Martínez-Romero C, Farias EF, et al: The Polycomb group protein
RING1B is overexpressed in ductal breast carcinoma and is required
to sustain FAK steady state levels in breast cancer epithelial
cells. Oncotarget. 5:2065–2076. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Su WJ, Fang JS, Cheng F, Liu C, Zhou F and
Zhang J: RNF2/Ring1b negatively regulates p53 expression in
selective cancer cell types to promote tumor development. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 110:pp. 1720–1725. 2013; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang L, Liu JL, Yu L, Liu XX, Wu HM, Lei
FY, Wu S and Wang X: Downregulated miR-495 [corrected] inhibits the
G1-S phase transition by targeting Bmi-1 in breast cancer.
Medicine. 94:e7182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jin M, Zhang T, Liu C, Badeaux MA, Liu B,
Liu R, Jeter C, Chen X, Vlassov AV and Tang DG: miRNA-128
suppresses prostate cancer by inhibiting BMI-1 to inhibit
tumor-initiating cells. Cancer Res. 74:4183–4195. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang F, Lv LZ, Cai QC and Jiang Y:
Potential roles of EZH2, Bmi-1 and miR-203 in cell proliferation
and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma cell line Hep3B. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:13268–13276. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang H, Wang L, Erdjument-Bromage H, Vidal
M, Tempst P, Jones RS and Zhang Y: Role of histone H2A
ubiquitination in Polycomb silencing. Nature. 431:873–878. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ward IM, Minn K, van Deursen J and Chen J:
p53 Binding protein 53BP1 is required for DNA damage responses and
tumor suppression in mice. Mol Cell Biol. 23:2556–2563. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Moudry P, Lukas C, Macurek L, Neumann B,
Heriche JK, Pepperkok R, Ellenberg J, Hodny Z, Lukas J and Bartek
J: Nucleoporin NUP153 guards genome integrity by promoting nuclear
import of 53BP1. Cell Death Differ. 19:798–807. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li DQ, Qiu M, Nie XM, Gui R and Huang MZ:
Oxidored-nitro domain-containing protein 1 expression is associated
with the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
11:3003–3008. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Song LB, Zeng MS, Liao WT, Zhang L, Mo HY,
Liu WL, Shao JY, Wu QL, Li MZ, Xia YF, et al: Bmi-1 is a novel
molecular marker of nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and
immortalizes primary human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Cancer
Res. 66:6225–6232. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang XX, Ma M, Sang MX, Wang XX, Song H,
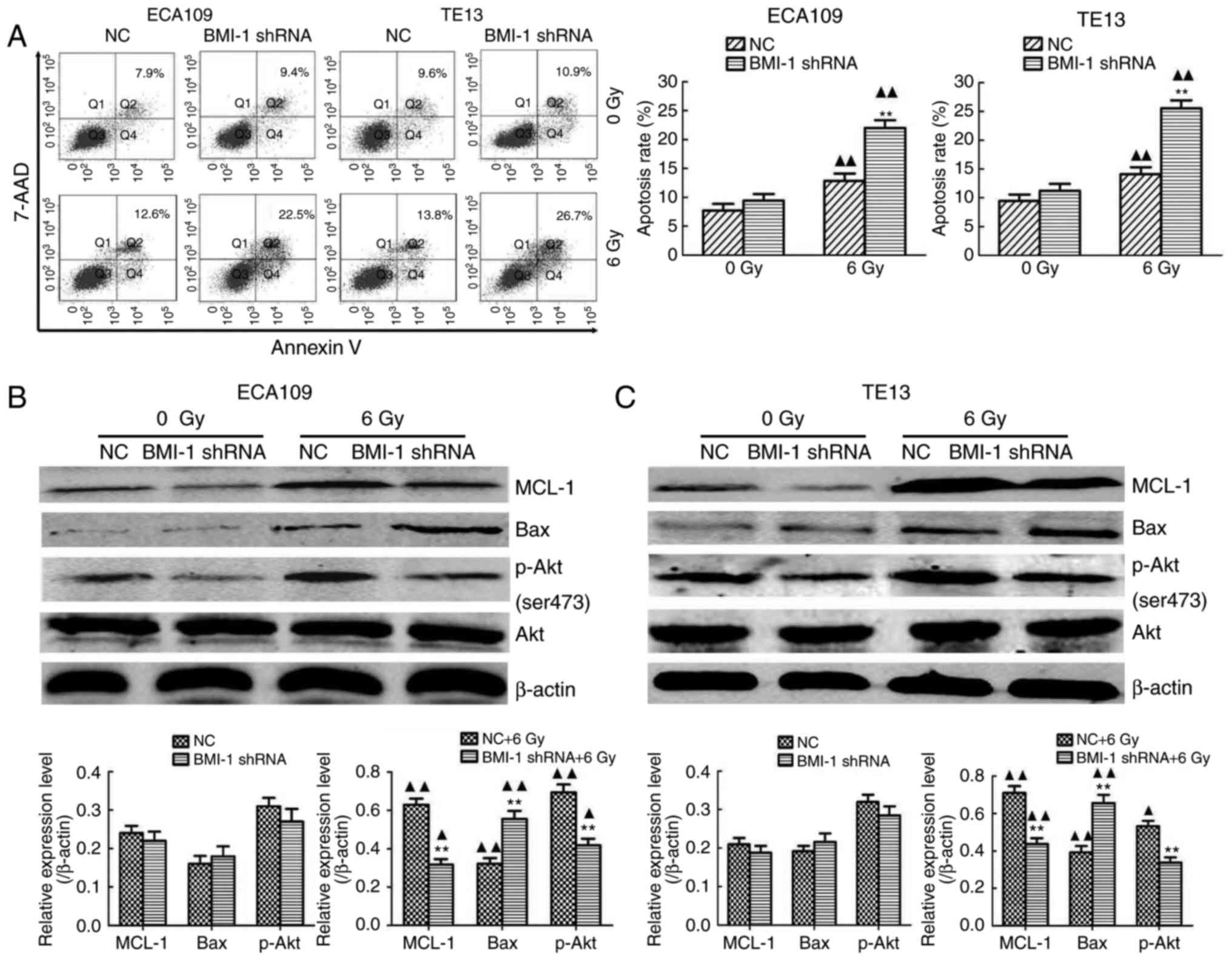
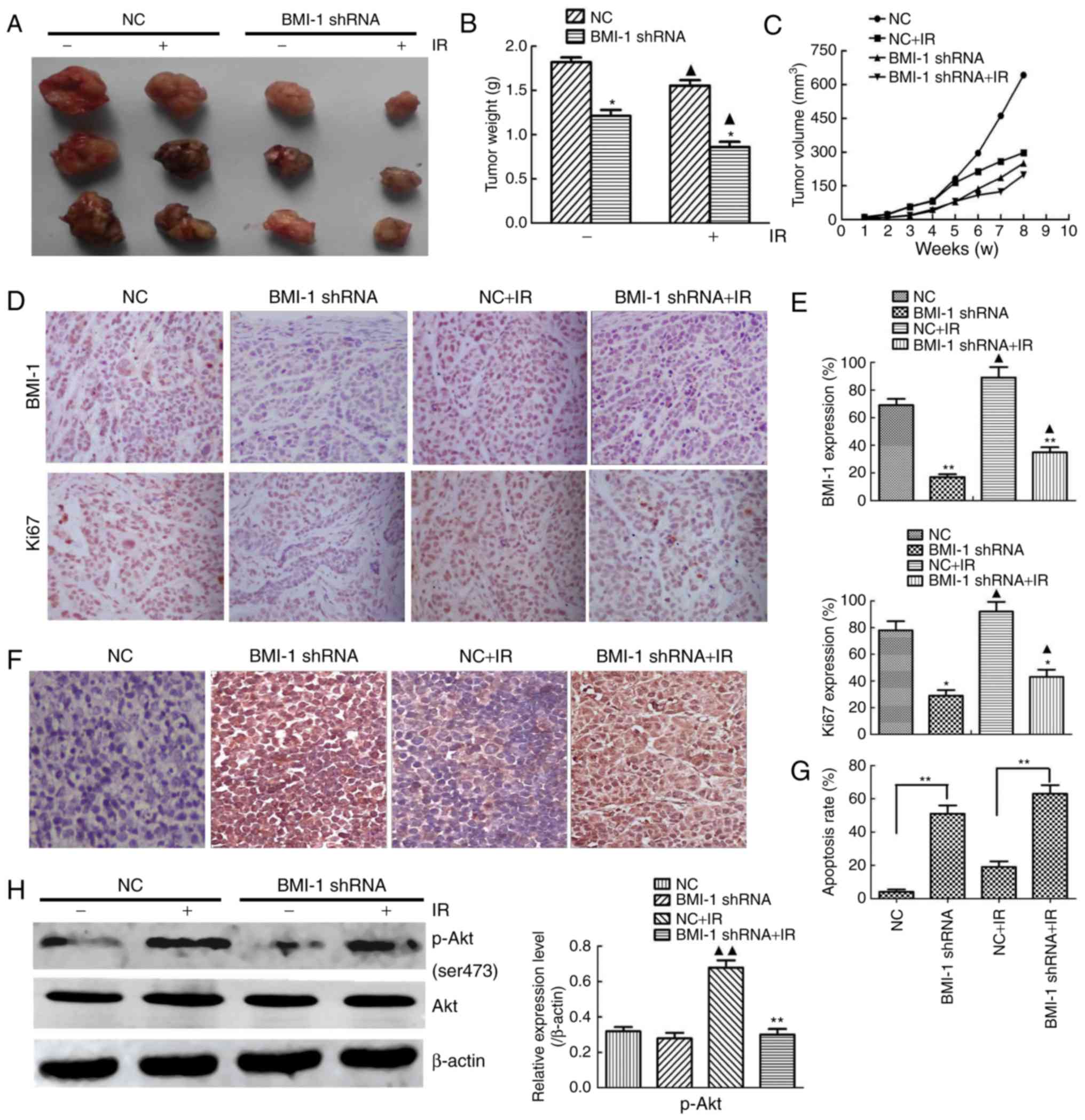
Liu ZK and Zhu SC: Radiosensitization of esophageal carcinoma cells
by knockdown of RNF2 expression. Int J Oncol. 48:1985–1996. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xie G, Zhan J, Tian Y, Liu Y, Chen Z, Ren
C, Sun Q, Lian J, Chen L, Ruan J, et al: Mammosphere cells from
high-passage MCF7 cell line show variable loss of tumorigenicity
and radioresistance. Cancer Lett. 316:53–61. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Allegra E, Puzzo L, Zuccalà V, Trapasso S,
Vasquez E, Garozzo A and Caltabiano R: Nuclear BMI-1 expression in
laryngeal carcinoma correlates with lymph node pathological status.
World J Surg Oncol. 10:206–211. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang XX, Sang MX, Zhu SC, Liu ZK and Ma M:
Radiosensitization of esophageal carcinoma cells by the silencing
of BMI-1. Oncol Rep. 35:3669–3678. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dong Q, Sharma S, Liu H, Chen L, Gu B, Sun
X and Wang G: HDAC inhibitors reverse acquired radio resistance of
KYSE-150R esophageal carcinoma cells by modulating Bmi-1
expression. Toxicol Lett. 224:121–129. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang MC, Jiao M, Wu T, Jing L, Cui J, Guo
H, Tian T, Ruan ZP, Wei YC, Jiang LL, et al: Polycomb complex
protein BMI-1 promotes invasion and metastasis of pancreatic cancer
stem cells by activating PI3K/AKT signaling, an ex vivo, in vitro,
and in vivo study. Oncotarget. 7:9586–9599. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liang W, Zhu D, Cui X, Su J, Liu H, Han J,
Zhao F and Xie W: Knockdown BMI1 expression inhibits proliferation
and invasion in human bladder cancer T24 cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
382:283–291. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma M, Zhao L, Sun G, Zhang C, Liu L, Du Y,
Yang X and Shan B: Mda-7/IL-24 enhances sensitivity of B cell
lymphoma to chemotherapy drugs. Oncol Rep. 35:3122–3130. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ginjala V, Nacerddine K, Kulkarni A, Oza
J, Hill SJ, Yao M, Citterio E, van Lohuizen M and Ganesan S: BMI1
is recruited to DNA breaks and contributes to DNA damage-induced
H2A ubiquitination and repair. Mol Cell Biol. 31:1972–1982. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang XJ, Yu HY, Cai YJ and Ke M: Lycium
barbarum polysaccharides inhibit proliferation and migration of
bladder cancer cell lines BIU87 by suppressing Pi3K/AKT pathway.
Oncotarget. 8:5936–5942. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fotouhi Ghiam A, Taeb S, Huang X, Huang V,
Ray J, Scarcello S, Hoey C, Jahangiri S, Fokas E, Loblaw A, et al:
Long non-coding RNA urothelial carcinoma associated 1 (UCA1)
mediates radiation response in prostate cancer. Oncotarget.
8:4668–4689. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu WL, Guo XZ, Zhang LJ, Wang JY, Zhang
G, Guan S, Chen YM, Kong QL, Xu LH, Li MZ, et al: Prognostic
relevance of Bmi-1 expression and autoantibodies in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 10:4672010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Min L, Dong-Xiang S, Xiao-Tong G, Ting G
and Xiao-Dong C: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of
Bmi-1 expression in human cervical cancer. Acta Obstet Gynecol
Scand. 90:737–745. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Boquoi A, Arora S, Chen T, Litwin S, Koh J
and Enders GH: Reversible cell cycle inhibition and premature aging
features imposed by conditional expression of p16Ink4a. Aging Cell.
14:139–147. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Blanco D, Vicent S, Fraga MF,
Fernandez-Garcia I, Freire J, Lujambio A, Esteller M,
Ortiz-de-Solorzano C, Pio R, Lecanda F, et al: Molecular analysis
of a multistep lung cancer model induced by chronic inflammation
reveals epigenetic regulation of p16 and activation of the DNA
damage response pathway. Neoplasia. 9:840–852. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wen W, Peng C, Kim MO, Ho Jeong C, Zhu F,
Yao K, Zykova T, Ma W, Carper A, Langfald A, et al: Knockdown of
RNF2 induces apoptosis by regulating MDM2 and p53 stability.
Oncogene. 33:421–428. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shapiro GI, Edwards CD, Ewen ME and
Rollins BJ: p16INK4A participates in a G1 arrest checkpoint in
response to DNA damage. Mol Cell Biol. 18:378–387. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yao XB, Wang XX, Liu H, Zhang SQ and Zhu
HL: Silencing Bmi-1 expression by RNA interference suppresses the
growth of laryngeal carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Med. 31:1262–1272.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Siddique HR, Parray A, Tarapore RS, Wang
L, Mukhtar H, Karnes RJ, Deng Y, Konety BR and Saleem M: BMI1
polycomb group protein acts as a master switch for growth and death
of tumor cells: Regulates TCF4-transcriptional factor-induced BCL2
signaling. PLoS One. 8:e606642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhu D, Wan X, Huang H, Chen X, Liang W,
Zhao F, Lin T, Han J and Xie W: Knockdown of Bmi1 inhibits the
stemness properties and tumorigenicity of human bladder cancer stem
cell-like side population cells. Oncol Rep. 31:727–736. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bussink J, van der Kogel AJ and Kaanders
JH: Activation of the PI3-K/AKT pathway and implications for
radioresistance mechanisms in head and neck cancer. Lancet Oncol.
9:288–296. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Deng R, Tang J, Ma JG, Chen SP, Xia LP,
Zhou WJ, Li DD, Feng GK, Zeng YX and Zhu XF: PKB/Akt promotes DSB
repair in cancer cells through upregulating Mre11 expression
following ionizing radiation. Oncogene. 30:944–955. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang Y, Zheng L, Ding Y, Li Q, Wang R,
Liu T, Sun Q, Yang H, Peng S, Wang W, et al: miR-20a induces cell
radioresistance by activating the PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
92:1132–1140. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ji Y, Zheng MF, Ye SG, Chen J and Chen Y:
PTEN and Ki67 expression is associated with clinicopathologic
features of non-small cell lung cancer. J Biomed Res. 28:462–467.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|