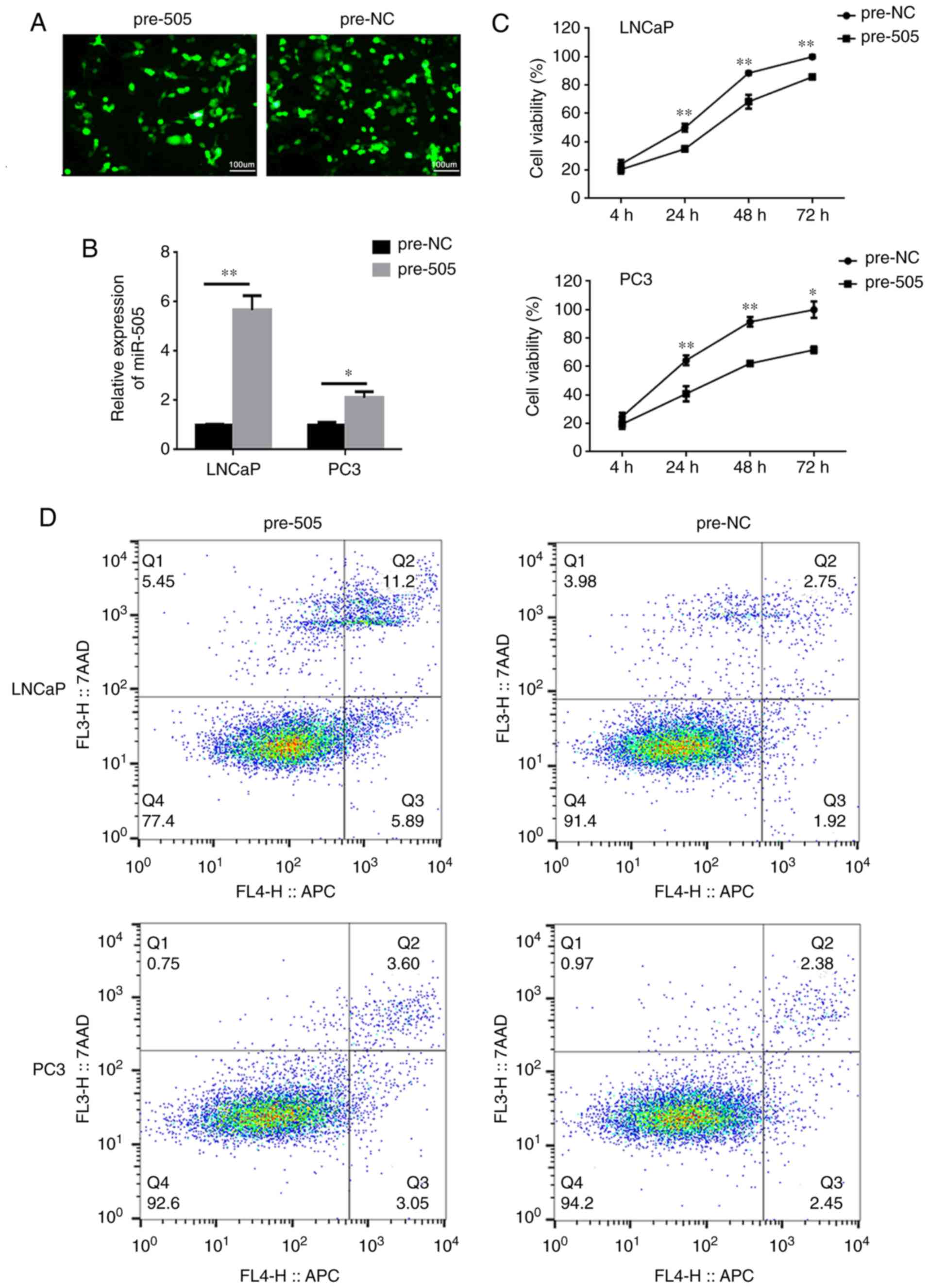
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bostwick DG, Burke HB, Djakiew D, Euling
S, Ho SM, Landolph J, Morrison H, Sonawane B, Shifflett T, Waters
DJ and Timms B: Human prostate cancer risk factors. Cancer. 101 (10
Suppl):S2371–S2490. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Schröder FH, Hugosson J, Roobol MJ,
Tammela TL, Zappa M, Nelen V, Kwiatkowski M, Lujan M, Määttänen L,
Lilja H, et al: Screening and prostate cancer mortality: Results of
the European randomised study of screening for prostate cancer
(ERSPC) at 13 years of follow-up. Lancet. 384:2027–2035. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
He HC, Han ZD, Dai QS, Ling XH, Fu X, Lin
ZY, Deng YH, Qin GQ, Cai C, Chen JH, et al: Global analysis of the
differentially expressed miRNAs of prostate cancer in Chinese
patients. BMC Genomics. 14:7572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Porkka KP, Pfeiffer MJ, Waltering KK,
Vessella RL, Tammela TL and Visakorpi T: MicroRNA expression
profiling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 67:6130–6135. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ozen M, Creighton CJ, Ozdemir M and
Ittmann M: Widespread deregulation of microRNA expression in human
prostate cancer. Oncogene. 27:1788–1793. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bell EH, Kirste S, Fleming JL, Stegmaier
P, Drendel V, Mo X, Ling S, Fabian D, Manring I, Jilg CA, et al: A
novel miRNA-based predictive model for biochemical failure
following post-prostatectomy salvage radiation therapy. PLoS One.
10:e01187452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Martens-Uzunova ES, Jalava SE, Dits NF,
van Leenders GJ, Møller S, Trapman J, Bangma CH, Litman T,
Visakorpi T and Jenster G: Diagnostic and prognostic signatures
from the small non-coding RNA transcriptome in prostate cancer.
Oncogene. 31:978–991. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Coarfa C, Fiskus W, Eedunuri VK,
Rajapakshe K, Foley C, Chew SA, Shah SS, Geng C, Shou J, Mohamed
JS, et al: Comprehensive proteomic profiling identifies the
androgen receptor axis and other signaling pathways as targets of
microRNAs suppressed in metastatic prostate cancer. Oncogene.
35:2345–2356. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang YQ, Ling XH, Yuan RQ, Chen ZY, Yang
SB, Huang HX, Zhong WD and Qiu SP: miR-30c suppresses prostate
cancer survival by targeting the ASF/SF2 splicing factor
oncoprotein. Mol Med Rep. 16:2431–2438. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin ZY, Chen G, Zhang YQ, He HC, Liang YX,
Ye JH, Liang YK, Mo RJ, Lu JM, Zhuo YJ, et al: MicroRNA-30d
promotes angiogenesis and tumor growth via MYPT1/c-JUN/VEGFA
pathway and predicts aggressive outcome in prostate cancer. Mol
Cancer. 16:482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cai C, Chen QB, Han ZD, Zhang YQ, He HC,
Chen JH, Chen YR, Yang SB, Wu YD, Zeng YR, et al: miR-195 inhibits
tumor progression by targeting RPS6KB1 in human prostate cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 21:4922–4934. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yamamoto Y, Yoshioka Y, Minoura K,
Takahashi RU, Takeshita F, Taya T, Horii R, Fukuoka Y, Kato T,
Kosaka N and Ochiya T: An integrative genomic analysis revealed the
relevance of microRNA and gene expression for drug-resistance in
human breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 10:1352011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen S, Sun KX, Liu BL, Zong ZH and Zhao
Y: MicroRNA-505 functions as a tumor suppressor in endometrial
cancer by targeting TGF-α. Mol Cancer. 15:112016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu L, Qiu C, Li D, Bai G, Liang J and Yang
Q: MicroRNA-505 suppresses proliferation and invasion in hepatoma
cells by directly targeting high-mobility group box 1. Life Sci.
157:12–18. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Grumet M: Nr-CAM: A cell adhesion molecule
with ligand and receptor functions. Cell Tissue Res. 290:423–428.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Grumet M, Mauro V, Burgoon MP, Edelman GM
and Cunningham BA: Structure of a new nervous system glycoprotein,
Nr-CAM, and its relationship to subgroups of neural cell adhesion
molecules. J Cell Biol. 113:1399–1412. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Conacci-Sorrell M, Kaplan A, Raveh S,
Gavert N, Sakurai T and Ben-Ze'ev A: The shed ectodomain of Nr-CAM
stimulates cell proliferation and motility, and confers cell
transformation. Cancer Res. 65:11605–11612. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y, Sui F, Ma J, Ren X, Guan H, Yang
Q, Shi J, Ji M, Shi B, Sun Y and Hou P: Positive feedback loops
between NrCAM and major signaling pathways contribute to thyroid
tumorigenesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 102:613–624.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chan JY, Ong CW and Salto-Tellez M:
Overexpression of neurone glial-related cell adhesion molecule is
an independent predictor of poor prognosis in advanced colorectal
cancer. Cancer Sci. 102:1855–1861. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tsourlakis MC, Walter E, Quaas A, Graefen
M, Huland H, Simon R, Sauter G, Steurer S, Schlomm T and Minner S:
High Nr-CAM expression is associated with favorable phenotype and
late PSA recurrence in prostate cancer treated by prostatectomy.
Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 16:159–164. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Maragkakis M, Alexiou P, Papadopoulos GL,
Reczko M, Dalamagas T, Giannopoulos G, Goumas G, Koukis E, Kourtis
K, Simossis VA, et al: Accurate microRNA target prediction
correlates with protein repression levels. BMC Bioinformatics.
10:2952009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Betel D, Koppal A, Agius P, Sander C and
Leslie C: Comprehensive modeling of microRNA targets predicts
functional non-conserved and non-canonical sites. Genome Biol.
11:R902010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk-database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
‘walking’ the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Verduci L, Simili M, Rizzo M, Mercatanti
A, Evangelista M, Mariani L, Rainaldi G and Pitto L: MicroRNA
(miRNA)-mediated interaction between leukemia/lymphoma-related
factor (LRF) and alternative splicing factor/splicing factor 2
(ASF/SF2) affects mouse embryonic fibroblast senescence and
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 285:39551–39556. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ma C, Xu B, Husaiyin S, Wang L,
Wusainahong K, Ma J, Zhu K and Niyazi M: MicroRNA-505 predicts
prognosis and acts as tumor inhibitor in cervical carcinoma with
inverse association with FZD4. Biomed Pharmacother. 92:586–594.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu M, Kuang Y, Wang M, Han X and Yang Q: A
microRNA expression signature as a predictor of survival for colon
adenocarcinoma. Neoplasma. 64:56–64. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mudduluru G, Ilm K, Fuchs S and Stein U:
Epigenetic silencing of miR-520c leads to induced S100A4 expression
and its mediated colorectal cancer progression. Oncotarget.
8:21081–21094. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Keller A, Backes C, Leidinger P, Kefer N,
Boisguerin V, Barbacioru C, Vogel B, Matzas M, Huwer H, Katus HA,
et al: Next-generation sequencing identifies novel microRNAs in
peripheral blood of lung cancer patients. Mol Biosyst. 7:3187–3199.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Du M, Shi D, Yuan L, Li P, Chu H, Qin C,
Yin C, Zhang Z and Wang M: Circulating miR-497 and miR-663b in
plasma are potential novel biomarkers for bladder cancer. Sci Rep.
5:104372015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jansson MD and Lund AH: MicroRNA and
cancer. Mol Oncol. 6:590–610. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cai X, Yang X, Jin C, Li L, Cui Q, Guo Y,
Dong Y, Yang X, Guo L and Zhang M: Identification and verification
of differentially expressed microRNAs and their target genes for
the diagnosis of esophageal cancer. Oncol Lett. 16:3642–3650.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zeng H, Ortiz A, Shen PF, Cheng CJ, Lee
YC, Yu G, Lin SC, Creighton CJ, Yu-Lee LY and Lin SH: Angiomotin
regulates prostate cancer cell proliferation by signaling through
the Hippo-YAP pathway. Oncotarget. 8:10145–10160. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang H and Fan Q: MicroRNA-205 inhibits
the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer by regulating AMOT
expression. Oncol Rep. 34:2163–2170. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ruan WD, Wang P, Feng S, Xue Y and Zhang
B: MicroRNA-497 inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and
invasion by targeting AMOT in human osteosarcoma cells. Onco
Targets Ther. 9:303–313. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu Y, Li Y, Hou R and Shu Z: Knockdown
GREM1 suppresses cell growth, angiogenesis, and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colon cancer. J Cell Biochem.
120:5583–5596. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fu C, Li D, Zhang X, Liu N, Chi G and Jin
X: LncRNA PVT1 facilitates tumorigenesis and progression of glioma
via regulation of MiR-128-3p/GREM1 axis and BMP signaling pathway.
Neurotherapeutics. 15:1139–1157. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee SR, Choi YD and Cho NH: Association
between pathologic factors and ERG expression in prostate cancer:
Finding pivotal networking. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 144:1665–1683.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xu L, Huang TJ, Hu H, Wang MY, Shi SM,
Yang Q, Lin F, Qiang YY, Mei Y, Lang YH, et al: The developmental
transcription factor IRF6 attenuates ABCG2 gene expression and
distinctively reverses stemness phenotype in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 431:230–243. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim JW, Cheng Y, Liu W, Li T,
Yegnasubramanian S, Zheng SL, Xu J, Isaacs WB and Chang BL: Genetic
and epigenetic inactivation of LPL gene in human prostate cancer.
Int J Cancer. 124:734–738. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|