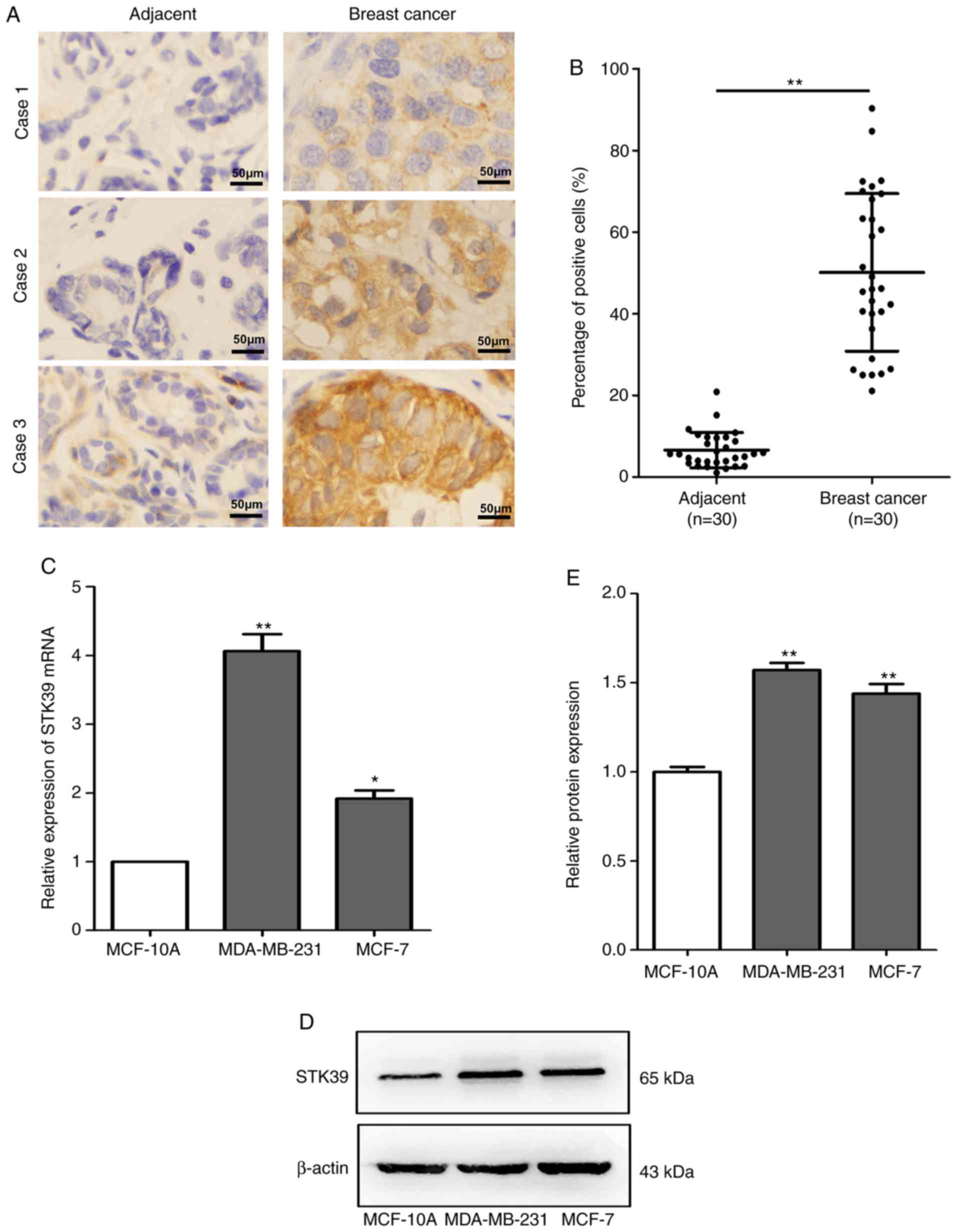
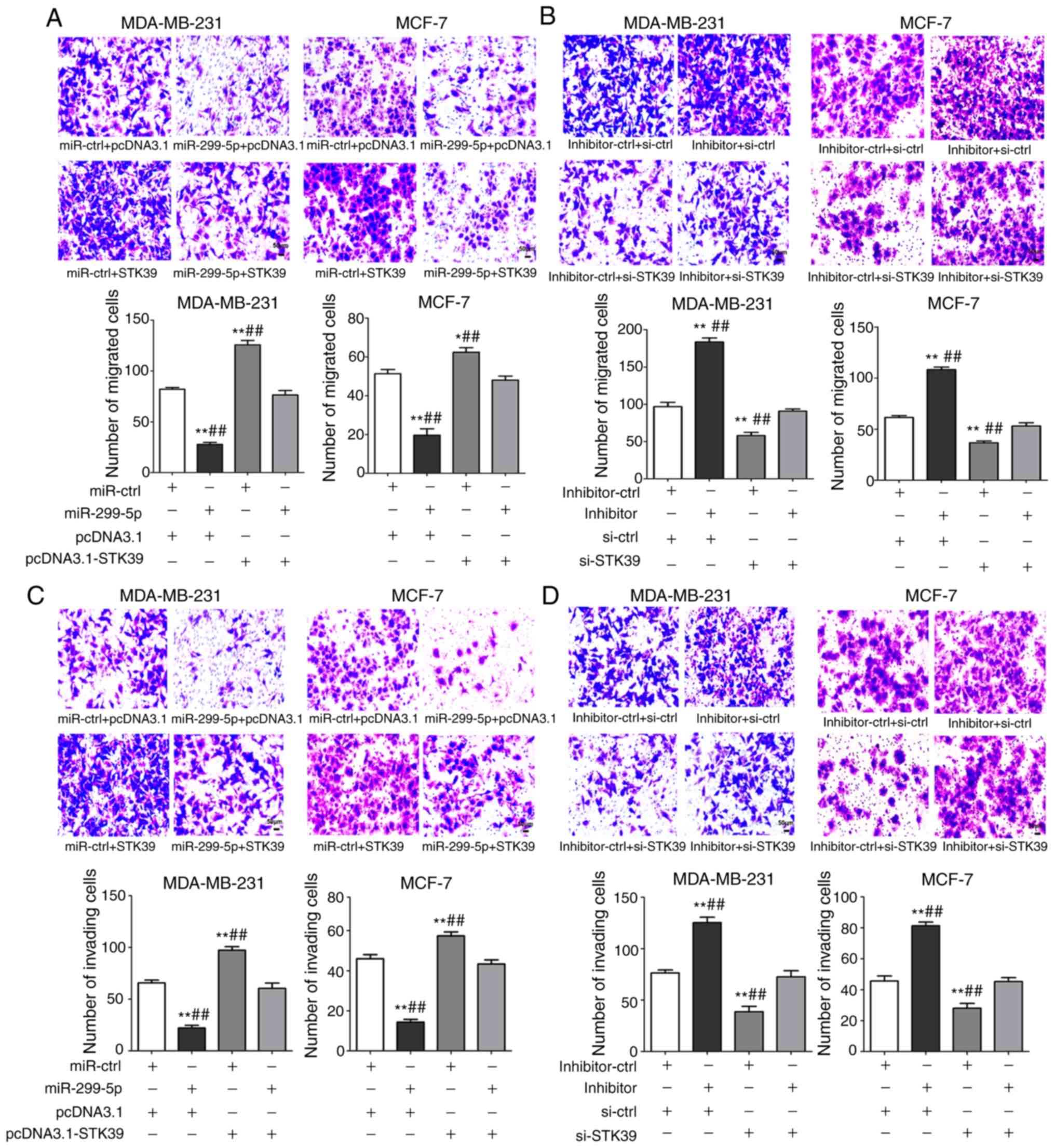
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cardoso F, Costa A, Senkus E, Aapro M,
André F, Barrios CH, Bergh J, Bhattacharyya G, Biganzoli L, Cardoso
MJ, et al: 3rd ESO-ESMO International Consensus Guidelines for
Advanced Breast Cancer (ABC 3). Ann Oncol. 28:31112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chaffer CL, San Juan BP, Lim E and
Weinberg RA: EMT, cell plasticity and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 35:645–654. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pickup MW, Mouw JK and Weaver VM: The
extracellular matrix modulates the hallmarks of cancer. EMBO Rep.
15:1243–1253. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xie F, Hosany S, Zhong S, Jiang Y, Zhang
F, Lin L, Wang X, Gao S and Hu X: MicroRNA-193a inhibits breast
cancer proliferation and metastasis by downregulating WT1. PLoS
One. 12:e01855652017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xue Y, Xu W, Zhao W, Wang W, Zhang D and
Wu P: miR-381 inhibited breast cancer cells proliferation,
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by targeting
CXCR4. Biomed Pharmacother. 86:426–433. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gong Y, He T, Yang L, Yang G, Chen Y and
Zhang X: The role of miR-100 in regulating apoptosis of breast
cancer cells. Sci Rep. 5:116502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Breunig C, Pahl J, Küblbeck M, Miller M,
Antonelli D, Erdem N, Wirth C, Will R, Bott A, Cerwenka A and
Wiemann S: MicroRNA-519a-3p mediates apoptosis resistance in breast
cancer cells and their escape from recognition by natural killer
cells. Cell Death Dis. 8:e29732017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang G, Zhang W, Li B, Stringer-Reasor E,
Chu C, Sun L, Bae S, Chen D, Wei S, Jiao K, et al: MicroRNA-200c
and microRNA-141 are regulated by a FOXP3-KAT2B axis and associated
with tumor metastasis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res.
19:732017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Samaeekia R, Adorno-Cruz V, Bockhorn J,
Chang YF, Huang S, Prat A, Ha N, Kibria G, Huo D, Zheng H, et al:
miR-206 inhibits stemness and metastasis of breast cancer by
targeting MKL1/IL11 pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 23:1091–1103. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen X, Wang YW, Xing AY, Xiang S, Shi DB,
Liu L, Li YX and Gao P: Suppression of SPIN1-mediated PI3K-Akt
pathway by miR-489 increases chemosensitivity in breast cancer. J
Pathol. 239:459–472. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xue J, Chi Y, Chen Y, Huang S, Ye X, Niu
J, Wang W, Pfeffer LM, Shao ZM, Wu ZH and Wu J: MiRNA-621
sensitizes breast cancer to chemotherapy by suppressing FBXO11 and
enhancing p53 activity. Oncogene. 35:448–458. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hammond SM: An overview of microRNAs. Adv
Drug Deliv Rev. 87:3–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bertoli G, Cava C and Castiglioni I:
MicroRNAs: New biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, therapy
prediction and therapeutic tools for breast cancer. Theranostics.
5:1122–1143. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nassar FJ, Nasr R and Talhouk R: MicroRNAs
as biomarkers for early breast cancer diagnosis, prognosis and
therapy prediction. Pharmacol Ther. 172:34–49. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schwarzenbach H, Milde-Langosch K,
Steinbach B, Muller V and Pantel K: Diagnostic potential of
PTEN-targeting miR-214 in the blood of breast cancer patients.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 134:933–941. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Si H, Sun X, Chen Y, Cao Y, Chen S, Wang H
and Hu C: Circulating microRNA-92a and microRNA-21 as novel
minimally invasive biomarkers for primary breast cancer. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 139:223–229. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Benetatos L, Hatzimichael E, Londin E,
Vartholomatos G, Loher P, Rigoutsos I and Briasoulis E: The
microRNAs within the DLK1-DIO3 genomic region: Involvement in
disease pathogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:795–814. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Z, He L, Sun W, Qin Y, Dong W, Zhang
T, Zhang P and Zhang H: miRNA-299-5p regulates estrogen receptor
alpha and inhibits migration and invasion of papillary thyroid
cancer cell. Cancer Manag Res. 10:6181–6193. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peng Y, He X, Chen H, Duan H, Shao B, Yang
F, Li H, Yang P, Zeng Y, Zheng J, et al: Inhibition of
microRNA-299-5p sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomide via
the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Biosci Rep. 38:2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Formosa A, Markert EK, Lena AM, Italiano
D, Finazzi-Agro' E, Levine AJ, Bernardini S, Garabadgiu AV, Melino
G and Candi E: MicroRNAs, miR-154, miR-299-5p, miR-376a, miR-376c,
miR-377, miR-381, miR-487b, miR-485-3p, miR-495 and miR-654-3p,
mapped to the 14q32.31 locus, regulate proliferation, apoptosis,
migration and invasion in metastatic prostate cancer cells.
Oncogene. 33:5173–5182. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
van Schooneveld E, Wouters MC, Van der
Auwera I, Peeters DJ, Wildiers H, Van Dam PA, Vergote I, Vermeulen
PB, Dirix LY and Van Laere SJ: Expression profiling of cancerous
and normal breast tissues identifies microRNAs that are
differentially expressed in serum from patients with (metastatic)
breast cancer and healthy volunteers. Breast Cancer Res.
14:R342012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gallolu Kankanamalage S, Karra AS and Cobb
MH: WNK pathways in cancer signaling networks. Cell Commun Signal.
16:722018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gagnon KB and Delpire E: Molecular
physiology of SPAK and OSR1: Two Ste20-related protein kinases
regulating ion transport. Physiol Rev. 92:1577–1617. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Delpire E and Gagnon KB: SPAK and OSR1:
STE20 kinases involved in the regulation of ion homoeostasis and
volume control in mammalian cells. Biochem J. 409:321–331. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Alessi DR, Zhang J, Khanna A, Hochdorfer
T, Shang Y and Kahle KT: The WNK-SPAK/OSR1 pathway: Master
regulator of cation-chloride cotransporters. Sci Signal. 7:re32014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li Z, Zhu W, Xiong L, Yu X, Chen X and Lin
Q: Role of high expression levels of STK39 in the growth, migration
and invasion of non-small cell type lung cancer cells. Oncotarget.
7:61366–61377. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang T, Zhou Y, Cao Y, Tao J, Zhou ZH and
Hang DH: STK39, overexpressed in osteosarcoma, regulates
osteosarcoma cell invasion and proliferation. Oncol Lett.
14:4599–4604. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao Q, Zhu Y, Liu L, Wang H, Jiang S, Hu
X and Guo J: STK39 blockage by RNA interference inhibits the
proliferation and induces the apoptosis of renal cell carcinoma.
Onco Targets Ther. 11:1511–1519. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Romano G, Veneziano D, Acunzo M and Croce
CM: Small non-coding RNA and cancer. Carcinogenesis. 38:485–491.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rupaimoole R and Slack FJ: MicroRNA
therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and
other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:203–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yan M, Xu H, Waddell N, Shield-Artin K,
Haviv I; kConFab authors, ; McKay MJ and Fox SB: Enhanced RAD21
cohesin expression confers poor prognosis in BRCA2 and BRCAX, but
not BRCA1 familial breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. 14:R692012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shevde LA, Metge BJ, Mitra A, Xi Y, Ju J,
King JA and Samant RS: Spheroid-forming subpopulation of breast
cancer cells demonstrates vasculogenic mimicry via hsa-miR-299-5p
regulated de novo expression of osteopontin. J Cell Mol Med.
14:1693–1706. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dong Q, Zhu X, Dai C, Zhang X, Gao X, Wei
J, Sheng Y, Zheng Y, Yu J, et al: Osteopontin promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma
through regulating vimentin. Oncotarget. 7:12997–13012. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang J, Karimy JK, Delpire E and Kahle
KT: Pharmacological targeting of SPAK kinase in disorders of
impaired epithelial transport. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
21:795–804. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou X, Naguro I, Ichijo H and Watanabe K:
Mitogen-activated protein kinases as key players in osmotic stress
signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1860:2037–2052. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang YT, Heist RS, Chirieac LR, Lin X,
Skaug V, Zienolddiny S, Haugen A, Wu MC, Wang Z, Su L, et al:
Genome-wide analysis of survival in early-stage non-small-cell lung
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:2660–2667. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Stanton SE, Gad E, Corulli LR, Lu H and
Disis ML: Tumor-associated antigens identified early in mouse
mammary tumor development can be effective vaccine targets.
Vaccine. 37:3552–3561. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mao J, Ladd J, Gad E, Rastetter L, Johnson
MM, Marzbani E, Childs JS, Lu H, Dang Y, Broussard E, et al: Mining
the pre-diagnostic antibody repertoire of TgMMTV-neu mice to
identify autoantibodies useful for the early detection of human
breast cancer. J Transl Med. 12:1212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rivenbark AG, O'Connor SM and Coleman WB:
Molecular and cellular heterogeneity in breast cancer: Challenges
for personalized medicine. Am J Pathol. 183:1113–1124. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|