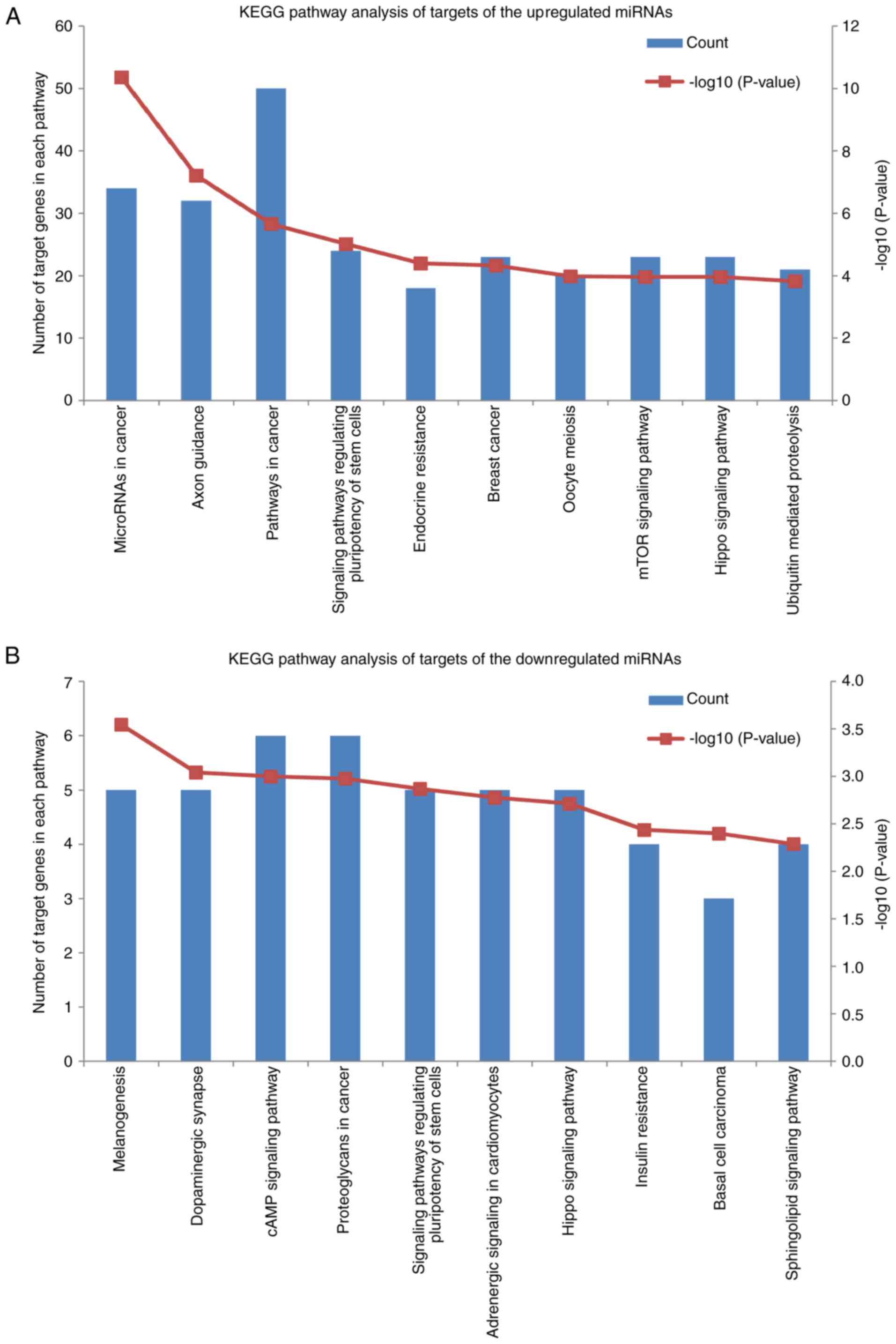
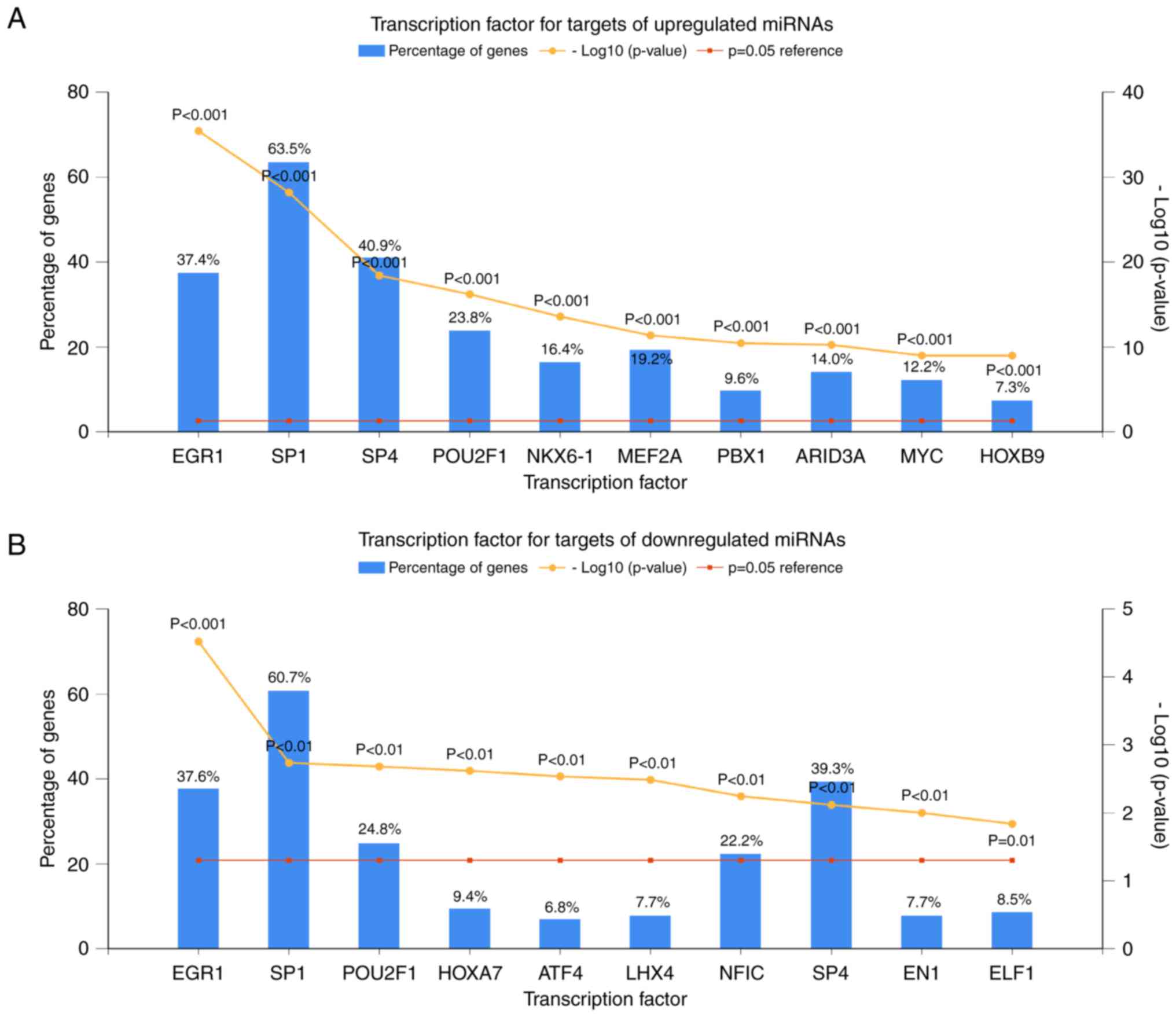
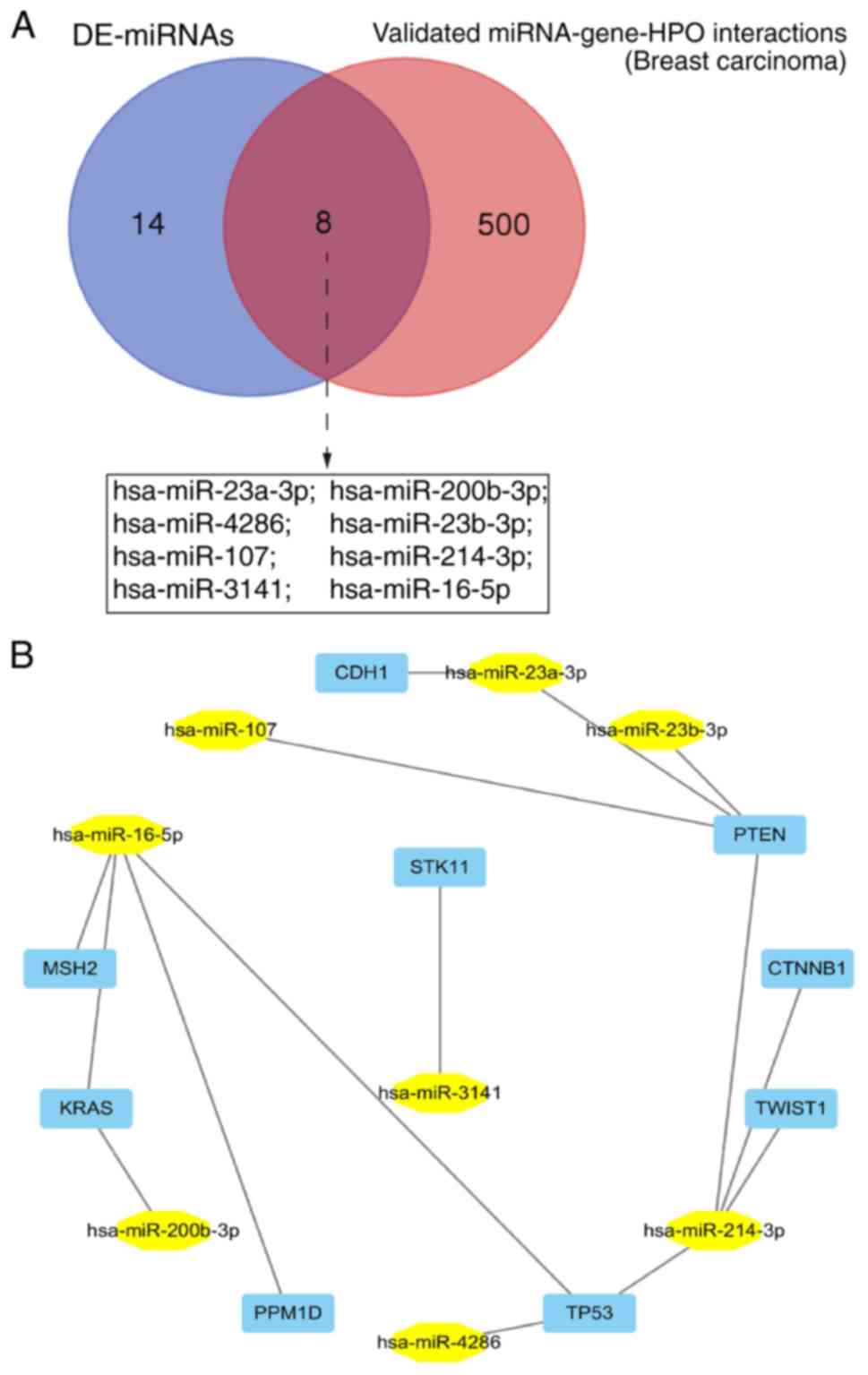
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kutanzi KR, Yurchenko OV, Beland FA,
Checkhun VF and Pogribny IP: MicroRNA-mediated drug resistance in
breast cancer. Clin Epigenetics. 2:171–185. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
ODriscoll L and Clynes M: Biomarkers and
multiple drug resistance in breast cancer. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 6:365–384. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang YW, Shi DB, Chen X, Gao C and Gao P:
Clinicopathological significance of microRNA-214 in gastric cancer
and its effect on cell biological behaviour. PLoS One.
9:e913072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang YW, Chen X, Gao JW, Zhang H, Ma RR,
Gao ZH and Gao P: High expression of cAMP-responsive
element-binding protein 1 (CREB1) is associated with metastasis,
tumor stage and poor outcome in gastric cancer. Oncotarget.
6:10646–10657. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen X, Wang YW, Xing AY, Xiang S, Shi DB,
Liu L, Li YX and Gao P: Suppression of SPIN1-mediated PI3K-Akt
pathway by miR-489 increases chemosensitivity in breast cancer. J
Pathol. 239:459–472. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang YW, Chen X, Ma R and Gao P:
Understanding the CREB1-miRNA feedback loop in human malignancies.
Tumour Biol. 37:8487–8502. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang K, Wang YW, Wang YY, Song Y, Zhu J,
Si PC and Ma R: Identification of microRNA biomarkers in the blood
of breast cancer patients based on microRNA profiling. Gene.
619:10–20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M and
Speed TP: A comparison of normalization methods for high density
oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias.
Bioinformatics. 19:185–193. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Deng W, Wang Y, Liu Z, Cheng H and Xue Y:
HemI: A toolkit for illustrating heatmaps. PLoS One. 9:e1119882014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dweep H and Gretz N: miRWalk2.0: A
comprehensive atlas of microRNA-target interactions. Nat Methods.
12:6972015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang J, Duncan D, Shi Z and Zhang B:
WEB-based GEne SeT AnaLysis toolkit (WebGestalt): Update 2013.
Nucleic Acids Research. 41:W77–W83. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
He X and Zhang J: Why do hubs tend to be
essential in protein networks? PLoS Genet. 2:e882006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pathan M, Keerthikumar S, Ang CS, Gangoda
L, Quek CY, Williamson NA, Mouradov D, Sieber OM, Simpson RJ, Salim
A, et al: FunRich: An open access standalone functional enrichment
and interaction network analysis tool. Proteomics. 15:2597–2601.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li Z, Meng Q, Pan A, Wu X, Cui J, Wang Y
and Li L: MicroRNA-455-3p promotes invasion and migration in triple
negative breast cancer by targeting tumor suppressor EI24.
Oncotarget. 8:19455–19466. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Georgakilas AG, Tsantoulis P, Kotsinas A,
Michalopoulos I, Townsend P and Gorgoulis VG: Are common fragile
sites merely structural domains or highly organized ‘functional’
units susceptible to oncogenic stress? Cell Mol Life Sci.
71:4519–4544. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou C, Grottkau BE and Zou S: regulators
of stem cells proliferation in tissue regeneration. Curr Stem Cell
Res Ther. 11:177–187. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Margariti N, Fox SB, Bottini A and
Generali D: ‘Overcoming breast cancer drug resistance with mTOR
inhibitors’. Could it be a myth or a real possibility in the
short-term future? Breast Cancer Res Treat. 128:599–606.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Carraway H and Hidalgo M: New targets for
therapy in breast cancer: Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)
antagonists. Breast Cancer Res. 6:219–224. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lai D, Visser-Grieve S and Yang X: Tumour
suppressor genes in chemotherapeutic drug response. Biosci Rep.
32:361–374. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shi P, Feng J and Chen C: Hippo pathway in
mammary gland development and breast cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys
Sin. 47:53–59. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rohlff C and Glazer RI: Regulation of
multidrug resistance through the cAMP and EGF signalling pathways.
Cell Signal. 7:431–443. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim B, Stephen SL, Hanby AM, Horgan K,
Perry SL, Richardson J, Roundhill EA, Valleley EM, Verghese ET,
Williams BJ, et al: Chemotherapy induces Notch1-dependent MRP1
up-regulation, inhibition of which sensitizes breast cancer cells
to chemotherapy. BMC Cancer. 15:6342015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao L, Ma Y, Gu F and Fu L: Inhibition of
Notch1 increases paclitaxel sensitivity to human breast cancer.
Chin Med J. 127:442–447. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Park EY, Chang E, Lee EJ, Lee HW, Kang HG,
Chun KH, Woo YM, Kong HK, Ko JY, Suzuki H, et al: Targeting of
miR34a-NOTCH1 axis reduced breast cancer stemness and
chemoresistance. Cancer Res. 74:7573–7582. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cleator S, Tsimelzon A, Ashworth A,
Dowsett M, Dexter T, Powles T, Hilsenbeck S, Wong H, Osborne CK,
O'Connell P and Chang JC: Gene expression patterns for doxorubicin
(Adriamycin) and cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) (AC) response and
resistance. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 95:229–233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tao W, Shi JF, Zhang Q, Xue B, Sun YJ and
Li CJ: Egr-1 enhances drug resistance of breast cancer by
modulating MDR1 expression in a GGPPS-independent manner. Biomed
Pharmacother. 67:197–202. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saha S, Mukherjee S, Mazumdar M, Manna A,
Khan P, Adhikary A, Kajal K, Jana D, Sa G, Mukherjee S, et al:
Mithramycin a sensitizes therapy-resistant breast cancer stem cells
toward genotoxic drug doxorubicin. Transl Res. 165:558–577. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang J, Su B, Gong C, Xi Q and Chao T:
miR-214 promotes apoptosis and sensitizes breast cancer cells to
doxorubicin by targeting the RFWD2-p53 cascade. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 478:337–342. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang X, Wan G, Mlotshwa S, Vance V,
Berger FG, Chen H and Lu X: Oncogenic Wip1 phosphatase is inhibited
by miR-16 in the DNA damage signaling pathway. Cancer Res.
70:7176–7186. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|