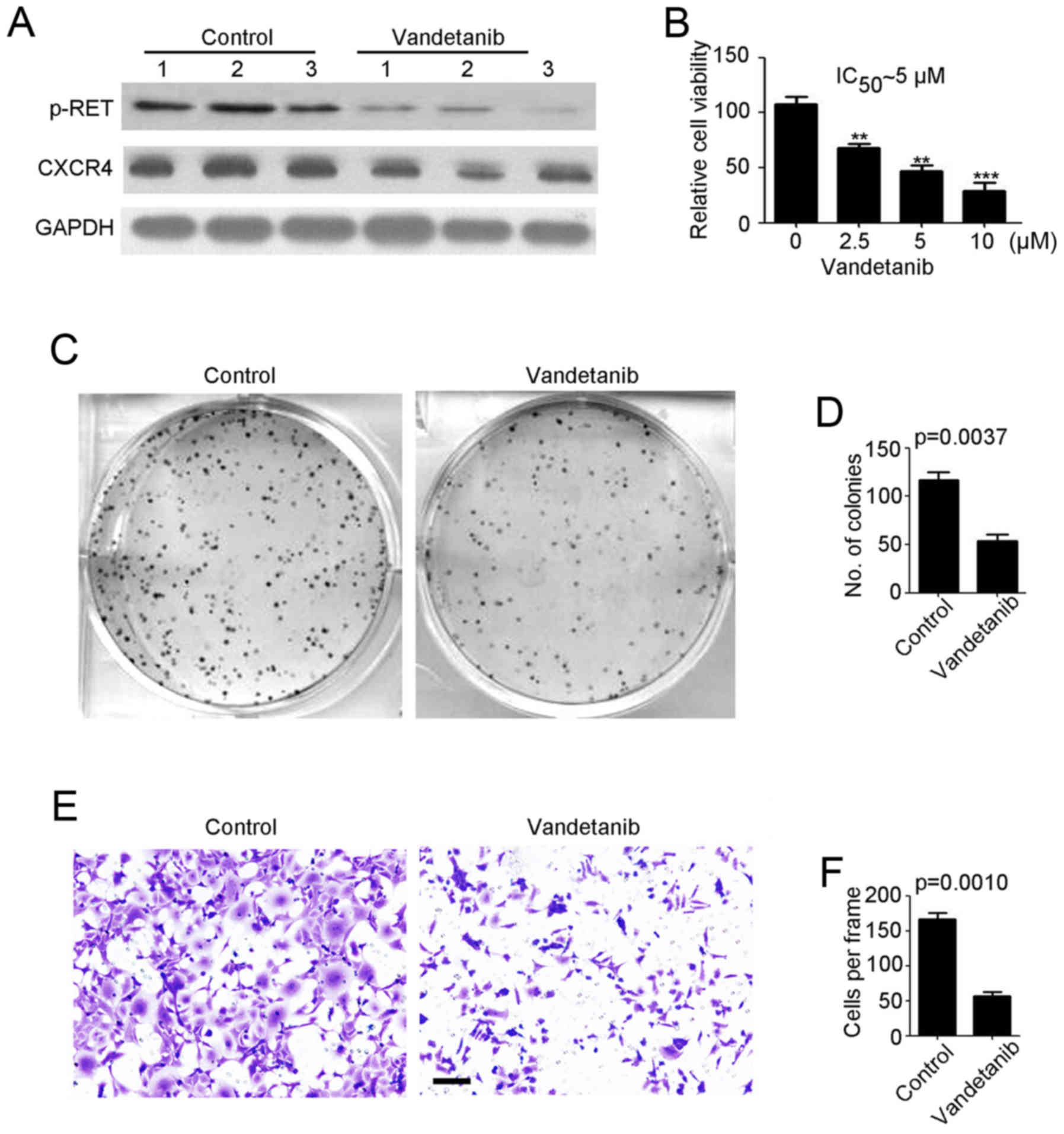
|
1
|
Nakazawa A, Haga C, Ohira M, Okita H,
Kamijo T and Nakagawara A: Correlation between the international
neuroblastoma pathology classification and genomic signature in
neuroblastoma. Cancer Sci. 106:766–771. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Maris JM: Recent advances in
neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med. 362:2202–2211. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Oeffinger KC, Mertens AC, Sklar CA,
Kawashima T, Hudson MM, Meadows AT, Friedman DL, Marina N, Hobbie
W, Kadan-Lottick NS, et al: Chronic health conditions in adult
survivors of childhood cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:1572–1582. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maris JM, Hogarty MD, Bagatell R and Cohn
SL: Neuroblastoma. Lancet (London, England). 369:2106–2120. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tao X: Antibody therapy and neuroblastoma.
N Engl J Med. 364:289–290. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Barone G, Anderson J, Pearson AD, Petrie K
and Chesler L: New strategies in neuroblastoma: Therapeutic
targeting of MYCN and ALK. Clin Cancer Res. 19:5814–5821. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brodeur GM, Iyer R, Croucher JL, Zhuang T,
Higashi M and Kolla V: Therapeutic targets for neuroblastomas.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 18:277–292. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Morgenstern DA, Baruchel S and Irwin MS:
Current and future strategies for relapsed neuroblastoma:
Challenges on the road to precision therapy. J Pediatr Hematol
Oncol. 35:337–347. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Alisi A, Cho WC, Locatelli F and Fruci D:
Multidrug resistance and cancer stem cells in neuroblastoma and
hepatoblastoma. Int J Mol Sci. 14:24706–24725. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fruci D, Cho WC, Nobili V, Locatelli F and
Alisi A: Drug transporters and multiple drug resistance in
pediatric solid tumors. Curr Drug Metab. 17:308–316. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Matthay KK, Reynolds CP, Seeger RC,
Shimada H, Adkins ES, Haas-Kogan D, Gerbing RB, London WB and
Villablanca JG: Long-term results for children with high-risk
neuroblastoma treated on a randomized trial of myeloablative
therapy followed by 13-cis-retinoic acid: A children's oncology
group study. J Clin Oncol. 27:1007–1013. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
De Bernardi B, Carli M, Casale F, Corciulo
P, Cordero di Montezemolo L, De Laurentis C, Bagnulo S, Brisigotti
M, Marchese N, Garaventa A, et al: Standard-dose and high-dose
peptichemio and cisplatin in children with disseminated poor-risk
neuroblastoma: Two studies by the Italian Cooperative Group for
Neuroblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 10:1870–1878. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Landier W, Knight K, Wong FL, Lee J,
Thomas O, Kim H, Kreissman SG, Schmidt ML, Chen L, London WB, et
al: Ototoxicity in children with high-risk neuroblastoma:
Prevalence, risk factors, and concordance of grading scales-a
report from the Children's Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol.
32:527–534. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vella S, Penna I, Longo L, Pioggia G,
Garbati P, Florio T, Rossi F and Pagano A: Perhexiline maleate
enhances antitumor efficacy of cisplatin in neuroblastoma by
inducing over-expression of NDM29 ncRNA. Sci Rep. 5:181442015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ryan J, Tivnan A, Fay J, Bryan K, Meehan
M, Creevey L, Lynch J, Bray IM, O'Meara A, Tracey L, et al:
MicroRNA-204 increases sensitivity of neuroblastoma cells to
cisplatin and is associated with a favourable clinical outcome. Br
J Cancer. 107:967–976. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cazes A, Lopez-Delisle L, Tsarovina K,
Pierre-Eugene C, De Preter K, Peuchmaur M, Nicolas A, Provost C,
Louis-Brennetot C, Daveau R, et al: Activated Alk triggers
prolonged neurogenesis and Ret upregulation providing a therapeutic
target in ALK-mutated neuroblastoma. Oncotarget. 5:2688–2702. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Futami H and Sakai R: RET protein promotes
non-adherent growth of NB-39-nu neuroblastoma cell line. Cancer
Sci. 100:1034–1039. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Meier R, Mühlethaler-Mottet A, Flahaut M,
Coulon A, Fusco C, Louache F, Auderset K, Bourloud KB, Daudigeos E,
Ruegg C, et al: The chemokine receptor CXCR4 strongly promotes
neuroblastoma primary tumour and metastatic growth, but not
invasion. PLoS One. 2:e10162007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liberman J, Sartelet H, Flahaut M,
Mühlethaler-Mottet A, Coulon A, Nyalendo C, Vassal G, Joseph JM and
Gross N: Involvement of the CXCR7/CXCR4/CXCL12 axis in the
malignant progression of human neuroblastoma. PLoS One.
7:e436652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wedge SR, Ogilvie DJ, Dukes M, Kendrew J,
Chester R, Jackson JA, Boffey SJ, Valentine PJ, Curwen JO, Musgrove
HL, et al: ZD6474 inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor
signaling, angiogenesis, and tumor growth following oral
administration. Cancer Res. 62:4645–4655. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vidal M, Wells S, Ryan A and Cagan R:
ZD6474 suppresses oncogenic RET isoforms in a Drosophila model for
type 2 multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes and papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 65:3538–3541. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wells SA Jr, Gosnell JE, Gagel RF, Moley
J, Pfister D, Sosa JA, Skinner M, Krebs A, Vasselli J and
Schlumberger M: Vandetanib for the treatment of patients with
locally advanced or metastatic hereditary medullary thyroid cancer.
J Clin Oncol. 28:767–772. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fox E, Widemann BC, Chuk MK, Marcus L,
Aikin A, Whitcomb PO, Merino MJ, Lodish M, Dombi E, Steinberg SM,
et al: Vandetanib in children and adolescents with multiple
endocrine neoplasia type 2B associated medullary thyroid carcinoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 19:4239–4248. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wells SA Jr, Robinson BG, Gagel RF, Dralle
H, Fagin JA, Santoro M, Baudin E, Elisei R, Jarzab B, Vasselli JR,
et al: Vandetanib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic
medullary thyroid cancer: A randomized, double-blind phase III
trial. J Clin Oncol. 30:134–141. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee EQ, Kaley TJ, Duda DG, Schiff D,
Lassman AB, Wong ET, Mikkelsen T, Purow BW, Muzikansky A,
Ancukiewicz M, et al: A multicenter, phase II, randomized,
noncomparative clinical trial of radiation and temozolomide with or
without vandetanib in newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients. Clin
Cancer Res. 21:3610–3618. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Siegfried JM, Gubish CT, Rothstein ME,
Henry C and Stabile LP: Combining the multitargeted tyrosine kinase
inhibitor vandetanib with the antiestrogen fulvestrant enhances its
antitumor effect in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol.
7:485–495. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gautschi O, Zander T, Keller FA, Strobel
K, Hirschmann A, Aebi S and Diebold J: A patient with lung
adenocarcinoma and RET fusion treated with vandetanib. J Thorac
Oncol. 8:e43–e44. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ding X, Xiang L, Wang N, Zhao Z and Jin X,
Sun Y, Duan W, Wang S and Jin X: Vandetanib-induced inhibition of
neuroblastoma cell migration and invasion is associated with
downregulation of the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis and matrix metalloproteinase
14. Oncol Rep. 31:1165–1174. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zage PE, Zeng L, Palla S, Fang W, Nilsson
MB, Heymach JV and Zweidler-McKay PA: A novel therapeutic
combination for neuroblastoma: The vascular endothelial growth
factor receptor/epidermal growth factor receptor/rearranged during
transfection inhibitor vandetanib with 13-cis-retinoic acid.
Cancer. 116:2465–2475. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sebaugh JL: Guidelines for accurate
EC50/IC50 estimation. Pharm Stat. 10:128–134.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dai L, Cui X, Zhang X, Cheng L, Liu Y,
Yang Y, Fan P, Wang Q, Lin Y, Zhang J, et al: SARI inhibits
angiogenesis and tumour growth of human colon cancer through
directly targeting ceruloplasmin. Nat Commun. 7:119962016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dai L, Cheng L, Zhang X, Jiang Q, Zhang S,
Wang S, Li Y, Chen X, Du T, Yang Y, et al: Plasmid-based
STAT3-siRNA efficiently inhibits breast tumor growth and metastasis
in mice. Neoplasma. 58:538–547. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang C, Tan J, Zhu J, Wang S and Wei G:
YAP promotes tumorigenesis and cisplatin resistance in
neuroblastoma. Oncotarget. 8:37154–37163. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Michaelis M, Bliss J, Arnold SC, Hinsch N,
Rothweiler F, Deubzer HE, Witt O, Langer K, Doerr HW, Wels WS, et
al: Cisplatin-resistant neuroblastoma cells express enhanced levels
of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and are sensitive to
treatment with EGFR-specific toxins. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6531–6537.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rössler J, Odenthal E, Geoerger B,
Gerstenmeyer A, Lagodny J, Niemeyer CM and Vassal G: EGFR
inhibition using gefitinib is not active in neuroblastoma cell
lines. Anticancer Res. 29:1327–1333. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bakir S, Yazgan ÜC, Ibiloglu I, Elbey B,
Kizil M and Kelle M: The protective effect of pomegranate extract
against cisplatin toxicity in rat liver and kidney tissue. Arch
Physiol Biochem. 121:152–156. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Katanić J, Matić S, Pferschy-Wenzig EM,
Kretschmer N, Boroja T, Mihailović V, Stanković V, Stanković N,
Mladenović M, Stanić S, et al: Filipendula ulmaria extracts
attenuate cisplatin-induced liver and kidney oxidative stress in
rats: In vivo investigation and LC-MS analysis. Food Chem Toxicol.
99:86–102. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Greco WR, Bravo G and Parsons JC: The
search for synergy: A critical review from a response surface
perspective. Pharmacol Rev. 47:331–385. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Minto CF, Schnider TW, Short TG, Gregg KM,
Gentilini A and Shafer SL: Response surface model for anesthetic
drug interactions. Anesthesiology. 92:1603–1616. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Papangeli I, Kim J, Maier I, Park S, Lee
A, Kang Y, Tanaka K, Khan OF, Ju H, Kojima Y, et al: MicroRNA
139-5p coordinates APLNR-CXCR4 crosstalk during vascular
maturation. Nat Commun. 7:112682016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu H, Liu Y, Liu W, Zhang W and Xu J:
EZH2-mediated loss of miR-622 determines CXCR4 activation in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun. 6:84942015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Geminder H, Sagi-Assif O, Goldberg L,
Meshel T, Rechavi G, Witz IP and Ben-Baruch A: A possible role for
CXCR4 and its ligand, the CXC chemokine stromal cell-derived
factor-1, in the development of bone marrow metastases in
neuroblastoma. J Immunol. 167:4747–4757. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Airoldi I, Raffaghello L, Piovan E, Cocco
C, Carlini B, Amadori A, Corrias MV and Pistoia V: CXCL12 does not
attract CXCR4+ human metastatic neuroblastoma cells: Clinical
implications. Clin Cancer Res. 12:77–82. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang L, Yeger H, Das B, Irwin MS and
Baruchel S: Tissue microenvironment modulates CXCR4 expression and
tumor metastasis in neuroblastoma. Neoplasia. 9:36–46. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Catani MV, Corasaniti MT, Navarra M,
Nisticò G, Finazzi-Agrò A and Melino G: gp120 induces cell death in
human neuroblastoma cells through the CXCR4 and CCR5 chemokine
receptors. J Neurochem. 74:2373–2379. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhi Y, Duan Y, Zhou X, Yin X, Guan G,
Zhang H, Dong Q and Yang K: NF-κB signaling pathway confers
neuroblastoma cells migration and invasion ability via the
regulation of CXCR4. Med Sci Monit. 20:2746–2752. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Clift IC, Bamidele AO, Rodriguez-Ramirez
C, Kremer KN and Hedin KE: β-Arrestin1 and distinct CXCR4
structures are required for stromal derived factor-1 to
downregulate CXCR4 cell-surface levels in neuroblastoma. Mol
Pharmacol. 85:542–552. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|