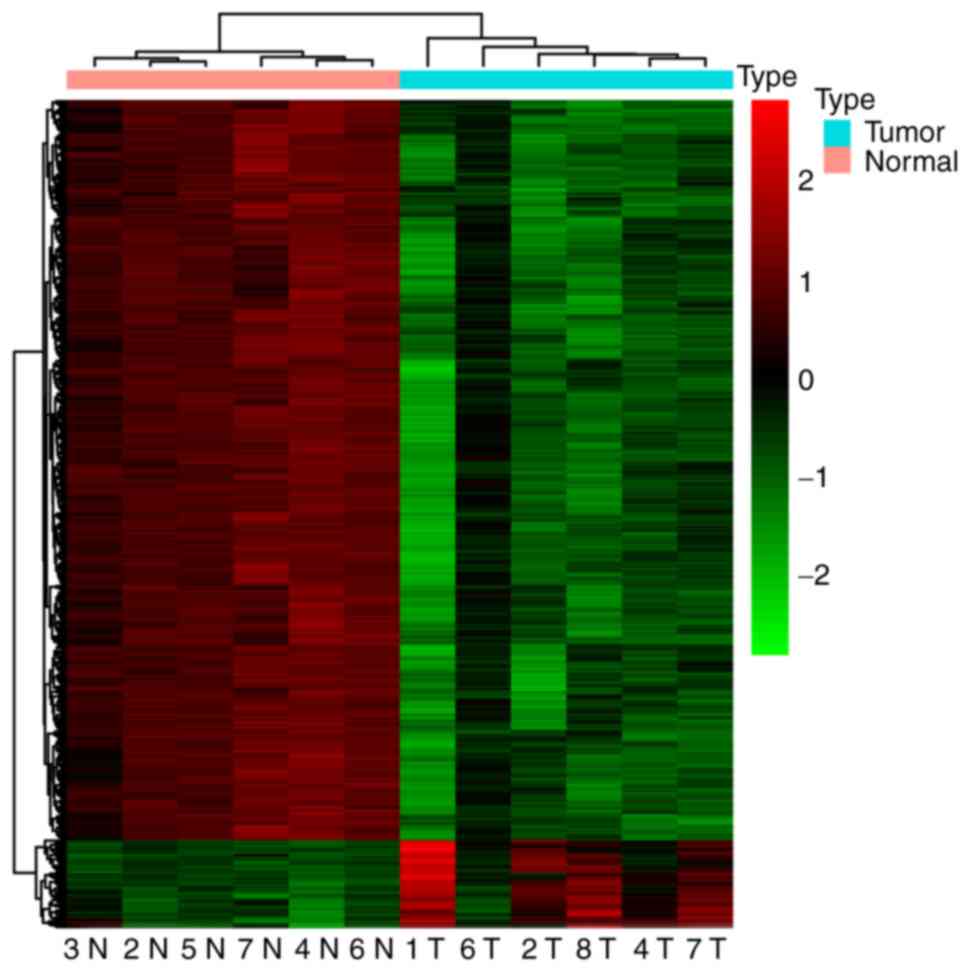
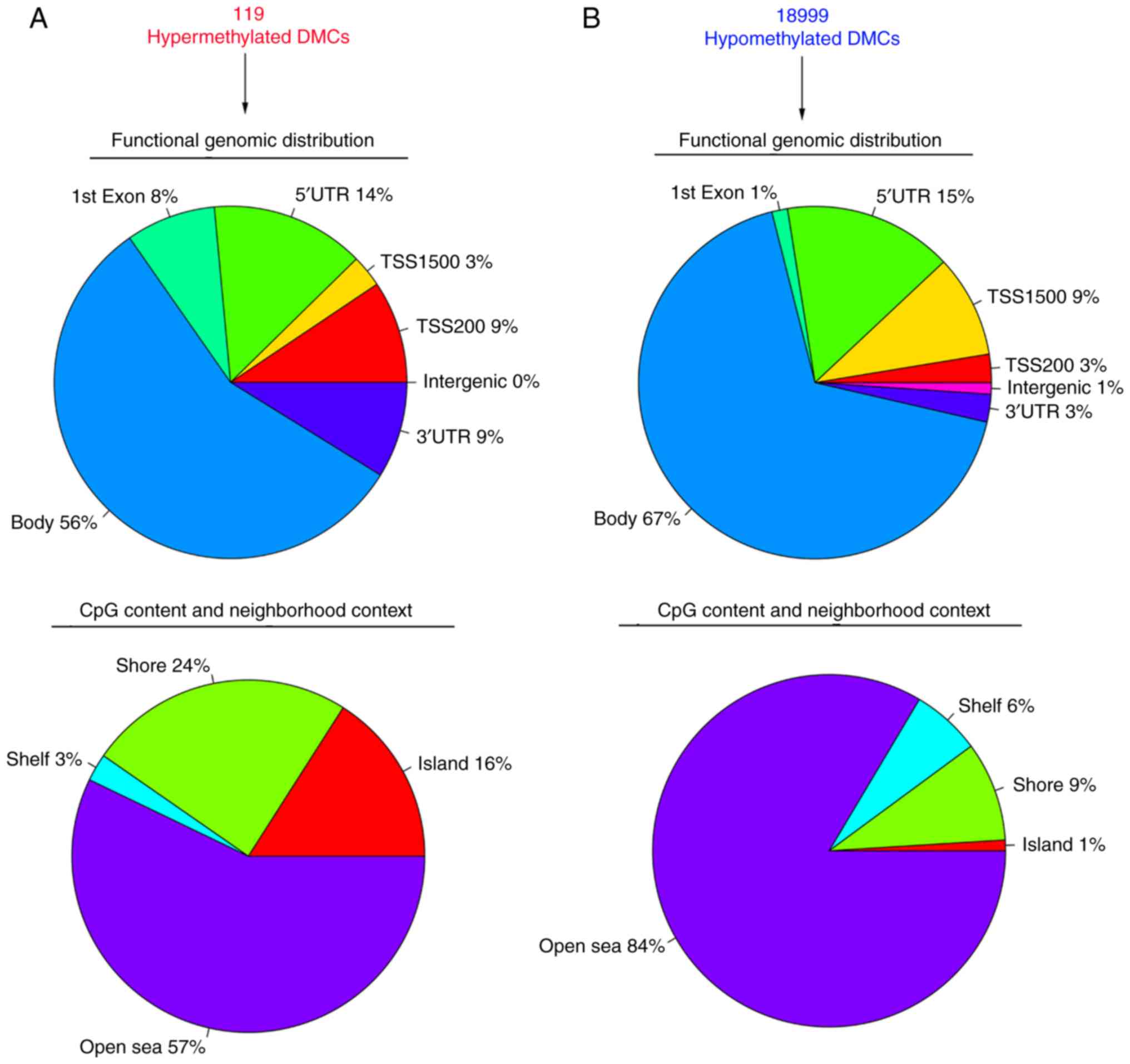
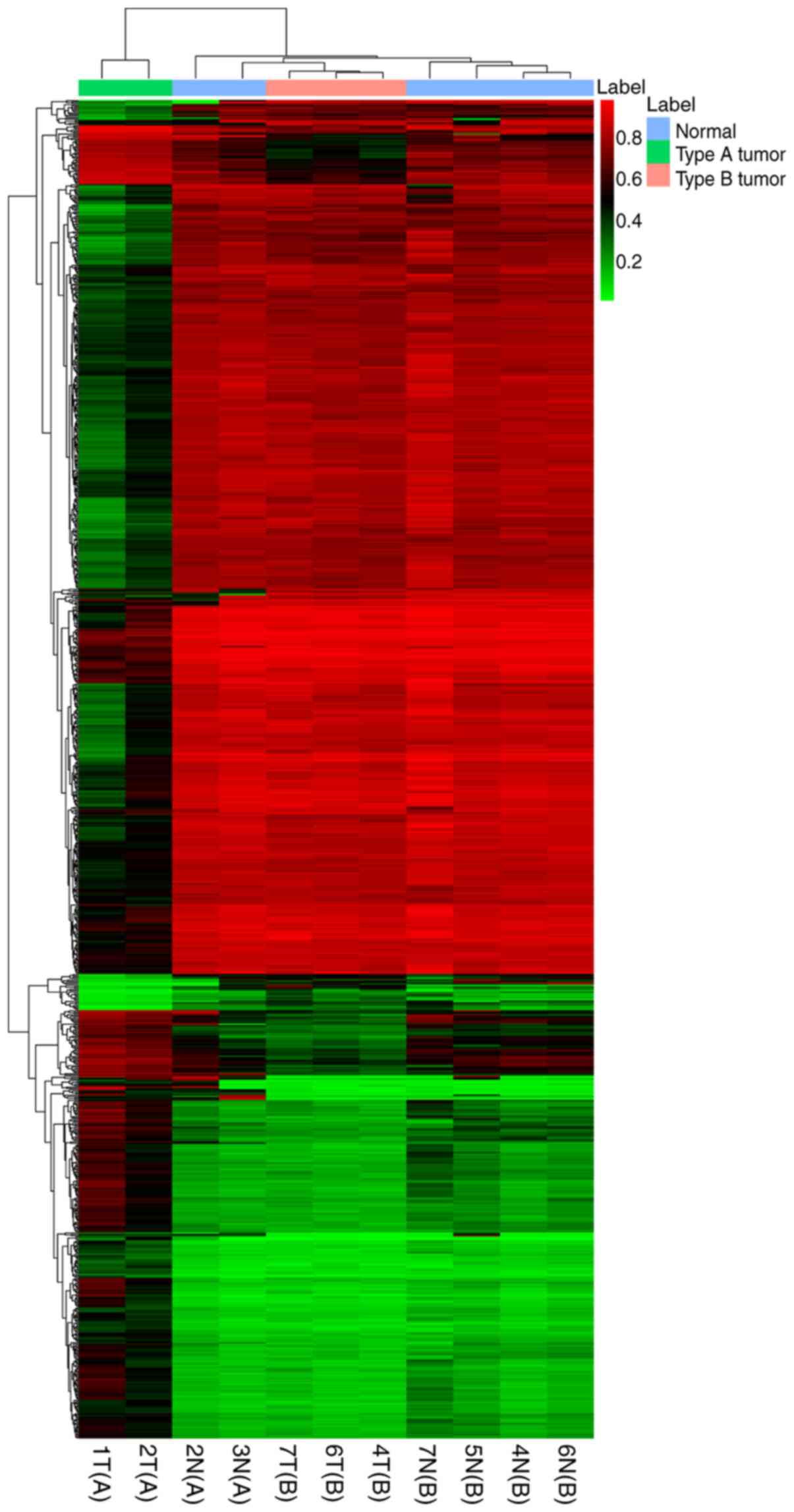
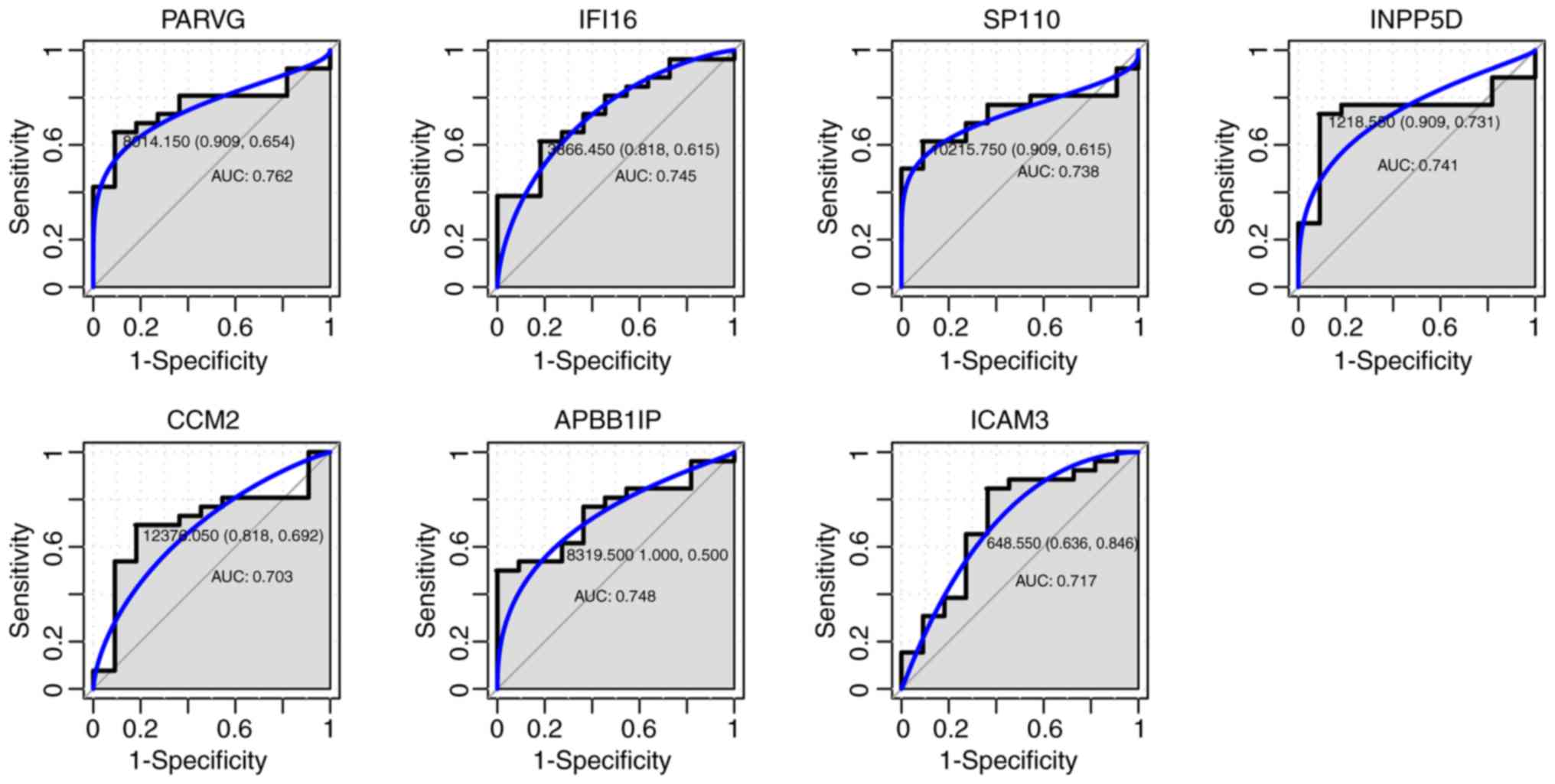
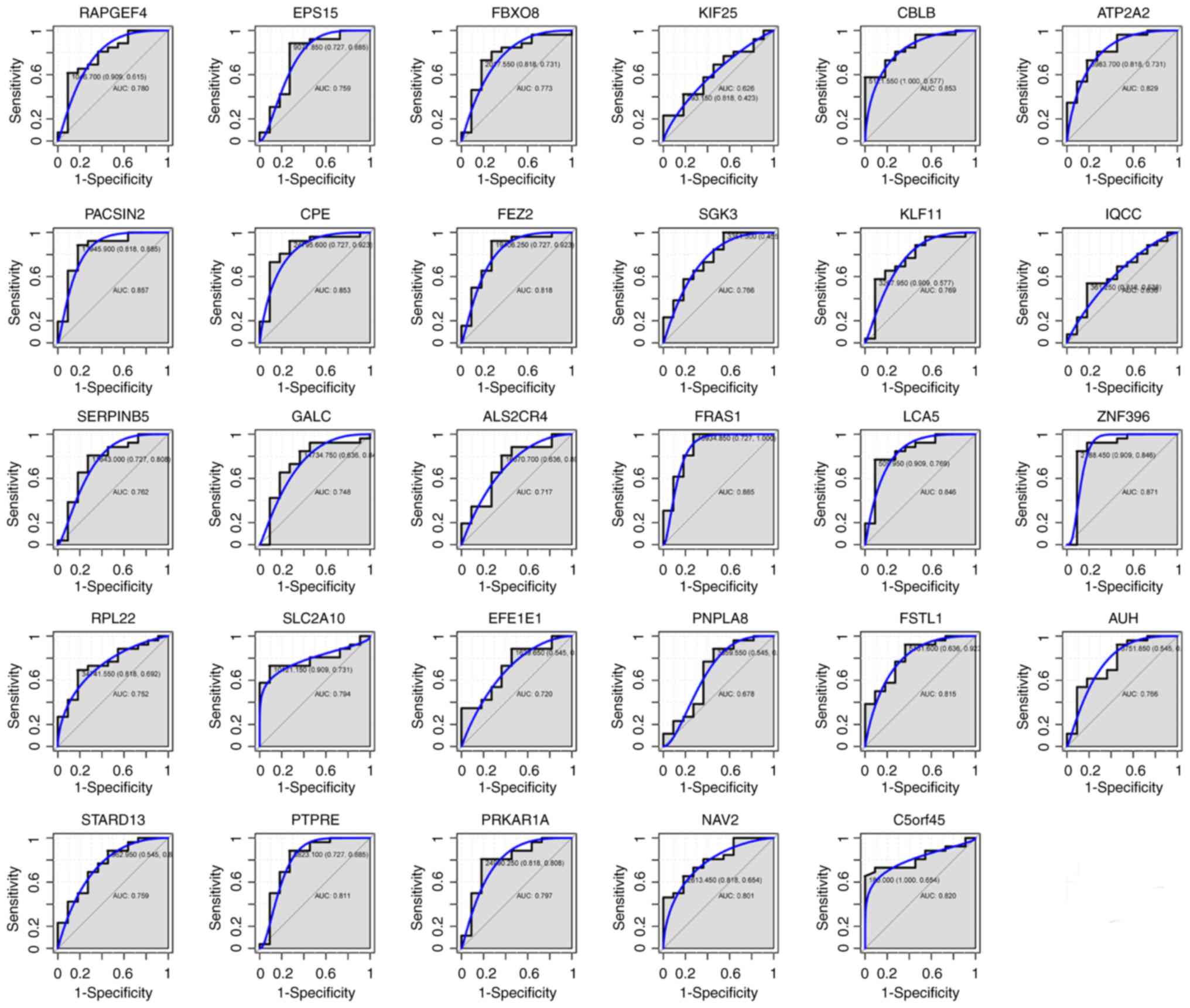
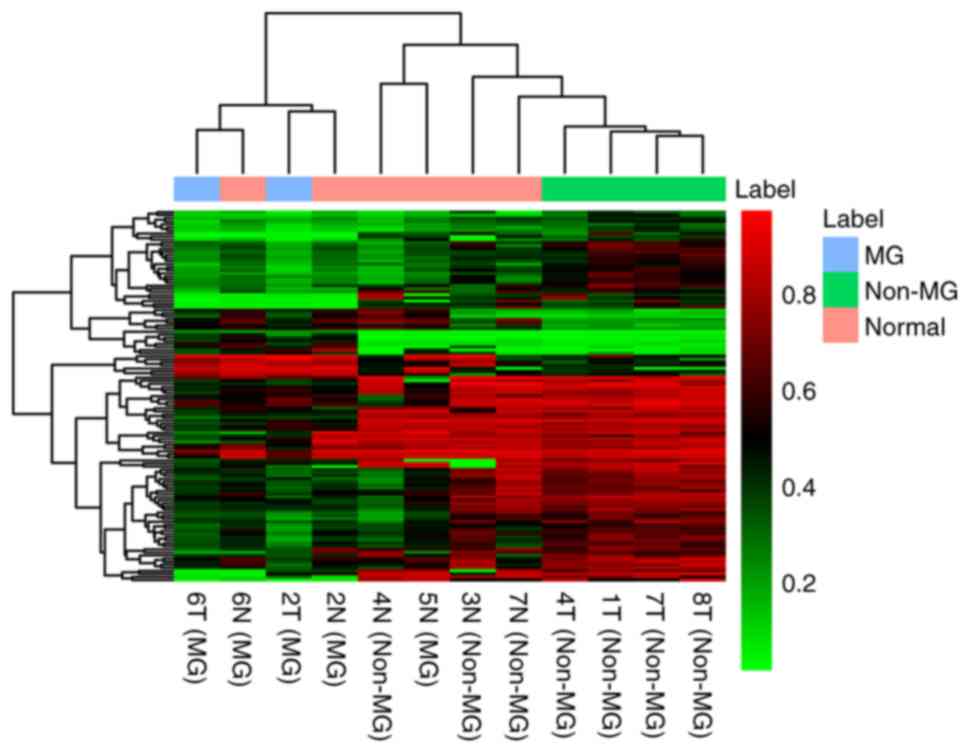
|
1
|
Guerrera F, Rendina EA, Venuta F,
Margaritora S, Ciccone AM, Novellis P, Novero D, Anile M, Bora G,
Rena O, et al: Does the World Health Organization histological
classification predict outcomes after thymomectomy? Results of a
multicentre study on 750 patients. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.
48:48–54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carter BW, Benveniste MF, Madan R, Godoy
MC, Groot PM, Truong MT, Rosado-de-Christenson ML and Marom EM:
IASLC/ITMIG staging system and lymph node Map for thymic epithelial
neoplasms. Radiographics. 37:758–776. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Marx A, Strobel P, Badve SS, Chalabreysse
L, Chan JK, Chen G, de Leval L, Detterbeck F, Girard N, Huang J, et
al: ITMIG consensus statement on the use of the WHO histological
classification of thymoma and thymic carcinoma: refined
definitions, histological criteria, and reporting. J Thorac Oncol.
9:596–611. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ried M, Marx A, Gotz A, Hamer O, Schalke B
and Hofmann HS: State of the art: Diagnostic tools and innovative
therapies for treatment of advanced thymoma and thymic carcinoma.
Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 49:1545–1552. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Okumura M, Fujii Y, Shiono H, Inoue M,
Minami M, Utsumi T, Kadota Y and Sawa Y: Immunological function of
thymoma and pathogenesis of paraneoplastic myasthenia gravis. Gen
Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 56:143–150. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Aydemir B: The effect of myasthenia gravis
as a prognostic factor in thymoma treatment. North Clin Istanb.
3:194–200. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jamilloux Y, Frih H, Bernard C, Broussolle
C, Petiot P, Girard N and Sève P: Thymoma and autoimmune diseases.
Rev Med Interne. 39:17–26. 2018.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Venza M, Visalli M, Biondo C, Oteri R,
Agliano F, Morabito S, Teti D and Venza I: Epigenetic marks
responsible for cadmium-induced melanoma cell overgrowth. Toxicol
In Vitro. 29:242–250. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Venza M, Visalli M, Beninati C, Biondo C,
Teti D and Venza I: Role of genetics and epigenetics in mucosal,
uveal, and cutaneous melanomagenesis. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
16:528–538. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bellissimo T, Ganci F, Gallo E, Sacconi A,
Tito C, De Angelis L, Pulito C, Masciarelli S, Diso D, Anile M, et
al: Thymic Epithelial Tumors phenotype relies on miR-145-5p
epigenetic regulation. Mol Cancer. 16:882017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wei J, Liu Z, Wu K, Yang D, He Y, Chen GG,
Zhang J and Lin J: Identification of prognostic and
subtype-specific potential miRNAs in thymoma. Epigenomics.
9:647–657. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Radovich M, Solzak JP, Hancock BA, Conces
ML, Atale R, Porter RF, Zhu J, Glasscock J, Kesler KA, Badve SS, et
al: A large microRNA cluster on chromosome 19 is a transcriptional
hallmark of WHO type A and AB thymomas. Br J Cancer. 114:477–484.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen C, Yin N, Yin B and Lu Q: DNA
methylation in thoracic neoplasms. Cancer Lett. 301:7–16. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mokhtar M, Kondo K, Namura T, Ali AH,
Fujita Y, Takai C, Takizawa H, Nakagawa Y, Toba H, Kajiura K, et
al: Methylation and expression profiles of MGMT gene in thymic
epithelial tumors. Lung Cancer. 83:279–287. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hirose Y, Kondo K, Takizawa H, Nagao T,
Nakagawa Y, Fujino H, Toba H, Kenzaki K, Sakiyama S and Tangoku A:
Aberrant methylation of tumour-related genes in thymic epithelial
tumours. Lung Cancer. 64:155–159. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lopomo A, Ricciardi R, Maestri M, De Rosa
A, Melfi F, Lucchi M, Mussi A, Coppedè F and Migliore L:
Gene-specific methylation analysis in thymomas of patients with
myasthenia gravis. Int J Mol Sci. 17:2121–2131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Zhu S, Wang ZT, Liu WZ, Zong SX and Li BS:
Invasive atypical thymic carcinoid: Three case reports and
literature review. Onco Targets Ther. 9:6171–6176. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Assenov Y, Muller F, Lutsik P, Walter J,
Lengauer T and Bock C: Comprehensive analysis of DNA methylation
data with RnBeads. Nat Methods. 11:1138–1140. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Badve S, Goswami C, Gokmen-Polar Y, Nelson
RP Jr, Henley J, Miller N, Zaheer NA, Sledge GW Jr, Li L, Kesler
KA, et al: Molecular analysis of thymoma. PLoS One. 7:e426692012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P,
Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH,
Sherman PM, Holko M, et al: NCBI GEO: Archive for functional
genomics data sets- - Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:D991–D995.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tabas-Madrid D, Nogales-Cadenas R and
Pascual-Montano A: GeneCodis3: A non-redundant and modular
enrichment analysis tool for functional genomics. Nucleic Acids
Res. 40:W478–W483. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene
Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucl Acids Res. 28:27–30. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Carey V and Redestig H: ROC: Utilities for
ROC, with uarray focus, 2003–2019, v. 1.24.0. http://www.bioconductor.org
|
|
25
|
Xie Y, Liu J, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Ward JM,
Logsdon D, Diwan BA and Waalkes MP: Aberrant DNA methylation and
gene expression in livers of newborn mice transplacentally exposed
to a hepatocarcinogenic dose of inorganic arsenic. Toxicology.
236:7–15. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vizoso M, Puig M, Carmona FJ, Maqueda M,
Velásquez A, Gómez A, Labernadie A, Lugo R, Gabasa M,
Rigat-Brugarolas LG, et al: Aberrant DNA methylation in non-small
cell lung cancer-associated fibroblasts. Carcinogenesis.
36:1453–1463. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lopomo A, Ricciardi R, Maestri M, De Rosa
A, Melfi F, Lucchi M, Mussi A, Coppedè F and Migliore L:
Gene-specific methylation analysis in thymomas of patients with
myasthenia gravis. Int J Mol Sci. 17(pii): E21212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ziller MJ, Gu H, Müller F, Donaghey J,
Tsai LT, Kohlbacher O, De Jager PL, Rosen ED, Bennett DA, Bernstein
BE, et al: Charting a dynamic DNA methylation landscape of the
human genome. Nature. 500:477–481. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Suzuki M, Chen H, Shigematsu H, Ando S,
Iida T, Nakajima T, Fujisawa T and Kimura H: Aberrant methylation:
common in thymic carcinomas, rare in thymomas. Oncol Rep.
14:1621–1624. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hirabayashi H, Fujii Y, Sakaguchi M,
Tanaka H, Yoon HE, Komoto Y, Inoue M, Miyoshi S and Matsuda H:
p16INK4, pRB, p53 and cyclin D1 expression and
hypermethylation of CDKN2 gene in thymoma and thymic
carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 73:639–644. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Quintanilla-Martinez L, Wilkins EW Jr,
Ferry JA and Harris NL: Thymoma- - morphologic subclassification
correlates with invasiveness and immunohistologic features: A study
of 122 cases. Hum Pathol. 24:958–969. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Quintanilla-Martinez L, Wilkins EW Jr,
Choi N, Efird J, Hug E and Harris NL: Thymoma. Histologic
subclassification is an independent prognostic factor. Cancer.
74:606–617. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Marx A and Muller-Hermelink HK: Thymoma
and thymic carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 23:739–742. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li B, Wang B, Niu LJ, Jiang L and Qiu CC:
Hypermethylation of multiple tumor-related genes associated with
DNMT3b up-regulation served as a biomarker for early diagnosis of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Epigenetics. 6:307–316. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|