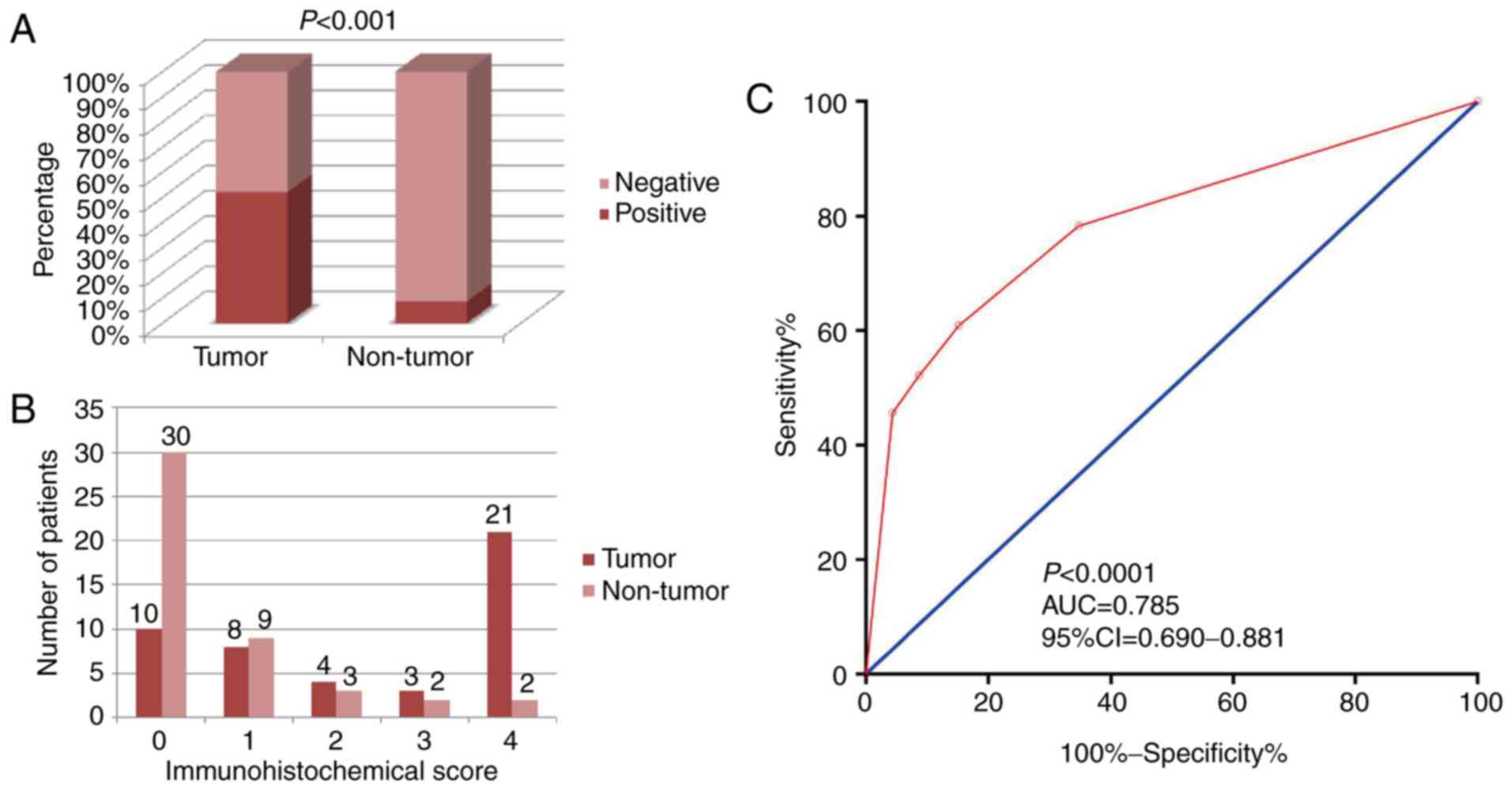
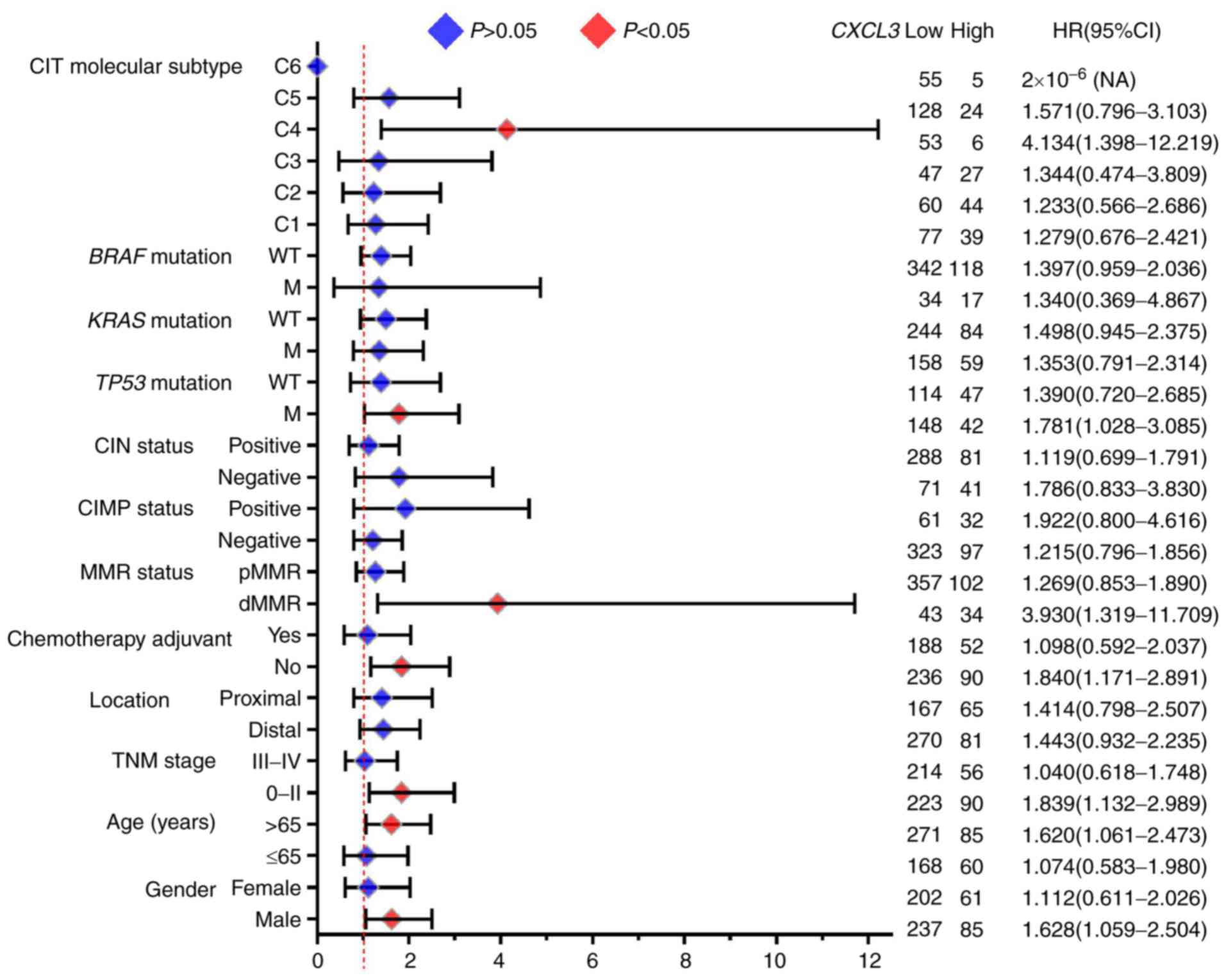
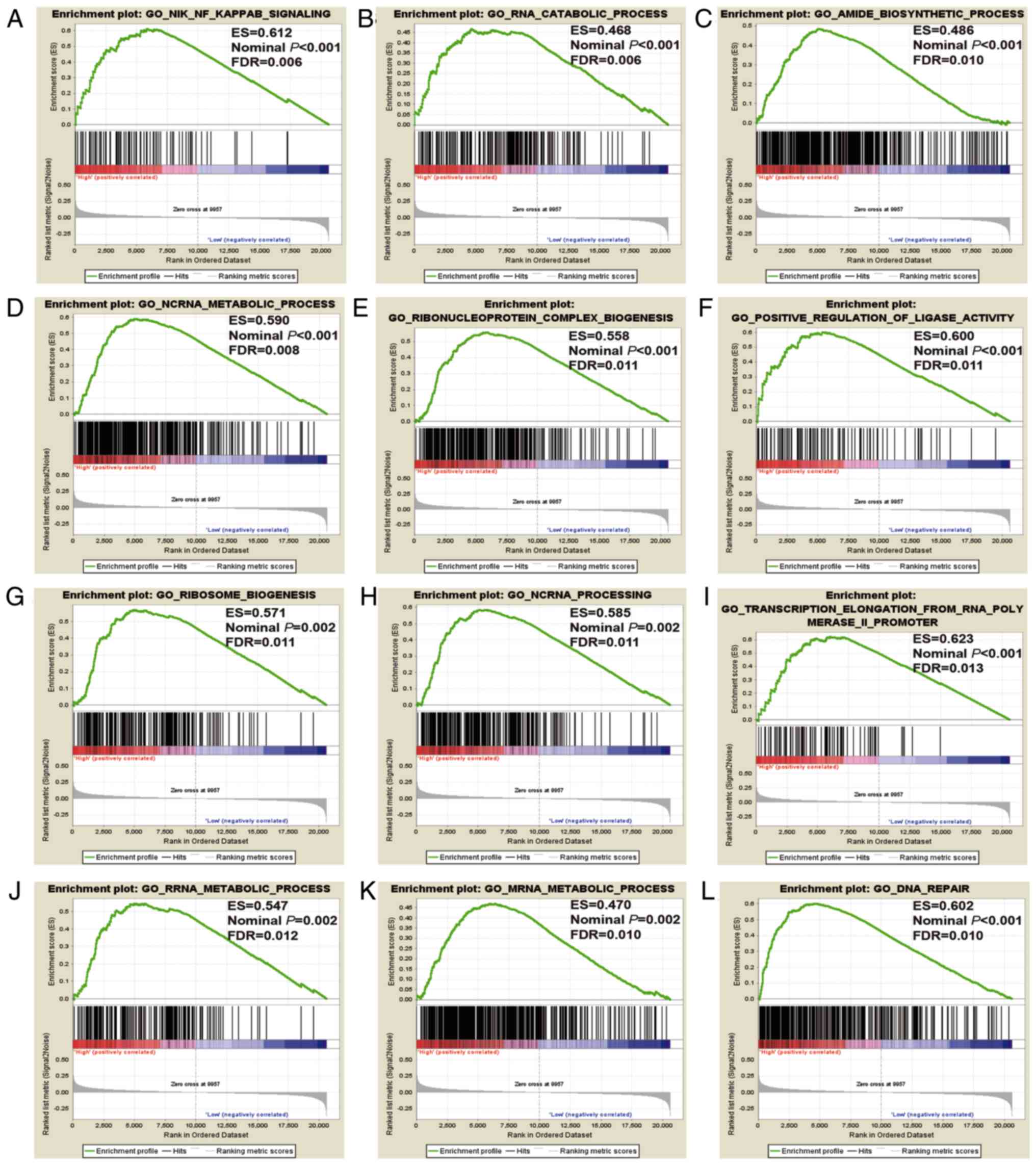
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Garborg K: Colorectal cancer screening.
Surg Clin North Am. 95:979–989. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pita-Fernández S, González-Sáez L,
López-Calviño B, Seoane-Pillado T, Rodríguez-Camacho E,
Pazos-Sierra A, González-Santamaría P and Pértega-Díaz S: Effect of
diagnostic delay on survival in patients with colorectal cancer: A
retrospective cohort study. BMC Cancer. 16:6642016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aran V, Victorino AP, Thuler LC and
Ferreira CG: Colorectal Cancer: Epidemiology disease mechanisms and
interventions to reduce onset and mortality. Clin Colorectal
Cancer. 15:195–203. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Clough E and Barrett T: The gene
expression omnibus database. Methods Mol Biol. 1418:93–110. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ahuja SK and Murphy PM: The CXC chemokines
growth-regulated oncogene (GRO) alpha, GRObeta, GROgamma,
neutrophil-activating peptide-2, and epithelial cell-derived
neutrophil-activating peptide-78 are potent agonists for the type
B, but not the type A, human interleukin-8 receptor. J Biol Chem.
271:20545–20550. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Smith DF, Galkina E, Ley K and Huo Y: GRO
family chemokines are specialized for monocyte arrest from flow. Am
J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 289:H1976–H1984. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Doll D, Keller L, Maak M, Boulesteix AL,
Siewert JR, Holzmann B and Janssen KP: Differential expression of
the chemokines GRO-2, GRO-3, and interleukin-8 in colon cancer and
their impact on metastatic disease and survival. Int J Colorectal
Dis. 25:573–581. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiong Y, You W, Wang R, Peng L and Fu Z:
Prediction and validation of hub genes associated with colorectal
cancer by integrating PPI network and gene expression data. Biomed
Res Int. 2017:24214592017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Magalhaes B, Peleteiro B and Lunet N:
Dietary patterns and colorectal cancer: Systematic review and
meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer Prev. 21:15–23. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rebbeck TR, Devesa SS, Chang BL, Bunker
CH, Cheng I, Cooney K, Eeles R, Fernandez P, Giri VN, Gueye SM, et
al: Global patterns of prostate cancer incidence, aggressiveness,
and mortality in men of african descent. Prostate Cancer.
2013:5608572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rong M, He R, Dang Y and Chen G:
Expression and clinicopathological significance of miR-146a in
hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. Ups J Med Sci. 119:19–24. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dai J, Wu H, Zhang Y, Gao K, Hu G, Guo Y,
Lin C and Li X: Negative feedback between TAp63 and Mir-133b
mediates colorectal cancer suppression. Oncotarget. 7:87147–87160.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Amin MB, Edge S, Greene F, Byrd DR,
Brookland RK, Washington MK, Gershenwald JE, Compton CC, Hess KR,
Sullivan DC, et al: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th. Springer;
Chicago, IL: pp. 202017
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y, Luo J, He R, Huang W, Li Z, Li P,
Dang Y, Chen G and Li S: Expression and clinicopathological
implication of DcR3 in lung cancer tissues: A tissue microarray
study with 365 cases. Onco Targets Ther. 9:4959–4968. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Uhlen M, Fagerberg L, Hallstrom BM,
Lindskog C, Oksvold P, Mardinoglu A, Sivertsson A, Kampf C,
Sjostedt E, Asplund A, et al: Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the
human proteome. Science. 347:12604192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G and Zhang Z:
GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling
and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:W98–W102. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Marisa L, de Reynies A, Duval A, Selves J,
Gaub MP, Vescovo L, Etienne-Grimaldi MC, Schiappa R, Guenot D,
Ayadi M, et al: Gene expression classification of colon cancer into
molecular subtypes: Characterization, validation, and prognostic
value. PLoS Med. 10:e10014532013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES, et al: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J Royal Stat Soc Series B (Methodological).
57:289–300. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Reiner A, Yekutieli D and Benjamini Y:
Identifying differentially expressed genes using false discovery
rate controlling procedures. Bioinformatics. 19:368–375. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
O'Donovan N, Galvin M and Morgan JG:
Physical mapping of the CXC chemokine locus on human chromosome 4.
Cytogenet Cell Genet. 84:39–42. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Airoldi I and Ribatti D: Regulation of
angiostatic chemokines driven by IL-12 and IL-27 in human tumors. J
Leukoc Biol. 90:875–882. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Simpson KJ, Henderson NC, Bone-Larson CL,
Lukacs NW, Hogaboam CM and Kunkel SL: Chemokines in the
pathogenesis of liver disease: So many players with poorly defined
roles. Clin Sci (Lond). 104:47–63. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luan J, Shattuck-Brandt R, Haghnegahdar H,
Owen JD, Strieter R, Burdick M, Nirodi C, Beauchamp D, Johnson KN
and Richmond A: Mechanism and biological significance of
constitutive expression of MGSA/GRO chemokines in malignant
melanoma tumor progression. J Leukoc Biol. 62:588–597. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
See AL, Chong PK, Lu SY and Lim YP: CXCL3
is a potential target for breast cancer metastasis. Curr Cancer
Drug Targets. 14:294–309. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gui SL, Teng LC, Wang SQ, Liu S, Lin YL,
Zhao XL, Liu L, Sui HY, Yang Y, Liang LC, et al: Overexpression of
CXCL3 can enhance the oncogenic potential of prostate cancer. Int
Urol Nephrol. 48:701–709. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li A, Varney ML and Singh RK: Constitutive
expression of growth regulated oncogene (gro) in human colon
carcinoma cells with different metastatic potential and its role in
regulating their metastatic phenotype. Clin Exp Metastasis.
21:571–579. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Farquharson AJ, Steele RJ, Carey FA and
Drew JE: Novel multiplex method to assess insulin, leptin and
adiponectin regulation of inflammatory cytokines associated with
colon cancer. Mol Biol Rep. 39:5727–5736. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kowalczuk O, Burzykowski T, Niklinska WE,
Kozlowski M, Chyczewski L and Niklinski J: CXCL5 as a potential
novel prognostic factor in early stage non-small cell lung cancer:
Results of a study of expression levels of 23 genes. Tumour Biol.
35:4619–4628. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang L, Li H, Ge C, Zhao F, Tian H, Chen
T, Jiang G, Xie H, Cui Y, Yao M, et al: CXCL3 contributes to
CD133(+) CSCs maintenance and forms a positive feedback regulation
loop with CD133 in HCC via Erk1/2 phosphorylation. Sci Rep.
6:274262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fagerberg L, Hallstrom BM, Oksvold P,
Kampf C, Djureinovic D, Odeberg J, Habuka M, Tahmasebpoor S,
Danielsson A, Edlund K, et al: Analysis of the human
tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of
transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics.
13:397–406. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dörsam B, Seiwert N, Foersch S, Stroh S,
Nagel G, Begaliew D, Diehl E, Kraus A, McKeague M, Minneker V, et
al: PARP-1 protects against colorectal tumor induction, but
promotes inflammation-driven colorectal tumor progression. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:E4061–E4070. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
AlDubayan SH, Giannakis M, Moore ND, Han
GC, Reardon B, Hamada T, Mu XJ, Nishihara R, Qian Z, Liu L, et al:
Inherited DNA-repair defects in colorectal cancer. Am J Hum Genet.
102:401–414. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Aggarwal N, Donald ND, Malik S, Selvendran
SS, McPhail MJ and Monahan KJ: The association of low-penetrance
variants in DNA repair genes with colorectal cancer: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 8:e1092017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Soreide K, Buter TC, Janssen EA,
Gudlaugsson E, Skaland I, Korner H and Baak JP: Cell-cycle and
apoptosis regulators (p16INK4A, p21CIP1, beta-catenin, survivin,
and hTERT) and morphometry-defined MPECs predict metachronous
cancer development in colorectal adenoma patients. Cell Oncol.
29:301–313. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Noda M, Okayama H, Kofunato Y, Chida S,
Saito K, Tada T, Ashizawa M, Nakajima T, Aoto K, Kikuchi T, et al:
Prognostic role of FUT8 expression in relation to p53 status in
stage II and III colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 13:e02003152018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wu Y, Li Y, Zhao X, Dong D, Tang C, Li E
and Geng Q: Combined detection of the expression of Nm23-H1 and p53
is correlated with survival rates of patients with stage II and III
colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 13:129–136. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Katkoori VR, Manne U, Chaturvedi LS,
Basson MD, Haan P, Coffey D and Bumpers HL: Functional consequence
of the p53 codon 72 polymorphism in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget.
8:76574–76586. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Howick J, Chalmers I, Glasziou P,
Greenhalgh T, Heneghan C, Liberati A, Moschetti I, Phillips B and
Thornton H: The 2011 Oxford CEBM Levels of Evidence (Introductory
Document). Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine. http://www.cebm.net/index.aspx?o=5653
|