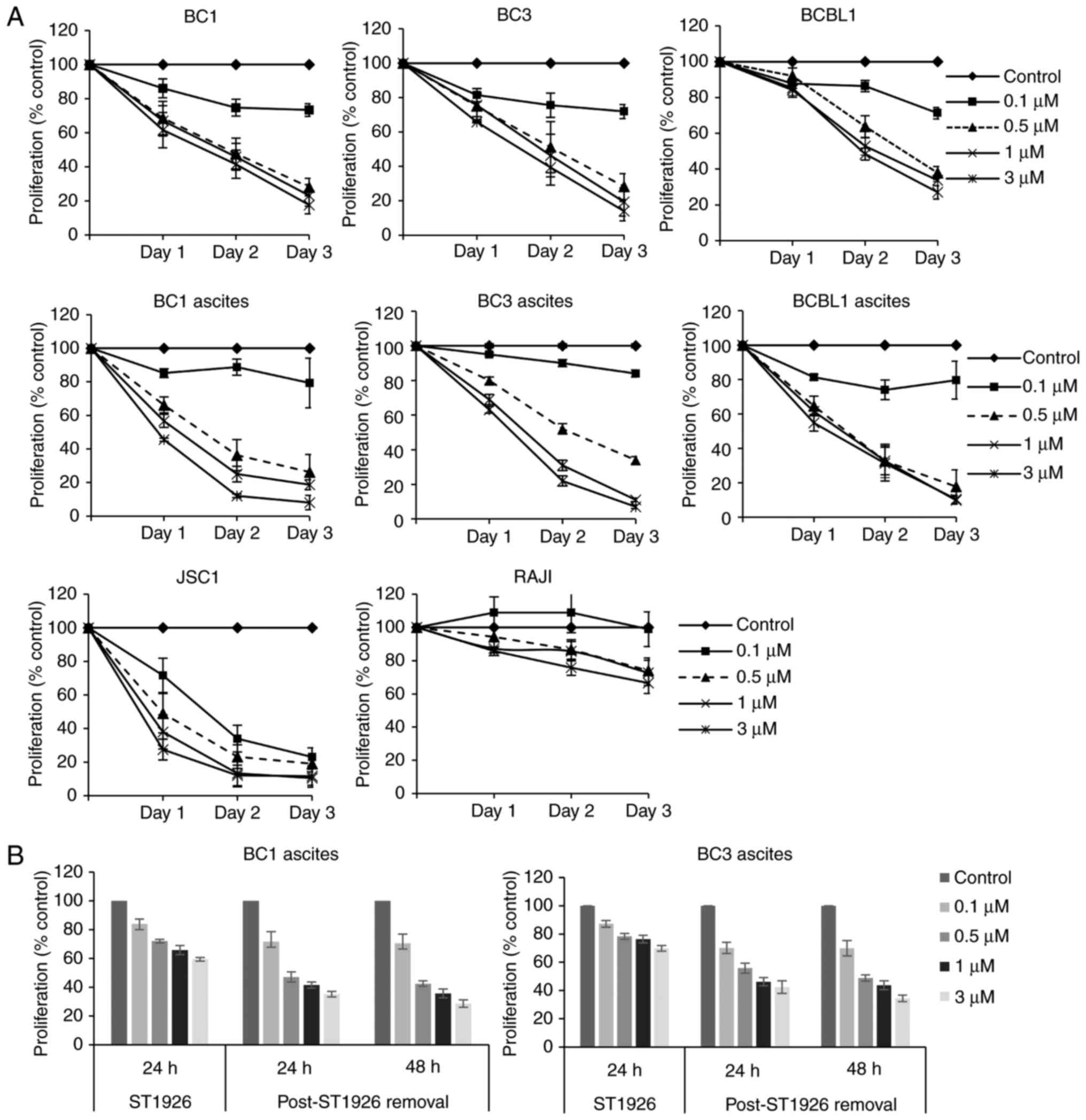
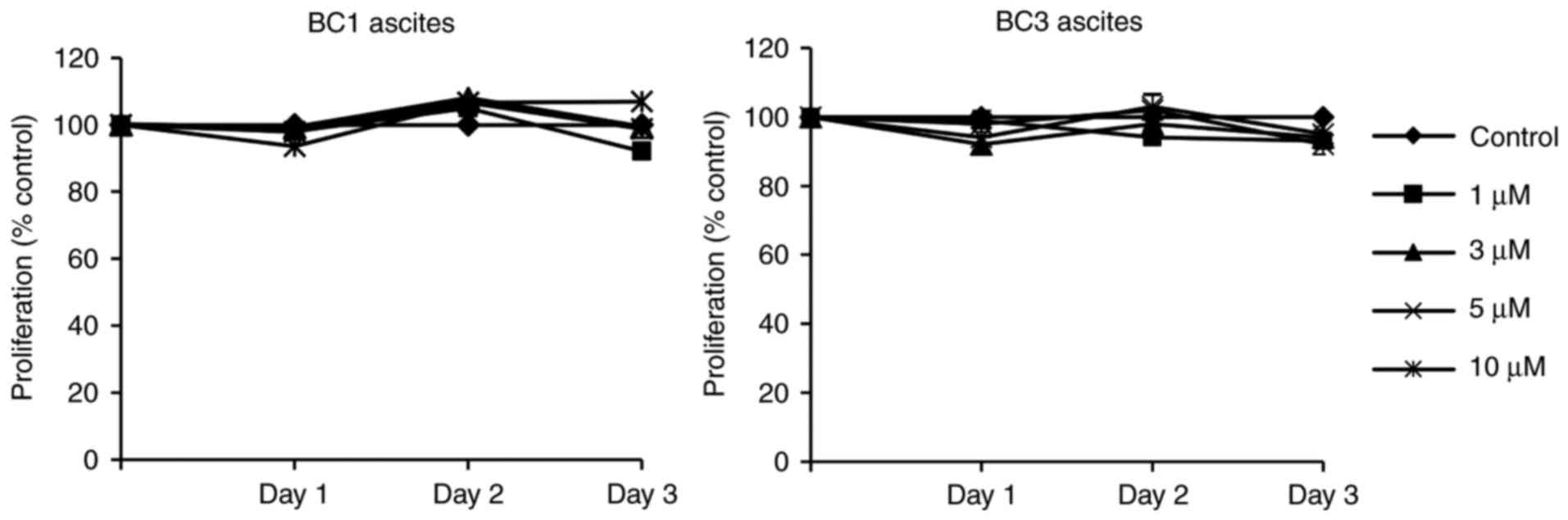
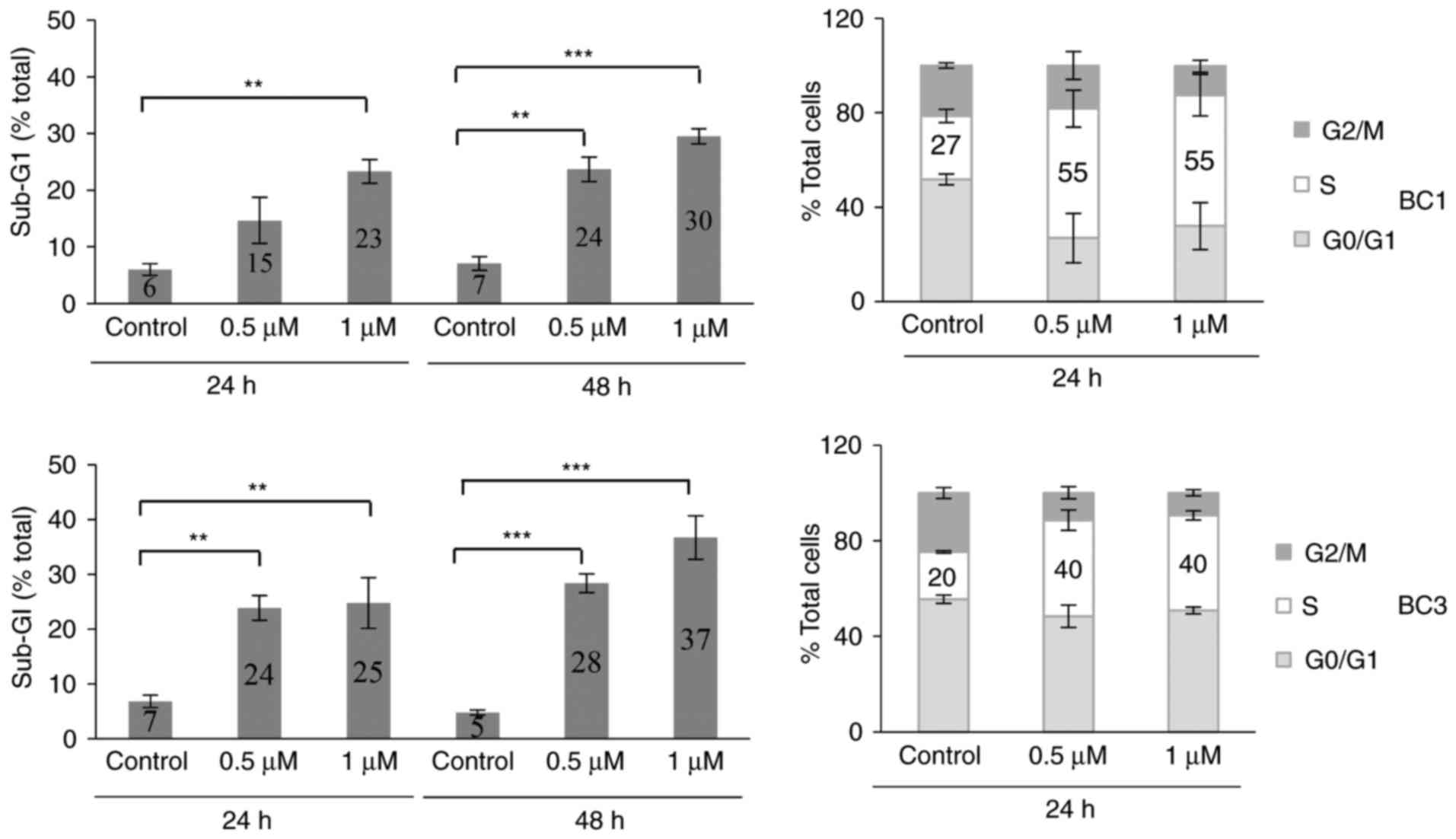
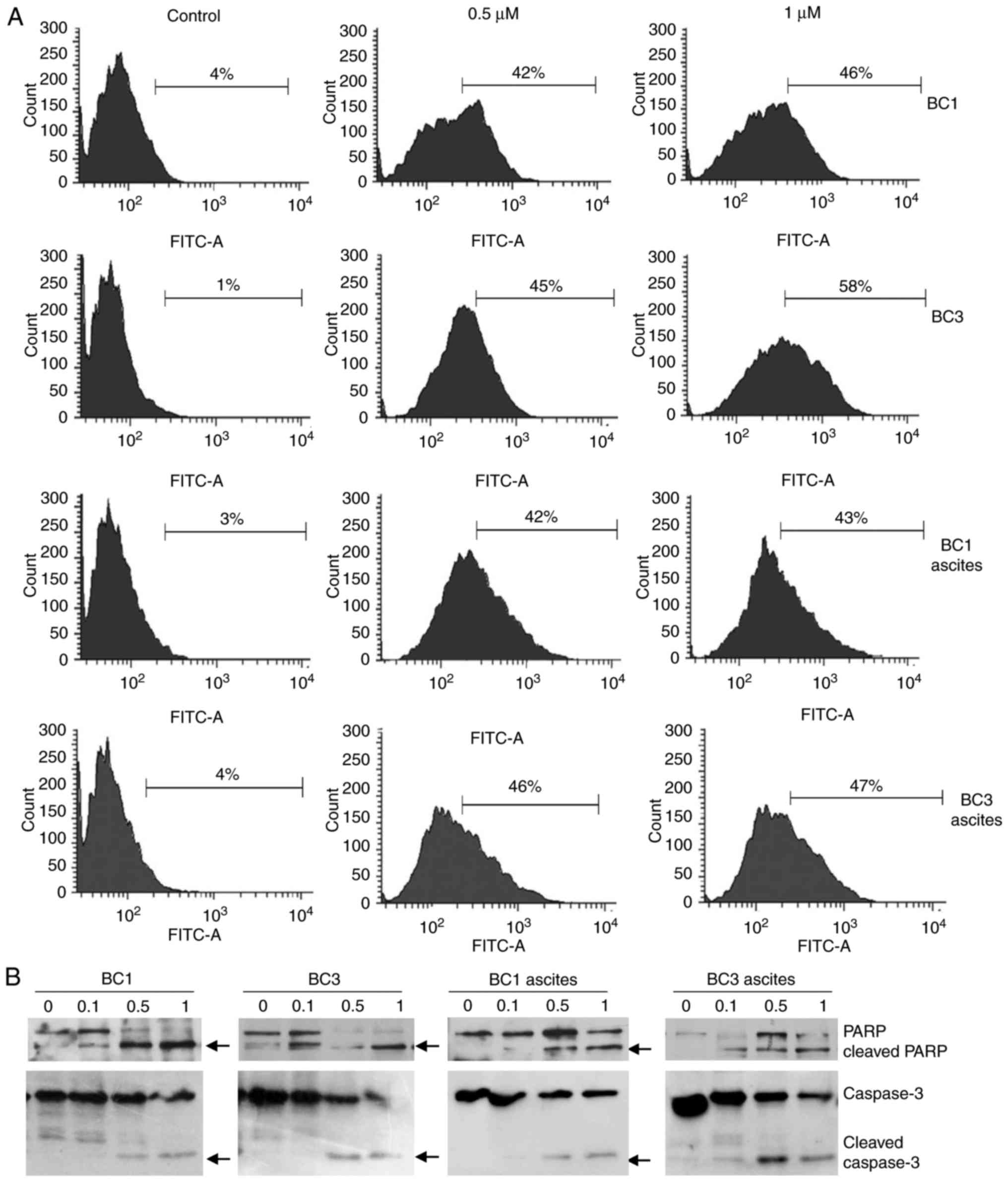
|
1
|
Cesarman E, Chang Y, Moore PS, Said JW and
Knowles DM: Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA
sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N Engl J
Med. 332:1186–1191. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen YB, Rahemtullah A and Hochberg E:
Primary effusion lymphoma. Oncologist. 12:569–576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Patel S and Xiao P: Primary effusion
lymphoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 137:1152–1154. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Boulanger E, Meignin V and Oksenhendler E:
Bortezomib (PS-341) in patients with human herpesvirus 8-associated
primary effusion lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 141:559–561. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jones D, Ballestas ME, Kaye KM, Gulizia
JM, Winters GL, Fletcher J, Scadden DT and Aster JC:
Primary-effusion lymphoma and Kaposi's sarcoma in a
cardiac-transplant recipient. N Engl J Med. 339:444–449. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Okada S, Goto H and Yotsumoto M: Current
status of treatment for primary effusion lymphoma. Intractable Rare
Dis Res. 3:65–74. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Metcalf RA, Wang L, Deos PH, Chock E,
Warnke RA and Natkunam Y: Extracavity primary effusion lymphoma
presenting in a lymph node without lymphomatous effusions. Hum
Pathol Case Rep. 2:36–41. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Pan ZG, Zhang QY, Lu ZB, Quinto T,
Rozenvald IB, Liu LT, Wilson D, Reddy V, Huang Q, Wang HY, et al:
Extracavitary KSHV-associated large B-Cell lymphoma: A distinct
entity or a subtype of primary effusion lymphoma? Study of 9 cases
and review of an additional 43 cases. Am J Surg Pathol.
36:1129–1140. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Carbone A, Gloghini A, Vaccher E, Cerri M,
Gaidano G, Dalla-Favera R and Tirelli U: Kaposi's
sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus type 8-positive
solid lymphomas: A tissue-based variant of primary effusion
lymphoma. J Mol Diagn. 7:17–27. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rivas C, Thlick A-E, Parravicini C, Moore
PS and Chang Y: Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus LANA2 is a
B-cell-specific latent viral protein that inhibits p53. J Virol.
75:429–438. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fakhari FD, Jeong JH, Kanan Y and Dittmer
DP: The latency-associated nuclear antigen of Kaposi
sarcoma-associated herpesvirus induces B cell hyperplasia and
lymphoma. J Clin Invest. 116:735–742. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wen KW and Damania B: Kaposi
sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV): Molecular biology and
oncogenesis. Cancer Lett. 289:140–150. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Carbone A, Cesarman E, Spina M, Gloghini A
and Schulz TF: HIV-associated lymphomas and gamma-herpesviruses.
Blood. 113:1213–1224. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Goncalves PH, Ziegelbauer J, Uldrick TS
and Yarchoan R: Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus-associated cancers and
related diseases. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 12:47–56. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hussain AR, Ahmed M, Ahmed S, Manogaran P,
Platanias LC, Alvi SN, Al-Kuraya KS and Uddin S: Thymoquinone
suppresses growth and induces apoptosis via generation of reactive
oxygen species in primary effusion lymphoma. Free Radic Biol Med.
50:978–987. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bhatt S, Ashlock BM, Toomey NL, Diaz LA,
Mesri EA, Lossos IS and Ramos JC: Efficacious proteasome/HDAC
inhibitor combination therapy for primary effusion lymphoma. J Clin
Invest. 123:2616–2628. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gopalakrishnan R, Matta H, Tolani B,
Triche T Jr and Chaudhary PM: Immunomodulatory drugs target
IKZF1-IRF4-MYC axis in primary effusion lymphoma in a
cereblon-dependent manner and display synergistic cytotoxicity with
BRD4 inhibitors. Oncogene. 35:1797–1810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Abou-Merhi R, Khoriaty R, Arnoult D, El
Hajj H, Dbouk H, Munier S, El-Sabban ME, Hermine O, Gessain A, de
Thé H, et al: PS-341 or a combination of arsenic trioxide and
interferon-alpha inhibit growth and induce caspase-dependent
apoptosis in KSHV/HHV-8-infected primary effusion lymphoma cells.
Leukemia. 21:1792–1801. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
El Hajj H, Ali J, Ghantous A, Hodroj D,
Daher A, Zibara K, Journo C, Otrock Z, Zaatari G, Mahieux R, et al:
Combination of arsenic and interferon-α inhibits expression of KSHV
latent transcripts and synergistically improves survival of mice
with primary effusion lymphomas. PLoS One. 8:e794742013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lippman SM and Lotan R: Advances in the
development of retinoids as chemopreventive agents. J Nutr. 130
Suppl 2S:479S–482S. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gudas LJ: Emerging roles for retinoids in
regeneration and differentiation in normal and disease states.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1821:213–221. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tan X, Sande JL, Pufnock JS, Blattman JN
and Greenberg PD: Retinoic acid as a vaccine adjuvant enhances CD8+
T cell response and mucosal protection from viral challenge. J
Virol. 85:8316–8327. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schlenk RF, Lübbert M, Benner A, Lamparter
A, Krauter J, Herr W, Martin H, Salih HR, Kündgen A, Horst HA, et
al German-Austrian Acute Myeloid Leukemia Study Group, : All-trans
retinoic acid as adjunct to intensive treatment in younger adult
patients with acute myeloid leukemia: Results of the randomized
AMLSG 07–04 study. Ann Hematol. 95:1931–1942. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schenk T, Stengel S and Zelent A:
Unlocking the potential of retinoic acid in anticancer therapy. Br
J Cancer. 111:2039–2045. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
de Thé H: Altered retinoic acid receptors.
FASEB J. 10:955–960. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fontana JA and Rishi AK: Classical and
novel retinoids: Their targets in cancer therapy. Leukemia.
16:463–472. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Parrella E, Giannì M, Fratelli M, Barzago
MM, Raska I Jr, Diomede L, Kurosaki M, Pisano C, Carminati P,
Merlini L, et al: Antitumor activity of the retinoid-related
molecules (E)-3-(4′-hydroxy-3′-adamantylbiphenyl-4-yl)acrylic acid
(ST1926) and 6-[3-(1-adamantyl)-4-hydroxyphenyl]-2-naphthalene
carboxylic acid (CD437) in F9 teratocarcinoma: Role of retinoic
acid receptor gamma and retinoid-independent pathways. Mol
Pharmacol. 70:909–924. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cincinelli R, Dallavalle S, Merlini L,
Penco S, Pisano C, Carminati P, Giannini G, Vesci L, Gaetano C,
Illy B, et al: A novel atypical retinoid endowed with proapoptotic
and antitumor activity. J Med Chem. 46:909–912. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Garattini E, Gianni M and Terao M:
Retinoid related molecules an emerging class of apoptotic agents
with promising therapeutic potential in oncology: Pharmacological
activity and mechanisms of action. Curr Pharm Des. 10:433–448.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zuco V, Zanchi C, Cassinelli G, Lanzi C,
Supino R, Pisano C, Zanier R, Giordano V, Garattini E and Zunino F:
Induction of apoptosis and stress response in ovarian carcinoma
cell lines treated with ST1926, an atypical retinoid. Cell Death
Differ. 11:280–289. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Basma H, Ghayad SE, Rammal G, Mancinelli
A, Harajly M, Ghamloush F, Dweik L, El-Eit R, Zalzali H, Rabeh W,
et al: The synthetic retinoid ST1926 as a novel therapeutic agent
in rhabdomyosarcoma. Int J Cancer. 138:1528–1537. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Garattini E, Parrella E, Diomede L,
Gianni' M, Kalac Y, Merlini L, Simoni D, Zanier R, Ferrara FF,
Chiarucci I, et al: ST1926, a novel and orally active
retinoid-related molecule inducing apoptosis in myeloid leukemia
cells: Modulation of intracellular calcium homeostasis. Blood.
103:194–207. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
El Hajj H, Khalil B, Ghandour B, Nasr R,
Shahine S, Ghantous A, Abdel-Samad R, Sinjab A, Hasegawa H, Jabbour
M, et al: Preclinical efficacy of the synthetic retinoid ST1926 for
treating adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood. 124:2072–2080.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nasr RR, Hmadi RA, El-Eit RM, Iskandarani
AN, Jabbour MN, Zaatari GS, Mahon FX, Pisano CC and Darwiche ND:
ST1926, an orally active synthetic retinoid, induces apoptosis in
chronic myeloid leukemia cells and prolongs survival in a murine
model. Int J Cancer. 137:698–709. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zuco V, Zanchi C, Lanzi C, Beretta GL,
Supino R, Pisano C, Barbarino M, Zanier R, Bucci F, Aulicino C, et
al: Development of resistance to the atypical retinoid, ST1926, in
the lung carcinoma cell line H460 is associated with reduced
formation of DNA strand breaks and a defective DNA damage response.
Neoplasia. 7:667–677. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Valli C, Paroni G, Di Francesco AM,
Riccardi R, Tavecchio M, Erba E, Boldetti A, Gianni' M, Fratelli M,
Pisano C, et al: Atypical retinoids ST1926 and CD437 are S
phase-specific agents causing DNA double-strand breaks:
Significance for the cytotoxic and antiproliferative activity. Mol
Cancer Ther. 7:2941–2954. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sun SY and Lotan R: Retinoids and their
receptors in cancer development and chemoprevention. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 41:41–55. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tomayko MM and Reynolds CP: Determination
of subcutaneous tumor size in athymic (nude) mice. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 24:148–154. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sala F, Zucchetti M, Bagnati R, D'Incalci
M, Pace S, Capocasa F and Marangon E: Development and validation of
a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the
determination of ST1926, a novel oral antitumor agent, adamantyl
retinoid derivative, in plasma of patients in a Phase I study. J
Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 877:3118–3126. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hemann MT and Lowe SW: The p53-Bcl-2
connection. Cell Death Differ. 13:1256–1259. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zuco V, Benedetti V, De Cesare M and
Zunino F: Sensitization of ovarian carcinoma cells to the atypical
retinoid ST1926 by the histone deacetylase inhibitor, RC307:
Enhanced DNA damage response. Int J Cancer. 126:1246–1255.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fratelli M, Fisher JN, Paroni G, Di
Francesco AM, Pierri F, Pisano C, Godl K, Marx S, Tebbe A, Valli C,
et al: New insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying
sensitivity/resistance to the atypical retinoid ST1926 in acute
myeloid leukaemia cells: The role of histone H2A.Z, cAMP-dependent
protein kinase A and the proteasome. Eur J Cancer. 49:1491–1500.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Aouad P, Saikali M, Abdel-Samad R, Fostok
S, El-Houjeiri L, Pisano C, Talhouk R and Darwiche N: Antitumor
activities of the synthetic retinoid ST1926 in two-dimensional and
three-dimensional human breast cancer models. Anticancer Drugs.
28:757–770. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Schulz TF: KSHV/HHV8-associated
lymphoproliferations in the AIDS setting. Eur J Cancer.
37:1217–1226. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Carbone A and Gloghini A:
KSHV/HHV8-associated lymphomas. Br J Haematol. 140:13–24.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wies E, Mori Y, Hahn A, Kremmer E, Stürzl
M, Fleckenstein B and Neipel F: The viral interferon-regulatory
factor-3 is required for the survival of KSHV-infected primary
effusion lymphoma cells. Blood. 111:320–327. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Degos L and Wang ZY: All trans retinoic
acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Oncogene. 20:7140–7145. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hassan M, Watari H, AbuAlmaaty A, Ohba Y
and Sakuragi N: Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in
cancer. BioMed Res Int. 2014:1508452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Di Francesco AM, Meco D, Torella AR,
Barone G, D'Incalci M, Pisano C, Carminati P and Riccardi R: The
novel atypical retinoid ST1926 is active in ATRA resistant
neuroblastoma cells acting by a different mechanism. Biochem
Pharmacol. 73:643–655. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Petre CE, Sin SH and Dittmer DP:
Functional p53 signaling in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus
lymphomas: Implications for therapy. J Virol. 81:1912–1922. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Florea AM and Büsselberg D: Cisplatin as
an anti-tumor drug: Cellular mechanisms of activity, drug
resistance and induced side effects. Cancers. 3:1351–1371. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hühn D, Bolck HA and Sartori AA: Targeting
DNA double-strand break signalling and repair: Recent advances in
cancer therapy. Swiss Med Wkly. 143:w138372013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zannini L, Delia D and Buscemi G: CHK2
kinase in the DNA damage response and beyond. J Mol Cell Biol.
6:442–457. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
O'Neill KL, Huang K, Zhang J, Chen Y and
Luo X: Inactivation of prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins activates Bax/Bak
through the outer mitochondrial membrane. Genes Dev. 30:973–988.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Luppi M, Trovato R, Barozzi P, Vallisa D,
Rossi G, Re A, Ravazzini L, Potenza L, Riva G, Morselli M, et al:
Treatment of herpesvirus associated primary effusion lymphoma with
intracavity cidofovir. Leukemia. 19:473–476. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cho HJ, Jeong SG, Park JE, Han JA, Kang
HR, Lee D and Song MJ: Antiviral activity of angelicin against
gammaherpesviruses. Antiviral Res. 100:75–83. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Williamson SJ, Nicol SM, Stürzl M, Sabbah
S and Hislop AD: Azidothymidine sensitizes primary effusion
lymphoma cells to Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-specific
CD4+ T cell control and inhibits vIRF3 function. PLoS Pathog.
12:e10060422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|