|
1
|
Manchanda R and Menon U: Setting the
threshold for surgical prevention in women at increased risk of
ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 28:34–42. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Oza AM, Cook AD, Pfisterer J, Embleton A,
Ledermann JA, Pujade-Lauraine E, Kristensen G, Carey MS, Beale P,
Cervantes A, et al: Standard chemotherapy with or without
bevacizumab for women with newly diagnosed ovarian cancer (ICON7):
Overall survival results of a phase 3 randomised trial. Lancet
Oncol. 16:928–936. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Prat J: Ovarian carcinomas: Five distinct
diseases with different origins, genetic alterations, and
clinicopathological features. Virchows Arch. 460:237–249. 2012.
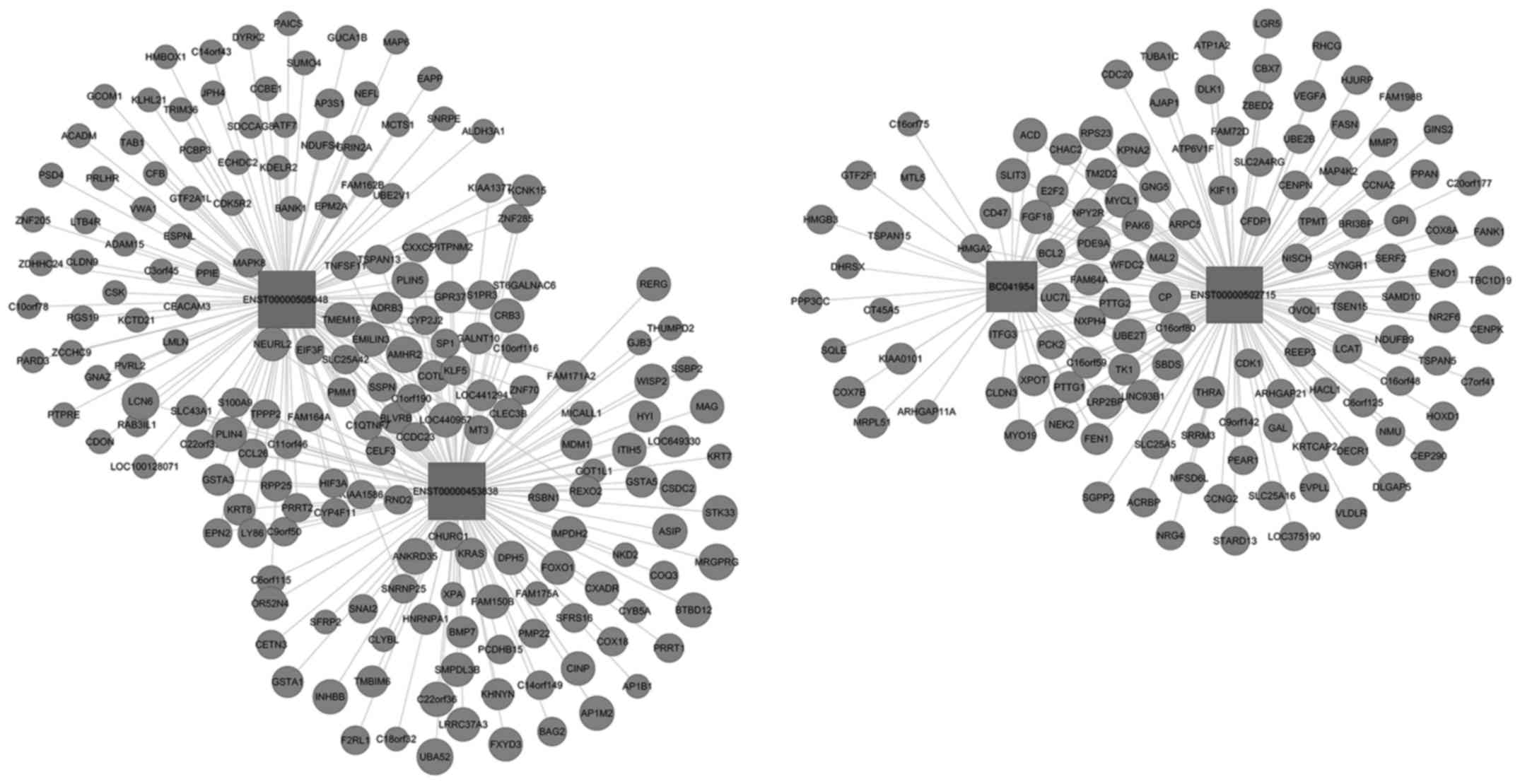
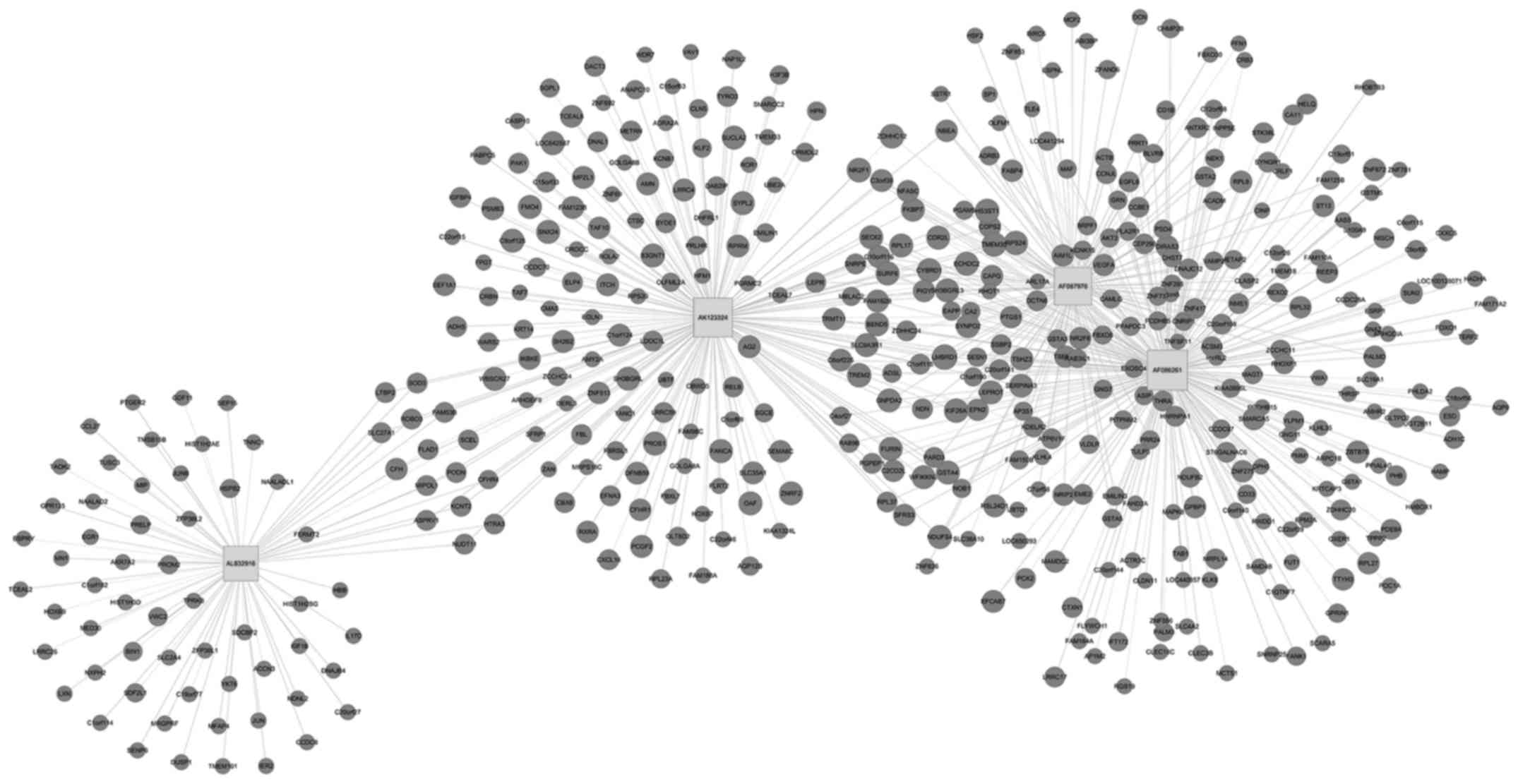
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schuijer M and Berns EM: TP53 and ovarian
cancer. Hum Mutat. 21:285–291. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Balch C, Fang F, Matei DE, Huang TH and
Nephew KP: Minireview: Epigenetic changes in ovarian cancer.
Endocrinology. 150:4003–4011. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Eddy SR: Non-coding RNA genes and the
modern RNA world. Nat Rev Genet. 2:919–929. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wilusz JE, Sunwoo H and Spector DL: Long
noncoding RNAs: Functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev.
23:1494–1504. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guttman M, Amit I, Garber M, French C, Lin
MF, Feldser D, Huarte M, Zuk O, Carey BW, Cassady JP, et al:
Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large
non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature. 458:223–227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mattick JS: The genetic signatures of
noncoding RNAs. PLoS Genet. 5:e10004592009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Geretto M, Pulliero A, Rosano C, Zhabayeva
D, Bersimbaev R and Izzotti A: Resistance to cancer
chemotherapeutic drugs is determined by pivotal microRNA
regulators. Am J Cancer Res. 7:1350–1371. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lu YM, Shang C, Ou YL, Yin D, Li YN, Li X,
Wang N and Zhang SL: miR-200c modulates ovarian cancer cell
metastasis potential by targeting zinc finger E-box-binding
homeobox 2 (ZEB2) expression. Med Oncol. 31:1342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guttman M and Rinn JL: Modular regulatory
principles of large non-coding RNAs. Nature. 482:339–346. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wapinski O and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs and human disease. Trends Cell Biol. 21:354–361. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gutschner T and Diederichs S: The
hallmarks of cancer: A long non-coding RNA point of view. RNA Biol.
9:703–719. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gibb EA, Vucic EA, Enfield KS, Stewart GL,
Lonergan KM, Kennett JY, Becker-Santos DD, MacAulay CE, Lam S,
Brown CJ and Lam WL: Human cancer long non-coding RNA
transcriptomes. PLoS One. 6:e259152011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang Z, Zhou L, Wu LM, Lai MC, Xie HY,
Zhang F and Zheng SS: Overexpression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR
predicts tumor recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma patients
following liver transplantation. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:1243–1250.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qiu JJ, Lin YY, Ye LC, Ding JX, Feng WW,
Jin HY, Zhang Y, Li Q and Hua KQ: Overexpression of long non-coding
RNA HOTAIR predicts poor patient prognosis and promotes tumor
metastasis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
134:121–128. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kogo R, Shimamura T, Mimori K, Kawahara K,
Imoto S, Sudo T, Tanaka F, Shibata K, Suzuki A, Komune S, et al:
Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR regulates polycomb-dependent chromatin
modification and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal
cancers. Cancer Res. 71:6320–6326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Szafron LM, Balcerak A, Grzybowska EA,
Pienkowska-Grela B, Podgorska A, Zub R, Olbryt M, Pamula-Pilat J,
Lisowska KM, Grzybowska E, et al: The putative oncogene, CRNDE, is
a negative prognostic factor in ovarian cancer patients.
Oncotarget. 6:43897–43910. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Barber HR, Sommers SC, Synder R and Kwon
TH: Histologic and nuclear grading and stromal reactions as indices
for prognosis in ovarian cancer. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 121:795–807.
1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
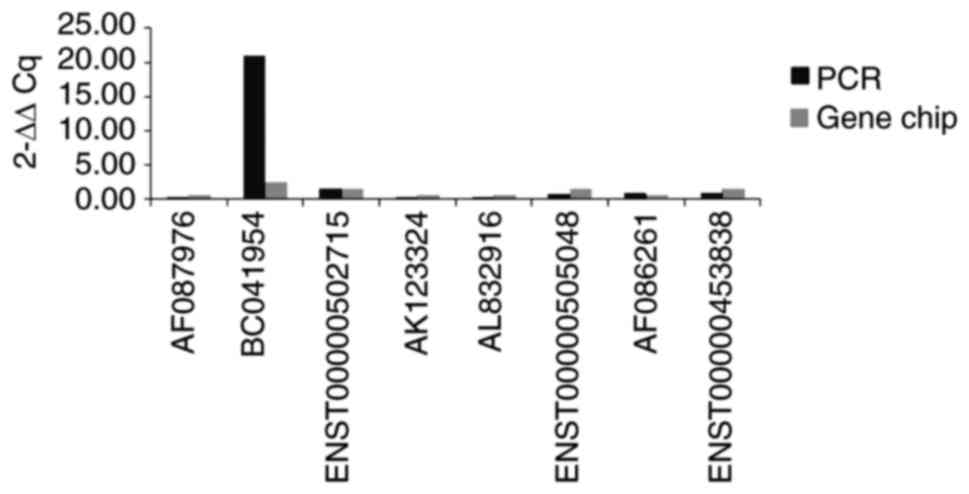
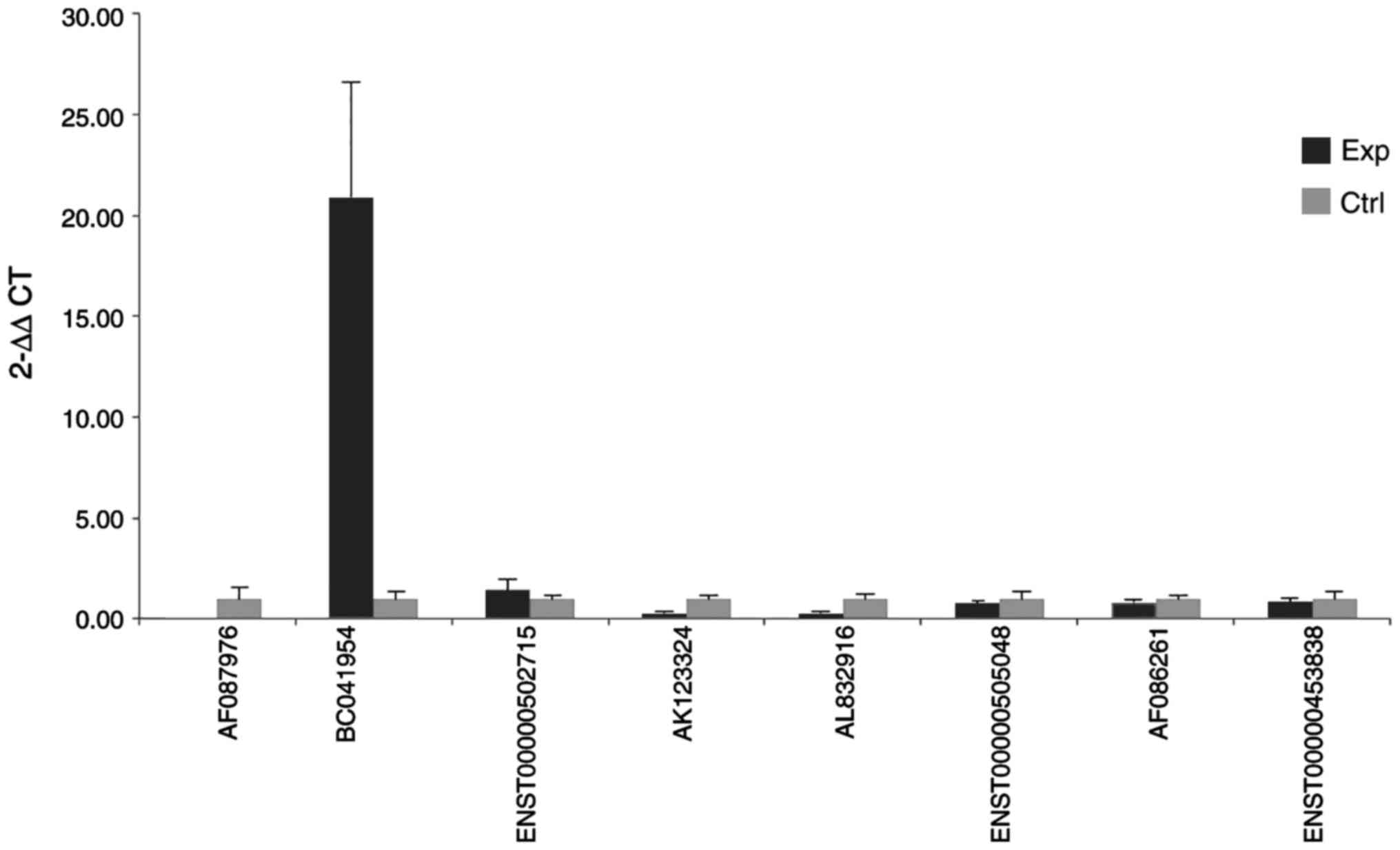
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rinn JL, Kertesz M, Wang JK, Squazzo SL,
Xu X, Brugmann SA, Goodnough LH, Helms JA, Farnham PJ, Segal E and
Chang HY: Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin
domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell. 129:1311–1323.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qin LX, Beyer RP, Hudson FN, Linford NJ,
Morris DE and Kerr KF: Evaluation of methods for oligonucleotide
array data via quantitative real-time PCR. BMC Bioinformatics.
7:232006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bhan A, Soleimani M and Mandal SS: Long
noncoding RNA and cancer: A new paradigm. Cancer Res. 77:3965–3981.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen S, Wu DD, Sang XB, Wang LL, Zong ZH,
Sun KX, Liu BL and Zhao Y: The lncRNA HULC functions as an oncogene
by targeting ATG7 and ITGB1 in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Cell
Death Dis. 8:e31182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fu X, Zhang L, Dan L, Wang K and Xu Y:
LncRNA EWSAT1 promotes ovarian cancer progression through targeting
miR-330-5p expression. Am J Transl Res. 9:4094–4103.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu J, Han Q and Cui Y: Decreased long
non-coding RNA SPRY4-IT1 contributes to ovarian cancer cell
metastasis partly via affecting epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Tumour Biol. 39:10104283177091292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhu FF, Zheng FY, Wang HO, Zheng JJ and
Zhang Q: Downregulation of lncRNA TUBA4B is associated with poor
prognosis for epithelial ovarian cancer. Pathol Oncol Res.
24:419–425. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guo L, Peng Y, Meng Y, Liu Y, Yang S, Jin
H and Li Q: Expression profiles analysis reveals an integrated
miRNA-lncRNA signature to predict survival in ovarian cancer
patients with wild-type BRCA1/2. Oncotarget. 8:68483–68492.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang L, Hu Y, Xiang X, Qu K and Teng Y:
Identification of long non-coding RNA signature for
paclitaxel-resistant patients with advanced ovarian cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:64191–64202. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cao Y, Shi H, Ren F, Jia Y and Zhang R:
Long non-coding RNA CCAT1 promotes metastasis and poor prognosis in
epithelial ovarian cancer. Exp Cell Res. 359:185–194. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shen L, Liu W, Cui J, Li J and Li C:
Analysis of long non-coding RNA expression profiles in ovarian
cancer. Oncol Lett. 14:1526–1530. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ding Y, Yang DZ, Zhai YN, Xue K, Xu F, Gu
XY and Wang SM: Microarray expression profiling of long non-coding
RNAs in epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncol Lett. 14:2523–2530. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kaur P, Tan JR, Karolina DS, Sepramaniam
S, Armugam A, Wong PT and Jeyaseelan K: A long non-coding RNA,
BC048612 and a microRNA, miR-203 coordinate the gene expression of
neuronal growth regulator 1 (NEGR1) adhesion protein. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1863:533–543. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ji J, Tang J, Deng L, Xie Y, Jiang R, Li G
and Sun B: LINC00152 promotes proliferation in hepatocellular
carcinoma by targeting EpCAM via the mTOR signaling pathway.
Oncotarget. 6:42813–42824. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen H, Du G, Song X and Li L: Non-coding
transcripts from enhancers: New insights into enhancer activity and
gene expression regulation. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics.
15:201–207. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|