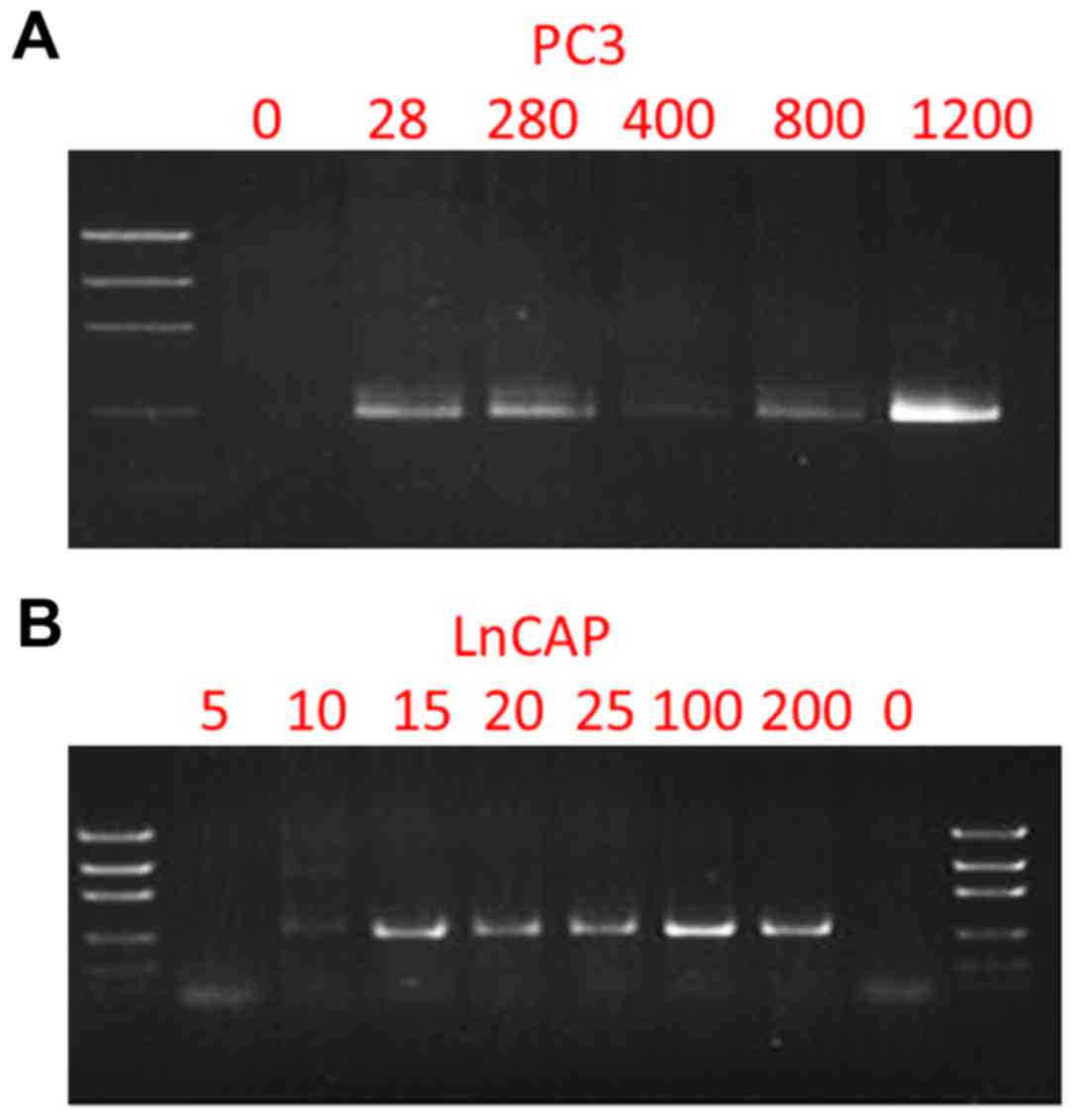
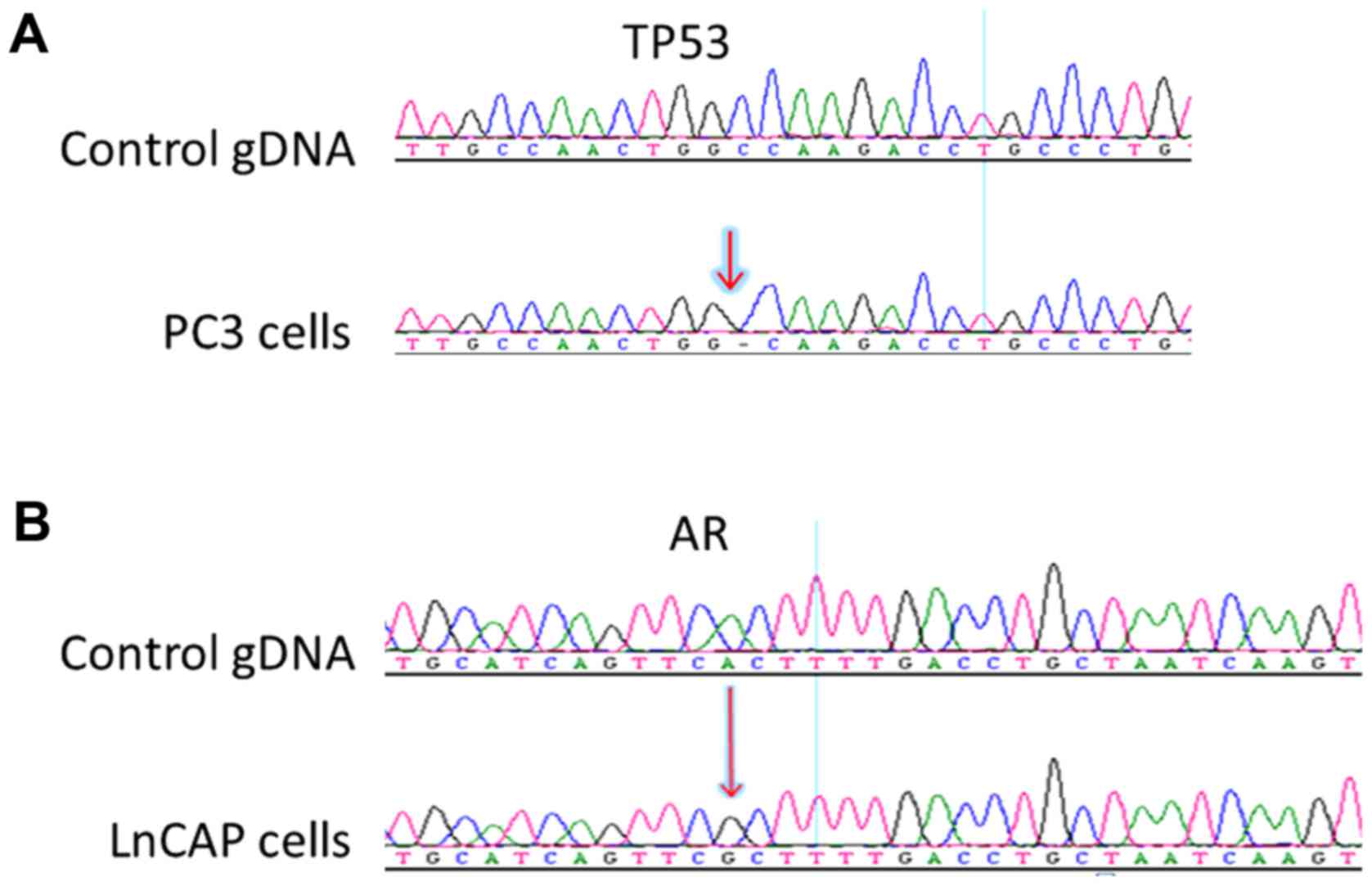
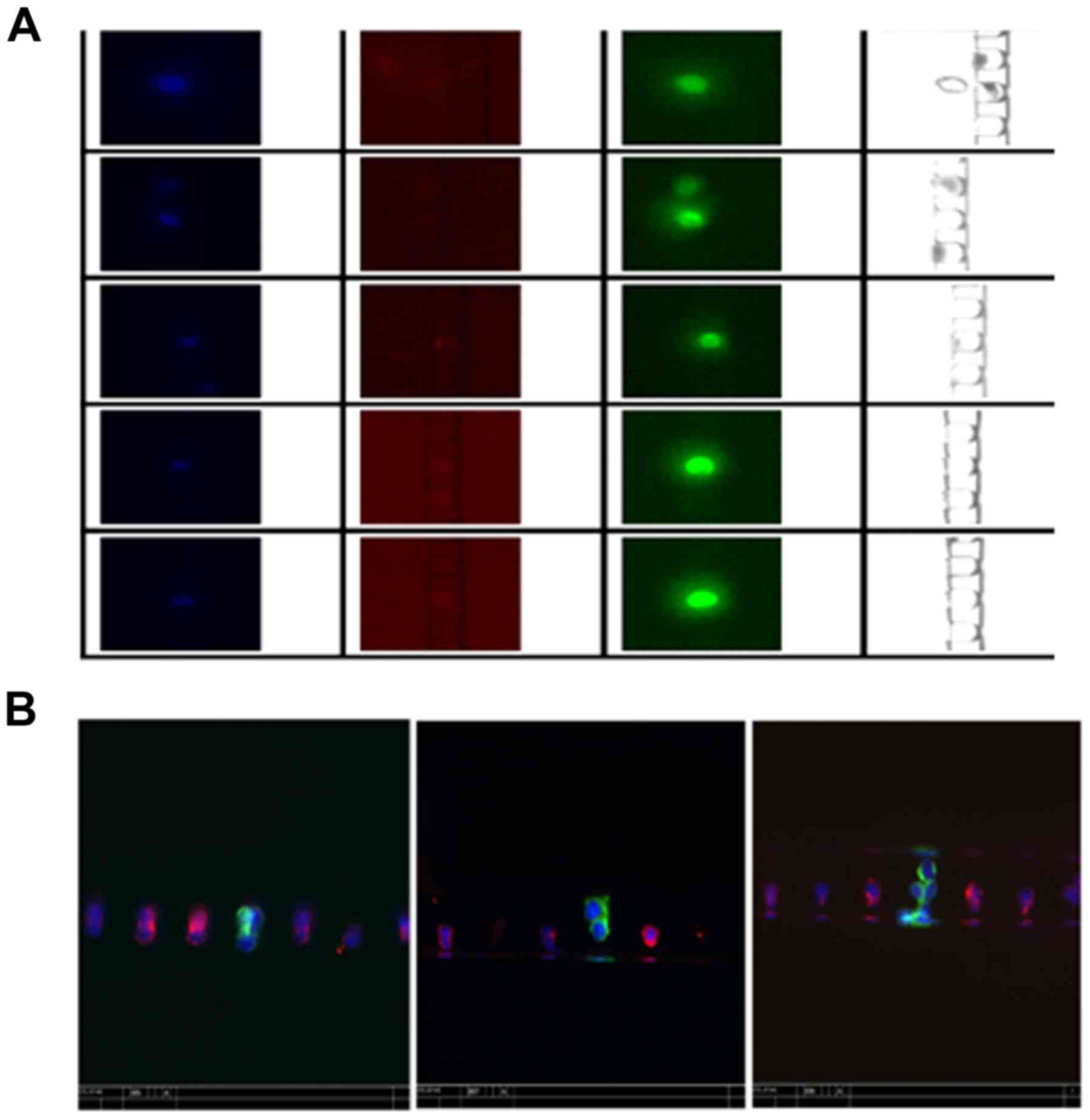
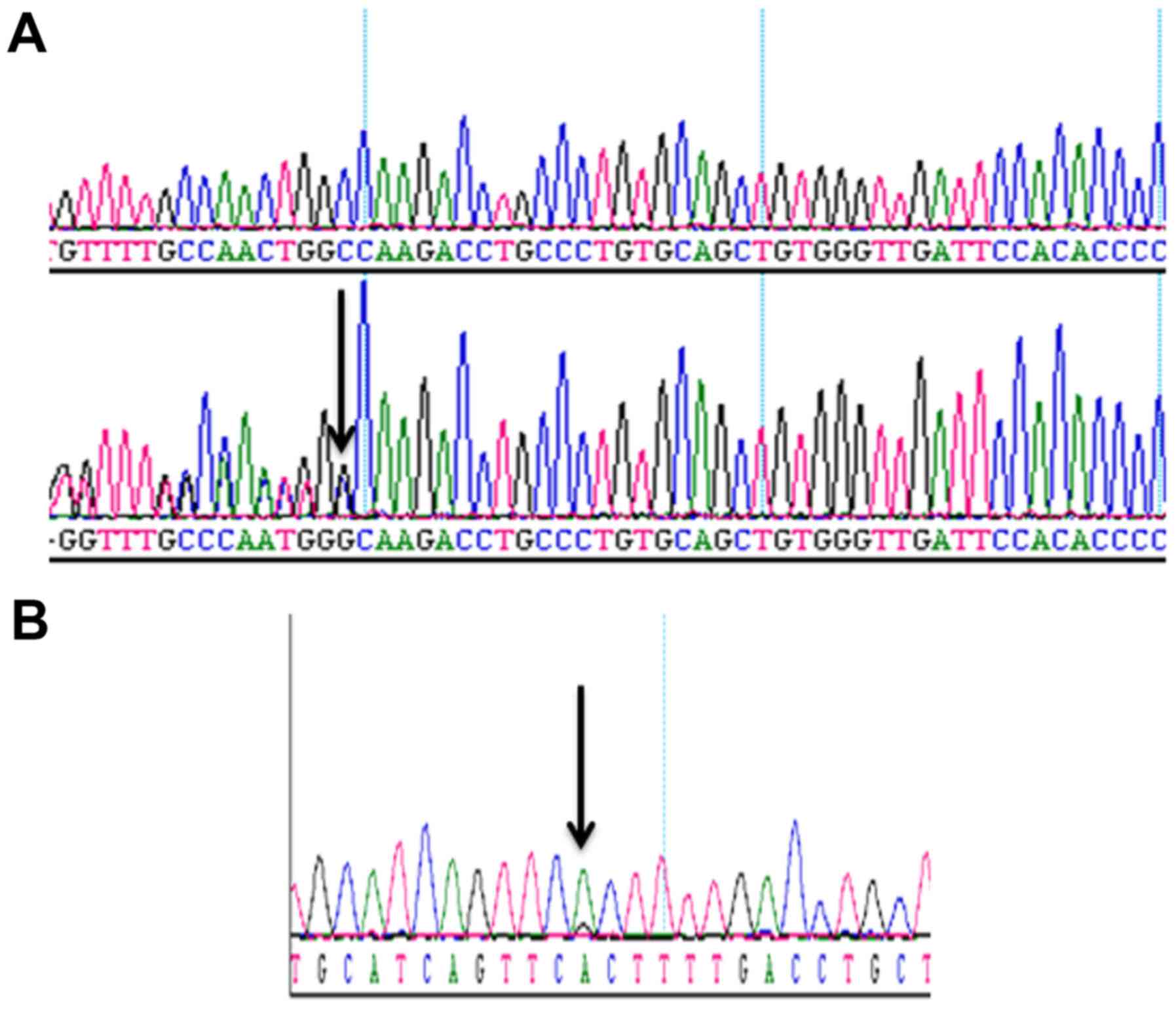
|
1
|
Pantel K and Alix-Panabières C:
Circulating tumor cells in cancer patients: Challenges and
perspectives. Trends Mol Med. 16:398–406. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Maheswaran S and Haber DA: Circulating
tumor cells: A window into cancer biology and metastasis. Curr Opin
Genet Dev. 20:96–99. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cristofanilli M, Budd GT, Ellis MJ,
Stopeck A, Matera J, Miller MC, Reuben JM, Doyle GV, Allard WJ,
Terstappen LW, et al: Circulating tumor cells, disease progression,
and survival in metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med.
351:781–791. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Punnoose EA, Atwal SK, Spoerke JM, Savage
H, Pandita A, Yeh RF, Pirzkall A, Fine BM, Amler LC, Chen DS and
Lackner MR: Molecular biomarker analyses using circulating tumor
cells. PLoS One. 5:e125712010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Allard WJ, Matera J, Miller MC, Repollet
M, Connelly MC, Rao C, Tibbe AG, Uhr JW and Terstappen LW: Tumor
cells circulate in the peripheral blood of all major carcinomas but
not in healthy subjects or patients with nonmalignant diseases.
Clin Cancer Res. 10:6897–6904. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Riethdorf S, Fritsche H, Müller V, Rau T,
Schindlbeck C, Rack B, Janni W, Coith C, Beck K, Jänicke F, et al:
Detection of circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood of
patients with metastatic breast cancer: A validation study of the
CellSearch system. Clin Cancer Res. 13:920–928. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nagrath S, Sequist LV, Maheswaran S, Bell
DW, Irimia D, Ulkus L, Smith MR, Kwak EL, Digumarthy S, Muzikansky
A, et al: Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer
patients by microchip technology. Nature. 450:1235–1239. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Khoo BL, Warkiani ME, Tan DS, Bhagat AA,
Irwin D, Lau DP, Lim AS, Lim KH, Krisna SS, Lim WT, et al: Clinical
validation of an ultra high-throughput spiral microfluidics for the
detection and enrichment of viable circulating tumor cells. PLoS
One. 9:e994092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stott SL, Hsu CH, Tsukrov DI, Yu M,
Miyamoto DT, Waltman BA, Rothenberg SM, Shah AM, Smas ME, Korir GK,
et al: Isolation of circulating tumor cells using a
microvortex-generating herringbone-chip. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:18392–18397. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Saliba AE, Saias L, Psychari E, Minc N,
Simon D, Bidard FC, Mathiot C, Pierga JY, Fraisier V, Salamero J,
et al: Microfluidic sorting and multimodal typing of cancer cells
in self-assembled magnetic arrays. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:14524–14529. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Powell AA, Talasaz AH, Zhang H, Coram MA,
Reddy A, Deng G, Telli ML, Advani RH, Carlson RW, Mollick JA, et
al: Single cell profiling of circulating tumor cells:
Transcriptional heterogeneity and diversity from breast cancer cell
lines. PLoS One. 7:e337882012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sieuwerts AM, Kraan J, Bolt-de Vries J,
van der Spoel P, Mostert B, Martens JW, Gratama JW, Sleijfer S and
Foekens JA: Molecular characterization of circulating tumor cells
in large quantities of contaminating leukocytes by a multiplex
real-time PCR. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 118:455–468. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Riahi R, Gogoi P, Sepehri S, Zhou Y,
Handique K, Godsey J and Wang Y: A novel microchannel-based device
to capture and analyze circulating tumor cells (CTCs) of breast
cancer. Int J Oncol. 44:1870–1878. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gogoi P, Sepehri S, Zhou Y, Gorin MA,
Paolillo C, Capoluongo E, Gleason K, Payne A, Boniface B,
Cristofanilli M, et al: Development of an automated and sensitive
microfluidic device for capturing and characterizing circulating
tumor cells (CTCs) from clinical blood samples. PLoS One.
11:e01474002016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chang H, Jackson DG, Kayne PS,
Ross-Macdonald PB, Ryseck RP and Siemers NO: Exome sequencing
reveals comprehensive genomic alterations across eight cancer cell
lines. PLoS One. 6:e210972011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Veldscholte J, Ris-Stalpers C, Kuiper GG,
Jenster G, Berrevoets C, Claassen E, van Rooij HC, Trapman J,
Brinkmann AO and Mulder E: A mutation in the ligand binding domain
of the androgen receptor of human LNCaP cells affects steroid
binding characteristics and response to anti-androgens. Biochem
Biophy Res Commun. 173:534–540. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|