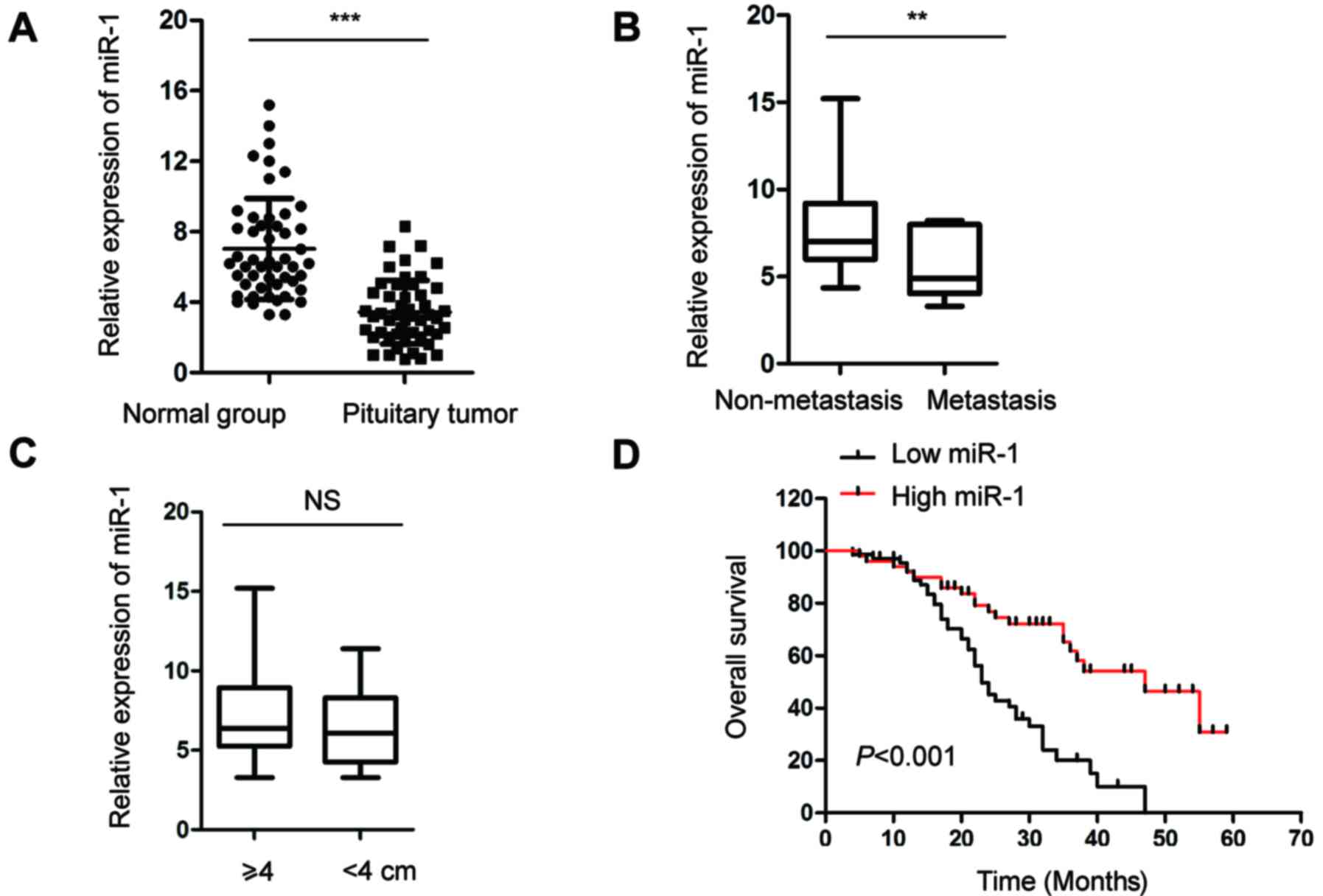
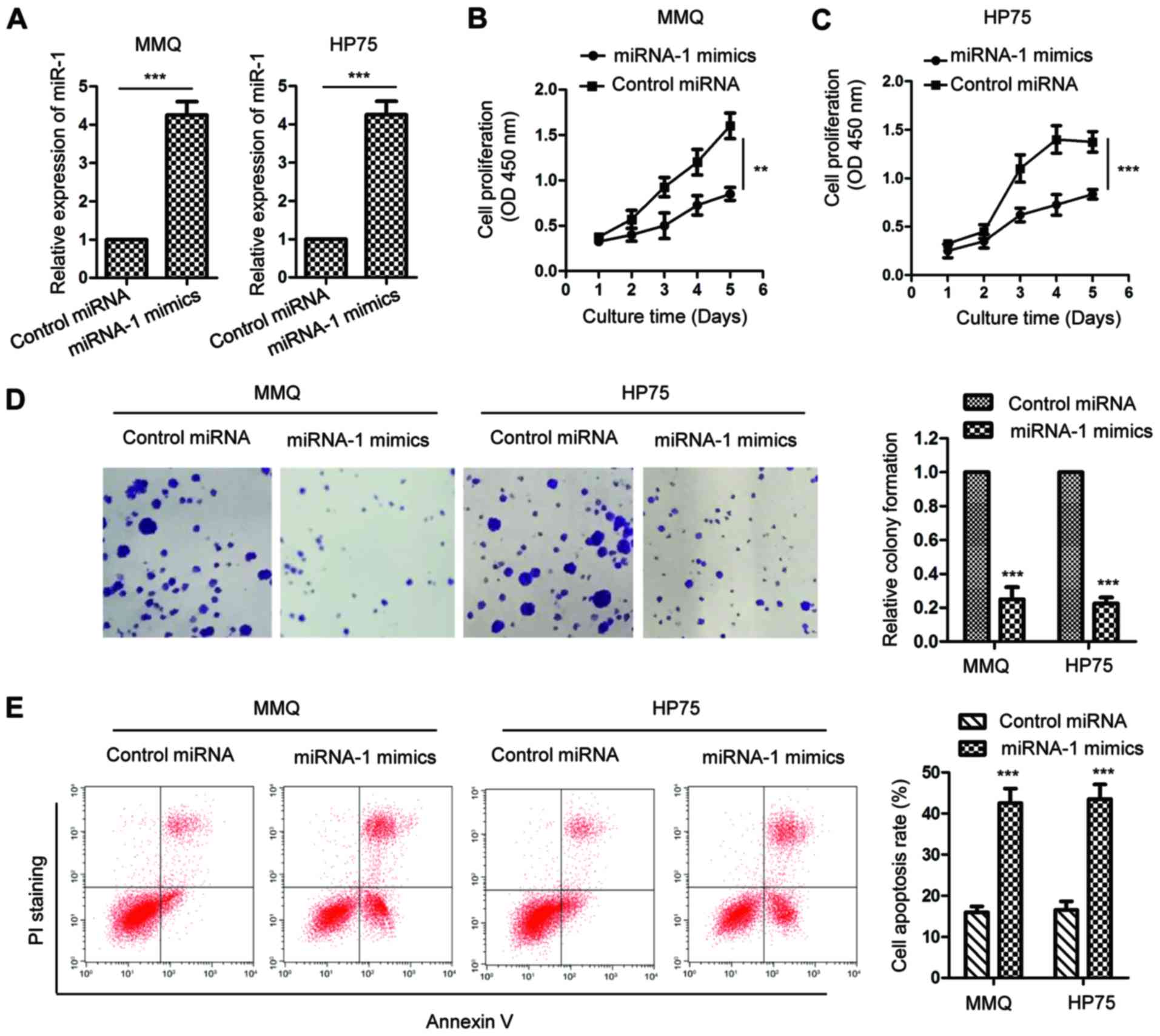
|
1
|
Laws ER: Pituitary tumor apoplexy: A
review. J Intensive Care Med. 23:146–147. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nasi D, Perano D, Ghadirpour R, Iaccarino
C, Servadei F and Romano A: Primary pituitary neuroendocrine tumor:
Case report and literature review. Surg Neurol Int. 8:1012017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ezzat S and Asa SL: Mechanisms of disease:
The pathogenesis of pituitary tumors. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol
Metab. 2:220–230. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jiang X and Zhang X: The molecular
pathogenesis of pituitary adenomas: An update. Endocrinol Metab.
28:245–254. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N and Filipowicz W:
Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Ann Rev
Biochem. 79:351–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mohr AM and Mott JL: Overview of microRNA
biology. Semin Liver Dis. 35:3–11. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stilling G, Sun Z, Zhang S, Jin L, Righi
A, Kovācs G, Korbonits M, Scheithauer BW, Kovacs K and Lloyd RV:
MicroRNA expression in ACTH-producing pituitary tumors:
Up-regulation of microRNA-122 and −493 in pituitary carcinomas.
Endocrine. 38:67–75. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kwak PB, Iwasaki S and Tomari Y: The
microRNA pathway and cancer. Cancer Sci. 101:2309–2315. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Farazi TA, Spitzer JI, Morozov P and
Tuschl T: miRNAs in human cancer. J Pathol. 223:102–115. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qu H, Xu W, Huang Y and Yang S:
Circulating miRNAs: Promising biomarkers of human cancer. Asian Pac
J Cancer Prev. 12:1117–1125. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sapochnik M, Nieto LE, Fuertes M and Arzt
E: Molecular mechanisms underlying pituitary pathogenesis. Biochem
Genet. 54:107–119. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang DS, Zhang HQ, Zhang B, Yuan ZB, Yu
ZK, Yang T, Zhang SQ, Liu Y and Jia XX: miR-133 inhibits pituitary
tumor cell migration and invasion via down-regulating FOXC1
expression. Genet Mol Res. 15:2016.
|
|
15
|
Yu C, Li J, Sun F, Cui J, Fang H and Sui
G: Expression and clinical significance of miR-26a and pleomorphic
adenoma gene 1 (PLAG1) in invasive pituitary adenoma. Med Sci
Monit. 22:5101–5108. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou K, Zhang T, Fan Y, Serick, Du G, Wu P
and Geng D: MicroRNA-106b promotes pituitary tumor cell
proliferation and invasion through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by
targeting PTEN. Tumour Biol. 37:13469–13477. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng Z, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Yang Y and Song
T: Effect of miR-106b on invasiveness of pituitary adenoma via
PTEN-PI3K/AKT. Med Sci Monit. 23:1277–1285. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wilfred BR, Wang WX and Nelson PT:
Energizing miRNA research: A review of the role of miRNAs in lipid
metabolism, with a prediction that miR-103/107 regulates human
metabolic pathways. Mol Genet Metab. 91:209–217. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Alamoudi AA, Alnoury A and Gad H: miRNA in
tumour metabolism and why could it be the preferred pathway for
energy reprograming. Brief Funct Genomics. 17:157–169. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Antoniali G, Serra F, Lirussi L, Tanaka M,
D'Ambrosio C, Zhang S, Radovic S, Dalla E, Ciani Y, Scaloni A, et
al: Mammalian APE1 controls miRNA processing and its interactome is
linked to cancer RNA metabolism. Nat Commun. 8:7972017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jordan SD, Krüger M, Willmes DM, Redemann
N, Wunderlich FT, Brönneke HS, Merkwirth C, Kashkar H, Olkkonen VM,
Böttger T, et al: Obesity-induced overexpression of miRNA-143
inhibits insulin-stimulated AKT activation and impairs glucose
metabolism. Nat Cell Biol. 13:434–446. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lynn FC: Meta-regulation: microRNA
regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 20:452–459. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ono K: MicroRNA links obesity and impaired
glucose metabolism. Cell Res. 21:864–866. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wamelink MM, Struys EA and Jakobs C: The
biochemistry, metabolism and inherited defects of the pentose
phosphate pathway: A review. J Inherit Metab Dis. 31:703–717. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang P, Du W and Wu M: Regulation of the
pentose phosphate pathway in cancer. Protein Cell. 5:592–602. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Patra KC and Hay N: The pentose phosphate
pathway and cancer. Trends Biochem Sci. 39:347–354. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cho ES, Cha YH, Kim HS, Kim NH and Yook
JI: The pentose phosphate pathway as a potential target for cancer
therapy. Biomol Ther. 26:29–38. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zheng J: Energy metabolism of cancer:
Glycolysis versus oxidative phosphorylation (Review). Oncol Lett.
4:1151–1157. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Akram M: Mini-review on glycolysis and
cancer. J Cancer Educ. 28:454–457. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li XB, Gu JD and Zhou QH: Review of
aerobic glycolysis and its key enzymes-new targets for lung cancer
therapy. Thorac Cancer. 6:17–24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang C, Zhang Z, Zhu Y and Qin S:
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: A biomarker and potential
therapeutic target for cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
14:280–289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Naik SN and Anderson DE: The association
between glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency and cancer in
American Negroes. Oncology. 25:356–364. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Messeri G, Tozzi P, Boddi V and Ciatto S:
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity and estrogen receptors
in human breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem. 19:1647–1650. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pisano M, Cocco P, Cherchi R, Onnis R and
Cherchi P: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency and lung
cancer: A hospital based case-control study. Tumori. 77:12–15.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tho LL, Lee WH and Candlish JK:
Erythrocytic enzymes decomposing reactive oxygen species and
glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Singapore Med J.
29:60–62. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cai T, Kuang Y, Zhang C, Zhang Z, Chen L,
Li B, Li Y, Wang Y, Yang H, Han Q and Zhu Y: Glucose-6-phosphate
dehydrogenase and NADPH oxidase 4 control STAT3 activity in
melanoma cells through a pathway involving reactive oxygen species,
c-SRC and SHP2. Am J Cancer Res. 5:1610–1620. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nadeem A, Al-Harbi NO, Ahmad SF, Ibrahim
KE, Siddiqui N and Al-Harbi MM: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
inhibition attenuates acute lung injury through reduction in NADPH
oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species. Clin Exp Immunol.
191:279–287. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Coda DM, Lingua MF, Morena D, Foglizzo V,
Bersani F, Ala U, Ponzetto C and Taulli R: SMYD1 and G6PD
modulation are critical events for miR-206-mediated differentiation
of rhabdomyosarcoma. Cell Cycle. 14:1389–1402. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hu T, Chang YF, Xiao Z, Mao R, Tong J,
Chen B, Liu GC, Hong Y, Chen HL, Kong SY, et al: miR-1 inhibits
progression of high-risk papillomavirus-associated human cervical
cancer by targeting G6PD. Oncotarget. 7:86103–86116. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang L, Yuan Y, Li J, Ren H, Cai Q, Chen
X, Liang H, Shan H, Fu ZD, Gao X, et al: MicroRNA-1 aggravates
cardiac oxidative stress by post-transcriptional modification of
the antioxidant network. Cell Stress Chaperones. 20:411–420. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gelman SJ, Naser F, Mahieu NG, McKenzie
LD, Dunn GP, Chheda MG and Patti GJ: Consumption of NADPH for 2-HG
synthesis increases pentose phosphate pathway flux and sensitizes
cells to oxidative stress. Cell Rep. 22:512–522. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Han C, Zhou Y, An Q, Li F, Li D, Zhang X,
Yu Z, Zheng L, Duan Z and Kan Q: MicroRNA-1 (miR-1) inhibits
gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting MET.
Tumour Biol. 36:6715–6723. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu R, Li J, Lai Y, Liao Y, Liu R and Qiu
W: Hsa-miR-1 suppresses breast cancer development by
down-regulating K-ras and long non-coding RNA MALAT1. Int J Biol
Macromol. 81:491–497. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xu W, Zhang Z, Zou K, Cheng Y, Yang M,
Chen H, Wang H, Zhao J, Chen P, He L, et al: MiR-1 suppresses tumor
cell proliferation in colorectal cancer by inhibition of
Smad3-mediated tumor glycolysis. Cell Death Dis. 8:e27612017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Peng CY, Liao YW, Lu MY, Yu CH, Yu CC and
Chou MY: Downregulation of miR-1 enhances tumorigenicity and
invasiveness in oral squamous cell carcinomas. J Formos Med Assoc.
116:782–789. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Qu W, Chen X, Wang J, Lv J and Yan D:
MicroRNA-1 inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and migration
through c-Met pathway. Clin Chim Acta. 473:237–244. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xie M, Dart DA, Guo T, Xing XF, Cheng XJ,
Du H, Jiang WG, Wen XZ and Ji JF: MicroRNA-1 acts as a tumor
suppressor microRNA by inhibiting angiogenesis-related growth
factors in human gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 21:41–54. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yu Q, Liu Y, Wen C, Zhao Y, Jin S, Hu Y,
Wang F, Chen L, Zhang B, Wang W, et al: MicroRNA-1 inhibits
tumorigenicity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and enhances
sensitivity to gefitinib. Oncol Lett. 15:963–971. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang X, Li X, Zhang X, Fan R, Gu H, Shi Y
and Liu H: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase expression is
correlated with poor clinical prognosis in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 41:1293–1299. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pu H, Zhang Q, Zhao C, Shi L, Wang Y, Wang
J and Zhang M: Overexpression of G6PD is associated with high risks
of recurrent metastasis and poor progression-free survival in
primary breast carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 13:3232015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lu M, Lu L, Dong Q, Yu G, Chen J, Qin L,
Wang L, Zhu W and Jia H: Elevated G6PD expression contributes to
migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Acta Biochim Biophys
Sin. 50:370–380. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang X, Wu G, Cao G, Yang L, Xu H, Huang J
and Hou J: Zoledronic acid inhibits the pentose phosphate pathway
through attenuating the Ras-TAp73-G6PD axis in bladder cancer
cells. Mol Med Rep. 12:4620–4625. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jiang P, Du W and Yang X: A critical role
of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in TAp73-mediated cell
proliferation. Cell Cycle. 12:3720–3726. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|