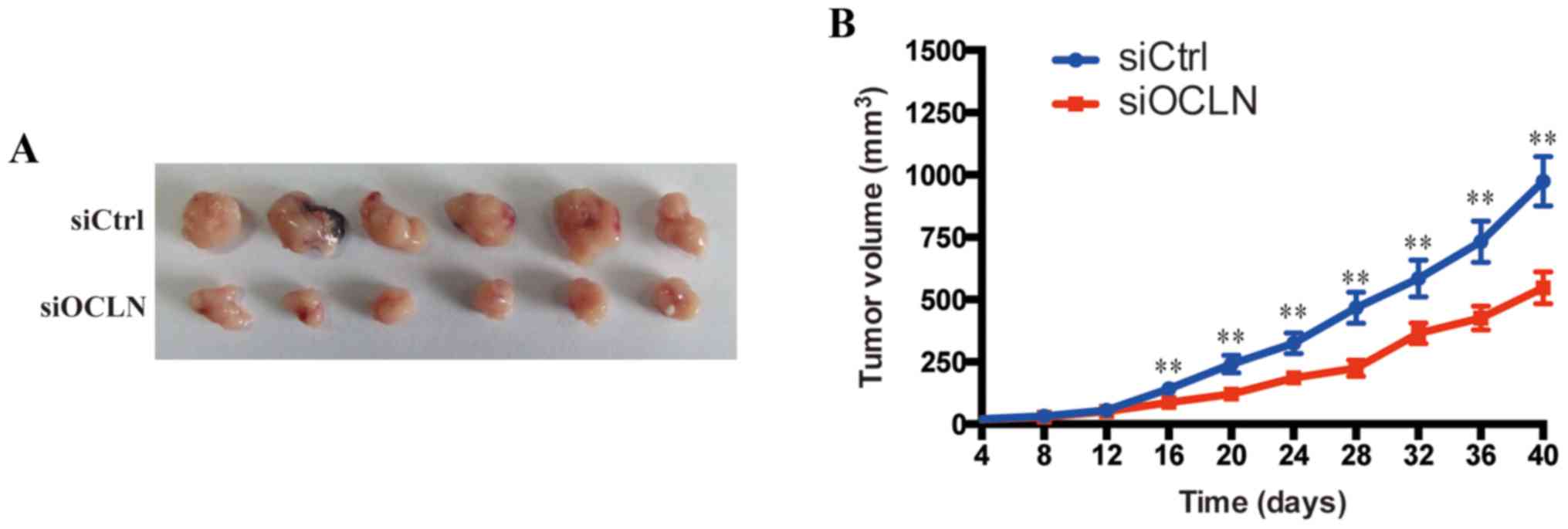
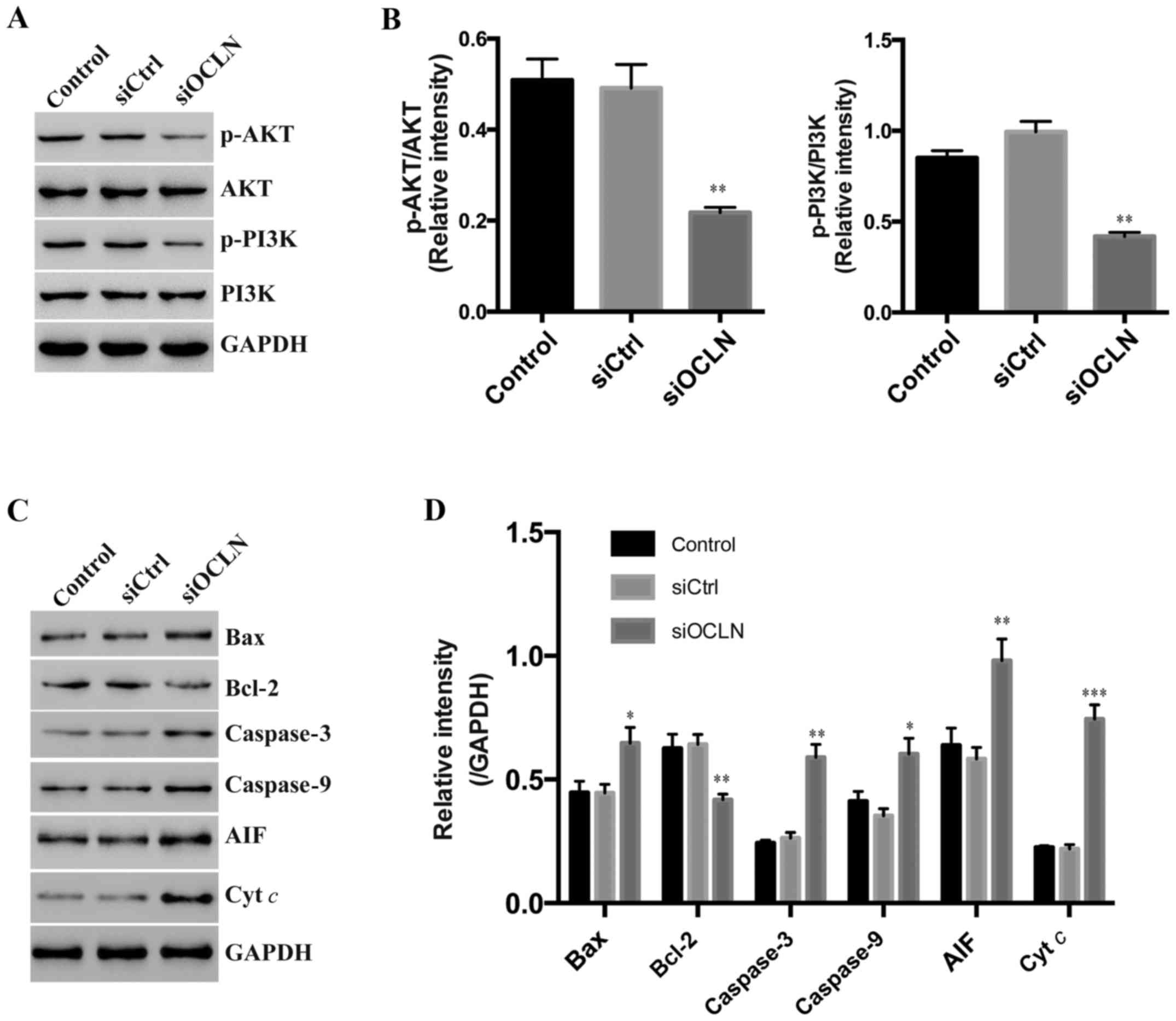
|
1
|
May M: Statistics: Attacking an epidemic.
Nature. 509:S50–S51. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fidler IJ: The pathogenesis of cancer
metastasis: The ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:453–458. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sone S and Yano S: Molecular pathogenesis
and its therapeutic modalities of lung cancer metastasis to bone.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 26:685–689. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tobioka H, Sawada N, Zhong Y and Mori M:
Enhanced paracellular barrier function of rat mesothelial cells
partially protects against cancer cell penetration. Br J Cancer.
74:439–445. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Haynes MD, Martin TA, Jenkins SA, Kynaston
HG, Matthews PN and Jiang WG: Tight junctions and bladder cancer
(Review). Int J Mol Med. 16:3–9. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Furuse M, Hirase T, Itoh M, Nagafuchi A,
Yonemura S and Tsukita S and Tsukita S: Occludin: A novel integral
membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J Cell Biol.
123:1777–1788. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang WG, Bryce RP, Horrobin DF and Mansel
RE: Regulation of tight junction permeability and occludin
expression by polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 244:414–420. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tsukita S, Furuse M and Itoh M:
Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
2:285–293. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wittchen ES, Haskins J and Stevenson BR:
Protein interactions at the tight junction. Actin has multiple
binding partners, and ZO-1 forms independent complexes with ZO-2
and ZO-3. J Biol Chem. 274:35179–35185. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aijaz S, Balda MS and Matter K: Tight
junctions: Molecular architecture and function. Int Rev Cytol.
248:261–298. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Murata M, Kojima T, Yamamoto T, Go M,
Takano K, Osanai M, Chiba H and Sawada N: Down-regulation of
survival signaling through MAPK and Akt in occludin-deficient mouse
hepatocytes in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 310:140–151. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Michl P, Barth C, Buchholz M, Lerch MM,
Rolke M, Holzmann KH, Menke A, Fensterer H, Giehl K, Löhr M, et al:
Claudin-4 expression decreases invasiveness and metastatic
potential of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 63:6265–6271.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Z, Mandell KJ, Parkos CA, Mrsny RJ
and Nusrat A: The second loop of occludin is required for
suppression of Raf1-induced tumor growth. Oncogene. 24:4412–4420.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hoevel T, Macek R, Swisshelm K and Kubbies
M: Reexpression of the TJ protein CLDN1 induces apoptosis in breast
tumor spheroids. Int J Cancer. 108:374–383. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li ZM, Tian T, Lv F, Chang Y, Wang X,
Zhang L, Li X, Li L, Ma W, Wu J and Zhang M: Six1 promotes
proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells via upregulation of cyclin
D1 expression. PLoS One n. 8:e592032013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Schneeberger EE and Lynch RD: Structure,
function, and regulation of cellular tight junctions. Am J Physiol.
262:L647–L661. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gumbiner BM: Breaking through the tight
junction barrier. J Cell Biol. 123:1631–1633. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Burgering BM and Coffer PJ: Protein kinase
B (c-Akt) in phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signal transduction.
Nature. 376:599–602. 1995. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Franke TF, Yang SI, Chan TO, Datta K,
Kazlauskas A, Morrison DK, Kaplan DR and Tsichlis PN: The protein
kinase encoded by the Akt proto-oncogene is a target of the
PDGF-activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Cell. 81:727–736.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fisher DE: Apoptosis in cancer therapy:
Crossing the threshold. Cell. 78:539–542. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Evan GI and Vousden KH: Proliferation,
cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature. 411:342–348. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gozani O, Boyce M, Yoo L, Karuman P and
Yuan J: Life and death in paradise. Nat Cell Biol. 4:E159–E162.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gu JM, Lim SO, Park YM and Jung G: A novel
splice variant of occludin deleted in exon 9 and its role in cell
apoptosis and invasion. FEBS J. 275:3145–3156. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Beeman NE, Baumgartner HK, Webb PG,
Schaack JB and Neville MC: Disruption of occludin function in
polarized epithelial cells activates the extrinsic pathway of
apoptosis leading to cell extrusion without loss of transepithelial
resistance. BMC Cell Biol. 10:852009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang X: The expanding role of mitochondria
in apoptosis. Genes Dev. 15:2922–2933. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Osanai M, Murata M, Nishikiori N, Chiba H,
Kojima T and Sawada N: Epigenetic silencing of occludin promotes
tumorigenic and metastatic properties of cancer cells via
modulations of unique sets of apoptosis-associated genes. Cancer
Res. 66:9125–9133. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bogenrieder T and Herlyn M: Axis of evil:
Molecular mechanisms of cancer metastasis. Oncogene. 22:6524–6536.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|