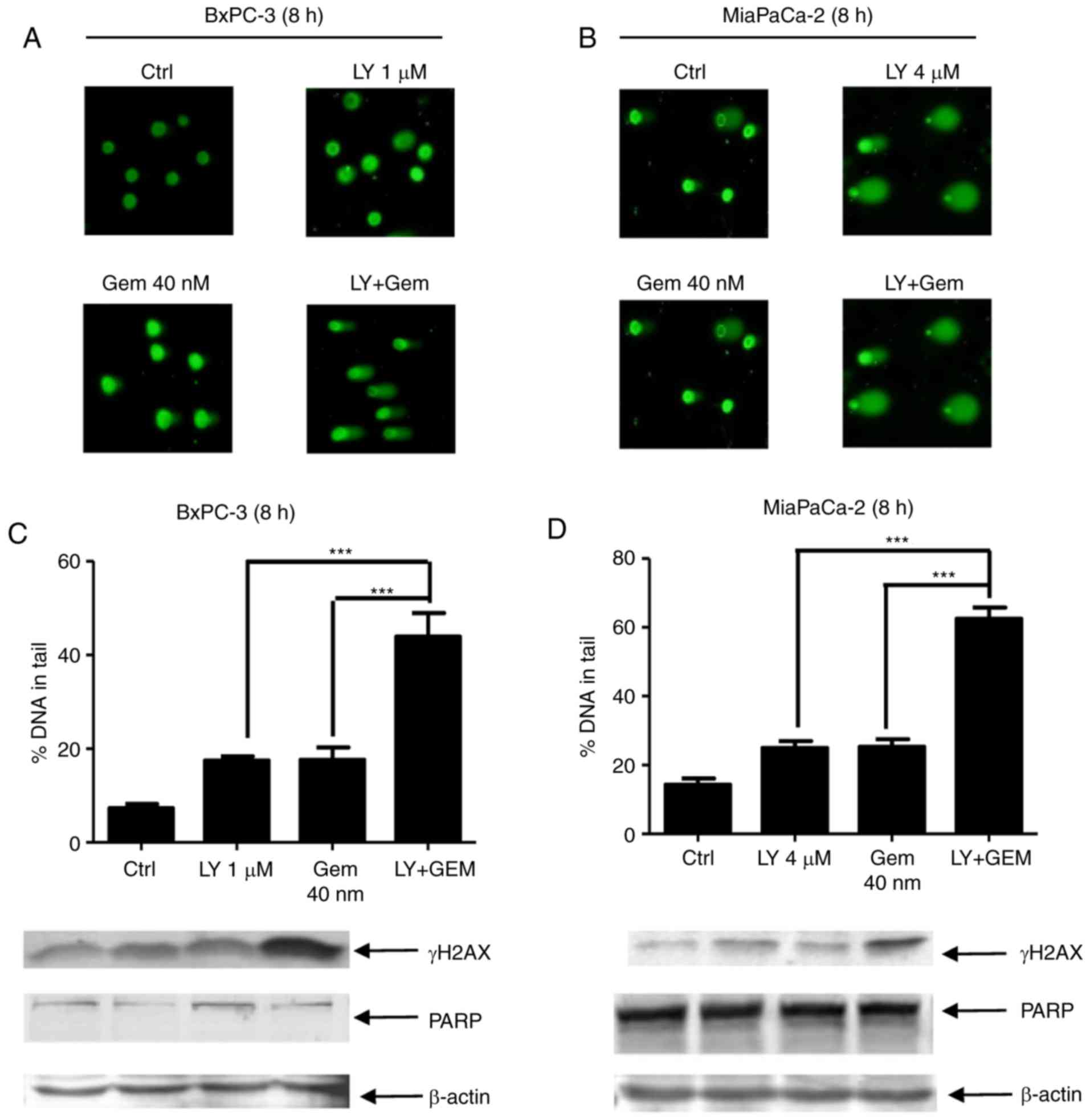
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J,
Murray T and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin.
58:71–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Burris HA III, Moore MJ, Andersen J, Green
MR, Rothenberg ML, Modiano MR, Cripps MC, Portenoy RK, Storniolo
AM, Tarassoff P, et al: Improvements in survival and clinical
benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with
advanced pancreas cancer: A randomized trial. J Clin Oncol.
15:2403–2413. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang P, Chubb S, Hertel LW, Grindey GB
and Plunkett W: Action of 2′,2′-difluorodeoxycytidine on DNA
synthesis. Cancer Res. 51:6110–6117. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kullmann F, Hollerbach S, Dollinger MM,
Harder J, Fuchs M, Messmann H, Trojan J, Gäbele E, Hinke A,
Hollerbach C and Endlicher E: Cetuximab plus
gemcitabine/oxaliplatin (GEMOXCET) in first-line metastatic
pancreatic cancer: A multicentre phase II study. Br J Cancer.
100:1032–1036. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li J and Saif MW: Advancements in the
management of pancreatic cancer. JOP. 10:109–117. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dai Y and Grant S: New insights into
checkpoint kinase 1 in the DNA damage response signaling network.
Clin Cancer Res. 16:376–383. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Löffler H, Rebacz B, Ho AD, Lukas J,
Bartek J and Kramer A: Chk1-dependent regulation of Cdc25B
functions to coordinate mitotic events. Cell Cycle. 5:2543–2547.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Scarpa A, Capelli P, Mukai K, Zamboni G,
Oda T, Iacono C and Hirohashi S: Pancreatic adenocarcinomas
frequently show p53 gene mutations. Am J Pathol. 142:1534–1543.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Morgan MA, Parsels LA, Zhao L, Parsels JD,
Davis MA, Hassan MC, Arumugarajah S, Hylander-Gans L, Morosini D,
Simeone DM, et al: Mechanism of radiosensitization by the Chk1/2
inhibitor AZD7762 involves abrogation of the G2 checkpoint and
inhibition of homologous recombinational DNA repair. Cancer Res.
70:4972–4981. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Buisson R, Boisvert JL, Benes CH and Zou
L: Distinct but concerted roles of ATR, DNA-PK, and Chk1 in
countering replication stress durings phase. Mol Cell.
59:1011–1024. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nordlund P and Reichard P: Ribonucleotide
reductases. Annu Rev Biochem. 75:681–706. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
King C, Diaz H, Barnard D, Barda D,
Clawson D, Blosser W, Cox K, Guo S and Marshall M: Characterization
and preclinical development of LY2603618: A selective and potent
Chk1 inhibitor. Invest New Drugs. 32:213–226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Calvo E, Chen VJ, Marshall M, Ohnmacht U,
Hynes SM, Kumm E, Diaz HB, Barnard D, Merzoug FF, Huber L, et al:
Preclinical analyses and phase I evaluation of LY2603618
administered in combination with pemetrexed and cisplatin in
patients with advanced cancer. Invest New Drugs. 32:955–968. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Taub JW, Huang X, Matherly LH, Stout ML,
Buck SA, Massey GV, Becton DL, Chang MN, Weinstein HJ and
Ravindranath Y: Expression of chromosome 21-localized genes in
acute myeloid leukemia: Differences between Down syndrome and
non-Down syndrome blast cells and relationship to in vitro
sensitivity to cytosine arabinoside and daunorubicin. Blood.
94:1393–1400. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xie C, Edwards H, Xu X, Zhou H, Buck SA,
Stout ML, Yu Q, Rubnitz JE, Matherly LH, Taub JW and Ge Y:
Mechanisms of synergistic antileukemic interactions between
valproic acid and cytarabine in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia.
Clin Cancer Res. 16:5499–5510. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chou TC: Theoretical basis, experimental
design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in
drug combination studies. Pharmacol Rev. 58:621–681. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang G, He J, Zhao J, Yun W, Xie C, Taub
JW, Azmi A, Mohammad RM, Dong Y, Kong W, et al: Class I and class
II histone deacetylases are potential therapeutic targets for
treating pancreatic cancer. PLoS One. 7:e520952012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Edwards H, Xie C, La Fiura KM, Dombkowski
AA, Buck SA, Boerner JL, Taub JW, Matherly LH and Ge Y: RUNX1
regulates phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway: Role in
chemotherapy sensitivity in acute megakaryocytic leukemia. Blood.
114:2744–2752. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xie C, Drenberg C, Edwards H, Caldwell JT,
Chen W, Inaba H, Xu X, Buck SA, Taub JW, Baker SD and Ge Y:
Panobinostat enhances cytarabine and daunorubicin sensitivities in
AML cells through suppressing the expression of BRCA1, CHK1, and
Rad51. PLoS One. 8:e791062013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang FZ, Fei HR, Cui YJ, Sun YK, Li ZM,
Wang XY, Yang XY, Zhang JG and Sun BL: The checkpoint 1 kinase
inhibitor LY2603618 induces cell cycle arrest, DNA damage response
and autophagy in cancer cells. Apoptosis. 19:1389–1398. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kasahara K, Goto H, Enomoto M, Tomono Y,
Kiyono T and Inagaki M: 14-3-3gamma mediates Cdc25A proteolysis to
block premature mitotic entry after DNA damage. EMBO J.
29:2802–2812. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Clarke CA and Clarke PR: DNA-dependent
phosphorylation of Chk1 and Claspin in a human cell-free system.
Biochem J. 388:705–712. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang YW, Otterness DM, Chiang GG, Xie W,
Liu YC, Mercurio F and Abraham RT: Genotoxic stress targets human
Chk1 for degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Mol Cell.
19:607–618. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Parsels LA, Morgan MA, Tanska DM, Parsels
JD, Palmer BD, Booth RJ, Denny WA, Canman CE, Kraker AJ, Lawrence
TS and Maybaum J: Gemcitabine sensitization by checkpoint kinase 1
inhibition correlates with inhibition of a Rad51 DNA damage
response in pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:45–54.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Matthews DJ, Yakes FM, Chen J, Tadano M,
Bornheim L, Clary DO, Tai A, Wagner JM, Miller N, Kim YD, et al:
Pharmacological abrogation of S-phase checkpoint enhances the
anti-tumor activity of gemcitabine in vivo. Cell Cycle. 6:104–110.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Barnard D, Diaz HB, Burke T, Donoho G,
Beckmann R, Jones B, Barda D, King C and Marshall M: LY2603618, a
selective CHK1 inhibitor, enhances the anti-tumor effect of
gemcitabine in xenograft tumor models. Invest New Drugs. 34:49–60.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Davidson JD, Ma L, Flagella M, Geeganage
S, Gelbert LM and Slapak CA: An increase in the expression of
ribonucleotide reductase large subunit 1 is associated with
gemcitabine resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines.
Cancer Res. 64:3761–3766. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bergman AM, Eijk PP, Ruiz van Haperen VW,
Smid K, Veerman G, Hubeek I, Van den Ijssel P, Ylstra B and Peters
GJ: In vivo induction of resistance to gemcitabine results in
increased expression of ribonucleotide reductase subunit M1 as the
major determinant. Cancer Res. 65:9510–9516. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|