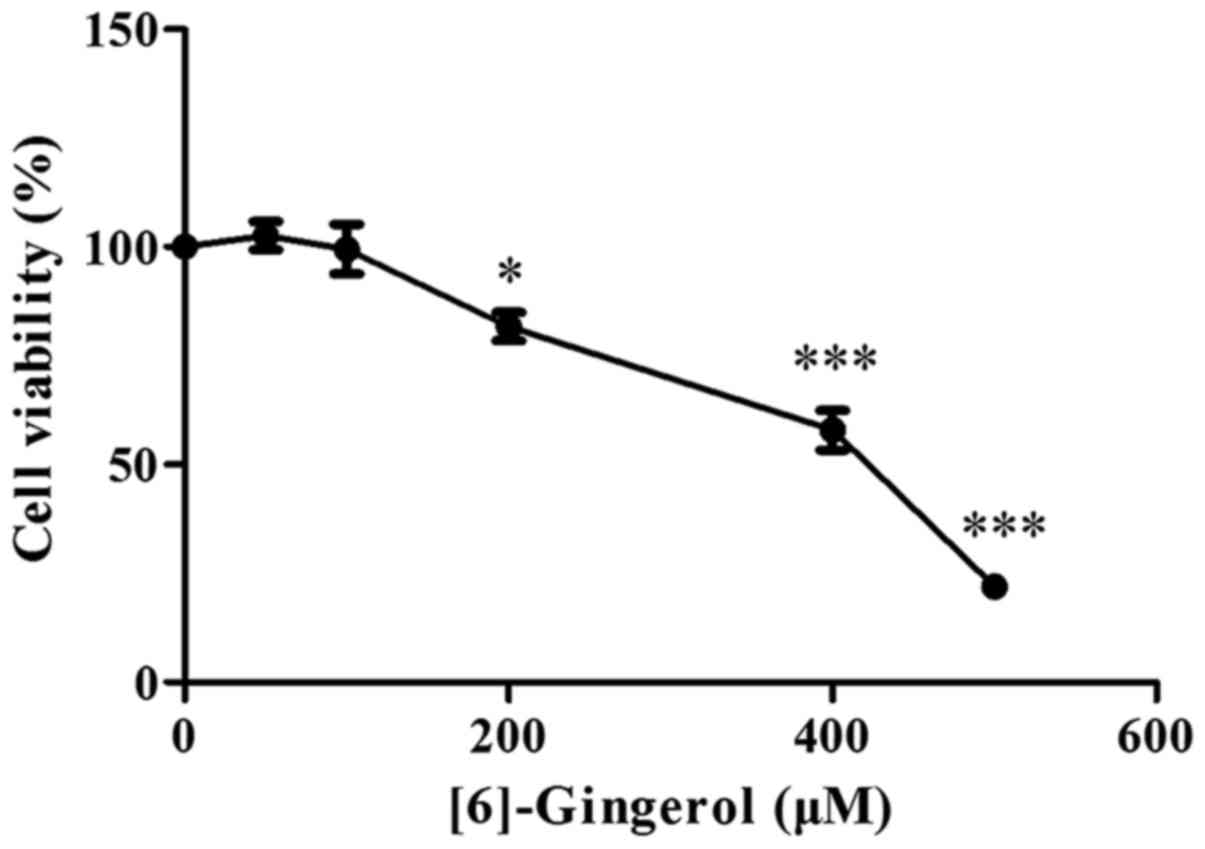
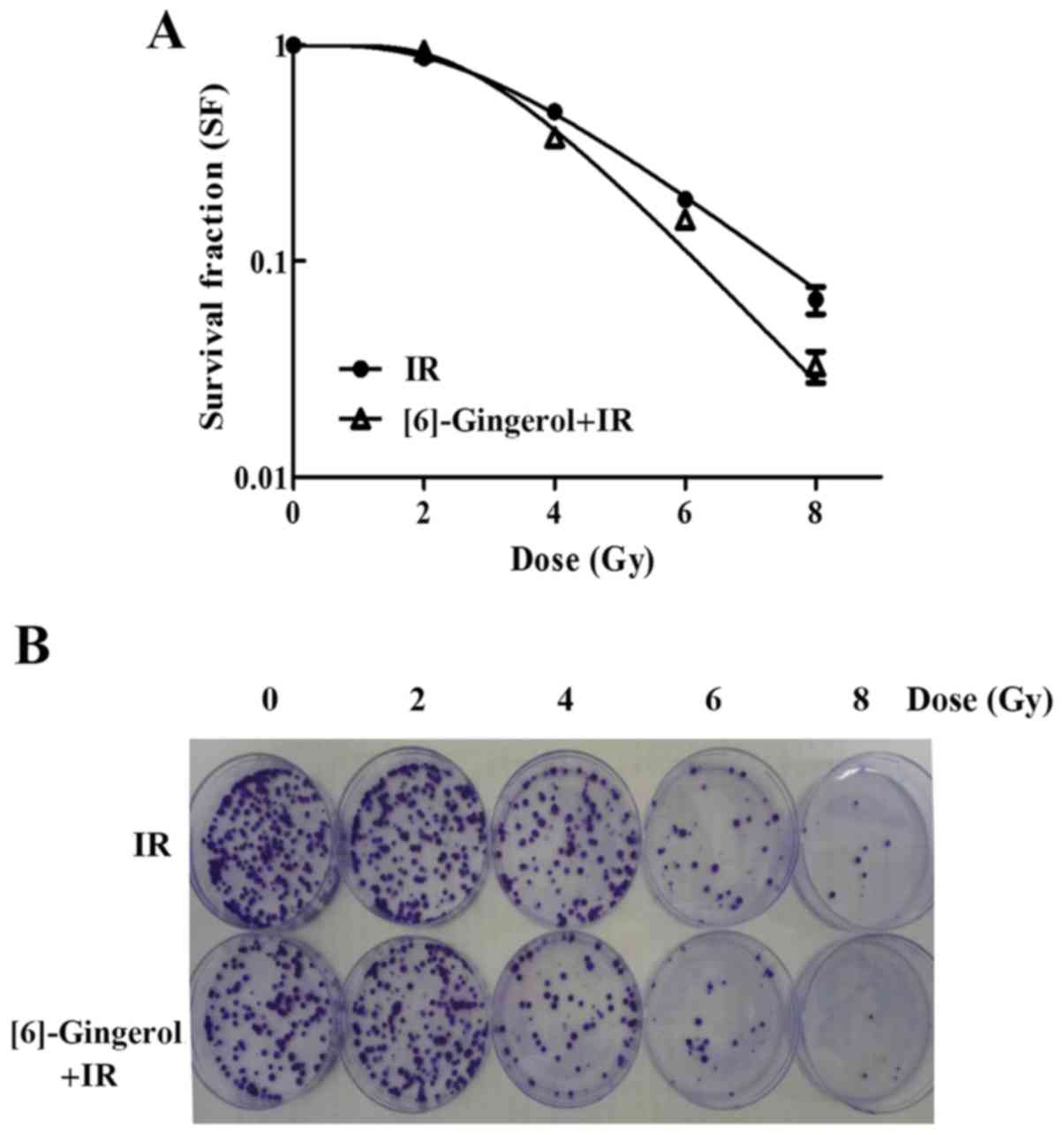
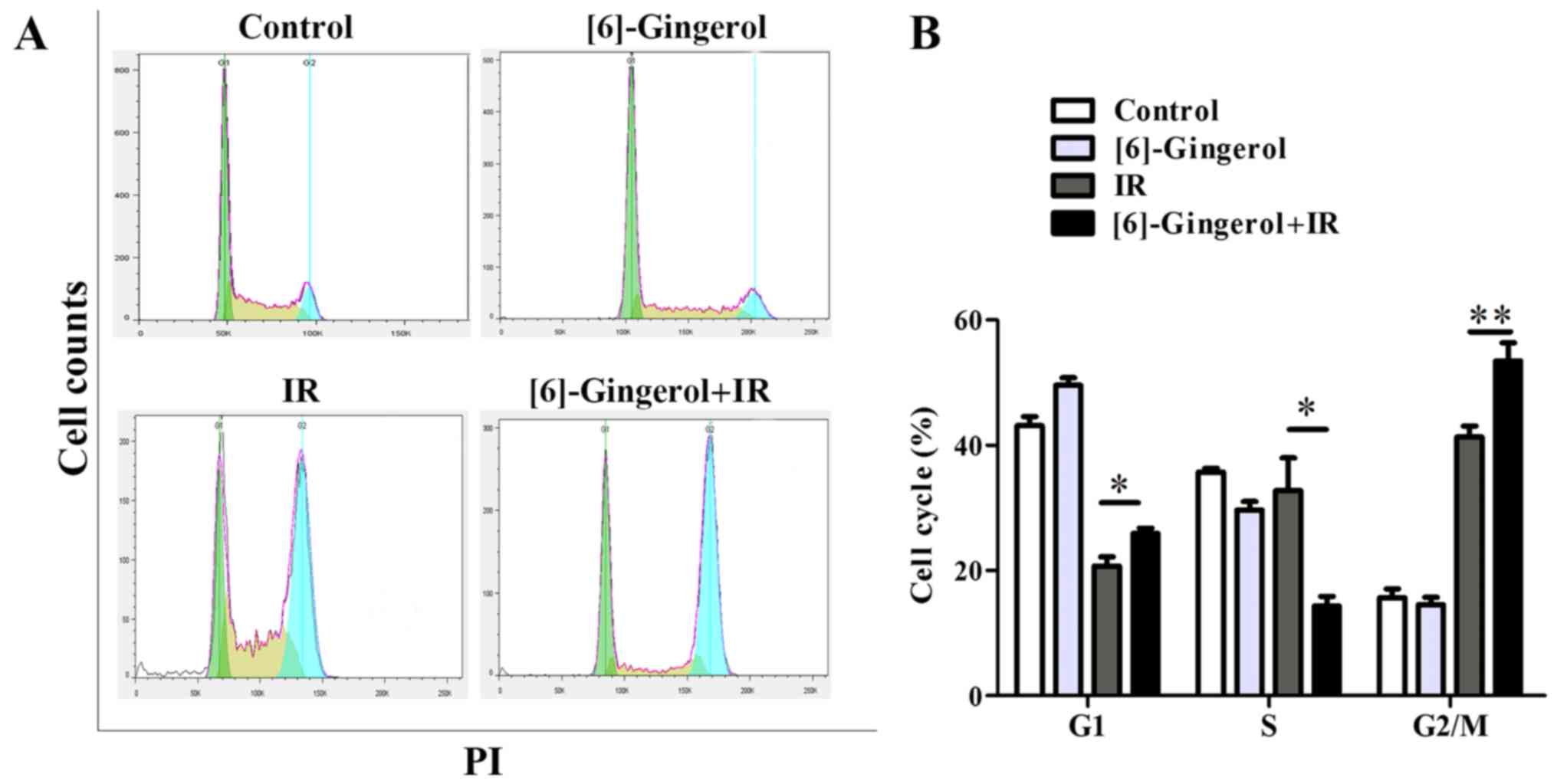
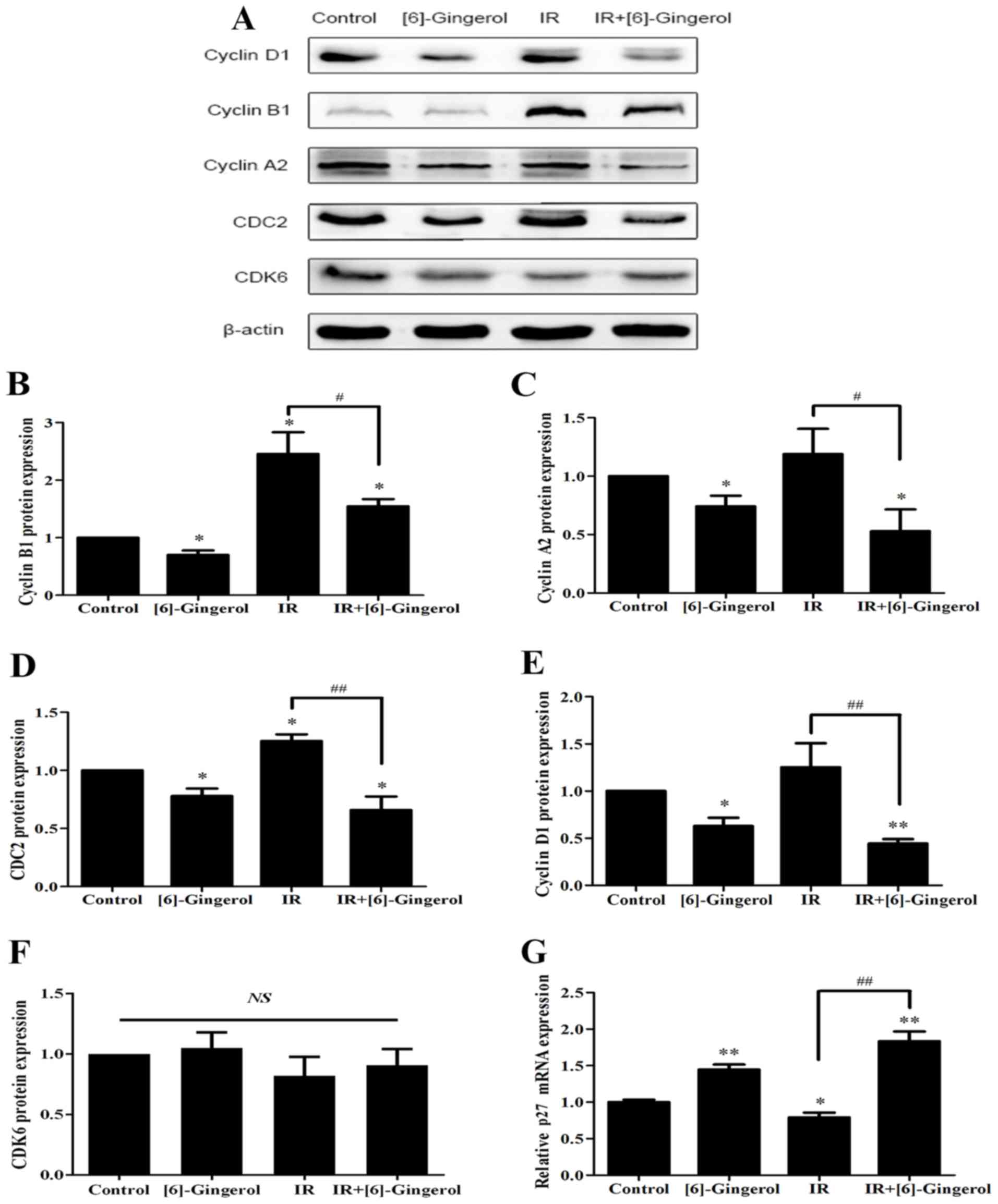
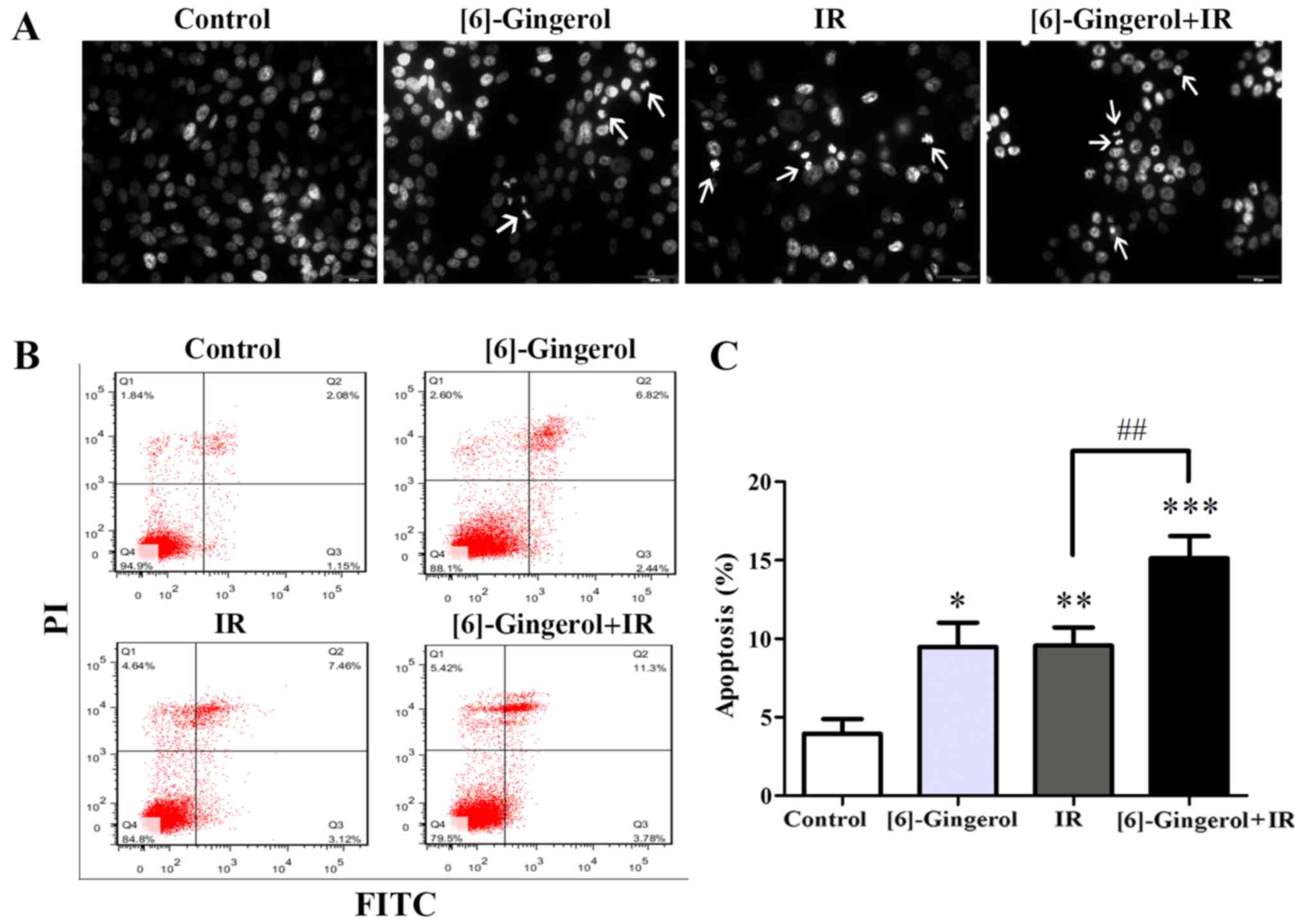
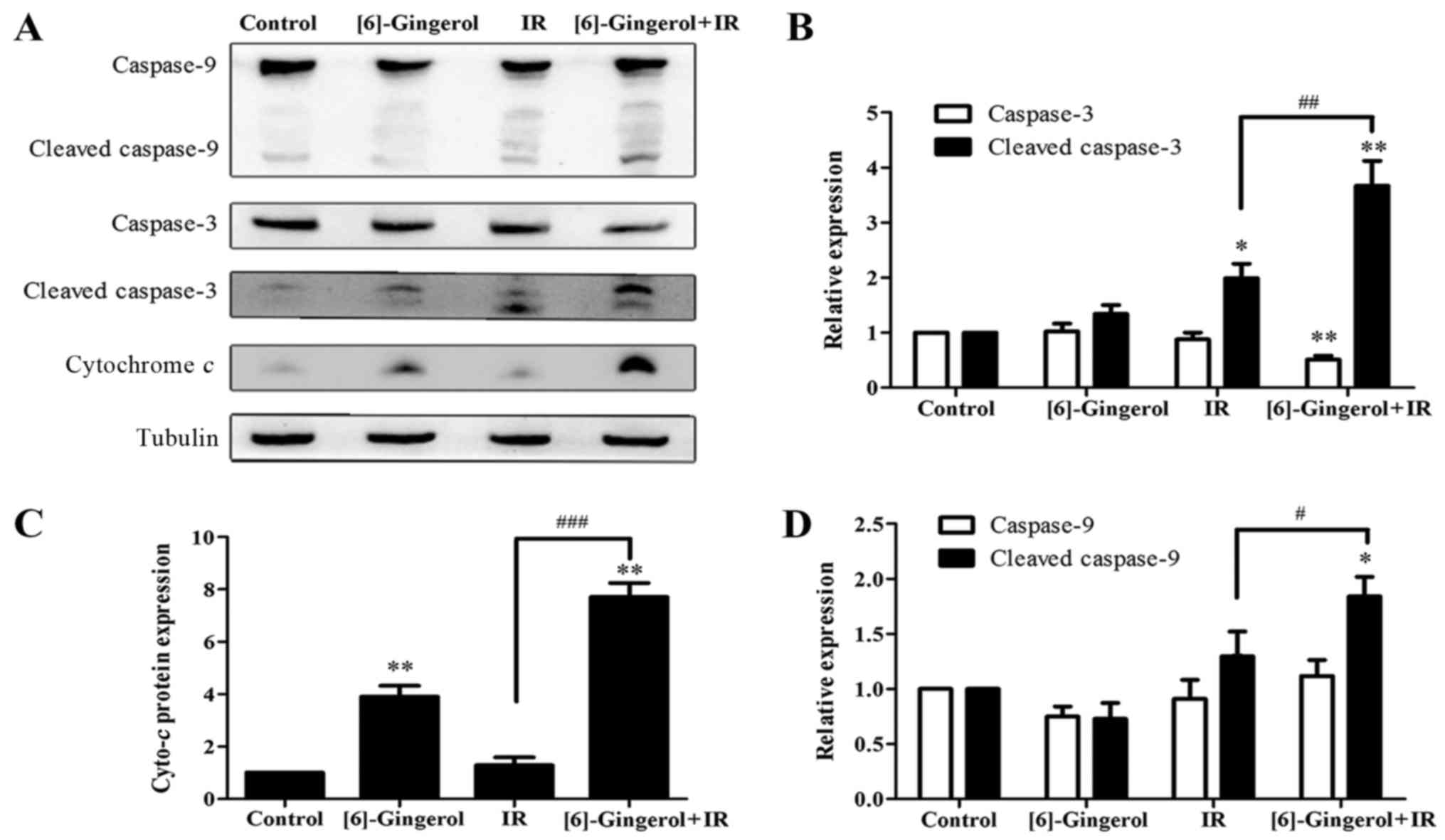
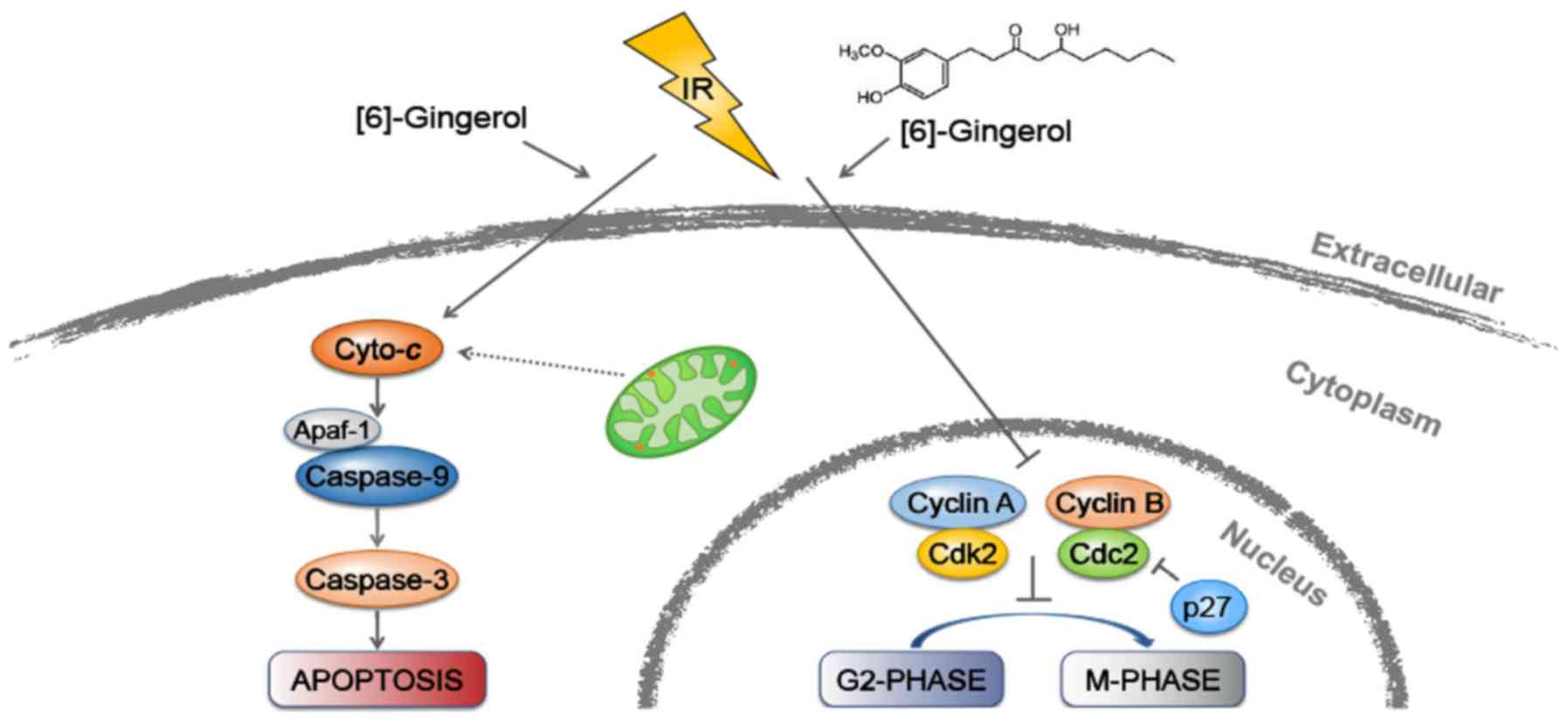
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Global Burden of Disease Cancer
Collaboration, . Fitzmaurice C, Dicker D, Pain A, Hamavid H,
Moradi-Lakeh M, MacIntyre MF, Allen C, Hansen G, Woodbrook R, Wolfe
C, et al: The global burden of cancer 2013. JAMA Oncol. 1:505–527.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Karimi P, Islami F, Anandasabapathy S,
Freedman ND and Kamangar F: Gastric cancer: Descriptive
epidemiology, risk factors, screening, and prevention. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 23:700–713. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang H, Sun LL, Meng YL, Song GY, Hu JJ,
Lu P and Ji B: Survival trends in gastric cancer patients of
Northeast China. World J Gastroenterol. 17:3257–3262.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang CY, Bai XY and Wang CH: Traditional
Chinese medicine: A treasured natural resource of anticancer drug
research and development. Am J Chin Med. 42:543–559. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wong RK, Jang R and Darling G:
Postoperative chemoradiotherapy vs. preoperative chemoradiotherapy
for locally advanced (operable) gastric cancer: Clarifying the role
and technique of radiotherapy. J Gastrointest Oncol. 6:89–107.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pang X, Wei W, Leng W, Chen Q, Xia H, Chen
L and Li R: Radiotherapy for gastric cancer: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 35:387–396. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Trip AK, Sikorska K, van Sandick JW, Heeg
M, Cats A, Boot H, Jansen EP and Verheij M: Radiation-induced
dose-dependent changes of the spleen following postoperative
chemoradiotherapy for gastric cancer. Radiother Oncol. 116:239–244.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dawson LA, Kavanagh BD, Paulino AC, Das
SK, Miften M, Li XA, Pan C, Ten Haken RK and Schultheiss TE:
Radiation-associated kidney injury. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
76 Suppl:S108–S115. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Surh YJ: Cancer chemoprevention with
dietary phytochemicals. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:768–780. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hu XQ, Sun Y, Lau E, Zhao M and Su SB:
Advances in synergistic combinations of Chinese herbal medicine for
the treatment of cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 16:346–356.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Baliga MS, Haniadka R, Pereira MM, D'Souza
JJ, Pallaty PL, Bhat HP and Popuri S: Update on the chemopreventive
effects of ginger and its phytochemicals. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr.
51:499–523. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Oyagbemi AA, Saba AB and Azeez OI:
Molecular targets of [6]-gingerol: Its potential roles in cancer
chemoprevention. Biofactors. 36:169–178. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Park KK, Chun KS, Lee JM, Lee SS and Surh
YJ: Inhibitory effects of [6]-gingerol, a major pungent principle
of ginger, on phorbol ester-induced inflammation, epidermal
ornithine decarboxylase activity and skin tumor promotion in ICR
mice. Cancer Lett. 129:139–144. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Weng CJ, Wu CF, Huang HW, Ho CT and Yen
GC: Anti-invasion effects of 6-shogaol and 6-gingerol, two active
components in ginger, on human hepatocarcinoma cells. Mol Nutr Food
Res. 54:1618–1627. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee SH, Cekanova M and Baek SJ: Multiple
mechanisms are involved in 6-gingerol-induced cell growth arrest
and apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells. Mol Carcinog.
47:197–208. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee HS, Seo EY, Kang NE and Kim WK:
[6]-Gingerol inhibits metastasis of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer
cells. J Nutr Biochem. 19:313–319. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim EC, Min JK, Kim TY, Lee SJ, Yang HO,
Han S, Kim YM and Kwon YG: [6]-Gingerol, a pungent ingredient of
ginger, inhibits angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 335:300–308. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Higgins GS, O'Cathail SM, Muschel RJ and
McKenna WG: Drug radiotherapy combinations: Review of previous
failures and reasons for future optimism. Cancer Treat Rev.
41:105–113. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Deorukhkar A, Ahuja N, Mercado AL,
Diagaradjane P, Raju U, Patel N, Mohindra P, Diep N, Guha S and
Krishnan S: Zerumbone increases oxidative stress in a
thiol-dependent ROS-independent manner to increase DNA damage and
sensitize colorectal cancer cells to radiation. Cancer Med.
4:278–292. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Orr WS, Denbo JW, Saab KR, Ng CY, Wu J, Li
K, Garner JM, Morton CL, Du Z, Pfeffer LM, et al: Curcumin
potentiates rhabdomyosarcoma radiosensitivity by suppressing NF-kB
activity. PLoS One. 8:513092013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liu JS, Che XM, Chang S, Qiu GL, He SC,
Fan L, Zhao W, Zhang ZL and Wang SF: β-elemene enhances the
radiosensitivity of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting Pak1
activation. World J Gastroenterol. 21:9945–9956. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun M, Pan D, Chen Y, Li Y, Gao K and Hu
B: Coroglaucigenin enhances the radiosensitivity of human lung
cancer cells through Nrf2/ROS pathway. Oncotarget. 8:32807–32820.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yao JX, Yao ZF, Li ZF and Liu YB:
Radio-sensitization by Piper longumine of human breast adenoma
MDA-MB-231 cells in vitro. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:3211–3217.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang P, Wang L, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Yuan
Y, Debeb BG, Chen D, Sun Y, You MJ, Liu Y, Dean DC, et al: miR-205
acts as a tumour radiosensitizer by targeting ZEB1 and Ubc13. Nat
Commun. 5:56712014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Azad A, Lim Yin S, D'Costa Z, Jones K,
Diana A, Sansom OJ, Kruger P, Liu S, McKenna WG, Dushek O, et al:
PD-L1 blockade enhances response of pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma to radiotherapy. EMBO Mol Med. 9:167–180. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rey S, Schito L, Koritzinsky M and Wouters
BG: Molecular targeting of hypoxia in radiotherapy. Adv Drug Deliv
Rev. 109:45–62. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Berdis AJ: Current and emerging strategies
to increase the efficacy of ionizing radiation in the treatment of
cancer. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 9:167–181. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ding M, Zhang E, He R and Wang X: Newly
developed strategies for improving sensitivity to radiation by
targeting signal pathways in cancer therapy. Cancer Sci.
104:1401–1410. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miyanaga S, Ninomiya I, Tsukada T, Okamoto
K, Harada S, Nakanuma S, Sakai S, Makino I, Kinoshita J, Hayashi H,
et al: Concentration-dependent radiosensitizing effect of docetaxel
in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol.
48:517–524. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rastogi N, Duggal S, Singh SK, Porwal K,
Srivastava VK, Maurya R, Bhatt ML and Mishra DP: Proteasome
inhibition mediates p53 reactivation and anti-cancer activity of
6-gingerol in cervical cancer cells. Oncotarget. 6:43310–43325.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dillon MT, Good JS and Harrington KJ:
Selective targeting of the G2/M cell cycle checkpoint to improve
the therapeutic index of radiotherapy. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol).
26:257–265. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yan Y, Black CP and Cowan KH:
Irradiation-induced G2/M checkpoint response requires ERK1/2
activation. Oncogene. 26:4689–4698. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Smits VA and Medema RH: Checking out the
G(2)/M transition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1519:1–12. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Furuno N, den Elzen N and Pines J: Human
cyclin A is required for mitosis until mid prophase. J Cell Biol.
147:295–306. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Payne SR, Zhang S, Tsuchiya K, Moser R,
Gurley KE, Longton G, deBoer J and Kemp CJ: p27kip1 deficiency
impairs G2/M arrest in response to DNA damage, leading to an
increase in genetic instability. Mol Cell Biol. 28:258–268. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Deng M, Zeng C, Lu X, He X, Zhang R, Qiu
Q, Zheng G, Jia X, Liu H and He Z: miR-218 suppresses gastric
cancer cell cycle progression through the CDK6/Cyclin D1/E2F1 axis
in a feedback loop. Cancer Lett. 403:175–185. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim BM and Hong Y, Lee S, Liu P, Lim JH,
Lee YH, Lee TH, Chang KT and Hong Y: Therapeutic implications for
overcoming radiation resistance in cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci.
16:26880–26913. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ishiguro K, Ando T, Maeda O, Ohmiya N,
Niwa Y, Kadomatsu K and Goto H: Ginger ingredients reduce viability
of gastric cancer cells via distinct mechanisms. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 362:218–223. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ghobrial IM, Witzig TE and Adjei AA:
Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer therapy. CA Cancer J Clin.
55:178–194. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee DH, Kim DW, Jung CH, Lee YJ and Park
D: Gingerol sensitizes TRAIL-induced apoptotic cell death of
glioblastoma cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 279:253–265. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang B, Wang Y and Su Y: Peroxiredoxins,
a novel target in cancer radiotherapy. Cancer Lett. 286:154–160.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|