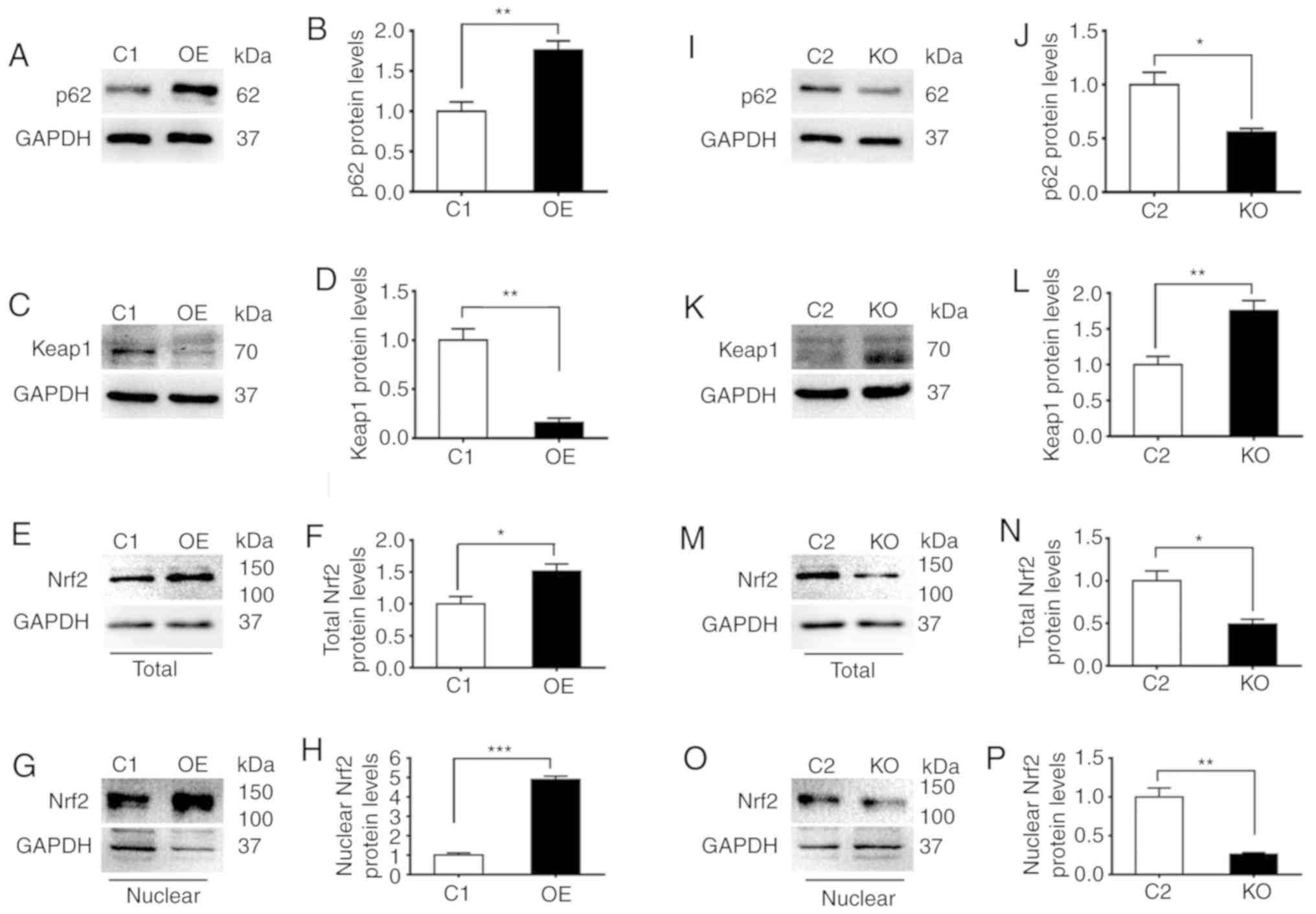
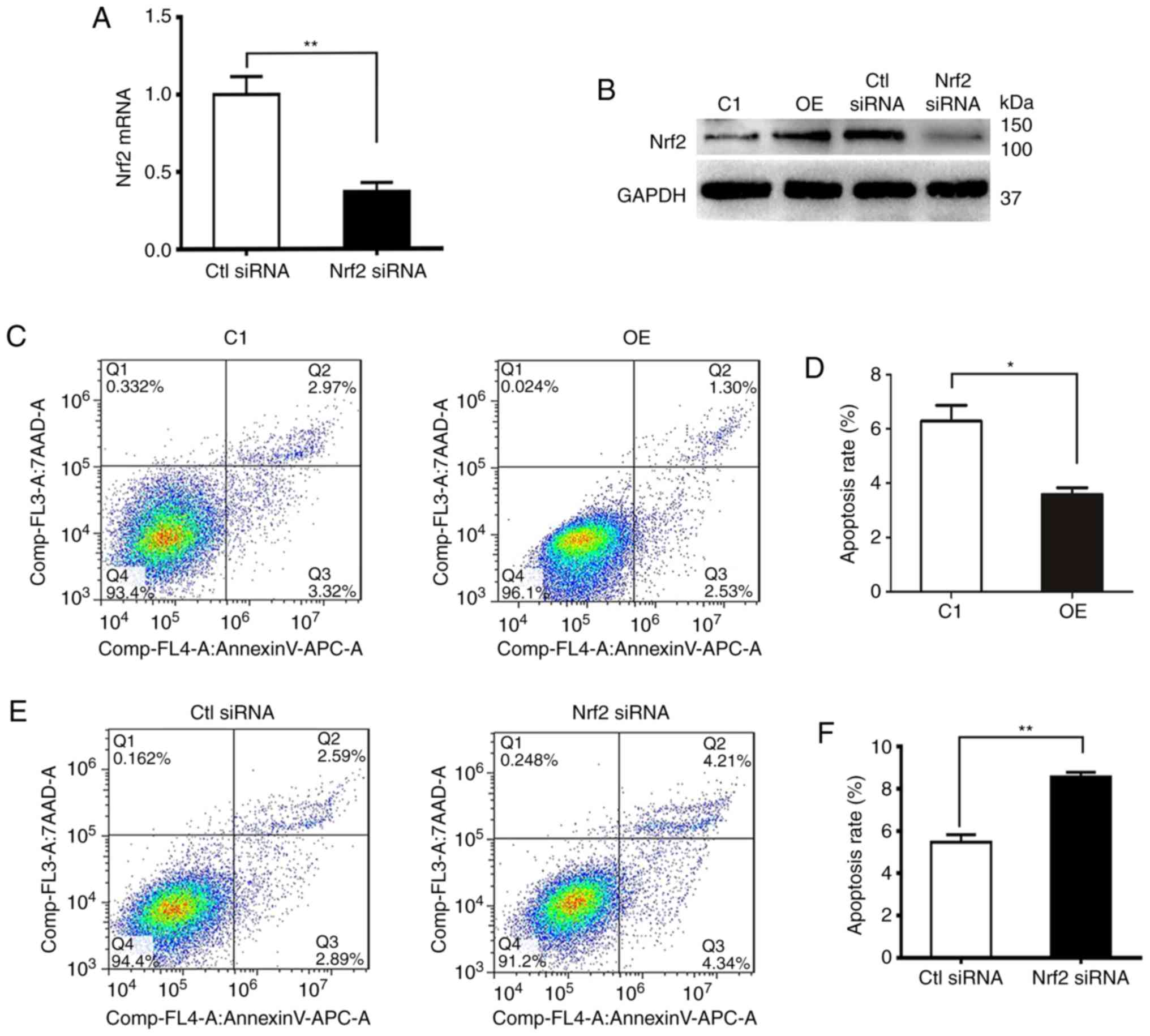
|
1
|
DeSantis CE, Siegel RL, Sauer AG, Miller
KD, Fedewa SA, Alcaraz KI and Jemal A: Cancer statistics for
African Americans, 2016: Progress and opportunities in reducing
racial disparities. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:290–308. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
de Bono JS, Logothetis CJ, Molina A,
Fizazi K, North S, Chu L, Chi KN, Jones RJ, Goodman OB Jr, Saad F,
et al: Abiraterone and increased survival in metastatic prostate
cancer. New Engl J Med. 364:1995–2005. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Scher HI, Fizazi K, Saad F, Taplin ME,
Sternberg CN, Miller K, de Wit R, Mulders P, Chi KN, Shore ND, et
al: Increased survival with enzalutamide in prostate cancer after
chemotherapy. New Engl J Med. 367:1187–1197. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sanchez P, De Carcer G, Sandoval IV,
Moscat J and Diaz-Meco MT: Localization of atypical protein kinase
C isoforms into lysosome-targeted endosomes through interaction
with p62. Mol Cell Biol. 18:3069–3080. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moscat J, Karin M and Diaz-Meco MT: p62 in
Cancer: Signaling Adaptor Beyond Autophagy. Cell. 167:606–609.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jaramillo MC and Zhang DD: The emerging
role of the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway in cancer. Gene Dev.
27:2179–2191. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Suzuki T and Yamamoto M: Molecular basis
of the Keap1-Nrf2 system. Free Rad Biol Med. 88:93–100. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kansanen E, Kuosmanen SM, Leinonen H and
Levonen AL: The Keap1-Nrf2 pathway: Mechanisms of activation and
dysregulation in cancer. Redox Biol. 1:45–49. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
O'Connell MA and Hayes JD: The Keap1/Nrf2
pathway in health and disease: From the bench to the clinic.
Biochem Soc Trans. 43:687–689. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hayes JD and Dinkova-Kostova AT:
Oncogene-stimulated congestion at the KEAP1 stress signaling hub
allows bypass of NRF2 and induction of NRF2-target genes that
promote tumor survival. Can Cell. 32:539–541. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Furukawa M and Xiong Y: BTB protein Keap1
targets antioxidant transcription factor Nrf2 for ubiquitination by
the Cullin 3-Roc1 ligase. Mol Cell Bol. 25:162–171. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
McMahon M, Itoh K, Yamamoto M and Hayes
JD: Keap1-dependent proteasomal degradation of transcription factor
Nrf2 contributes to the negative regulation of antioxidant response
element-driven gene expression. J Biol Chem. 278:21592–21600. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jain A, Lamark T, Sjottem E, Larsen KB,
Awuh JA, Overvatn A, McMahon M, Hayes JD and Johansen T: p62/SQSTM1
is a target gene for transcription factor NRF2 and creates a
positive feedback loop by inducing antioxidant response
element-driven gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 285:22576–22591.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Komatsu M, Kurokawa H, Waguri S, Taguchi
K, Kobayashi A, Ichimura Y, Sou YS, Ueno I, Sakamoto A, Tong KI, et
al: The selective autophagy substrate p62 activates the stress
responsive transcription factor Nrf2 through inactivation of Keap1.
Nat Cell Biol. 12:213–223. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lau A, Wang XJ, Zhao F, Villeneuve NF, Wu
T, Jiang T, Sun Z, White E and Zhang DD: A noncanonical mechanism
of Nrf2 activation by autophagy deficiency: Direct interaction
between Keap1 and p62. Mol Cell Biol. 30:3275–3285. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Inami Y, Waguri S, Sakamoto A, Kouno T,
Nakada K, Hino O, Watanabe S, Ando J, Iwadate M, Yamamoto M, et al:
Persistent activation of Nrf2 through p62 in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol. 193:275–284. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xia M, Yu H, Gu S, Xu Y, Su J, Li H, Kang
J and Cui M: p62/SQSTM1 is involved in cisplatin resistance in
human ovarian cancer cells via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE system. Intern J
Oncol. 45:2341–2348. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang Y, Zhang J, Huang ZH, Huang XH, Zheng
WB, Yin XF, Li YL, Li B and He QY: Isodeoxyelephantopin induces
protective autophagy in lung cancer cells via Nrf2-p62-keap1
feedback loop. Cell Death Dis. 8:e28762017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang L, Kim D, Wise JTF, Shi X, Zhang Z
and DiPaola RS: p62 as a therapeutic target for inhibition of
autophagy in prostate cancer. Prostate. 78:390–400. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang X, Zhong W, Huang H, He H, Jiang F,
Chen Y, Yue F, Zou J, Li X, He Y, et al: Autophagy defects
suggested by low levels of autophagy activator MAP1S and high
levels of autophagy inhibitor LRPPRC predict poor prognosis of
prostate cancer patients. Mol Carcinog. 54:1194–1204. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jiang X, Li X, Huang H, Jiang F, Lin Z, He
H, Chen Y, Yue F, Zou J, He Y, et al: Elevated levels of
mitochondrion-associated autophagy inhibitor LRPPRC are associated
with poor prognosis in patients with prostate cancer. Cancer.
120:1228–1236. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang X, Huang Y, Liang X, Jiang F, He Y,
Li T, Xu G, Zhao H, Yang W, Jiang G, et al: Metastatic prostate
cancer-associated P62 inhibits autophagy flux and promotes
epithelial to mesenchymal transition by sustaining the level of
HDAC6. Prostate. 78:426–434. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kobayashi A, Kang MI, Okawa H, Ohtsuji M,
Zenke Y, Chiba T, Igarashi K and Yamamoto M: Oxidative stress
sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to
regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol Cell Biol.
24:7130–7139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Taguchi K, Motohashi H and Yamamoto M:
Molecular mechanisms of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in stress response
and cancer evolution. Gene Cell. 16:123–140. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Duran A, Linares JF, Galvez AS,
Wikenheiser K, Flores JM, Diaz-Meco MT and Moscat J: The signaling
adaptor p62 is an important NF-kappaB mediator in tumorigenesis.
Can Cell. 13:343–354. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Moscat J and Diaz-Meco MT: p62: A
versatile multitasker takes on cancer. Trend Biochem Sci.
37:230–236. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang DD: Mechanistic studies of the
Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway. Drug Metab Rev. 38:769–789. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ichimura Y, Waguri S, Sou YS, Kageyama S,
Hasegawa J, Ishimura R, Saito T, Yang Y, Kouno T, Fukutomi T, et
al: Phosphorylation of p62 activates the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway during
selective autophagy. Mol Cell. 51:618–631. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lau A, Villeneuve NF, Sun Z, Wong PK and
Zhang DD: Dual roles of Nrf2 in cancer. Pharmacol Res. 58:262–270.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sample A, Zhao B, Wu C, Qian S, Shi X,
Aplin A and He YY: The autophagy receptor adaptor p62 is
Up-regulated by UVA radiation in melanocytes and in melanoma cells.
Photochem Photobiol. 94:432–437. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sena LA and Chandel NS: Physiological
roles of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Mol Cell.
48:158–167. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wiseman H and Halliwell B: Damage to DNA
by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: Role in inflammatory
disease and progression to cancer. Biochem J. 313:17–29. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Trachootham D, Alexandre J and Huang P:
Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: A radical
therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 8:579–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Taguchi K, Fujikawa N, Komatsu M, Ishii T,
Unno M, Akaike T, Motohashi H and Yamamoto M: Keap1 degradation by
autophagy for the maintenance of redox homeostasis. Proce Nat Acad
Sci USA. 109:13561–13566. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kerr F, Sofola-Adesakin O, Ivanov DK,
Gatliff J, Gomez Perez-Nievas B, Bertrand HC, Martinez P, Callard
R, Snoeren I, Cocheme HM, et al: Direct Keap1-Nrf2 disruption as a
potential therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease. PLoS Genet.
13:e10065932017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rodriguez A, Duran A, Selloum M, Champy
MF, Diez-Guerra FJ, Flores JM, Serrano M, Auwerx J, Diaz-Meco MT
and Moscat J: Mature-onset obesity and insulin resistance in mice
deficient in the signaling adapter p62. Cell Metabol. 3:211–222.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Huang J, Duran A, Reina-Campos M, Valencia
T, Castilla EA, Muller TD, Tschop MH, Moscat J and Diaz-Meco MT:
Adipocyte p62/SQSTM1 suppresses tumorigenesis through opposite
regulations of metabolism in adipose tissue and tumor. Can Cell.
33:770–784.e776. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Huo L, Su Y, Xu G, Zhai L and Zhao J:
Sulforaphane protects the male reproductive system of mice from
obesity-induced damage: Involvement of oxidative stress and
autophagy. Intern J Environ Res Public Health. 16(pii): E37592019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ebato C, Uchida T, Arakawa M, Komatsu M,
Ueno T, Komiya K, Azuma K, Hirose T, Tanaka K, Kominami E, et al:
Autophagy is important in islet homeostasis and compensatory
increase of beta cell mass in response to high-fat diet. Cell
Metabol. 8:325–332. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yamada M, Iwata M, Warabi E, Oishi H, Lira
VA and Okutsu M: p62/SQSTM1 and Nrf2 are essential for
exercise-mediated enhancement of antioxidant protein expression in
oxidative muscle. FASEB J. 33:8022–8032. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|