|
1
|
Ryerson AB, Eheman CR, Altekruse SF, Ward
JW, Jemal A, Sherman RL, Henley SJ, Holtzman D, Lake A, Noone AM,
et al: Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer,
1975–2012, featuring the increasing incidence of liver cancer.
Cancer. 122:1312–1337. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
de Martel C, Maucort-Boulch D, Plummer M
and Franceschi S: World-wide relative contribution of hepatitis B
and C viruses in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
62:1190–1200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Herath NI, Leggett BA and MacDonald GA:
Review of genetic and epigenetic alterations in
hepatocarcinogenesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:15–21. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kondoh N, Wakatsuki T, Hada A, Shuda M,
Tanaka K, Arai M and Yamamoto M: Genetic and epigenetic events in
human hepatocarcinogenesis. Int J Oncol. 18:1271–1278.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fujimoto A, Totoki Y, Abe T, Boroevich KA,
Hosoda F, Nguyen HH, Aoki M, Hosono N, Kubo M, Miya F, et al:
Whole-genome sequencing of liver cancers identifies etiological
influences on mutation patterns and recurrent mutations in
chromatin regulators. Nat Genet. 44:760–764. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kan Z, Zheng H, Liu X, Li S, Barber TD,
Gong Z, Gao H, Hao K, Willard MD, Xu J, et al: Whole-genome
sequencing identifies recurrent mutations in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Genome Res. 23:1422–1433. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sharma S, Kelly TK and Jones PA:
Epigenetics in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 31:27–36. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fatemi M, Pao MM, Jeong S, Gal-Yam EN,
Egger G, Weisenberger DJ and Jones PA: Footprinting of mammalian
promoters: Use of a CpG DNA methyltransferase revealing nucleosome
positions at a single molecule level. Nucleic Acids Res.
33:e1762005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Gorden A, Farina M,
Lee JS, Conner EA, Schroeder I, Factor VM and Thorgeirsson SS:
Mechanistic and prognostic significance of aberrant methylation in
the molecular pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Clin Invest. 117:2713–2722. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pogribny IP and Rusyn I: Role of
epigenetic aberrations in the development and progression of human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 342:223–230. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wahid B, Ali A, Rafique S and Idrees M:
New insights into the epigenetics of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Biomed Res Int. 2017:16095752017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yoshikawa H, Matsubara K, Qian GS, Jackson
P, Groopman JD, Manning JE, Harris CC and Herman JG: SOCS-1, a
negative regulator of the JAK/STAT pathway, is silenced by
methylation in human hepatocellular carcinoma and shows
growth-suppression activity. Nat Genet. 28:29–35. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Niwa Y, Kanda H, Shikauchi Y, Saiura A,
Matsubara K, Kitagawa T, Yamamoto J, Kubo T and Yoshikawa H:
Methylation silencing of SOCS-3 promotes cell growth and migration
by enhancing JAK/STAT and FAK signalings in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncogene. 24:6406–6417. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kubo T, Yamamoto J, Shikauchi Y, Niwa Y,
Matsubara K and Yoshikawa H: Apoptotic speck protein-like, a highly
homologous protein to apoptotic speck protein in the pyrin domain,
is silenced by DNA methylation and induces apoptosis in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 64:5172–5177. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
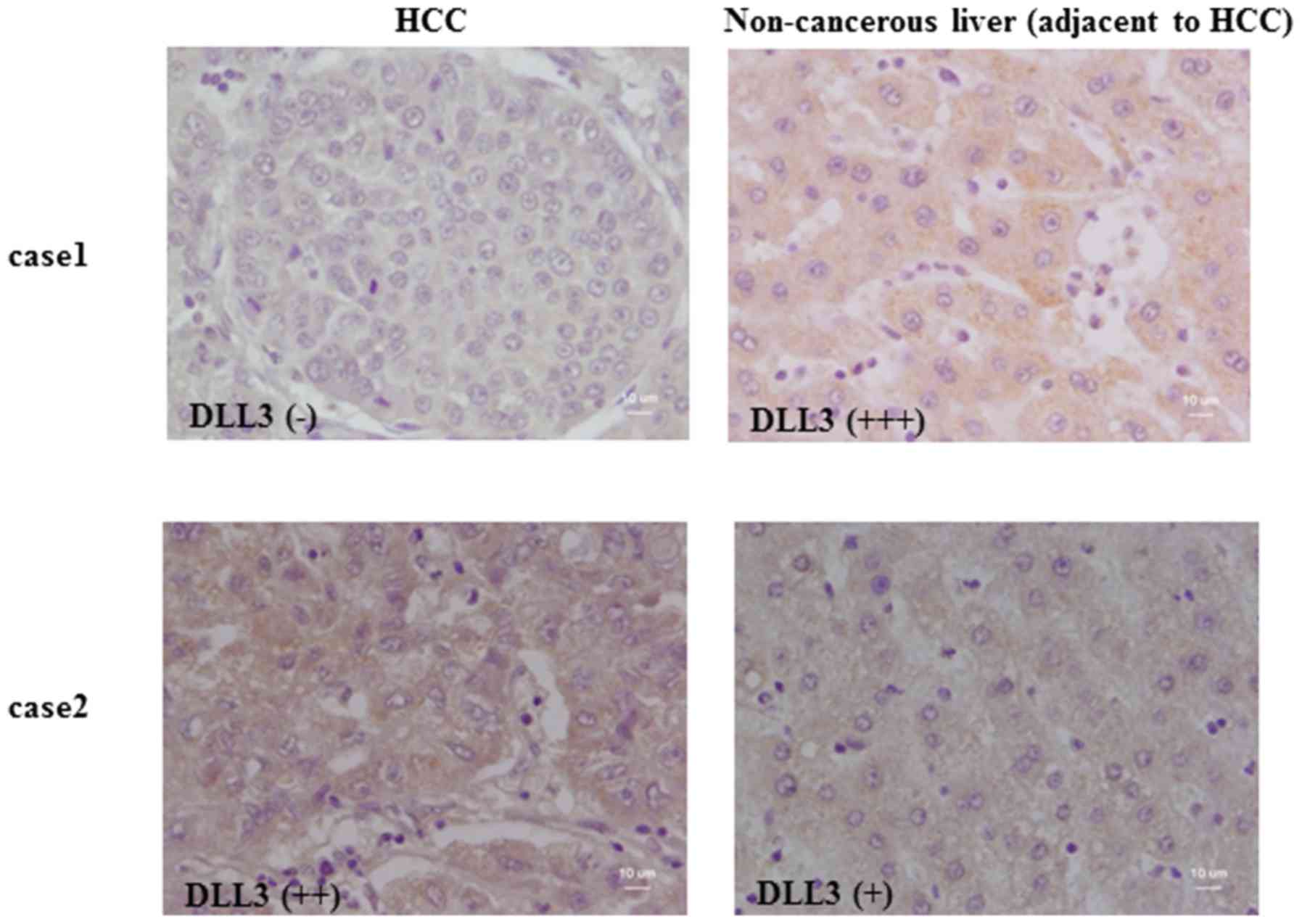
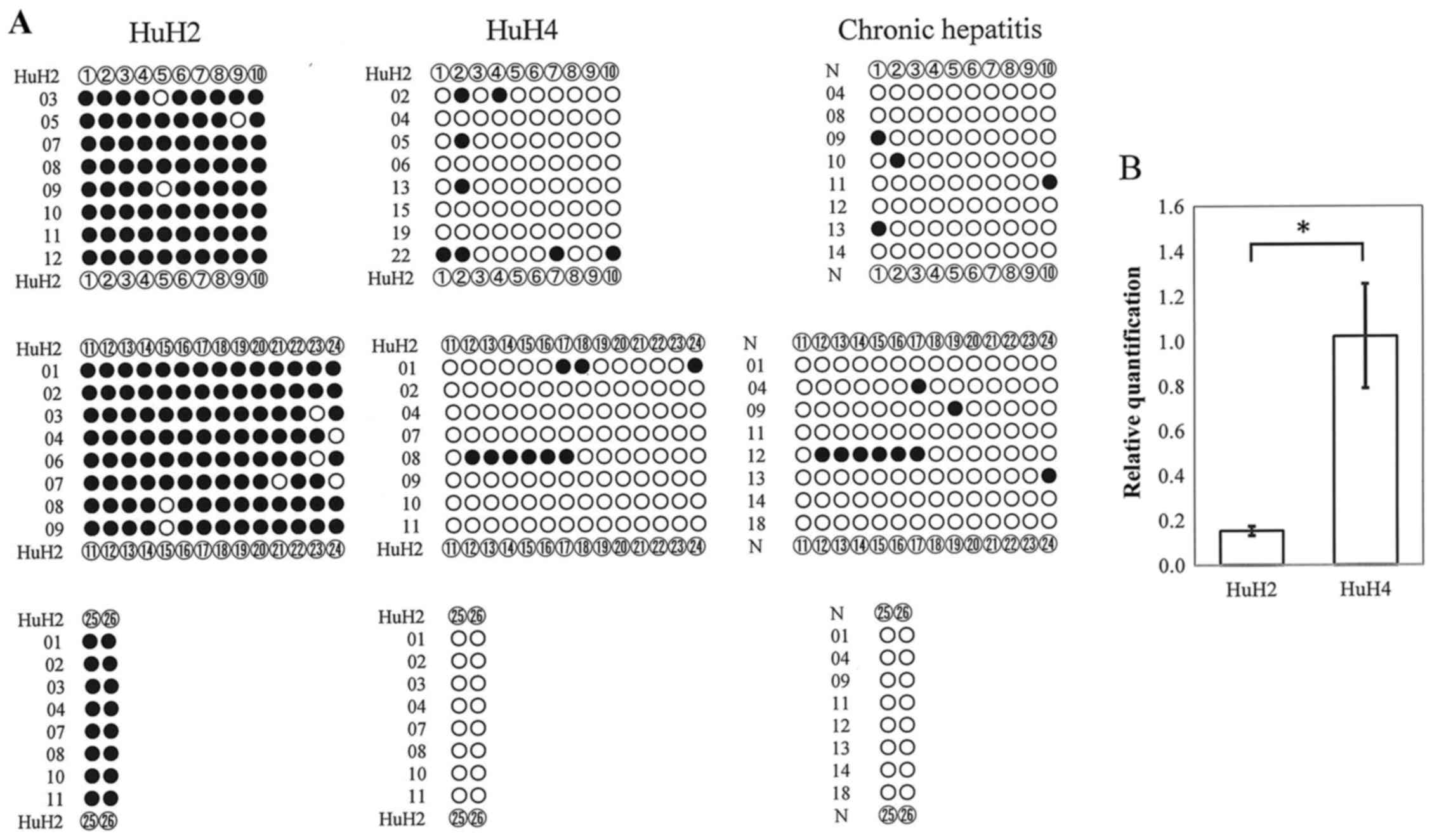
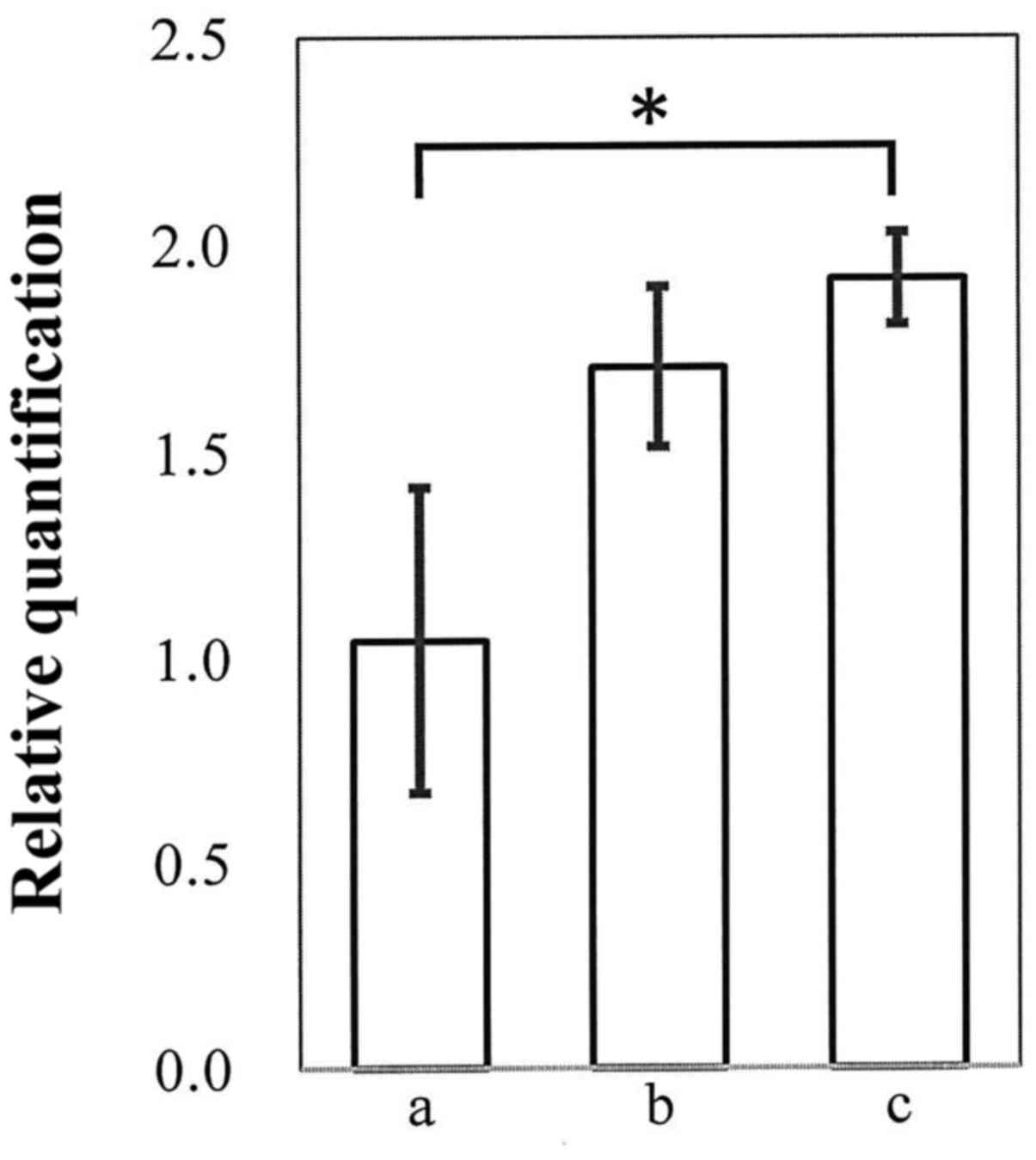
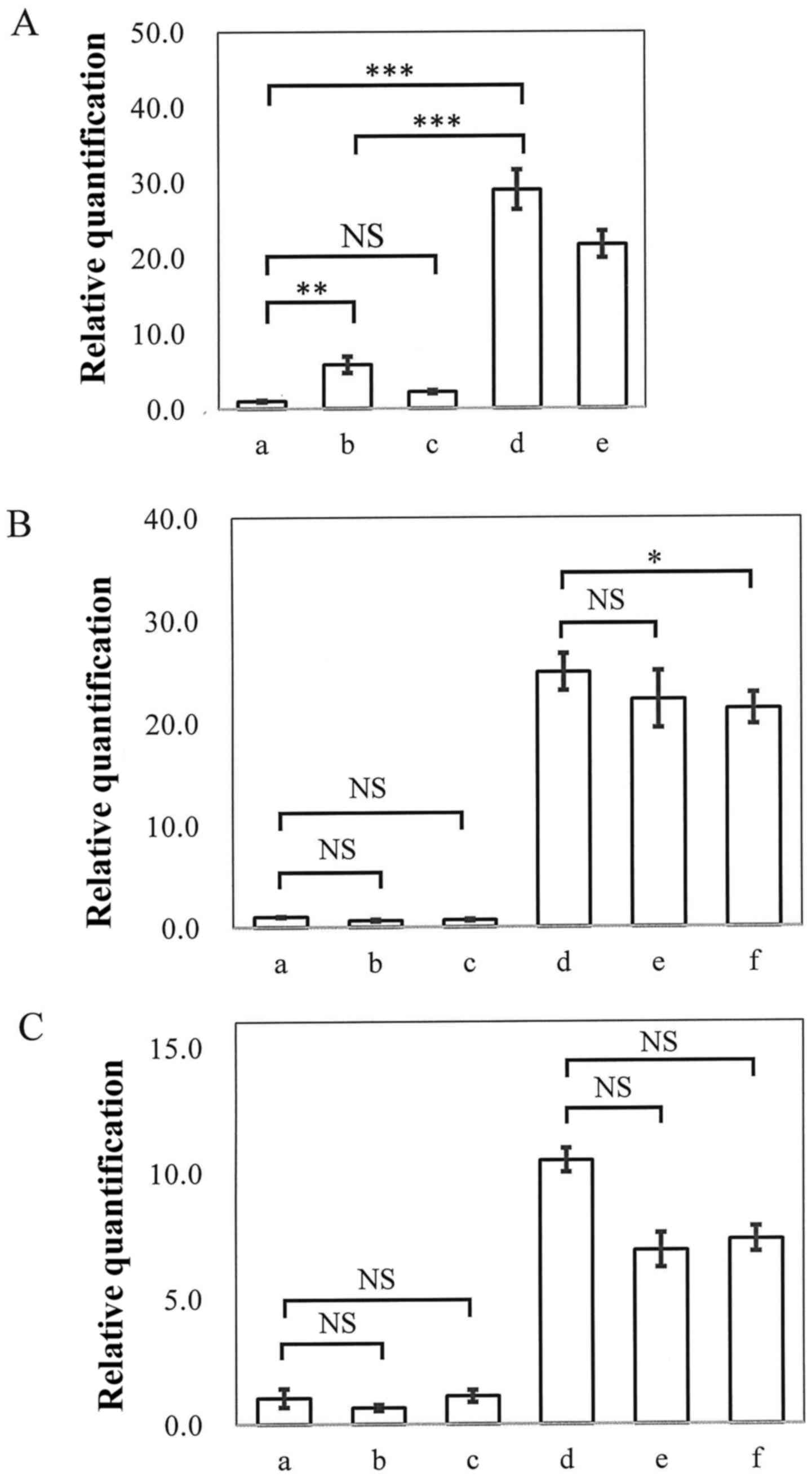
Maemura K, Yoshikawa H, Yokoyama K, Ueno
T, Kurose H, Uchiyama K and Otsuki Y: Delta-like 3 is silenced by
methylation and induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 42:817–822. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tachibana M, Sugimoto K, Fukushima T and
Shinkai Y: Set domain-containing protein, G9a, is a novel
lysine-preferring mammalian histone methyltransferase with
hyperactivity and specific selectivity to lysines 9 and 27 of
histone H3. J Biol Chem. 276:25309–25317. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Glazer RI, Knode MC, Tseng CK, Haines DR
and Marquez VE: 3-Deazaneplanocin A: A new inhibitor of
S-adenosylhomocysteine synthesis and its effects in human colon
carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 35:4523–4527. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jüttermann R, Li E and Jaenisch R:
Toxicity of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine to mammalian cells is mediated
primarily by covalent trapping of DNA methyltransferase rather than
DNA demethylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:11797–11801. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bird A: DNA methylation patterns and
epigenetic memory. Genes Dev. 16:6–21. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Choy MK, Movassagh M, Goh HG, Bennett MR,
Down TA and Foo RS: Genome-wide conserved consensus transcription
factor binding motifs are hyper-methylated. BMC Genomics.
11:5192010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kouzarides T: Chromatin modifications and
their function. Cell. 128:693–705. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang T, Cooper S and Brockdorff N: The
interplay of histone modifications-writers that read. EMBO Rep.
16:1467–1481. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jin B, Li Y and Robertson KD: DNA
methylation: Superior or subordinate in the epigenetic hierarchy?
Genes Cancer. 2:607–617. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Eberharter A and Becker PB: Histone
acetylation: A switch between repressive and permissive chromatin.
Second in review series on chromatin dynamics. EMBO Rep. 3:224–229.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Farria A, Li W and Dent SY: KATs in
cancer: Functions and therapies. Oncogene. 34:4901–4913. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
de Ruijter AJ, van Gennip AH, Caron HN,
Kemp S and van Kuilenburg AB: Histone deacetylases (HDACs):
Characterization of the classical HDAC family. Biochem J.
370:737–749. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Delcuve GP, Khan DH and Davie JR: Roles of
histone deacetylases in epigenetic regulation: emerging paradigms
from studies with inhibitors. Clinical Epigenetics. 4:52012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu WS, Parmigiani RB and Marks PA: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors: Molecular mechanisms of action. Oncogene.
26:5541–5552. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
West AC and Johnstone RW: New and emerging
HDAC inhibitors for cancer treatment. J Clin Invest. 124:30–39.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Eckschlager T, Plch J, Stiborova M and
Hrabeta J: Histone deacetylase inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Int
J Mol Sci. 18:E14142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Richon VM: Cancer biology: Mechanism of
antitumour action of vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid),
a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor. Br J Cancer. 95(S1): S2–S6.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Li B, Carey M and Workman JL: The role of
chromatin during transcription. Cell. 128:707–719. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Geffers I, Serth K, Chapman G, Jaekel R,
Schuster-Gossler K, Cordes R, Sparrow DB, Kremmer E, Dunwoodie SL,
Klein T, et al: Divergent functions and distinct localization of
the Notch ligands DLL1 and DLL3 in vivo. J Cell Biol. 178:465–476.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kodama Y, Hijikata M, Kageyama R,
Shimotohno K and Chiba T: The role of notch signaling in the
development of intrahepatic bile ducts. Gastroenterology.
127:1775–1786. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ader T, Norel R, Levoci L and Rogler LE:
Transcriptional profiling implicates TGFbeta/BMP and Notch
signaling pathways in ductular differentiation of fetal murine
hepatoblasts. Mech Dev. 123:177–194. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zong Y, Panikkar A, Xu J, Antoniou A,
Raynaud P, Lemaigre F and Stanger BZ: Notch signaling controls
liver development by regulating biliary differentiation.
Development. 136:1727–1739. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Villanueva A, Alsinet C, Yanger K, Hoshida
Y, Zong Y, Toffanin S, Rodriguez-Carunchio L, Solé M, Thung S,
Stanger BZ, et al: Notch signaling is activated in human
hepatocellular carcinoma and induces tumor formation in mice.
Gastroenterology. 143:1660–1669.e7. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Issa JP, Ottaviano YL, Celano P, Hamilton
SR, Davidson NE and Baylin SB: Methylation of the oestrogen
receptor CpG island links ageing and neoplasia in human colon. Nat
Genet. 7:536–540. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hsieh CJ, Klump B, Holzmann K, Borchard F,
Gregor M and Porschen R: Hypermethylation of the p16INK4a promoter
in colectomy specimens of patients with long-standing and extensive
ulcerative colitis. Cancer Res. 58:3942–3945. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kondo Y, Kanai Y, Sakamoto M, Mizokami M,
Ueda R and Hirohashi S: Genetic instability and aberrant DNA
methylation in chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis - A comprehensive
study of loss of heterozygosity and microsatellite instability at
39 loci and DNA hypermethylation on 8 CpG islands in microdissected
specimens from patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
32:970–979. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang JS, Guo M, Montgomery EA, Thompson
RE, Cosby H, Hicks L, Wang S, Herman JG and Canto MI: DNA promoter
hypermethylation of p16 and APC predicts neoplastic progression in
Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 104:2153–2160. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chang MS, Uozaki H, Chong JM, Ushiku T,
Sakuma K, Ishikawa S, Hino R, Barua RR, Iwasaki Y, Arai K, et al:
CpG island methylation status in gastric carcinoma with and without
infection of Epstein-Barr virus. Clin Cancer Res. 12:2995–3002.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Park SY, Yoo EJ, Cho NY, Kim N and Kang
GH: Comparison of CpG island hypermethylation and repetitive DNA
hypomethylation in premalignant stages of gastric cancer,
stratified for Helicobacter pylori infection. J Pathol.
219:410–416. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|