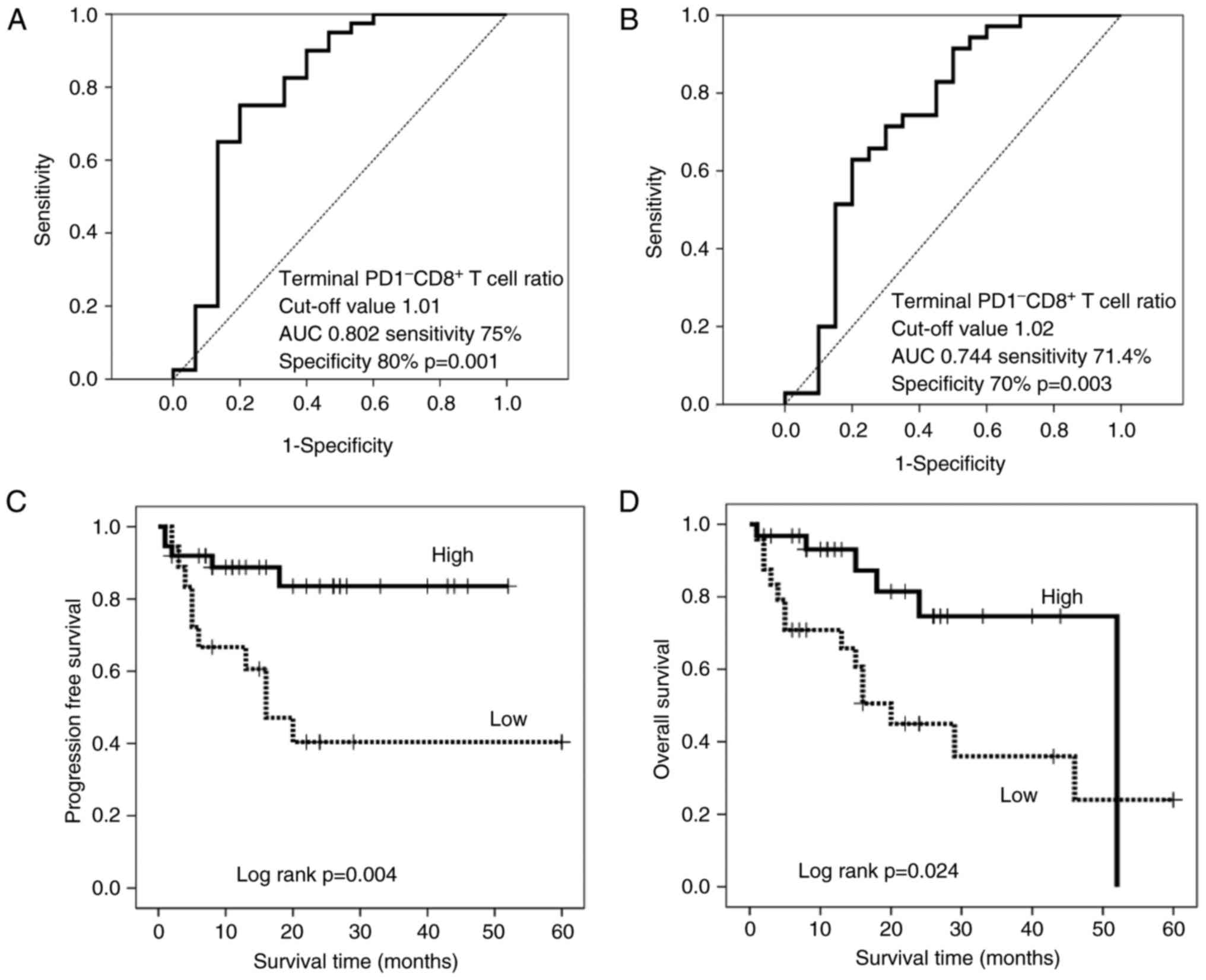
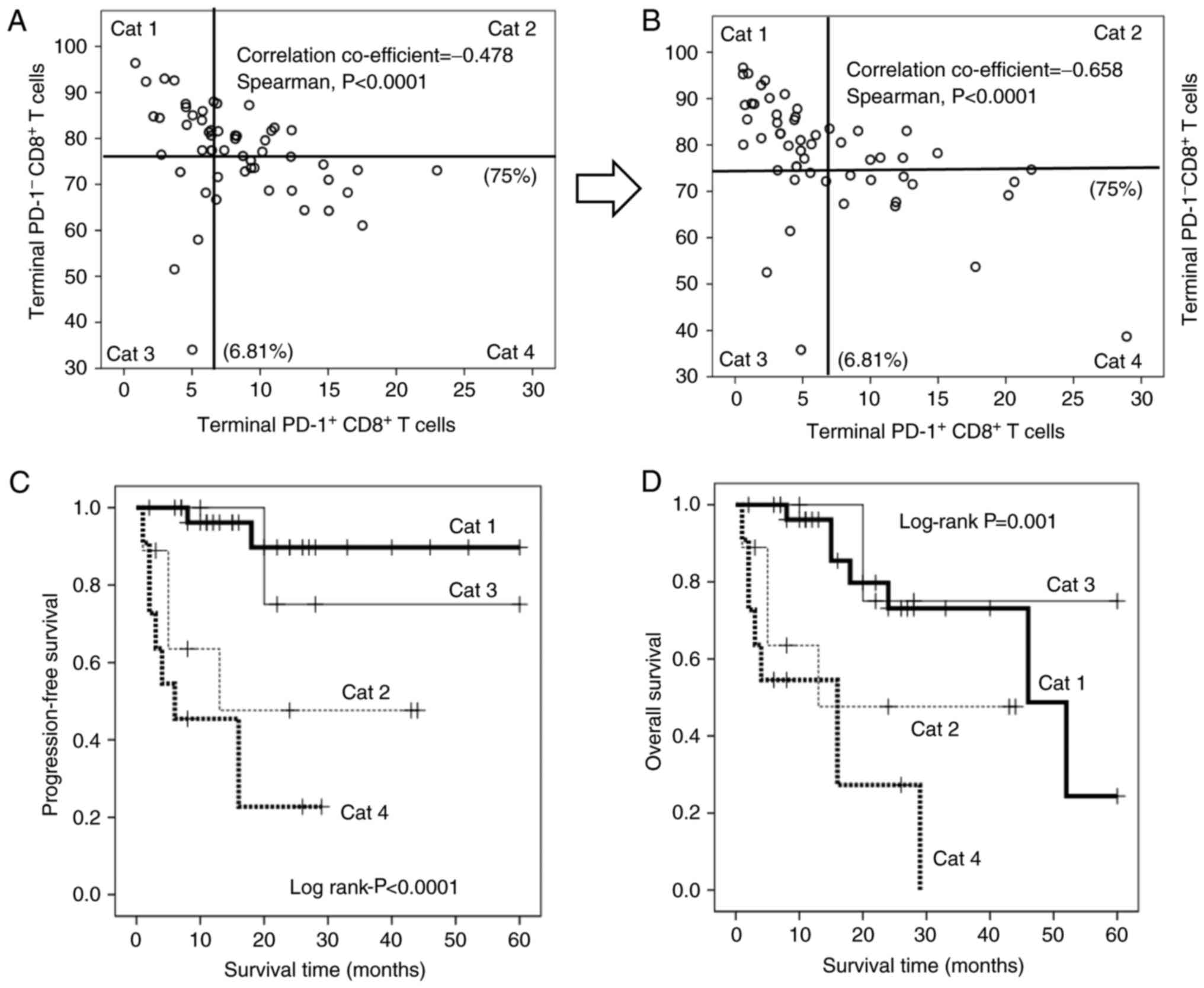
|
1
|
Barber DL, Wherry EJ, Masopust D, Zhu B,
Allison JP, Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ and Ahmed R: Restoring function
in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature.
439:682–687. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wherry EJ: T cell exhaustion. Nat Immunol.
12:492–499. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ahmadzadeh M, Johnson LA, Heemskerk B,
Wunderlich JR, Dudley ME, White DE and Rosenberg SA: Tumor
antigen-specific CD8 T cells infiltrating the tumor express high
levels of PD-1 and are functionally impaired. Blood. 114:1537–1544.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun S, Fei X, Mao Y, Wang X, Garfield DH,
Huang O, Wang J, Yuan F, Sun L, Yu Q, et al: PD-1+
immune cell infiltration inversely correlates with survival of
operable breast cancer patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
63:395–406. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zarour HM: Reversing T-Cell dysfunction
and exhaustion in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 22:1856–1864. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lu X, Yang L, Yao D, Wu X, Li J, Liu X,
Deng L, Huang C, Wang Y, Li D, et al: Tumor antigen-specific
CD8+ T cells are negatively regulated by PD-1 and Tim-3
in human gastric cancer. Cell Immunol. 313:43–51. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Scharping NE, Menk AV, Moreci RS,
Whetstone RD, Dadey RE, Watkins SC, Ferris RL and Delgoffe GM: The
tumor microenvironment represses T cell mitochondrial biogenesis to
drive intratumoral T cell metabolic insufficiency and dysfunction.
Immunity. 45:374–388. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gros A, Parkhurst MR, Tran E, Pasetto A,
Robbins PF, Ilyas S, Prickett TD, Gartner JJ, Crystal JS, Roberts
IM, et al: Prospective identification of neoantigen-specific
lymphocytes in the peripheral blood of melanoma patients. Nat Med.
22:433–438. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K,
Watanabe M, Nishimaki K, Yamagata K, Katsura KI, Katayama Y, Asoh S
and Ohta S: Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by
selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med.
13:688–694. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou L, Wang X, Xue W, Xie K, Huang Y,
Chen H, Gong G and Zeng Y: Beneficial effects of hydrogen-rich
saline against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in rabbits.
Brain Res. 1517:150–160. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hayashida K, Sano M, Ohsawa I, Shinmura K,
Tamaki K, Kimura K, Endo J, Katayama T, Kawamura A, Kohsaka S, et
al: Inhalation of hydrogen gas reduces infarct size in the rat
model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 373:30–35. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zheng X, Zheng X, Mao Y, Cai J, Li Y, Liu
W, Sun P, Zhang JH, Sun X and Yuan H: Hydrogen-rich saline protects
against intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Free Radic
Res. 43:478–484. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee JW, Kim JI, Lee YA, Lee DH, Song CS,
Cho YJ and Han JS: Inhaled hydrogen gas therapy for prevention of
testicular ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Pediatr Surg.
4:736–742. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang F, Yu G, Liu SY, Li JB, Wang JF, Bo
LL, Qian LR, Sun XJ and Deng XM: Hydrogen-rich saline protects
against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Surg Res.
167:e339–e344. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ji X, Tian Y, Xie K, Liu W, Qu Y and Fei
Z: Protective effects of hydrogen-rich saline in a rat model of
traumatic brain injury via reducing oxidative stress. J Surg Res.
178:e9–e16. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen T, Tao Y, Yan W, Yang G, Chen X, Cao
R, Zhang L, Xue J and Zhang Z: Protective effects of hydrogen-rich
saline against N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced photoreceptor
degeneration. Exp Eye Res. 148:65–73. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ren JD, Ma J, Hou J, Xiao WJ, Jin WH, Wu J
and Fan KH: Hydrogen-rich saline inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome
activation and attenuates experimental acute pancreatitis in mice.
Mediators Inflamma. 2014:9308942014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Nakao A, Toyoda Y, Sharma P, Evans M and
Guthrie N: Effectiveness of hydrogen rich water on antioxidant
status of subjects with potential metabolic syndrome-an open label
pilot study. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 46:140–149. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Amitani H, Asakawa A, Cheng K, Amitani M,
Kaimoto K, Nakano M, Ushikai M, Li Y, Tsai M, Li JB, et al:
Hydrogen improves glycemic control in type1 diabetic animal model
by promoting glucose uptake into skeletal muscle. PLoS One.
8:e539132013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li GM, Ji MH, Sun XJ, Zeng QT, Tian M, Fan
YX, Li WY, Li N and Yang JJ: Effects of hydrogen-rich saline
treatment on polymicrobial sepsis. J Surg Res. 181:279–286. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo SX, Jin YY, Fang Q, You CG, Wang XG,
Hu XL and Han CM: Beneficial effects of hydrogen-rich saline on
early burn-wound progression in rats. PLoS One. 10:e01248972015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kikkawa YS, Nakagawa T, Taniguchi M and
Ito J: Hydrogen protects auditory hair cells from cisplatin-induced
free radicals. Neurosci Lett. 579:125–129. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Watanabe S, Fujita M, Ishihara M,
Tachibana S, Yamamoto Y, Kaji T, Kawauchi T and Kanatani Y:
Protective effect of inhalation of hydrogen gas on
radiation-induced dermatitis and skin injury in rats. J Radiat Res.
55:1107–1113. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ushida T, Kotani T, Tsuda H, Imai K,
Nakano T, Hirako S, Ito Y, Li H, Mano Y, Wang J, et al: Molecular
hydrogen ameliorates several characteristics of preeclampsia in the
Reduced Uterine Perfusion Pressure (RUPP) rat model. Free Radic
Biol Med. 101:524–533. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ge L, Yang M, Yang NN, Yin XX and Song WG:
Molecular hydrogen: A preventive and therapeutic medical gas for
various diseases. Oncotarget. 8:102653–102673. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Runtuwene J, Amitani H, Amitani M, Asakawa
A, Cheng KC and Inui A: Hydrogen-water enhances
5-fluorouracil-induced inhibition of colon cancer. PeerJ.
3:e8592015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang D, Wang L, Zhang Y, Zhao Y and Chen
G: Hydrogen gas inhibits lung cancer progression through targeting
SMC3. Biomed Pharmacother. 104:788–797. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kamimura N, Ichimiya H, Iuchi K and Ohta
S: Molecular hydrogen stimulates the gene expression of
transcriptional coactivator PGC-1α to enhance fatty acid
metabolism. NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2:160082016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Handschin C and Spiegelman BM: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 coactivators,
energy homeostasis, and metabolism. Endocr Rev. 27:728–735. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sobin LH and Wittekind CH: UICC TNM
Classification of malignant tumors. John Wiley and Sons; New York:
1997,
|
|
31
|
Tamura T, Hayashida K, Sano M, Suzuki M,
Shibusawa T, Yoshizawa J, Kobayashi Y, Suzuki T, Ohta S, Morisaki
H, et al: Feasibility and safety of hydrogen gas inhalation for
post-cardiac arrest syndrome-First-in-Human Pilot Study. Circ J.
80:1870–1873. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cancer therapy evaluation program, common
terminology criteria for adverse events, Version 3.0, DCTD, NCI,
NIH, DHHS. Int J Clin Oncol 9. (Sup PIII). S1–S82. 2004.
|
|
33
|
Crespo J, Sun H, Welling TH, Tian Z and
Zou W: T cell anergy, exhaustion, senescence, and stemness in the
tumor microenvironment. Curr Opin Immunol. 25:214–221. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|