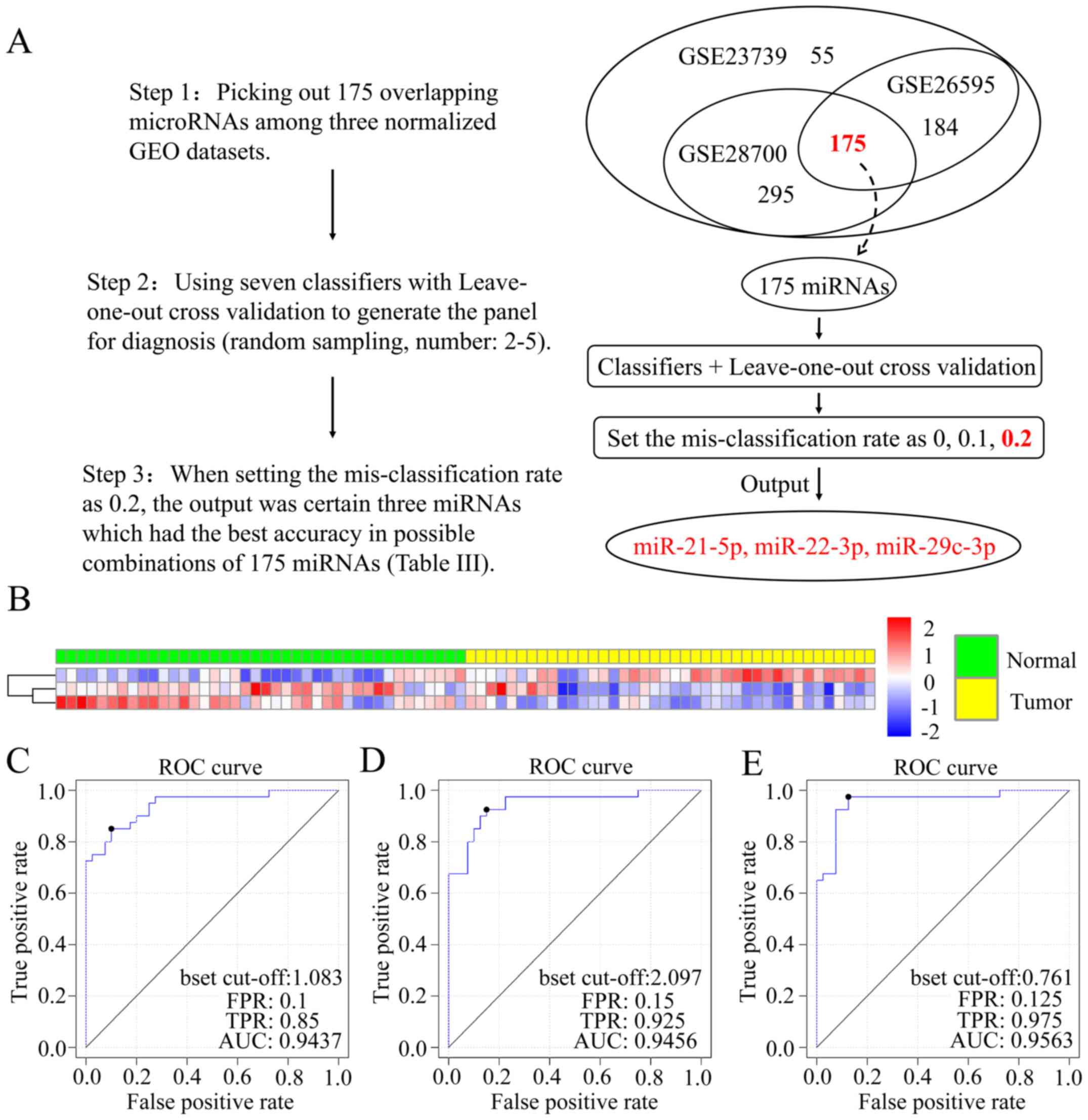
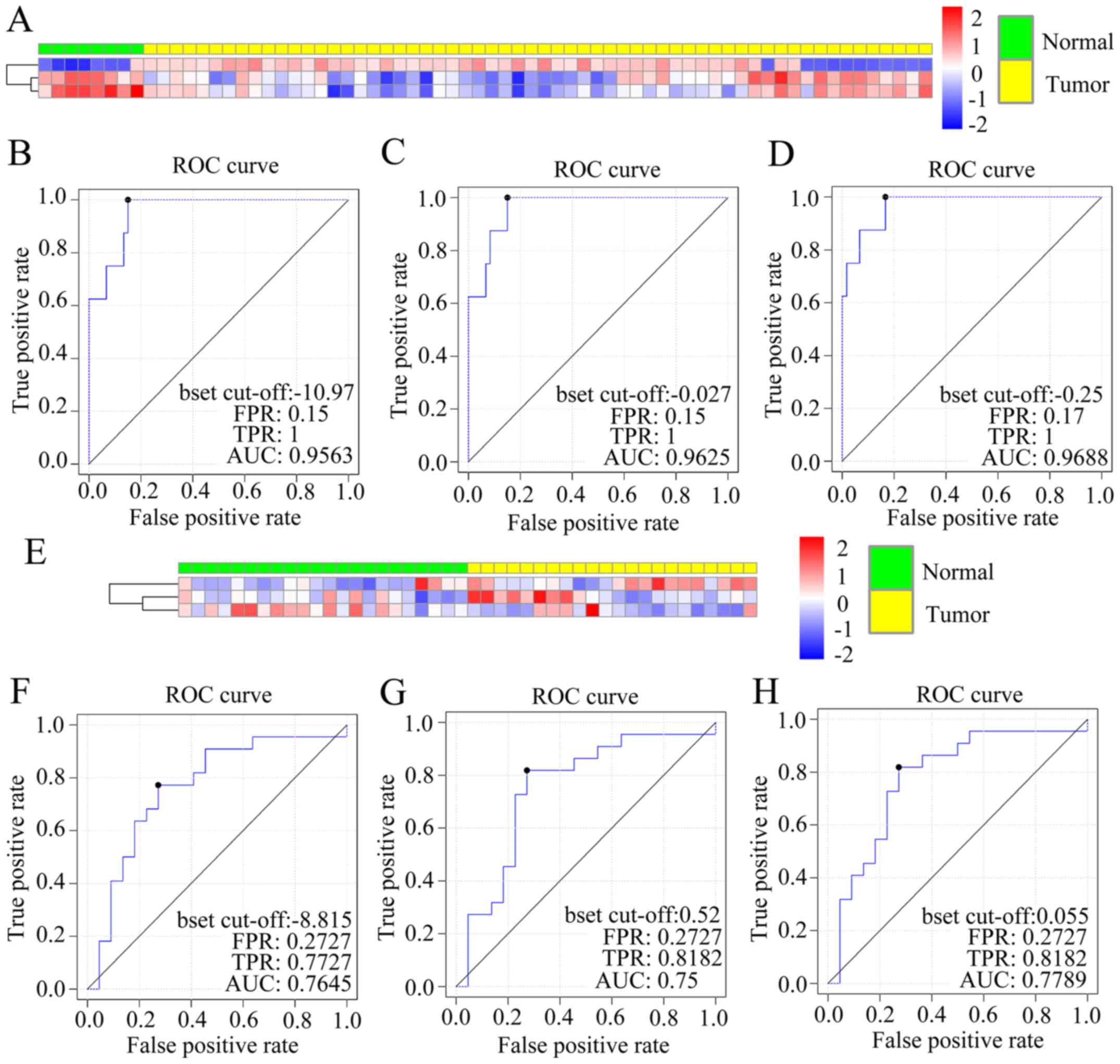
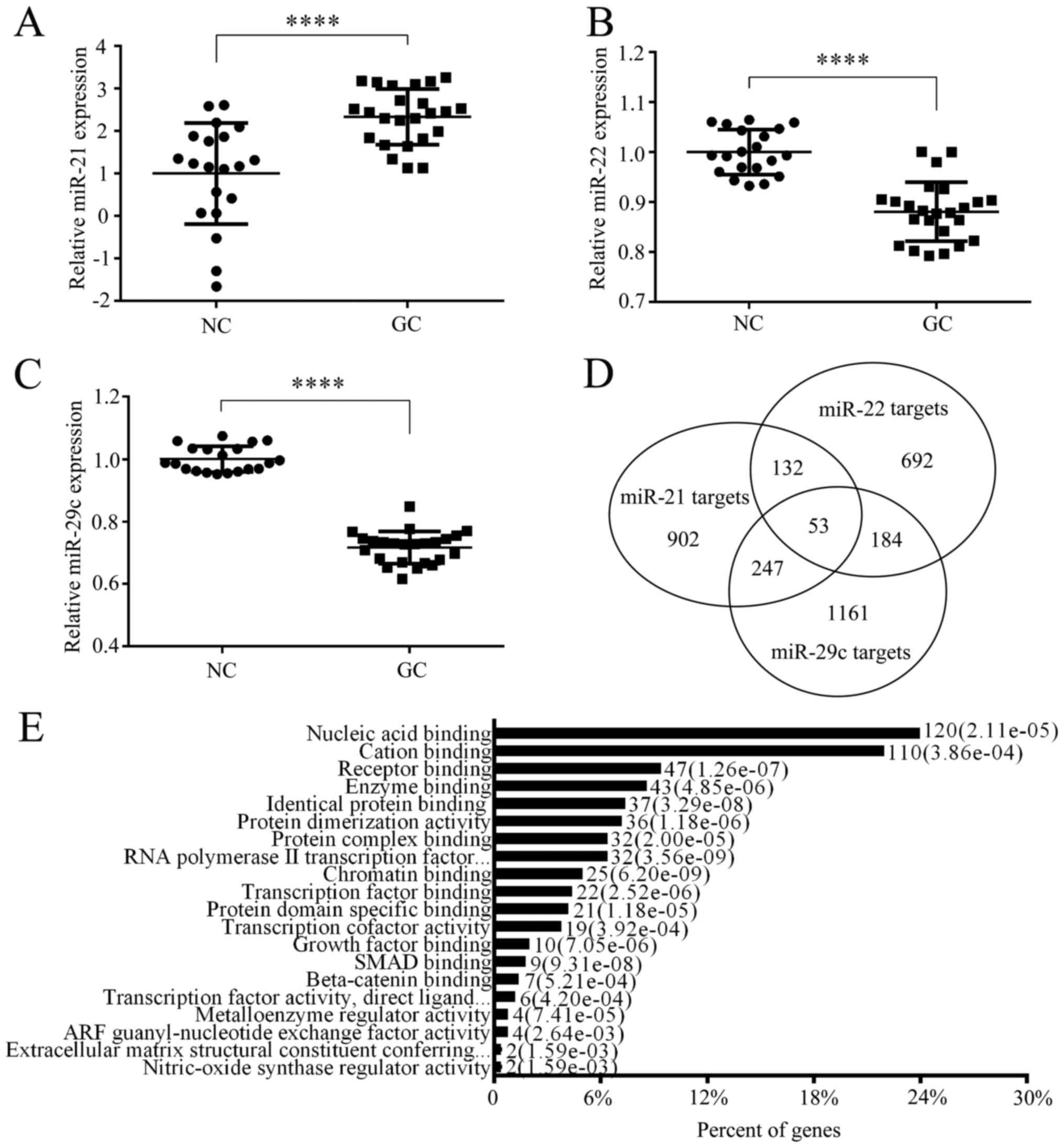
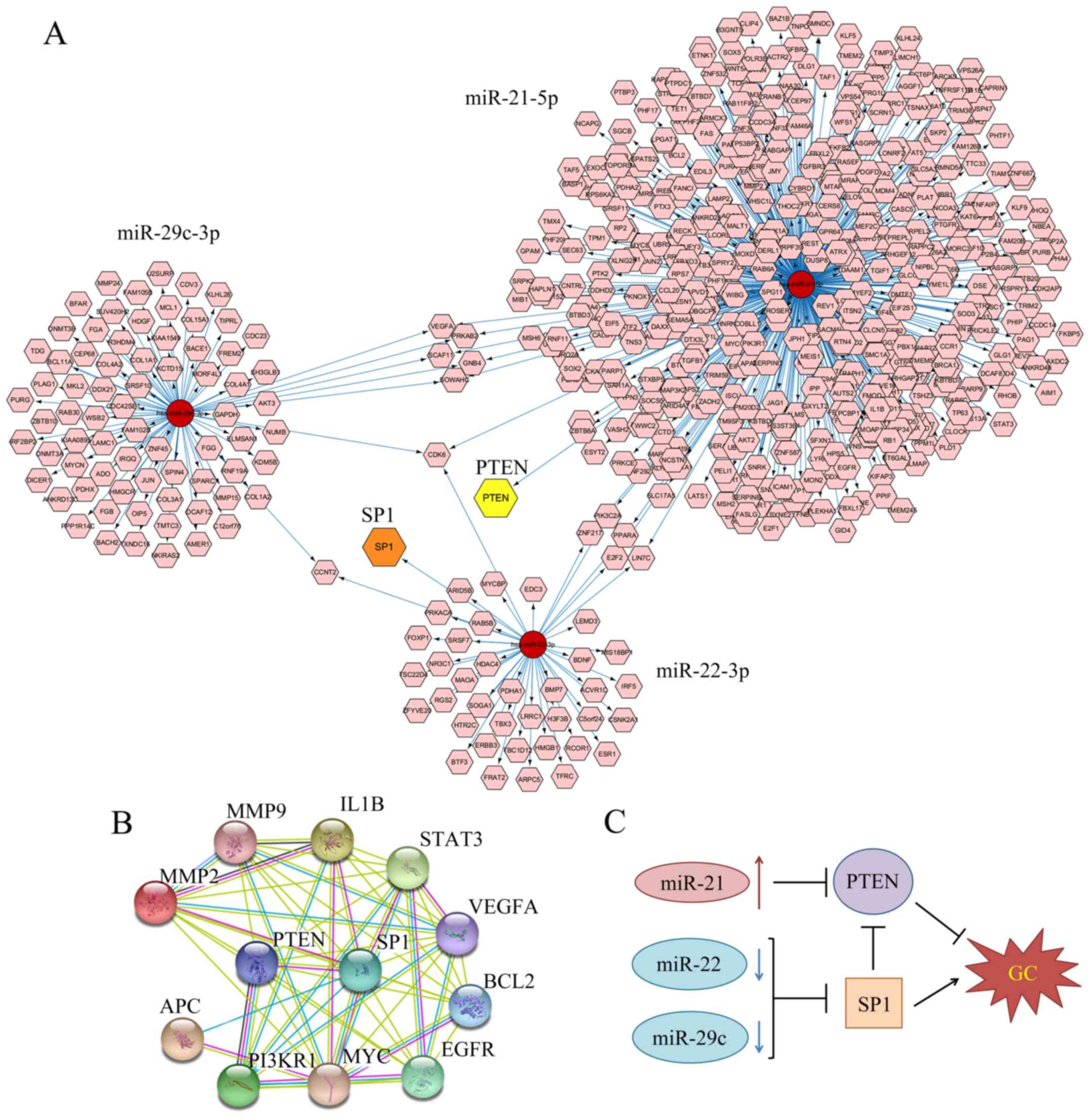
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Song JH and Meltzer SJ: MicroRNAs in
pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of gastroesophageal cancers.
Gastroenterology. 143:35–47.e2. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li BS, Zhao YL, Guo G, Li W, Zhu ED, Luo
X, Mao XH, Zou QM, Yu PW, Zuo QF, et al: Plasma microRNAs, miR-223,
miR-21 and miR-218, as novel potential biomarkers for gastric
cancer detection. PLoS One. 7:e416292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ventura A and Jacks T: MicroRNAs and
cancer: Short RNAs go a long way. Cell. 136:586–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shrestha S, Hsu SD, Huang WY, Huang HY,
Chen W, Weng SL and Huang HD: A systematic review of microRNA
expression profiling studies in human gastric cancer. Cancer Med.
3:878–888. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Berrar DP, Dubitzky W and Granzow M: A
practical approach to microarray data analysis. Springer; New York:
pp. 3682003
|
|
10
|
Radmacher MD, McShane LM and Simon R: A
paradigm for class prediction using gene expression profiles. J
Comput Biol. 9:505–511. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dudoit S, Fridlyand J and Speed TP:
Comparison of discrimination methods for the classification of
tumors using gene expression data. J Am Stat Assoc. 97:77–87. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Efron B, Tibshirani R, Storey JD and
Tusher V: Empirical Bayes analysis of a microarray experiment. J Am
Stat Assoc. 96:1151–1160. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wright G, Tan B, Rosenwald A, Hurt EH,
Wiestner A and Staudt LM: A gene expression-based method to
diagnose clinically distinct subgroups of diffuse large B cell
lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:pp. 9991–9996. 2003;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li L, Darden TA, Weinberg CR, Levine AJ
and Pedersen LG: Gene assessment and sample classification for gene
expression data using a genetic algorithm/k-nearest neighbor
method. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 4:727–739. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pal M: Modified nearest neighbour
classifier for hyperspectral data classification. Int J Remote
Sens. 32:9207–9217. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Furey TS, Cristianini N, Duffy N,
Bednarski DW, Schummer M and Haussler D: Support vector machine
classification and validation of cancer tissue samples using
microarray expression data. Bioinformatics. 16:906–914. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kutmon M, Kelder T, Mandaviya P, Evelo CT
and Coort SL: CyTargetLinker: A cytoscape app to integrate
regulatory interactions in network analysis. PLoS One.
8:e821602013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang JL, Hu Y, Kong X, Wang ZH, Chen HY,
Xu J and Fang JY: Candidate microRNA biomarkers in human gastric
cancer: A systematic review and validation study. PLoS One.
8:e736832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang W, Jin Z, Zhou F, Cui J and Wang L
and Wang L: High co-expression of Sp1 and HER-2 is correlated with
poor prognosis of gastric cancer patients. Surg Oncol. 24:220–225.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang HW, Wang EW, Li LX, Yi SH, Li LC, Xu
FL, Wang DL, Wu YZ and Nian WQ: A regulatory loop involving miR-29c
and Sp1 elevates the TGF-β1 mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition in lung cancer. Oncotarget. 7:85905–85916.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang BG, Li JF, Yu BQ, Zhu ZG, Liu BY and
Yan M: microRNA-21 promotes tumor proliferation and invasion in
gastric cancer by targeting PTEN. Oncol Rep. 27:1019–1026. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zheng P, Chen L, Yuan X, Luo Q, Liu Y, Xie
G, Ma Y and Shen L: Exosomal transfer of tumor-associated
macrophage-derived miR-21 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric
cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Eto K, Iwatsuki M, Watanabe M, Ida S,
Ishimoto T, Iwagami S, Baba Y, Sakamoto Y, Miyamoto Y, Yoshida N,
et al: The microRNA-21/PTEN pathway regulates the sensitivity of
HER2-positive gastric cancer cells to trastuzumab. Ann Surg Oncol.
21:343–350. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang SM, Huang C, Li XF, Yu MZ, He Y and
Li J: miR-21 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells
by regulating PTEN. Toxicology. 306:162–168. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cai H, Yuan Y, Hao YF, Guo TK, Wei X and
Zhang YM: Plasma microRNAs serve as novel potential biomarkers for
early detection of gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 30:4522013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kourou K, Exarchos TP, Exarchos KP,
Karamouzis MV and Fotiadis DI: Machine learning applications in
cancer prognosis and prediction. Comput Struct Biotechnol J.
13:8–17. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pan L, Liu G, Lin F, Zhong S, Xia H, Sun X
and Liang H: Machine learning applications for prediction of
relapse in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci Rep.
7:74022017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen Y, Luo Y, Huang W, Hu D, Zheng RQ,
Cong SZ, Meng FK, Yang H, Lin HJ, Sun Y, et al:
Machine-learning-based classification of real-time tissue
elastography for hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic
hepatitis B. Comput Biol Med. 89:18–23. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang B, He X, Ouyang F, Gu D, Dong Y,
Zhang L, Mo X, Huang W, Tian J and Zhang S: Radiomic
machine-learning classifiers for prognostic biomarkers of advanced
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 403:21–27. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sekar D, Krishnan R, Thirugnanasambantham
K, Rajasekaran B, Islam VIH and Sekar P: Significance of microRNA
21 in gastric cancer. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 40:538–545.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang Z, Li Z, Gao C, Chen P, Chen J, Liu
W, Xiao S and Lu H: miR-21 plays a pivotal role in gastric cancer
pathogenesis and progression. Lab Invest. 88:1358–1366. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chan SH, Wu CW, Li AF, Chi CW and Lin WC:
miR-21 microRNA expression in human gastric carcinomas and its
clinical association. Anticancer Res. 28:907–911. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Karimi Kurdistani Z, Saberi S, Tsai KW and
Mohammadi M: MicroRNA-21: Mechanisms of Oncogenesis and its
Application in Diagnosis and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer. Arch Iran
Med. 18:524–536. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang D, Fan Z, Liu F and Zuo J: Hsa-miR-21
and Hsa-miR-29 in tissue as potential diagnostic and prognostic
biomarkers for gastric cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 37:1454–1462.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Y, Zhang X, Li H, Yu J and Ren X: The
role of miRNA-29 family in cancer. Eur J Cell Biol. 92:123–128.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Han TS, Hur K, Xu G, Choi B, Okugawa Y,
Toiyama Y, Oshima H, Oshima M, Lee HJ, Kim VN, et al: MicroRNA-29c
mediates initiation of gastric carcinogenesis by directly targeting
ITGB1. Gut. 64:203–214. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang W, Li F, Zhang Y, Tu Y, Yang Q and
Gao X: Reduced expression of miR-22 in gastric cancer is related to
clinicopathologic characteristics or patient prognosis. Diagn
Pathol. 8:1022013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Guo MM, Hu LH, Wang YQ, Chen P, Huang JG,
Lu N, He JH and Liao CG: miR-22 is down-regulated in gastric
cancer, and its overexpression inhibits cell migration and invasion
via targeting transcription factor Sp1. Med Oncol. 30:5422013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tan NY and Khachigian LM: Sp1
phosphorylation and its regulation of gene transcription. Mol Cell
Biol. 29:2483–2488. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang L, Wei D, Huang S, Peng Z, Le X, Wu
TT, Yao J, Ajani J and Xie K: Transcription factor Sp1 expression
is a significant predictor of survival in human gastric cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 9:6371–6380. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xiao S, Yang Z, Qiu X, Lv R, Liu J, Wu M,
Liao Y and Liu Q: miR-29c contribute to glioma cells temozolomide
sensitivity by targeting O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferases
indirectely. Oncotarget. 7:50229–50238. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li C, Song L, Zhang Z, Bai XX, Cui MF and
Ma LJ: MicroRNA-21 promotes TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in gastric cancer through up-regulating PTEN expression.
Oncotarget. 7:66989–67003. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kou XX, Hao T, Meng Z, Zhou YH and Gan YH:
Acetylated Sp1 inhibits PTEN expression through binding to PTEN
core promoter and recruitment of HDAC1 and promotes cancer cell
migration and invasion. Carcinogenesis. 34:58–67. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|