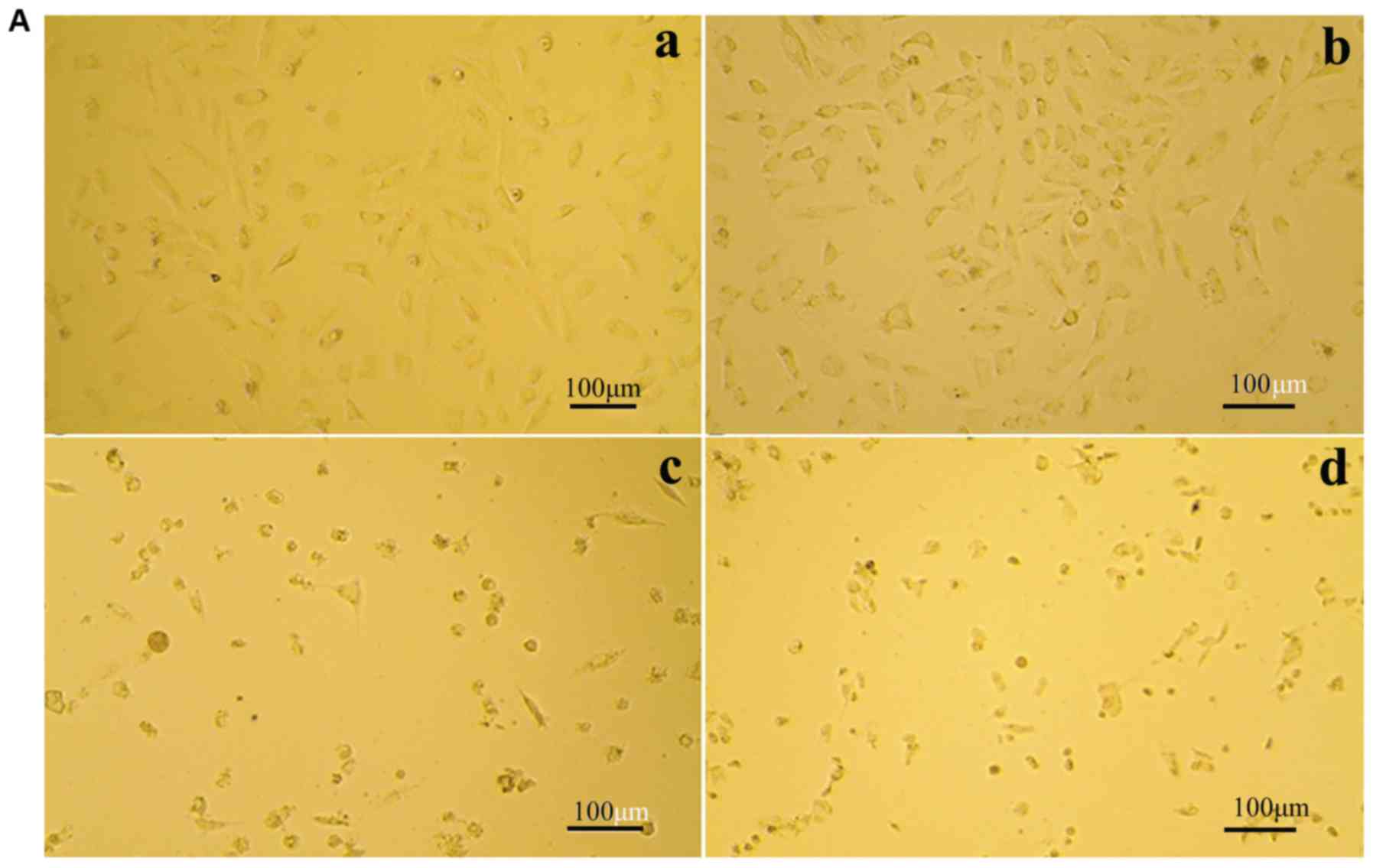
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer.
94:153–156. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Beadsmoore CJ and Screaton NJ:
Classification, staging and prognosis of lung cancer. Eur J Radiol.
45:8–17. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:742005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim SY, Gao JJ, Lee WC, Ryu KS, Lee KR and
Kim YC: Antioxidative flavonoids from the leaves of Morus alba.
Arch Pharm Res. 22:81–85. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Asano N, Yamashita T, Yasuda K, Ikeda K,
Kizu H, Kameda Y, Kato A, Nash RJ, Lee HS and Ryu KS:
Polyhydroxylated alkaloids isolated from mulberry trees (Morus
alba L.) and silkworms (Bombyx mori L). J Agric Food
Chem. 49:4208–4213. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Oh H, Ko EK, Jun JY, Oh MH, Park SU, Kang
KH, Lee HS and Kim YC: Hepatoprotective and free radical scavenging
activities of prenylflavonoids, coumarin, and stilbene from
Morus alba. Planta Med. 68:932–934. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Qiu F, Komatsu K, Kawasaki K, Saito K, Yao
XS and Kano Y: A novel stilbene glucoside, oxyresveratrol
3′-O-β-glucopyranoside, from the root bark of Morus
alba. Planta Med. 62:559–561. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Piao SJ, Qiu F, Chen LX, Pan Y and Dou DQ:
New stilbene, benzofuran, and coumarin glycosides from Morus
alba. Helvetica Chimica Acta. 92:579–587. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Piao SJ, Chen LX, Kang N and Qiu F:
Simultaneous determination of five characteristic stilbene
glycosides in root bark of Morus alba L. (Cortex mori) using
high-performance liquid chromatography. Phytochem Anal. 22:230–235.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nomura T, Fukai T, Yamada S and Katayanagi
M: Studies on the constituents of the cultivated mulberry tree. I.
Three new phenylflavones from the root bark of Morus alba L.
Chem Pharm Bul. 26:1394–1402. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ferlinahayati, Syah YM, Juliawaty LD,
Achmad SA, Hakim EH, Takayama H, Said IM and Latip J: Phenolic
constituents from the wood of Morus australis with cytotoxic
activity. Z Naturforsch C. 63:35–39. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Suhartati T, Yandri AS, Hadi S and Jhons
FS: Morusin, a Bioactive Compound from the Root Bark of Artocarpus
dadah. Eur J Sci Res. 38:643–648. 2009.
|
|
13
|
Mazimba O, Majinda RRT and Motlhanka D:
Antioxidant and antibacterial constituents from Morus nigra. Afc J
Pharm Pharmaco. 5:751–754. 2011.
|
|
14
|
Guptaa G, Duaa K, Kazmi I and Anwar F:
Anticonvulsant activity of Morusin isolated from Morus alba:
Modulation of GABA receptor. Biomed Aging Pathology. 4:29–32. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Luo SD, Nemec J and Ning BM: Anti-HIV
flavonoids from Morus alba. Acta Botanica Yunnanica.
17:89–95. 1995.
|
|
16
|
Cho JK, Ryu YB, Curtis-Long MJ, Kim JY,
Kim D, Lee S, Lee WS and Park KH: Inhibition and structural
reliability of prenylated flavones from the stem bark of Morus lhou
on b-secretase (BACE-1). Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 21:2945–2948. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim JY, Lee WS, Kim YS, Curtis-Long MJ,
Lee BW, Ryu YB and Park KH: Isolation of cholinesterase-inhibiting
flavonoids from Morus lhou. J Agr Food Chem. 59:4589–4596. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yoshizawa S, Suganuma M, Fujiki H, Fukai
T, Nomura T and Sugimura T: Morusin, isolated from root bark of
Morus alba L., inhibits tumour promotion of teleocidin.
Phytotherapy Res. 3:193–195. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fujiki H, Suganuma M, Takagi K, Yoshizawa
S, Furuya HS, Yoshizawa S, Nishiwaki S, Kobayashi M, Okuda T,
Nomura T, et al: Sarcophytols A and B, (−)-epigallocatechin gallate
(EGCG), and morusin, anticarcinogenesis radiation Protection.
2:357–362. 1991.
|
|
20
|
Wang F, Zhang D, Mao J, Ke XX, Zhang R,
Yin C, Gao N and Cui H: Morusin inhibits cell proliferation and
tumor growth by down-regulating c-Myc in human gastric cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:57187–57200. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao JL: Morusin induces human colorectal
cancer cell death via apoptosisNational Cheng Kung University;
2003
|
|
22
|
Lee JC, Won SJ, Chao CL, Wu FL, Liu HS,
Ling P, Lin CN and Su CL: Morusin induces apoptosis and suppresses
NF-κB activity in human colorectal cancer HT-29 cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 372:236–242. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin WL, Lai DY, Lee YJ, Chen NF and Tseng
TH: Antitumor progression potential of morusin suppressing STAT3
and NFκB in human hepatoma SK-Hep1 cells. Toxicol Lett.
232:490–498. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim C, Kim JH, Oh EY, Nam D, Lee SG, Lee
J, Kim SH, Shim BS and Ahn KS: Blockage of STAT3 signaling pathway
by morusin induces apoptosis and inhibits invasion in human
pancreatic tumor cells. Pancreas. 45:409–419. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang L, Guo H, Yang L, Dong L, Lin C,
Zhang J, Lin P and Wan X: Morusin inhibits human cervical cancer
stem cell growth and migration through attenuation of NF-κB
activity and apoptosis induction. Mol Cell Biochem. 379:7–18. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wan LZ, Ma B and Zhang YQ: Preparation of
morusin from Ramulus mori and its effects on mice with transplanted
H22 hepatocarcinoma. Biofactors. 40:636–645. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ding B, Lv Y and Zhang YQ: Anti-tumor
effect of morusin from the branch bark of cultivated mulberry in
Bel-7402 cells via the MAPK pathway. Rsc Adv. 6:17396–17404. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mosmann T: Rapid colorimetric assay for
cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and
cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Medthods. 65:55–63. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Petit PX, Susin SA, Zamzami N, Mignotte B
and Kroemer G: Mitochondria and programmed cell death: Back to the
future. FEBS Lett. 396:7–13. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Prager GW, Lackner EM, Krauth MT, Unseld
M, Poettler M, Laffer S, Cerny-Reiterer S, Lamm W, Kornek GV,
Binder BR, et al: Targeting of VEGF-dependent transendothelial
migration of cancer cells by bevacizumab. Mol Oncol. 4:150–160.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gong C, Xu C, Ji L and Wang Z: A novel
semi-synthetic andrographolide analogue A5 inhibits tumor
angiogenesis via blocking the VEGFR2-p38/ERK1/2 signal pathway.
Biosci Trends. 7:230–236. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen LH, Fang J, Li H, Demark-Wahnefried W
and Lin X: Enterolactone induces apoptosis in human prostate
carcinoma LNCaP cells via a mitochondrial-mediated,
caspase-dependent pathway. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:2581–2590. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen M, Guerrero AD, Huang L, Shabier Z,
Pan M, Tan TH and Wang J: Caspase-9-induced mitochondrial
disruption through cleavage of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members.
J Biol Chem. 282:33888–33895. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sikora J: Tumor angiogenesis in human lung
adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 76:915–916. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim TJ, Lee YS, Kang JH, Kim YS and Kang
CS: Prognostic significance of expression of VEGF and Cox-2 in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its association with expression of
C-erbB2 and EGFR. J Surg Oncol. 103:46–52. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rundhaug JE, Mikulec C, Pavone A and
Fischer SM: A role for cyclooxygenase-2 in ultraviolet
light-induced skin carcinogenesis. Mol Carcinog. 46:692–698. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cao Y and Prescott SM: Many actions of
cyclooxygenase-2 in cellular dynamics and in cancer. J Cell
Physiol. 190:279–286. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bremnes RM, Camps C and Sirera R:
Angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer: The prognostic impact
of neoangiogenesis and the cytokines VEGF and bFGF in tumours and
blood. Lung Cancer. 51:143–158. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ferrara N and Kerbel RS: Angiogenesis as a
therapeutic target. Nature. 438:967–974. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Izuta H, Shimazawa M, Tsuruma K, Araki Y,
Mishima S and Hara H: Bee products prevent VEGF-induced
angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 9:452009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|