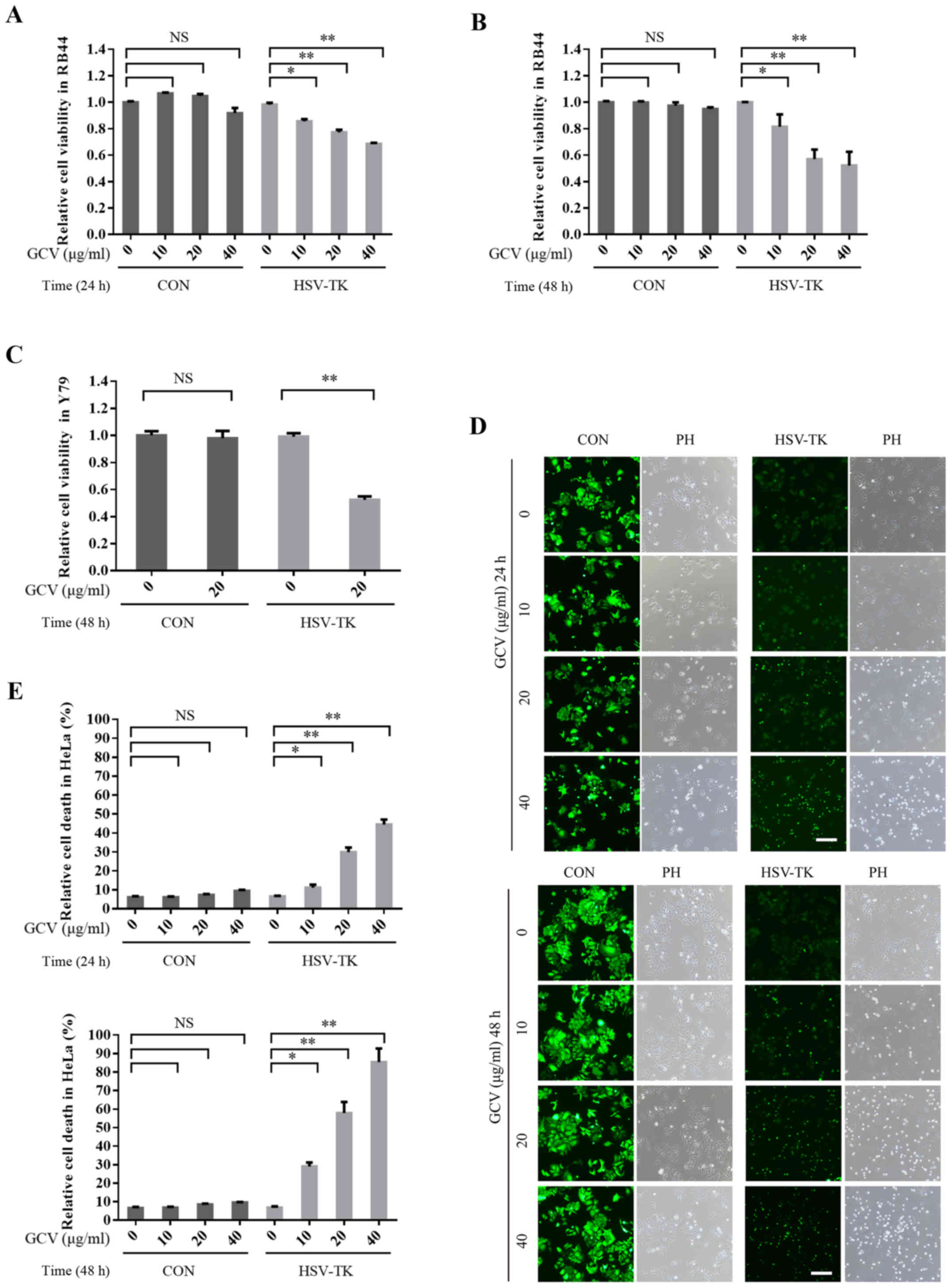
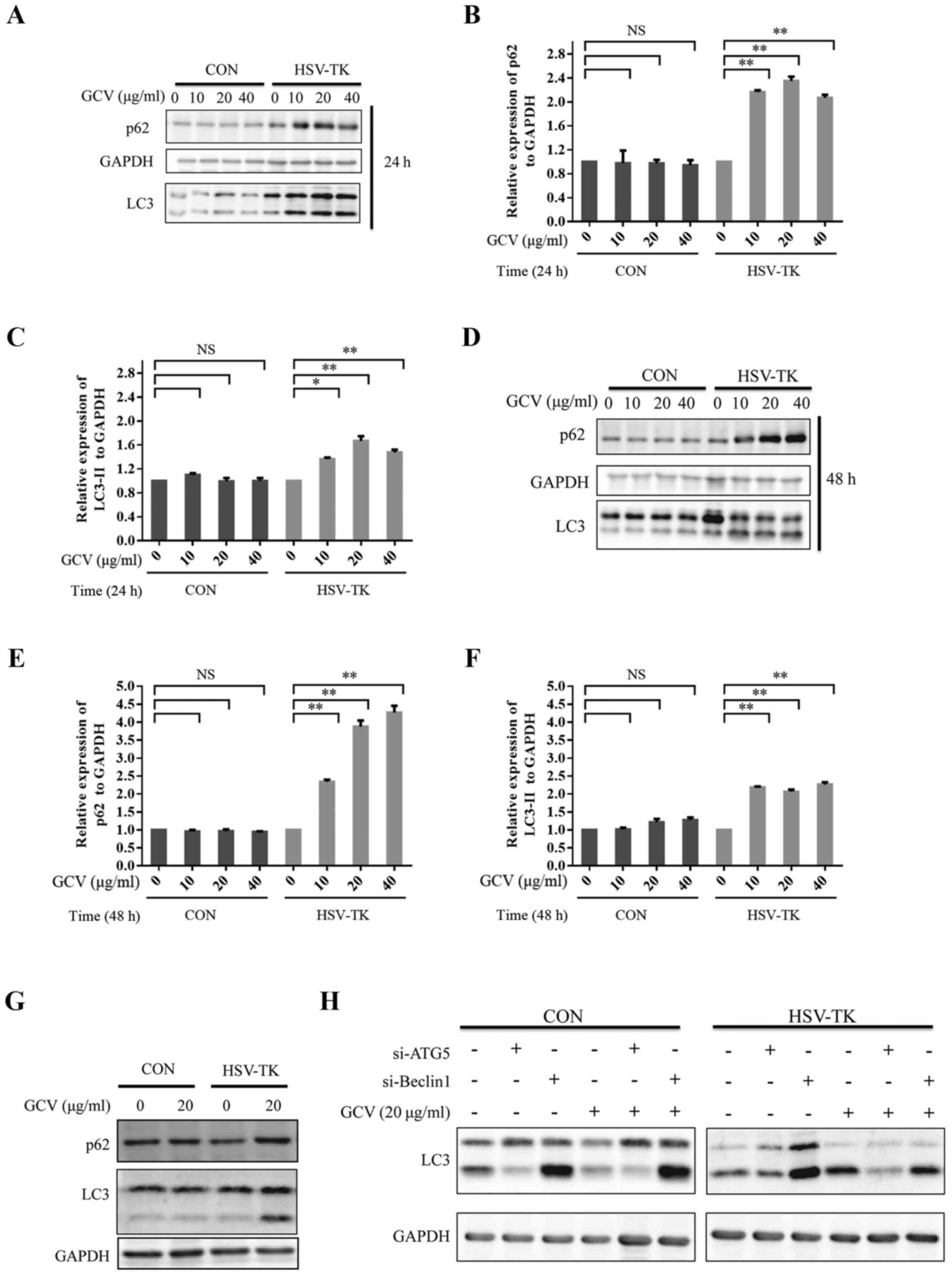
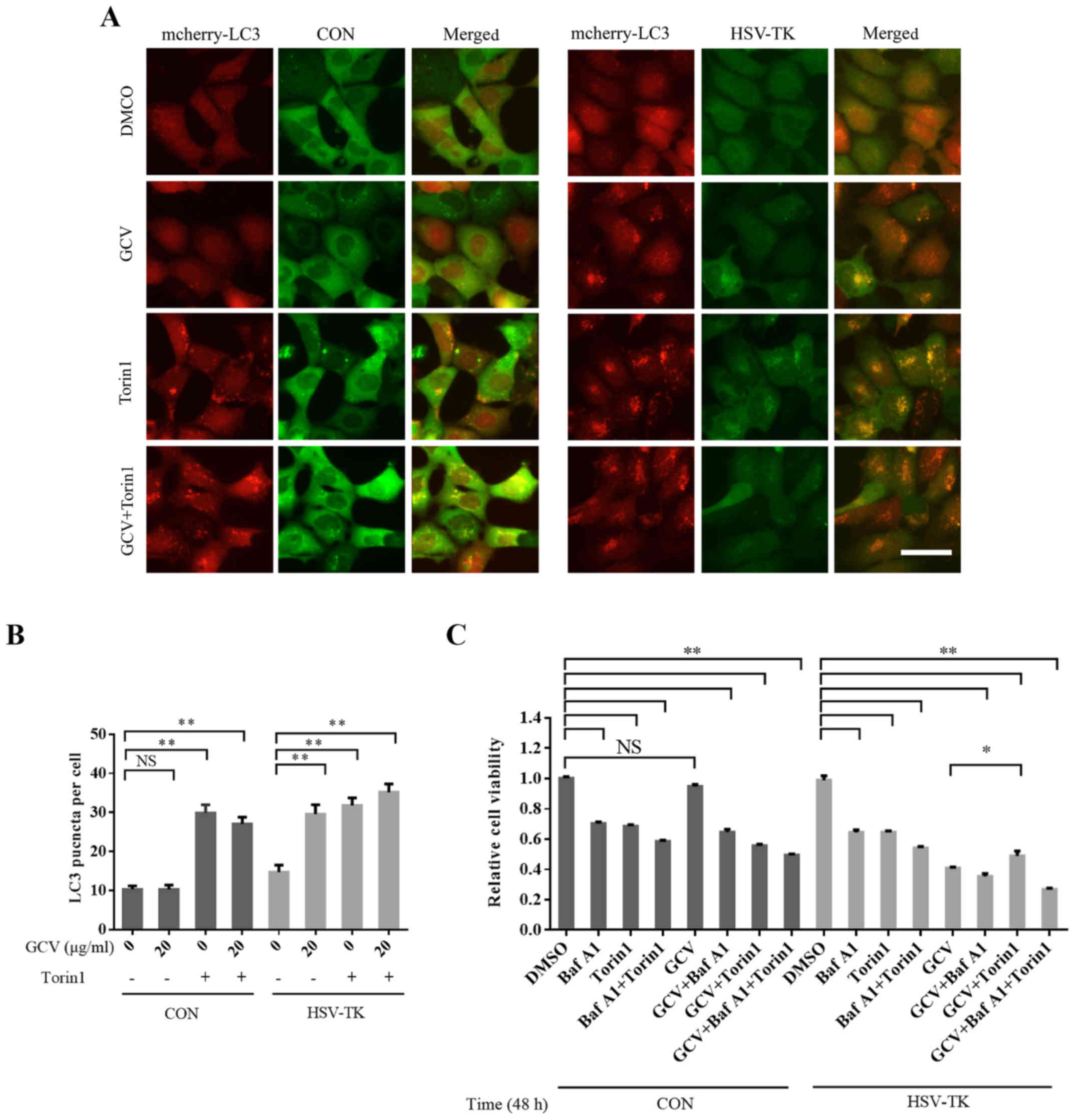
|
1
|
Abramson DH: Retinoblastoma in the 20th
century: Past success and future challenges the Weisenfeld lecture.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 46:2683–2691. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rodriguezgalindo C, Wilson MW, Chantada G,
Fu L, Qaddoumi I, Antoneli C, Leal-Leal C, Sharma T, Barnoya M,
Epelman S, et al: Retinoblastoma: One world, one vision.
Pediatrics. 122:e763–e770. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bornfeld N, Schüler A, Bechrakis N, Henze
G and Havers W: Preliminary results of primary chemotherapy in
retinoblastoma. Klin Padiatr. 209:216–221. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shields CL and Shields JA: Recent
developments in the management of retinoblastoma. J Pediatr
Ophthalmol Strabismus. 36:8–18; quiz 35–36. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shields CL, Mashayekhi A, Cater J, Shelil
A, Meadows AT and Shields JA: Chemoreduction for retinoblastoma:
Analysis of tumor control and risks for recurrence in 457 tumors.
Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 102:35–44. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Abramson DH, Dunkel IJ, Brodie SE, Kim JW
and Gobin YP: A phase I/II study of direct intraarterial
(ophthalmic artery) chemotherapy with melphalan for intraocular
retinoblastoma initial results. Ophthalmology. 115:1398–1404. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shields CL and Shields JA: Retinoblastoma
management: advances in enucleation, intravenous chemoreduction,
and intra-arterial chemotherapy. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 21:203–212.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rodriguez-Galindo C, Chantada GL, Haik BG
and Wilson MW: Treatment of retinoblastoma: Current status and
future perspectives. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 9:294–307. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu HJ, Zhou Y, Ji W, Perng GS, Kruzelock
R, Kong CT, Bast RC, Mills GB, Li J and Hu SX: Reexpression of the
retinoblastoma protein in tumor cells induces senescence and
telomerase inhibition. Oncogene. 15:2589–2596. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hayashi N, Ido E, Ohtsuki Y and Ueno H: An
experimental application of gene therapy for human retinoblastoma.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 40:265–272. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cullinan AE, Lindstrom MJ, Sabet S, Albert
DM and Brandt CR: Evaluation of the antitumor effects of Herpes
simplex virus lacking ribonucleotide reductase in a murine
retinoblastoma model. Current Eye Res. 29:167–172. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Marshall E: Gene therapy a suspect in
leukemia-like disease. Science. 298:34–35. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hossain JA, Ystaas LR, Mrdalj J, Välk K,
Riecken K, Fehse B, Bjerkvig R, Grønli J and Miletic H: Lentiviral
HSV-Tk.007 mediated suicide gene therapy is not toxic for normal
brain cells. J Gene Med. 18:234–243. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Howard BD, Boenicke L, Schniewind B,
Henne-Bruns D and Kalthoff H: Transduction of human pancreatic
tumor cells with vesicular stomatitis virus G-pseudotyped
retroviral vectors containing a herpes simplex virus thymidine
kinase mutant gene enhances bystander effects and sensitivity to
ganciclovir. Cancer Gene Ther. 7:927–938. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kenney S and Pagano JS: Viruses as
oncolytic agents: a new age for ‘therapeutic’ viruses? J Natl
Cancer Inst. 86:1185–1186. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lou E: Oncolytic herpes viruses as a
potential mechanism for cancer therapy. Acta Oncol. 42:660–671.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moolten FL: Tumor chemosensitivity
conferred by inserted herpes thymidine kinase genes: Paradigm for a
prospective cancer control strategy. Cancer Res. 46:5276–5281.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thust R: Ganciclovir-induced apoptosis in
HSV-1 thymidine kinase expressing cells: critical role of DNA
breaks, Bcl-2 decline and caspase-9 activation. Oncogene.
21:2141–2153. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Beltinger C, Fulda S, Kammertoens T, Meyer
E, Uckert W and Debatin KM: Herpes simplex virus thymidine
kinase/ganciclovir-induced apoptosis involves ligand-independent
death receptor aggregation and activation of caspases. P Natl Acad
Sci USA. 96:8699–8704. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wygoda MR, Wilson MR, Davis MA, Trosko JE,
Rehemtulla A and Lawrence TS: Protection of herpes simplex virus
thymidine kinase-transduced cells from ganciclovir-mediated
cytotoxicity by bystander cells: The good samaritan effect. Cancer
Res. 57:1699–1703. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Touraine RL, Ishiimorita H, Ramsey WJ and
Blaese RM: The bystander effect in the HSVtk/ganciclovir system and
its relationship to gap junctional communication. Gene Ther.
5:1705–1711. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Seino J, Wang L, Harada Y, Huang C, Ishii
K, Mizushima N and Suzuki T: Basal autophagy is required for the
efficient catabolism of sialyloligosaccharides. J Biol Chem.
288:26898–27907. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kroemer G, Mariño G and Levine B:
Autophagy and the integrated stress response. Mol Cell. 40:280–293.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nakai A, Yamaguchi O, Takeda T, Higuchi Y,
Hikoso S, Taniike M, Omiya S, Mizote I, Matsumura Y, Asahi M, et
al: The role of autophagy in cardiomyocytes in the basal state and
in response to hemodynamic stress. Nat Med. 13:619–624. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mizushima N and Komatsu M: Autophagy:
Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 147:728–741. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tsukada M and Ohsumi Y: Isolation and
characterization of autophagy-defective mutants of Saccharomyces
cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 333:169–174. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Menzies FM, Fleming A and Rubinsztein DC:
Compromised autophagy and neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 16:345–357. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhong Z, Sanchezlopez E and Karin M:
Autophagy, inflammation and immunity: A troika governing cancer and
its treatment. Cell. 166:288–298. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shirakabe A, Ikeda Y, Sciarretta S,
Zablocki DK and Sadoshima J: Aging and autophagy in the heart. Circ
Res. 118:1563–1576. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim KH and Lee MS: Autophagy[mdash]a key
player in cellular and body metabolism. Nat Rev Endocrinol.
10:322–337. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brech A, Ahlquist T, Lothe RA and Stenmark
H: Autophagy in tumour suppression and promotion. Mol Oncol.
3:366–375. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Paglin S, Hollister T, Delohery T, Hackett
N, McMahill M, Sphicas E, Domingo D and Yahalom J: A novel response
of cancer cells to radiation involves autophagy and formation of
acidic vesicles. Cancer Res. 61:439–444. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Macintosh RL, Timpson P, Thorburn J,
Anderson KI, Thorburn A and Ryan KM: Inhibition of autophagy
impairs tumor cell invasion in an organotypic model. Cell Cycle.
11:2022–2029. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gavilán E, Sánchez-Aguayo I, Daza P and
Ruano D: GSK-3β signaling determines autophagy activation in the
breast tumor cell line MCF7 and inclusion formation in the
non-tumor cell line MCF10A in response to proteasome inhibition.
Cell Death Dis. 4:e5722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun K, Guo XL, Zhao QD, Jing YY, Kou XR,
Xie XQ, Zhou Y, Cai N, Gao L, Zhao X, et al: Paradoxical role of
autophagy in the dysplastic and tumor-forming stages of
hepatocarcinoma development in rats. Cell Death Dis. 4:e5012013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Colecchia D, Rossi M, Sasdelli F, Sanzone
S, Strambi A and Chiariello M: MAPK15 mediates BCR-ABL1-induced
autophagy and regulates oncogene-dependent cell proliferation and
tumor formation. Autophagy. 11:1790–1802. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jiang PD, Zhao YL, Shi W, Deng XQ, Xie G,
Mao YQ, Li ZG, Zheng YZ, Yang SY and Wei YQ: Cell growth
inhibition, G2/M cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis induced by
chloroquine in human breast cancer cell line Bcap-37. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 22:431–440. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sasaki K, Tsuno NH, Sunami E, Tsurita G,
Kawai K, Okaji Y, Nishikawa T, Shuno Y, Hongo K, Hiyoshi M, et al:
Chloroquine potentiates the anti-cancer effect of 5-fluorouracil on
colon cancer cells. Bmc Cancer. 10:3702010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Maycotte P, Aryal S, Cummings CT, Thorburn
J, Morgan MJ and Thorburn A: Chloroquine sensitizes breast cancer
cells to chemotherapy independent of autophagy. Autophagy.
8:200–212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zou Y, Ling YH, Sironi J, Schwartz EL,
Perezsoler R and Piperdi B: The autophagy inhibitor chloroquine
overcomes the innate resistance of wild-type EGFR non-small-cell
lung cancer cells to erlotinib. J Thorac Oncol. 8:693–702. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kao C, Chao A, Tsai CL, Chuang WC, Huang
WP, Chen GC, Lin CY, Wang TH, Wang HS and Lai CH: Bortezomib
enhances cancer cell death by blocking the autophagic flux through
stimulating ERK phosphorylation. Cell Death Dis. 5:e15102014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jahreiss L, Menzies FM and Rubinsztein DC:
The itinerary of autophagosomes: From peripheral formation to
kiss-and-run fusion with lysosomes. Traffic. 9:574–587. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fung C, Lock R, Gao S, Salas E and Debnath
J: Induction of autophagy during extracellular matrix detachment
promotes cell survival. Mol Biol Cell. 19:797–806. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Moscat J and Diazmeco MT: p62 at the
crossroads of autophagy, apoptosis, and cancer. Cell.
137:1001–1004. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zheng YT, Shahnazari S, Brech A, Lamark T,
Johansen T and Brumell JH: The adaptor protein p62/SQSTM1 targets
invading bacteria to the autophagy pathway. J Immunol.
183:5909–5916. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Komatsu M and Ichimura Y: Physiological
significance of selective degradation of p62 by autophagy. FEBS
Lett. 584:1374–1378. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Komatsu M, Kurokawa H, Waguri S, Taguchi
K, Kobayashi A, Ichimura Y, Sou YS, Ueno I, Sakamoto A, Tong KI, et
al: The selective autophagy substrate p62 activates the stress
responsive transcription factor Nrf2 through inactivation of Keap1.
Nat Cell Biol. 12:213–223. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sancak Y, Peterson TR, Shaul YD, Lindquist
RA, Thoreen CC, Bar-Peled L and Sabatini DM: The rag GTPases bind
raptor and mediate amino acid signaling to mTORC1. Science.
320:1496–1501. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang W and Liu HT: MAPK signal pathways
in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell
Res. 12:9–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ling MT, Wang X, Ouyang XS, Lee TK, Fan
TY, Xu K, Tsao SW and Wong YC: Activation of MAPK signaling pathway
is essential for Id-1 induced serum independent prostate cancer
cell growth. Oncogene. 21:8498–8505. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cui G, Qin X, Zhang Y, Gong Z, Ge B and
Zang YQ: Berberine differentially modulates the activities of ERK,
p38 MAPK, and JNK to suppress Th17 and Th1 T cell differentiation
in type 1 diabetic mice. J Biol Chem. 284:28420–28429. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hu Q, Li B, Xu R, Chen D, Mu C, Fei E and
Wang G: The protease Omi cleaves the mitogen-activated protein
kinase kinase MEK1 to inhibit microglial activation. Sci Signal.
5:ra612012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Corcelle E, Djerbi N, Mari M, Nebout M,
Fiorini C, Fénichel P, Hofman P, Poujeol P and Mograbi B: Control
of the autophagy maturation step by the MAPK ERK and p38: Lessons
from environmental carcinogens. Autophagy. 3:57–59. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Cagnol S and Chambard JC: ERK and cell
death: Mechanisms of ERK-induced cell death - apoptosis, autophagy
and senescence. FEBS J. 277:2–21. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Feng Y, He D, Yao Z and Klionsky DJ: The
machinery of macroautophagy. Cell Res. 24:242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B and Guan KL:
AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of
Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 13:132–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wei SJ, Chao Y, Hung YM, Lin WC, Yang DM,
Shih YL, Ch'ang LY, Whang-Peng J and Yang WK: S- and G2-phase cell
cycle arrests and apoptosis induced by ganciclovir in murine
melanoma cells transduced with herpes simplex virus thymidine
kinase. Exp Cell Res. 241:66–75. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wei SJ, Chao Y, Shih YL, Yang DM, Hung YM
and Yang WK: Involvement of Fas (CD95/APO-1) and Fas ligand in
apoptosis induced by ganciclovir treatment of tumor cells
transduced with herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase. Gene Ther.
6:420–431. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A and
Kroemer G: Self-eating and self-killing: crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:741–752. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Gerolami R, Cardoso J, Lewin M, Bralet MP,
Sa Cunha A, Clément O, Bréchot C and Tran PL: Evaluation of HSV-tk
gene therapy in a rat model of chemically induced hepatocellular
carcinoma by intratumoral and intrahepatic artery routes. Cancer
Res. 60:993–1001. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Rainov NG: A phase III clinical evaluation
of herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase and ganciclovir
gene therapy as an adjuvant to surgical resection and radiation in
adults with previously untreated glioblastoma multiforme. Hum Gene
Ther. 11:2389–2401. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Song JS and Kim HP: Adenovirus-mediated
HSV-TK gene therapy using the human telomerase promoter induced
apoptosis of small cell lung cancer cell line. Oncol Rep.
12:443–447. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Pan JG, Zhou X, Luo R and Han RF: The
adeno-associated virus-mediated HSV-TK/GCV suicide system: A
potential strategy for the treatment of bladder carcinoma. Med
Oncol. 29:1938–1947. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Leinonen HM, Ruotsalainen AK, Määttä AM,
Laitinen HM, Kuosmanen SM, Kansanen E, Pikkarainen JT, Lappalainen
JP, Samaranayake H, Lesch HP, et al: Oxidative stress-regulated
lentiviral TK/GCV gene therapy for lung cancer treatment. Cancer
Res. 72:6227–6235. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Colombo F, Barzon L, Franchin E, Pacenti
M, Pinna V, Danieli D, Zanusso M and Palù G: Combined HSV-TK/IL-2
gene therapy in patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme:
Biological and clinical results. Cancer Gene Ther. 12:835–848.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|