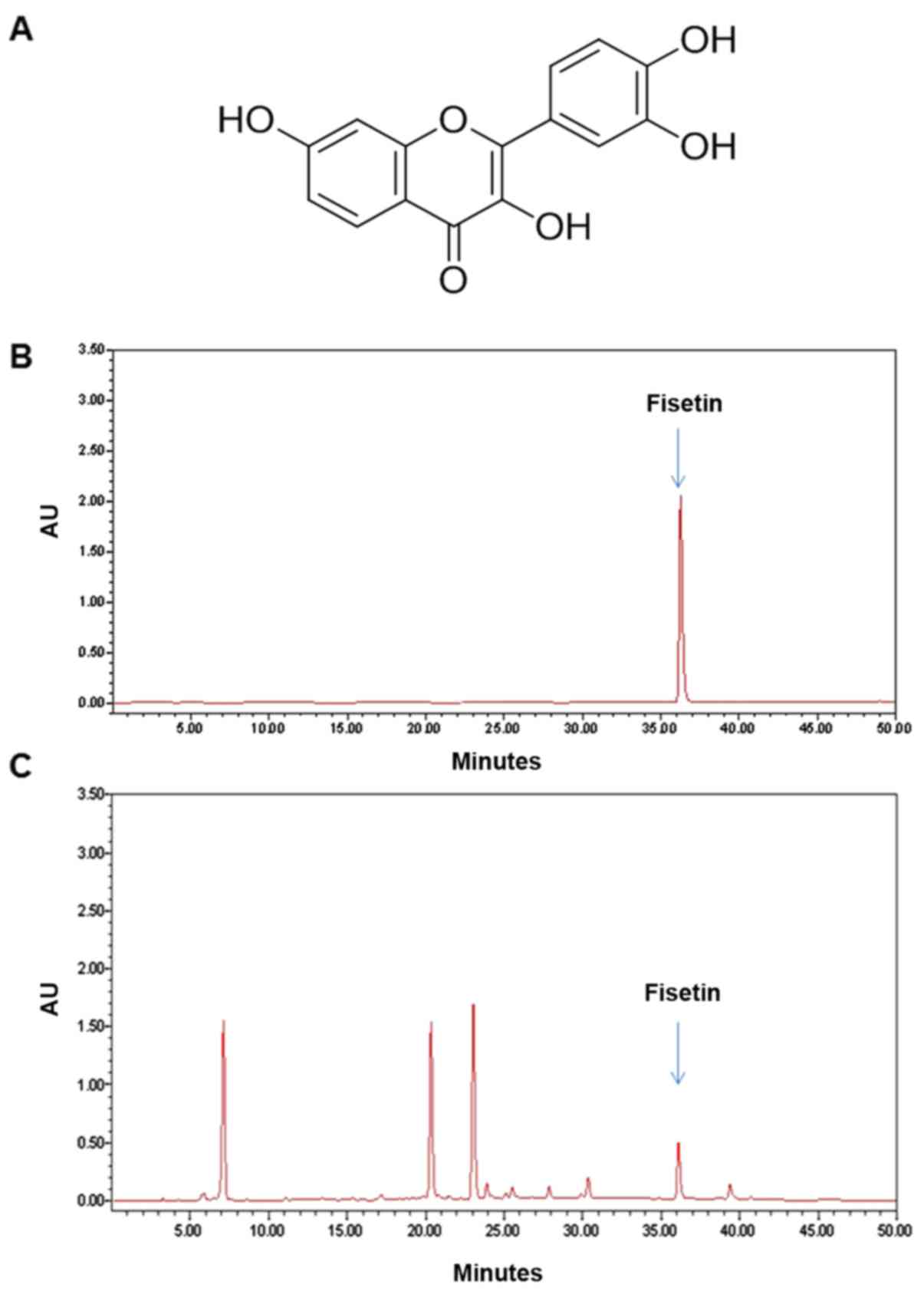
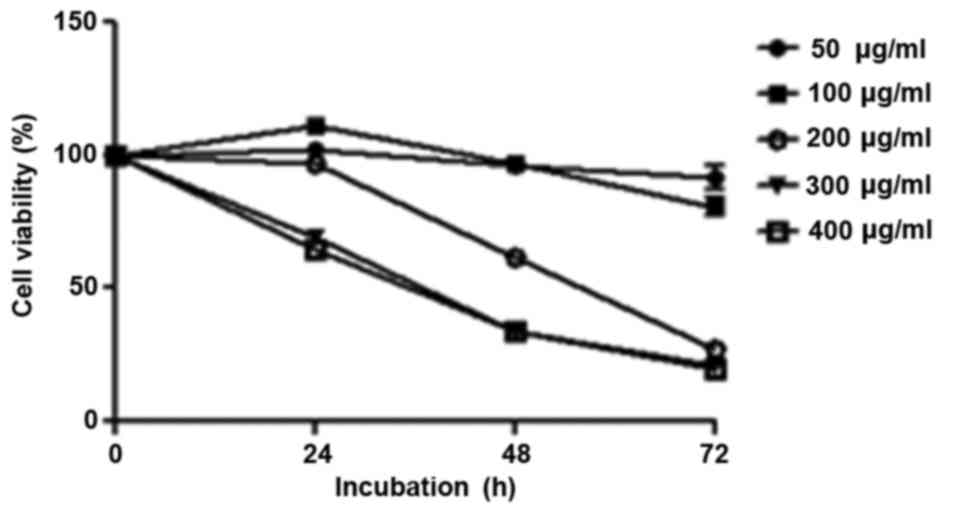
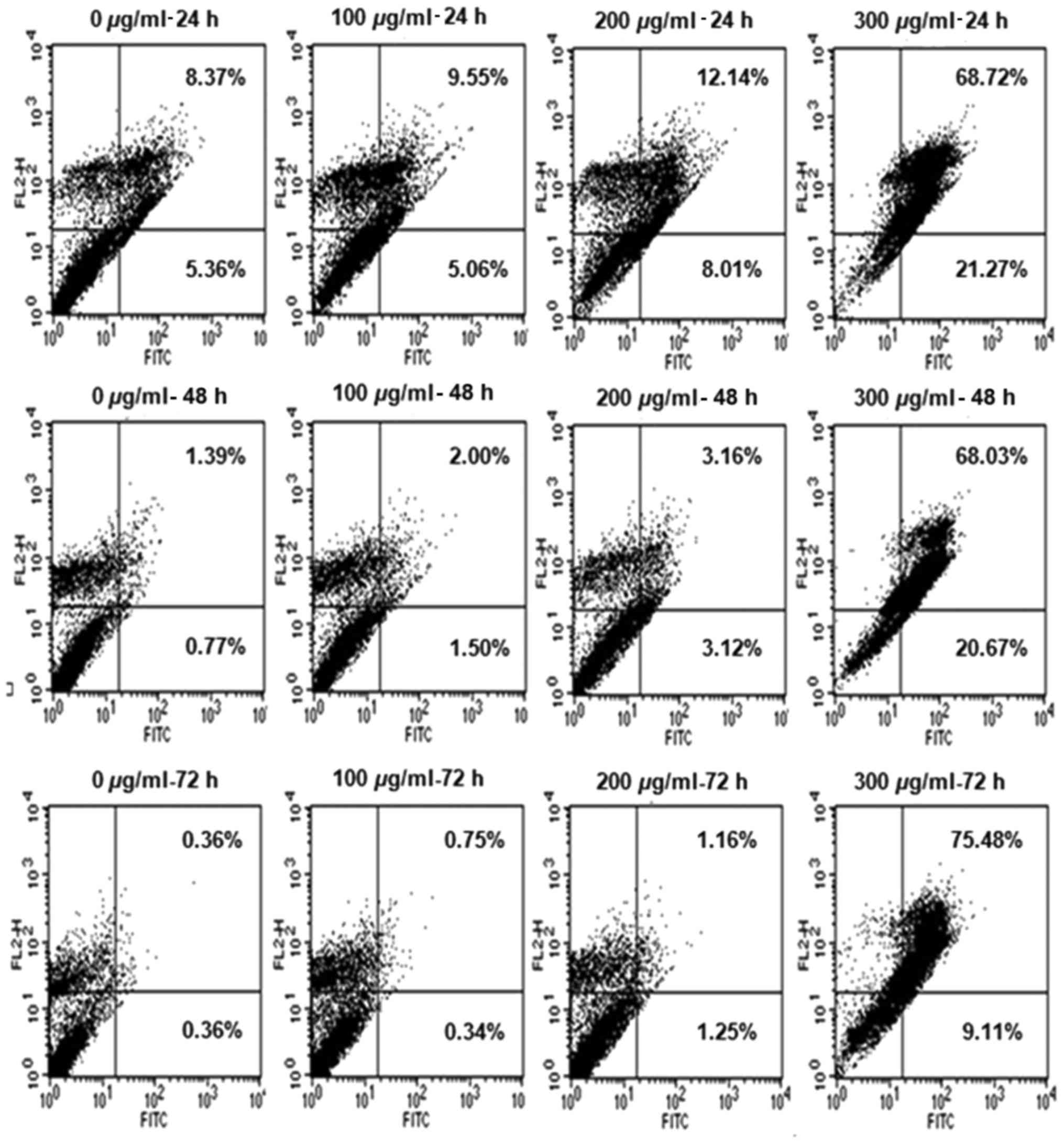
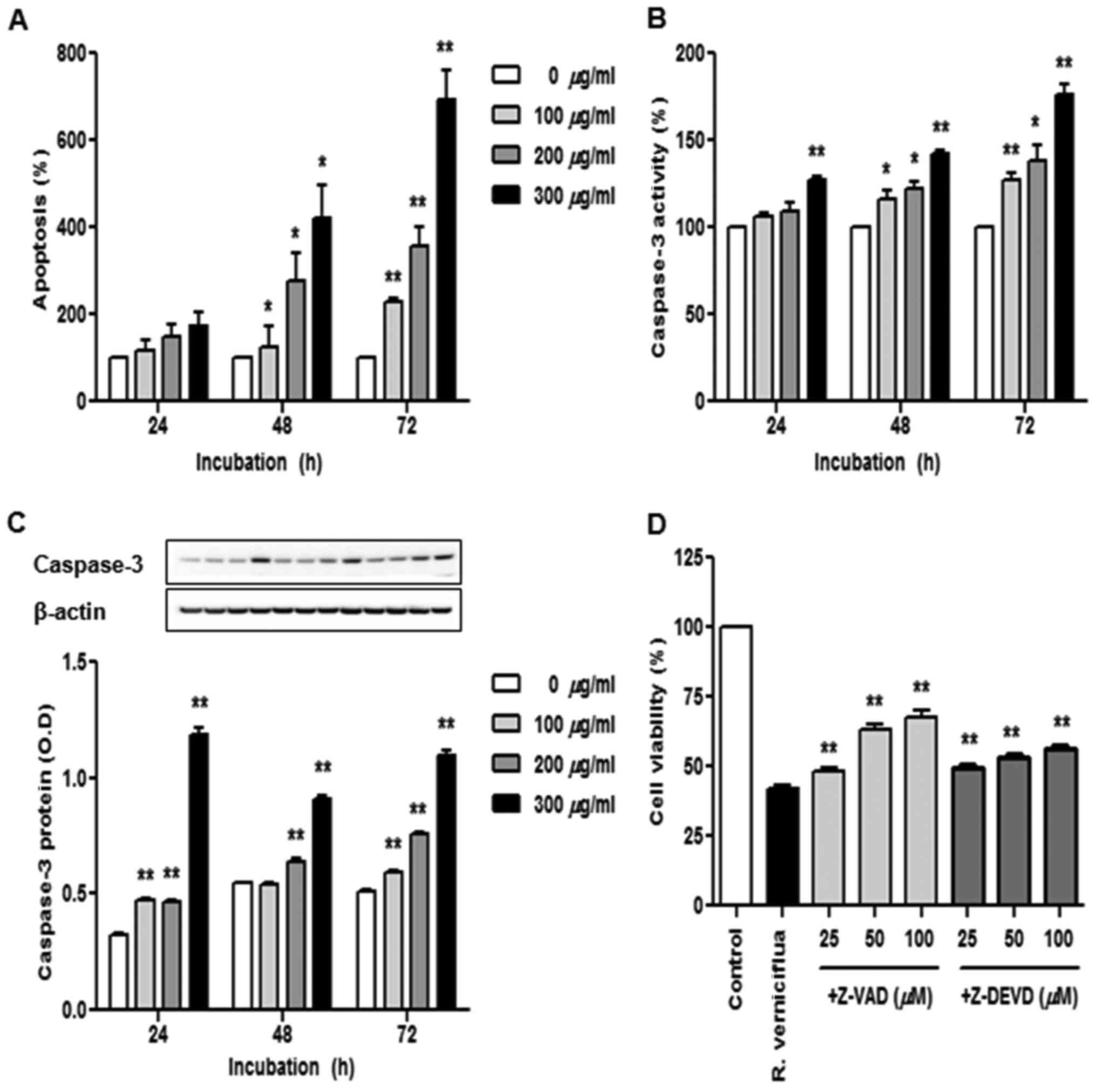
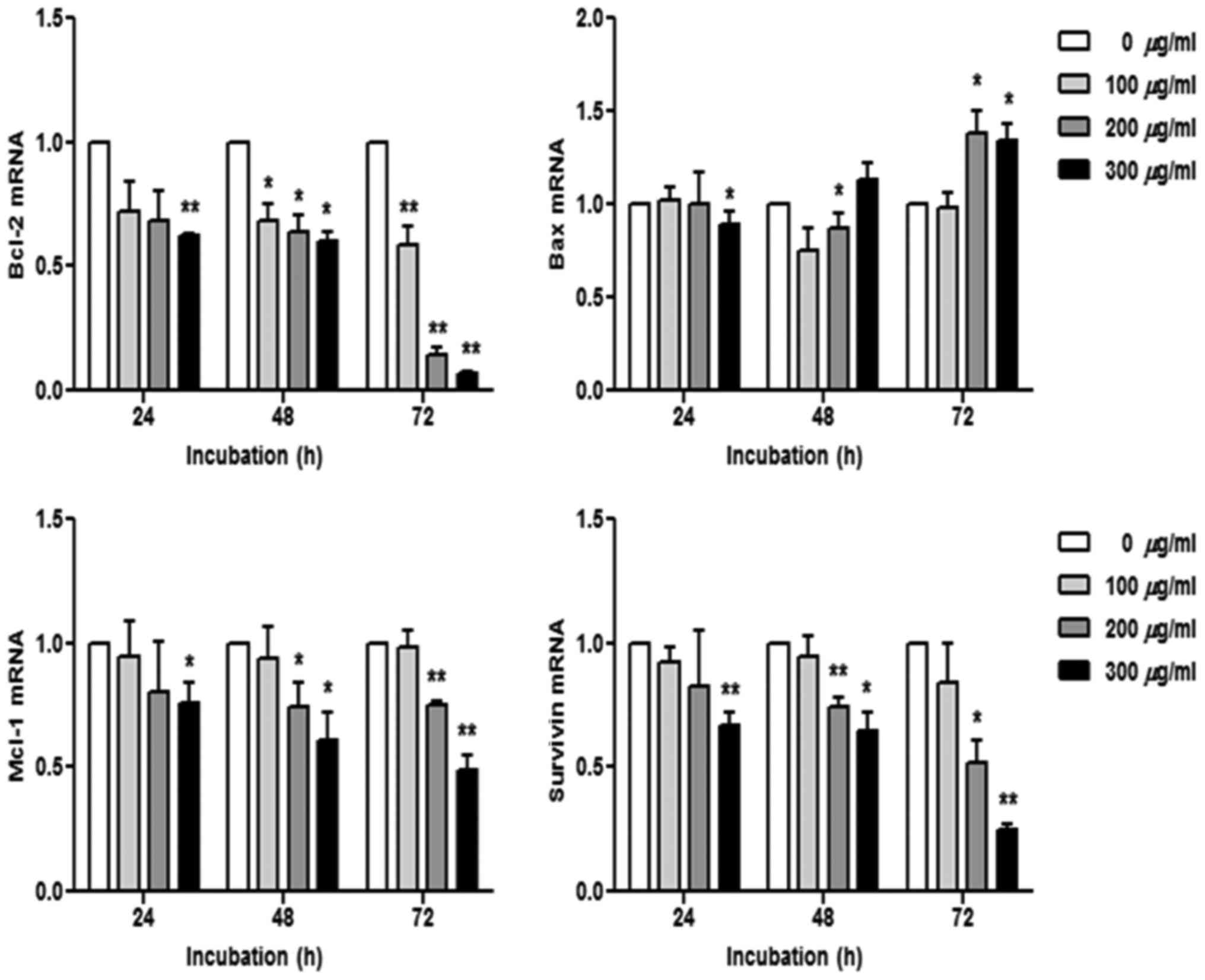
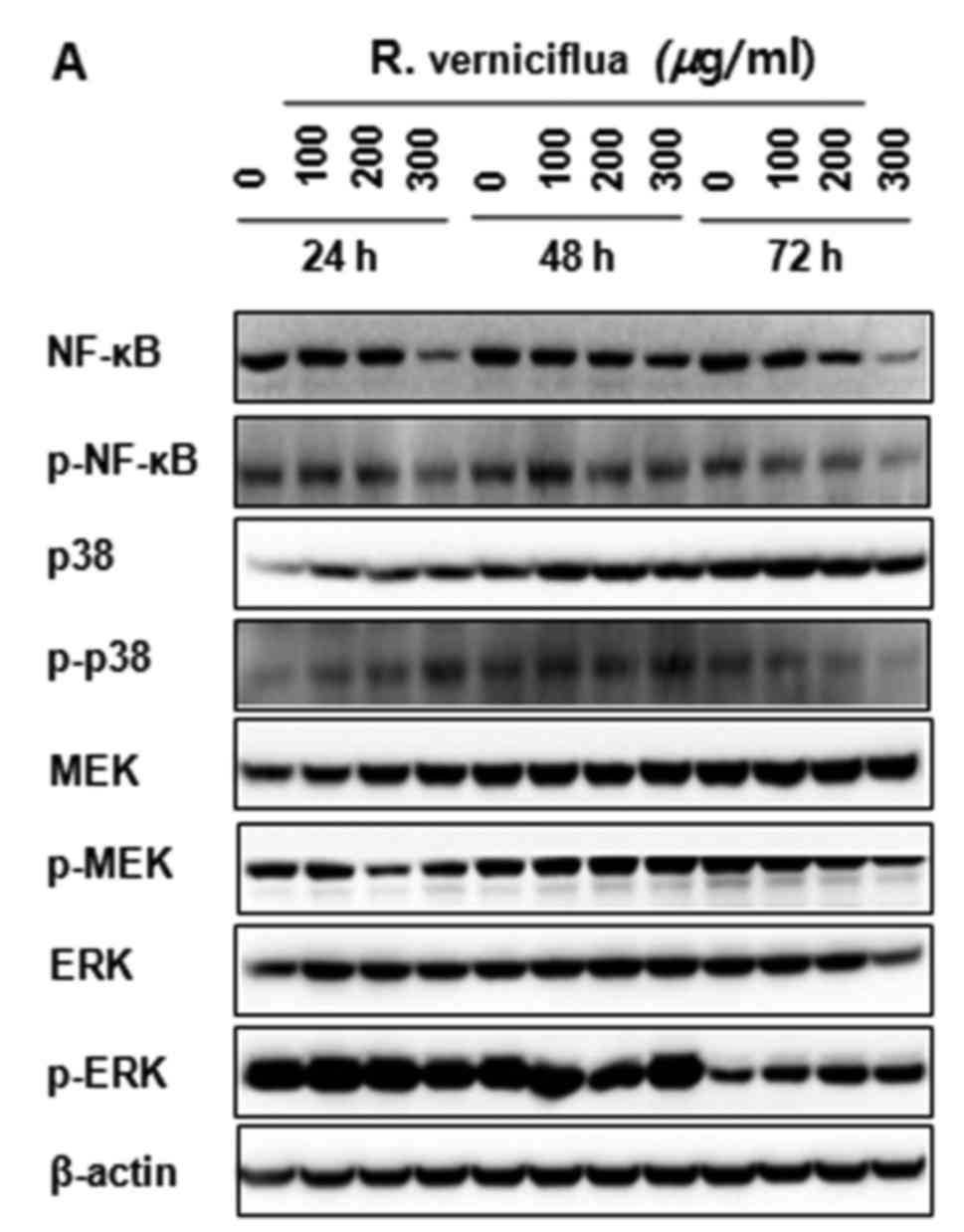
|
1
|
Choi W, Jung H, Kim K and Lee S, Yoon S,
Park J, Kim S, Cheon S, Eo W and Lee S: Rhus verniciflua stokes
against advanced cancer: A perspective from the Korean Integrative
Cancer Center. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012:8742762012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lim KT, Hu C and Kitts DD: Antioxidant
activity of a Rhus verniciflua Stokes ethanol extract. Food Chem
Toxicol. 39:229–237. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kitts DD and Lim KT: Antitumorigenic and
cytotoxic properties of an ethanol extract derived from Rhus
verniciflua Stokes (RVS). J Toxicol Environ Health A. 64:357–371.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee JD, Huh JE, Jeon G, Yang HR, Woo HS,
Choi DY and Park DS: Flavonol-rich RVHxR from Rhus verniciflua
Stokes and its major compound fisetin inhibits inflammation-related
cytokines and angiogenic factor in rheumatoid arthritic
fibroblast-like synovial cells and in vivo models. Int
Immunopharmacol. 9:268–276. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee JC, Lim KT and Jang YS: Identification
of Rhus verniciflua Stokes compounds that exhibit free radical
scavenging and anti-apoptotic properties. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1570:181–191. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee JC, Lee KY, Kim J, Na CS, Jung NC,
Chung GH and Jang YS: Extract from Rhus verniciflua Stokes is
capable of inhibiting the growth of human lymphoma cells. Food Chem
Toxicol. 42:1383–1388. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jang HS, Kook SH, Son YO, Kim JG, Jeon YM,
Jang YS, Choi KC, Kim J, Han SK, Lee KY, et al: Flavonoids purified
from Rhus verniciflua Stokes actively inhibit cell growth and
induce apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1726:309–316. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee JC, Kim J and Jang YS: Ethanol-eluted
extract of Rhus verniciflua stokes inhibits cell growth and induces
apoptosis in human lymphoma cells. J Biochem Mol Biol. 36:337–343.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR:
Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging
implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 26:239–257. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wyllie AH, Kerr JF and Currie AR: Cell
death: The significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 68:251–306.
1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Levine B, Sinha S and Kroemer G: Bcl-2
family members: Dual regulators of apoptosis and autophagy.
Autophagy. 4:600–606. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Stanciu M, Wang Y, Kentor R, Burke N,
Watkins S, Kress G, Reynolds I, Klann E, Angiolieri MR, Johnson JW,
et al: Persistent activation of ERK contributes to
glutamate-induced oxidative toxicity in a neuronal cell line and
primary cortical neuron cultures. J Biol Chem. 275:12200–12206.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Aggarwal BB: Nuclear factor-kappaB: The
enemy within. Cancer Cell. 6:203–208. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yun-Yang W, Yu-Min D, Fang-Xing Y, Ying X,
Rong-Zhi C and Kennedy JF: Purification and characterization of
hydrosoluble components from the sap of Chinese lacquer tree Rhus
vernicifera. Int J Biol Macromol. 38:232–240. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee SH, Choi WC and Yoon SW: Impact of
standardized Rhus verniciflua stokes extract as complementary
therapy on metastatic colorectal cancer: A Korean single-center
experience. Integr Cancer Ther. 8:148–152. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Choi HS, Seo HS, Kim SR, Choi YK, Jang BH,
Shin YC and Ko SG: Anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative effects
of Rhus verniciflua Stokes in RAW264.7 cells. Mol Med Rep.
9:311–315. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Park SW and Kim YI: Triptolide induces
apoptosis of PMA-treated THP-1 cells through activation of
caspases, inhibition of NF-κB and activation of MAPKs. Int J Oncol.
43:1169–1175. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li J and Yuan J: Caspases in apoptosis and
beyond. Oncogene. 27:6194–6206. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yin Y, Chen W, Tang C, Ding H, Jang J,
Weng M, Cai Y and Zou G: NF-κB, JNK and p53 pathways are involved
in tubeimoside-1-induced apoptosis in HepG2 cells with oxidative
stress and G2/M cell cycle arrest. Food Chem Toxicol.
49:3046–3054. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Burlacu A: Regulation of apoptosis by
Bcl-2 family proteins. J Cell Mol Med. 7:249–257. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kuwana T and Newmeyer DD: Bcl-2-family
proteins and the role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 15:691–699. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Reed JC: Apoptosis-targeted therapies for
cancer. Cancer Cell. 3:17–22. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu W, Hu H, Qiu P and Yan G: Triptolide
induces apoptosis in human anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells by a
p53-independent but NF-kappaB-related mechanism. Oncol Rep.
22:1397–1401. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rubinfeld H and Seger R: The ERK cascade:
A prototype of MAPK signaling. Mol Biotechnol. 31:151–174. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cui Q, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Minami M and
Ikejima T: Autophagy preceded apoptosis in oridonin-treated human
breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:859–864. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee SJ, Park K, Ha SD, Kim WJ and Moon SK:
Gleditsia sinensis thorn extract inhibits human colon cancer cells:
The role of ERK1/2, G2/M-phase cell cycle arrest and p53
expression. Phytother Res. 24:1870–1876. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yim NH, Kim A, Liang C, Cho WK and Ma JY:
Guibitang, a traditional herbal medicine, induces apoptotic death
in A431 cells by regulating the activities of mitogen-activated
protein kinases. BMC Complement Altern Med. 14:3442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Du J, Chen C, Sun Y, Zheng L and Wang W:
Ponicidin suppresses HT29 cell growth via the induction of G1 cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 12:5816–5820. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|