|
1
|
Minton K: Cancer immunotherapy: Cell cycle
inhibitors boost tumour immunogenicity. Nat Rev Drug Dis.
16:6792017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hamilton E and Infante JR: Targeting
CDK4/6 in patients with cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 45:129–138. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhou J, Zhang S, Chen X, Zheng X, Yao Y,
Lu G and Zhou J: Palbociclib, a selective CDK4/6 inhibitor,
enhances the effect of selumetinib in RAS-driven non-small cell
lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 408:130–137. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bilgin B, Sendur MA, Şener Dede D, Akıncı
MB and Yalçın B: A current and comprehensive review of
cyclin-dependent kinase ınhibitors for the treatment of metastatic
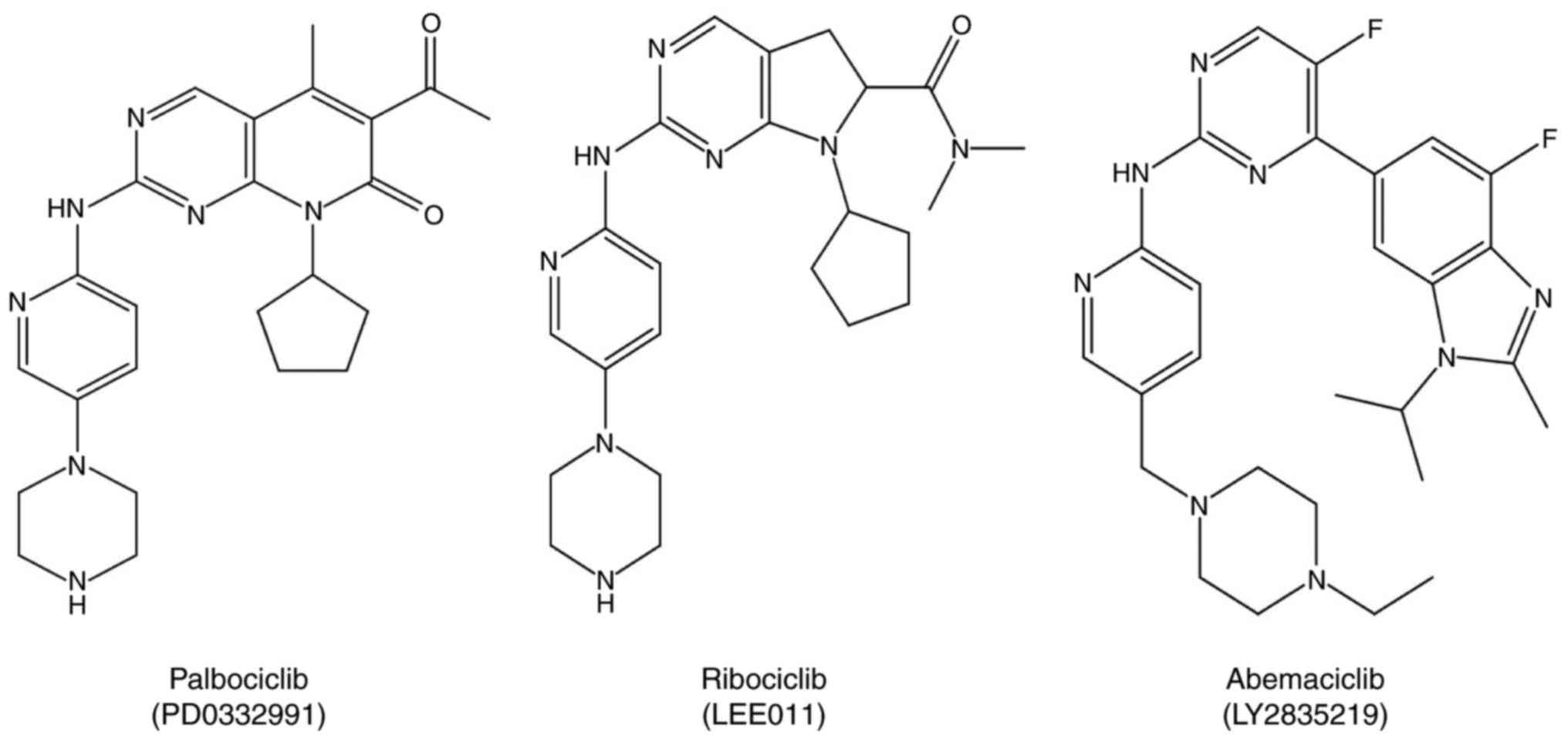
breast cancer. Curr Med Res Opin. 33:1559–1569. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen L and Pan J: Dual cyclin-dependent
kinase 4/6 inhibition by PD-0332991 induces apoptosis and
senescence in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Br J
Pharmacol. 174:2427–2443. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Patel P, Asbach B, Shteyn E, Gomez C,
Coltoff A, Bhuyan S, Tyner AL, Wagner R and Blain SW: Brk/Protein
tyrosine kinase 6 phosphorylates p27KIP1, regulating the activity
of cyclin D-cyclin-dependent kinase 4. Mol Cell Biol. 35:1506–1522.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Malumbres M, Harlow E, Hunt T, Hunter T,
Lahti JM, Manning G, Morgan DO, Tsai LH and Wolgemuth DJ:
Cyclin-dependent kinases: A family portrait. Nat Cell Biol.
11:1275–1276. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Malumbres M: Cyclin-dependent kinases.
Genome Biology. 15:1222014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ubersax JA, Woodbury EL, Quang PN, Paraz
M, Blethrow JD, Shah K, Shokat KM and Morgan DO: Targets of the
cyclin-dependent kinase Cdk1. Nature. 425:859–864. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baker SJ and Reddy EP: CDK4: A key player
in the cell cycle, development, and cancer. Genes Cancer.
3:658–669. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
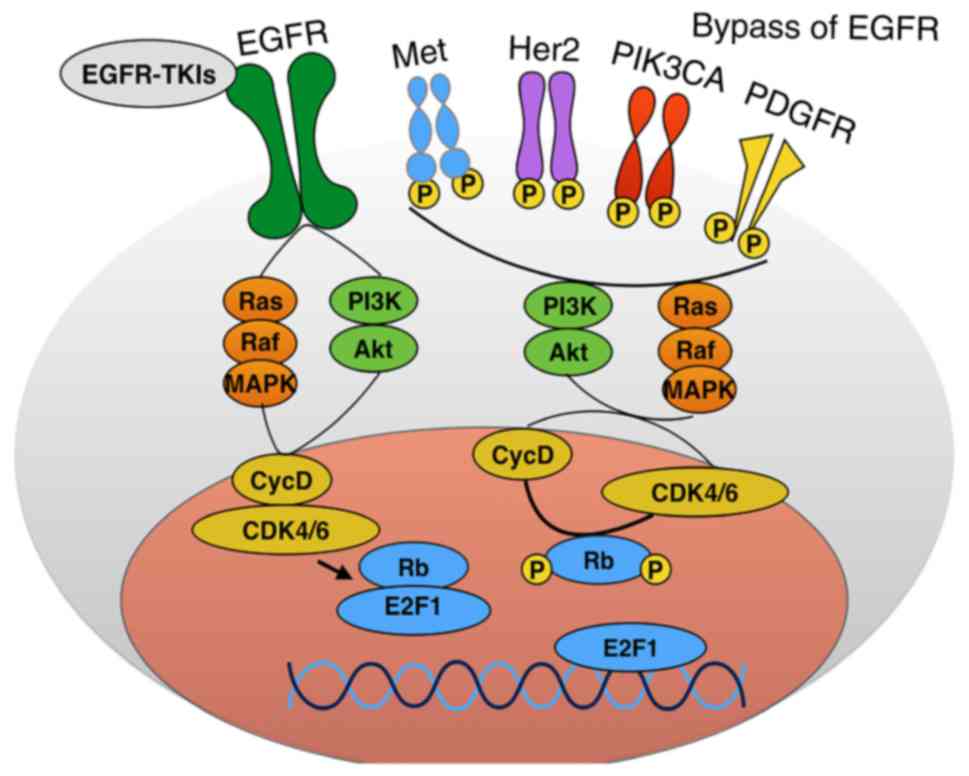
|
Shah K and Lahiri DK: Cdk5 activity in the
brain-multiple paths of regulation. J Cell Sci. 127:2391–2400.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pinhero R and Yankulov K: Expression and
purification of recombinant CDKs: CDK7, CDK8, and CDK9. Methods Mol
Biol. 1336:13–28. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Galbraith MD, Donner AJ and Espinosa JM:
CDK8: A positive regulator of transcription. Transcription. 1:4–12.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Krystof V, Baumli S and Fürst R:
Perspective of cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (CDK9) as a drug target.
Curr Pharm Des. 18:2883–2890. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hu D, Mayeda A, Trembley JH, Lahti JM and
Kidd VJ: CDK11 complexes promote pre-mRNA splicing. J Biol Chem.
278:8623–8629. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chi Y, Huang S, Peng H, Liu M, Zhao J,
Shao Z and Wu J: Critical role of CDK11(p58) in human breast cancer
growth and angiogenesis. BMC Cancer. 15:7012015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bajić VP, Su B, Lee HG, Kudo W, Siedlak
SL, Zivković L, Spremo-Potparević B, Djelic N, Milicevic Z, Singh
AK, et al: Mislocalization of CDK11/PITSLRE, a regulator of the
G2/M phase of the cell cycle, in Alzheimer disease. Cell Mol Biol
Lett. 16:359–372. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou Y, Han C, Li D, Yu Z, Li F, Li F, An
Q, Bai H, Zhang X, Duan Z and Kan Q: Cyclin-dependent kinase
11(p110) (CDK11(p110)) is crucial for human breast cancer cell
proliferation and growth. Sci Rep. 5:104332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: Mammalian
cyclin-dependent kinases. Trends Biochem Sci. 30:630–641. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shapiro GI: Cyclin-dependent kinase
pathways as targets for cancer treatment. J Clin Oncol.
24:1770–1783. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sakurikar N and Eastman A: Critical
reanalysis of the methods that discriminate the activity of CDK2
from CDK1. Cell Cycle. 15:1184–1188. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sherr CJ: G1 phase progression: Cycling on
cue. Cell. 79:551–555. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li Y, Zhang J, Gao W, Zhang L, Pan Y,
Zhang S and Wang Y: Insights on structural characteristics and
ligand binding mechanisms of CDK2. Int J Mol Sci. 16:9314–9340.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Flores O, Wang Z, Knudsen KE and Burnstein
KL: Nuclear targeting of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 reveals
essential roles of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 localization and
cyclin E in vitamin D-mediated growth inhibition. Endocrinology.
151:896–908. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ali S, Heathcote DA, Kroll SH, Jogalekar
AS, Scheiper B, Pate H, Brackow J, Siwicka A, Fuchter MJ,
Periyasamy M, et al: The development of a selective
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor that shows antitumor activity.
Cancer Res. 69:6208–6215. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kawana H, Tamaru J, Tanaka T, Hirai A,
Saito Y, Kitagawa M, Mikata A, Harigaya K and Kuriyama T: Role of
p27Kip1 and cyclin-dependent kinase 2 in the proliferation of
non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Pathol. 153:505–513. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Morgan DO: Cyclin-dependent kinases:
Engines, clocks, and microprocessors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
13:261–291. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Clark AS, Karasic TB, DeMichele A, Vaughn
DJ, O'Hara M, Perini R, Zhang P, Lal P, Feldman M, Gallagher M and
O'Dwyer PJ: Palbociclib (PD0332991) - a selective and potent
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor: A review of pharmacodynamics and
clinical development. JAMA Oncol. 2:253–260. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dean JL, McClendon AK and Knudsen ES:
Modification of the DNA damage response by therapeutic CDK4/6
inhibition. J Biol Chem. 287:29075–29087. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rader J, Russell MR, Hart LS, Nakazawa MS,
Belcastro LT, Martinez D, Li Y, Carpenter EL, Attiyeh EF, Diskin
SJ, et al: Dual CDK4/CDK6 inhibition induces cell-cycle arrest and
senescence in neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 19:6173–6182. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee Y, Dominy JE, Choi YJ, Jurczak M,
Tolliday N, Camporez JP, Chim H, Lim JH, Ruan HB, Yang X, et al:
Cyclin D1-Cdk4 controls glucose metabolism independently of cell
cycle progression. Nature. 510:547–551. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Weijts BGMW, Westendorp B, Hien BT,
Martínez-López LM, Zijp M, Thurlings I, Thomas RE, Schulte-Merker
S, Bakker WJ and de Bruin A: Atypical E2Fs inhibit tumor
angiogenesis. Oncogene. Sep 18–2017.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wirt SE and Sage J: p107 in the public
eye: An Rb under study and more. Cell Div. 5:92010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sadasivam S and DeCaprio JA: The DREAM
complex: Master coordinator of cell cycle-dependent gene
expression. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:585–595. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee MH, Williams BO, Mulligan G, Mukai S,
Bronson RT, Dyson N, Harlow E and Jacks T: Targeted disruption of
p107: Functional overlap between p107 and Rb. Genes Dev.
10:1621–1632. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cobrinik D, Lee MH, Hannon G, Mulligan G,
Bronson RT, Dyson N, Harlow E, Beach D, Weinberg RA and Jacks T:
Shared role of the pRB-related p130 and p107 proteins in limb
development. Genes Dev. 10:1633–1644. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shen Y, Nar R, Fan AX, Aryan M, Hossain
MA, Gurumurthy A, Wassel PC, Tang M, Lu J, Strouboulis J and
Bungert J: Functional interrelationship between TFII-I and E2F
transcription factors at specific cell cycle gene loci. J Cell
Biochem. 119:712–722. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kent LN, Bae S, Tsai SY, Tang X,
Srivastava A, Koivisto C, Martin CK, Ridolfi E, Miller GC, Zorko
SM, et al: Dosage-dependent copy number gains in E2f1 and E2f3
drive hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Invest. 127:830–842. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Conklin JF and Sage J: Keeping an eye on
retinoblastoma control of human embryonic stem cells. J Cell
Biochem. 108:1023–1030. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dyson N: The regulation of E2F by
pRB-family proteins. Genes Dev. 12:2245–2262. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lukas J, Petersen BO, Holm K, Bartek J and
Helin K: Deregulated expression of E2F family members induces
S-phase entry and overcomes p16INK4A-mediated growth suppression.
Mol Cell Biol. 16:1047–1057. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Asano M, Nevins JR and Wharton RP: Ectopic
E2F expression induces S phase and apoptosis in Drosophila imaginal
discs. Genes Dev. 10:1422–1432. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
DeGregori J, Leone G, Ohtani K, Miron A
and Nevins JR: E2F-1 accumulation bypasses a G1 arrest resulting
from the inhibition of G1 cyclin-dependent kinase activity. Genes
Dev. 9:2873–2887. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Allen KE, La Luna de S, Kerkhoven RM,
Bernards R and La Thangue NB: Distinct mechanisms of nuclear
accumulation regulate the functional consequence of E2F
transcription factors. J Cell Sci. 110:2819–2831. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Müller H, Moroni MC, Vigo E, Petersen BO,
Bartek J and Helin K: Induction of S-phase entry by E2F
transcription factors depends on their nuclear localization. Mol
Cell Biol. 17:5508–5520. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wu Z, Zheng S and Yu Q: The E2F family and
the role of E2F1 in apoptosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
41:2389–2397. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li J, Ran C, Li E, Gordon F, Comstock G,
Siddiqui H, Cleghorn W, Chen HZ, Kornacker K, Liu CG, et al:
Synergistic function of E2F7 and E2F8 is essential for cell
survival and embryonic development. Dev Cell. 14:62–75. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Westendorp B, Mokry M, Groot Koerkamp MJ,
Holstege FC, Cuppen E and de Bruin A: E2F7 represses a network of
oscillating cell cycle genes to control S-phase progression.
Nucleic Acids Res. 40:3511–3523. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lundberg AS and Weinberg RA: Functional
inactivation of the retinoblastoma protein requires sequential
modification by at least two distinct cyclin-cdk complexes. Mol
Cell Biol. 18:753–761. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ezhevsky SA, Ho A, Becker-Hapak M, Davis
PK and Dowdy SF: Differential regulation of retinoblastoma tumor
suppressor protein by G(1) cyclin-dependent kinase complexes in
vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 21:4773–4784. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Harbour JW, Luo RX, Dei Santi A, Postigo
AA and Dean DC: Cdk phosphorylation triggers sequential
intramolecular interactions that progressively block Rb functions
as cells move through G1. Cell. 98:859–869. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
van den Heuvel S and Harlow E: Distinct
roles for cyclin-dependent kinases in cell cycle control. Science.
262:2050–2054. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Garber K: The cancer drug that almost
wasn't. Science. 345:865–867. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Dolman ME, Poon E, Ebus ME, den Hartog IJ,
van Noesel CJ, Jamin Y, Hallsworth A, Robinson SP, Petrie K,
Sparidans RW, et al: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor AT7519 as a
potential drug for MYCN-dependent neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res.
21:5100–5109. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Rigas AC, Robson CN and Curtin NJ:
Therapeutic potential of CDK inhibitor NU2058 in
androgen-independent prostate cancer. Oncogene. 26:7611–7619. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Joshi KS, Rathos MJ, Mahajan P, Wagh V,
Shenoy S, Bhatia D, Chile S, Sivakumar M, Maier A, Fiebig HH and
Sharma S: P276-00, a novel cyclin-dependent inhibitor induces G1-G2
arrest, shows antitumor activity on cisplatin-resistant cells and
significant in vivo efficacy in tumor models. Mol Cancer Ther.
6:926–934. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Joshi KS, Rathos MJ, Joshi RD, Sivakumar
M, Mascarenhas M, Kamble S, Lal B and Sharma S: In vitro antitumor
properties of a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, P276-00.
Mol Cancer Ther. 6:918–925. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Giordano A, Rossi A, Romano G and Bagella
L: Tumor suppressor pRb2/p130 gene and its derived product Spa310
spacer domain as perspective candidates for cancer therapy. J Cell
Physiol. 213:403–406. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
De Azevedo WF, Leclerc S, Meijer L,
Havlicek L, Strnad M and Kim SH: Inhibition of cyclin-dependent
kinases by purine analogues: Crystal structure of human cdk2
complexed with roscovitine. Eur J Biochem. 243:518–526. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lee B, Sandhu S and McArthur G: Cell cycle
control as a promising target in melanoma. Curr Opin Oncol.
27:141–150. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Dange Y, Bhinge S and Salunkhe V:
Optimization and validation of RP-HPLC method for simultaneous
estimation of palbociclib and letrozole. Toxicol Mech Methods 1–8.
2017.
|
|
62
|
Guha M: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors
move into Phase III. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 11:892–894. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Cardoso F, Bischoff J, Brain E, Zotano ÁG,
Lück HJ, Tjan-Heijnen VC, Tanner M and Aapro M: A review of the
treatment of endocrine responsive metastatic breast cancer in
postmenopausal women. Cancer Treat Rev. 39:457–465. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sammons SL, Topping DL and Blackwell KL:
HR+, HER2 advanced breast cancer and CDK4/6 inhibitors:
mode of action, clinical activity, and safety profiles. Current
Cancer Drug Targets. 17:637–649. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Costa R, Costa RB, Talamantes SM,
Helenowski I, Peterson J, Kaplan J, Carneiro BA, Giles FJ and
Gradishar WJ: Meta-analysis of selected toxicity endpoints of
CDK4/6 inhibitors: Palbociclib and ribociclib. Breast. 35:1–7.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Iwata H, Im SA, Masuda N, Im YH, Inoue K,
Rai Y, Nakamura R, Kim JH, Hoffman JT, Zhang K, et al: PALOMA-3:
Phase III trial of fulvestrant with or without palbociclib in
premenopausal and postmenopausal women with hormone
receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor
2-negative metastatic breast cancer that progressed on prior
endocrine therapy-safety and efficacy in Asian patients. J Global
Oncol. 3:289–303. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Loibl S, Turner NC, Ro J, Cristofanilli M,
Iwata H, Im SA, Masuda N, Loi S, André F, Harbeck N, et al:
Palbociclib combined with fulvestrant in premenopausal women with
advanced breast cancer and prior progression on endocrine therapy:
PALOMA-3 Results. Oncologist. 22:1028–1038. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Schwartz GK, LoRusso PM, Dickson MA,
Randolph SS, Shaik MN, Wilner KD, Courtney R and O'Dwyer PJ: Phase
I study of PD 0332991, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor,
administered in 3-week cycles (Schedule 2/1). Br J Cancer.
104:1862–1868. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Fribbens C, OLeary B, Kilburn L, Hrebien
S, Garcia-Murillas I, Beaney M, Cristofanilli M, Andre F, Loi S,
Loibl S, et al: Plasma ESR1 mutations and the treatment of estrogen
receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
34:2961–2968. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Gelsomino L, Gu G, Rechoum Y, Beyer AR,
Pejerrey SM, Tsimelzon A, Wang T, Huffman K, Ludlow A, Andò S and
Fuqua SAW: ESR1 mutations affect anti-proliferative responses to
tamoxifen through enhanced cross-talk with IGF signaling. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 157:253–265. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Kuehl WM and Bergsagel PL: Molecular
pathogenesis of multiple myeloma and its premalignant precursor. J
Clin Invest. 122:3456–3463. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ocio EM, Mitsiades CS, Orlowski RZ and
Anderson KC: Future agents and treatment directions in multiple
myeloma. Expert Rev Hematol. 7:127–141. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Castelli R, Gualtierotti R, Orofino N,
Losurdo A, Gandolfi S and Cugno M: Current and emerging treatment
options for patients with relapsed myeloma. Clin Med Insights
Oncol. 7:209–219. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Niesvizky R, Badros AZ, Costa LJ, Ely SA,
Singhal SB, Stadtmauer EA, Haideri NA, Yacoub A, Hess G, Lentzsch
S, et al: Phase 1/2 study of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)4/6
inhibitor palbociclib (PD-0332991) with bortezomib and
dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Leuk
Lymphoma. 56:3320–3328. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Richardson PG, Barlogie B, Berenson J,
Singhal S, Jagannath S, Irwin D, Rajkumar SV, Srkalovic G, Alsina
M, Alexanian R, et al: A phase 2 study of bortezomib in relapsed,
refractory myeloma. N Engl J Med. 348:2609–2617. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Perumal D, Kuo PY, Leshchenko VV, Jiang Z,
Divakar SK, Cho HJ, Chari A, Brody J, Reddy MV, Zhang W, et al:
Dual targeting of CDK4 and ARK5 using a novel kinase inhibitor
ON123300 exerts potent anticancer activity against multiple
myeloma. Cancer Res. 76:1225–1236. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Liu L, Ulbrich J, Müller J, Wüstefeld T,
Aeberhard L, Kress TR, Muthalagu N, Rycak L, Rudalska R, Moll R, et
al: Deregulated MYC expression induces dependence upon AMPK-related
kinase 5. Nature. 483:608–612. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Sequist LV, Yang JC, Yamamoto N, O'Byrne
K, Hirsh V, Mok T, Geater SL, Orlov S, Tsai CM, Boyer M, et al:
Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in
patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J
Clin Oncol. 31:3327–3334. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Liu M, Xu S, Wang Y, Li Y, Li Y, Zhang H,
Liu H and Chen J: PD 0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6
inhibitor, sensitizes lung cancer cells to treatment with epidermal
growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncotarget.
7:84951–84964. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Shaw AT, Winslow MM, Magendantz M, Ouyang
C, Dowdle J, Subramanian A, Lewis TA, Maglathin RL, Tolliday N and
Jacks T: Selective killing of K-ras mutant cancer cells by small
molecule inducers of oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:pp. 8773–8778. 2011; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Montagut C and Settleman J: Targeting the
RAF-MEK-ERK pathway in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 283:125–134.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Tao Z, Le Blanc JM, Wang C, Zhan T, Zhuang
H, Wang P, Yuan Z and Lu B: Coadministration of trametinib and
palbociclib radiosensitizes KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancers
in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 22:122–133. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, .
Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung
cancers. Nature. 489:519–525. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Chikara S, Lindsey K, Dhillon H, Mamidi S,
Kittilson J, Christofidou-Solomidou M and Reindl KM: Enterolactone
induces G1-phase cell cycle arrest in nonsmall cell lung cancer
cells by downregulating cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases. Nutr
Cancer. 69:652–662. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Chen DH and Zhang XS: Targeted therapy:
Resistance and re-sensitization. Chin J Cancer. 34:496–501. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Lee JE, Park HS, Lee D, Yoo G, Kim T, Jeon
H, Yeo MK, Lee CS, Moon JY, Jung SS, et al: Hippo pathway effector
YAP inhibition restores the sensitivity of EGFR-TKI in lung
adenocarcinoma having primary or acquired EGFR-TKI resistance.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 474:154–160. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Cross DA, Ashton SE, Ghiorghiu S, Eberlein
C, Nebhan CA, Spitzler PJ, Orme JP, Finlay MR, Ward RA, Mellor MJ,
et al: AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated
resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov.
4:1046–1061. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Luque-Cabal M, García-Teijido P,
Fernández-Pérez Y, Sánchez-Lorenzo L and Palacio-Vázquez I:
Mechanisms behind the resistance to trastuzumab in her2-amplified
breast cancer and strategies to overcome it. Clin Med Insights
Oncol. 10 Suppl 1:S21–S30. 2016.
|
|
89
|
Teh JL, Purwin TJ, Greenawalt EJ,
Chervoneva I, Goldberg A, Davies MA and Aplin AE: An in vivo
reporter to quantitatively and temporally analyze the effects of
CDK4/6 inhibitor-based therapies in melanoma. Cancer Res.
76:5455–5466. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Kwiatkowski N, Zhang T, Rahl PB, Abraham
BJ, Reddy J, Ficarro SB, Dastur A, Amzallag A, Ramaswamy S, Tesar
B, et al: Targeting transcription regulation in cancer with a
covalent CDK7 inhibitor. Nature. 511:616–620. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|