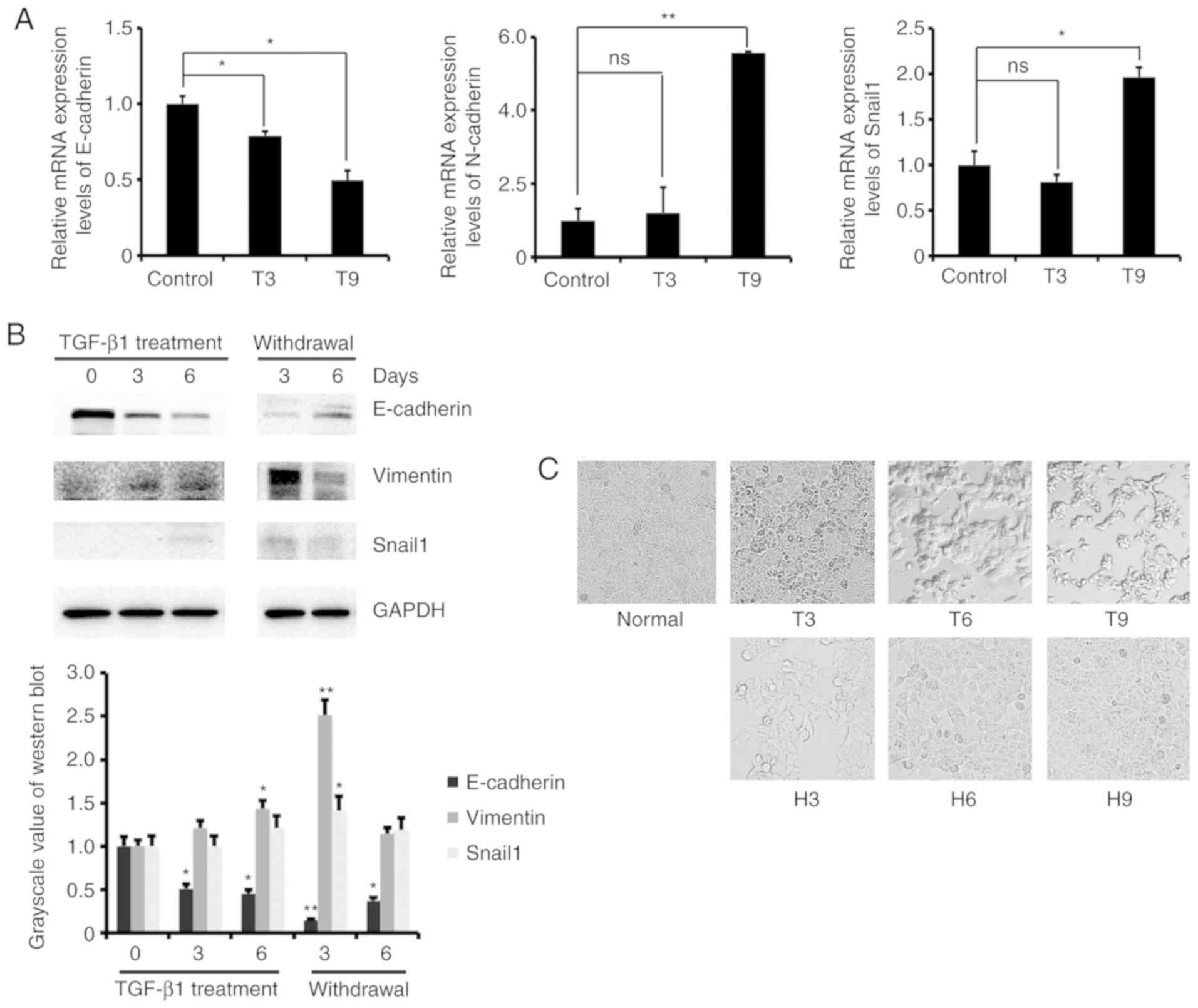
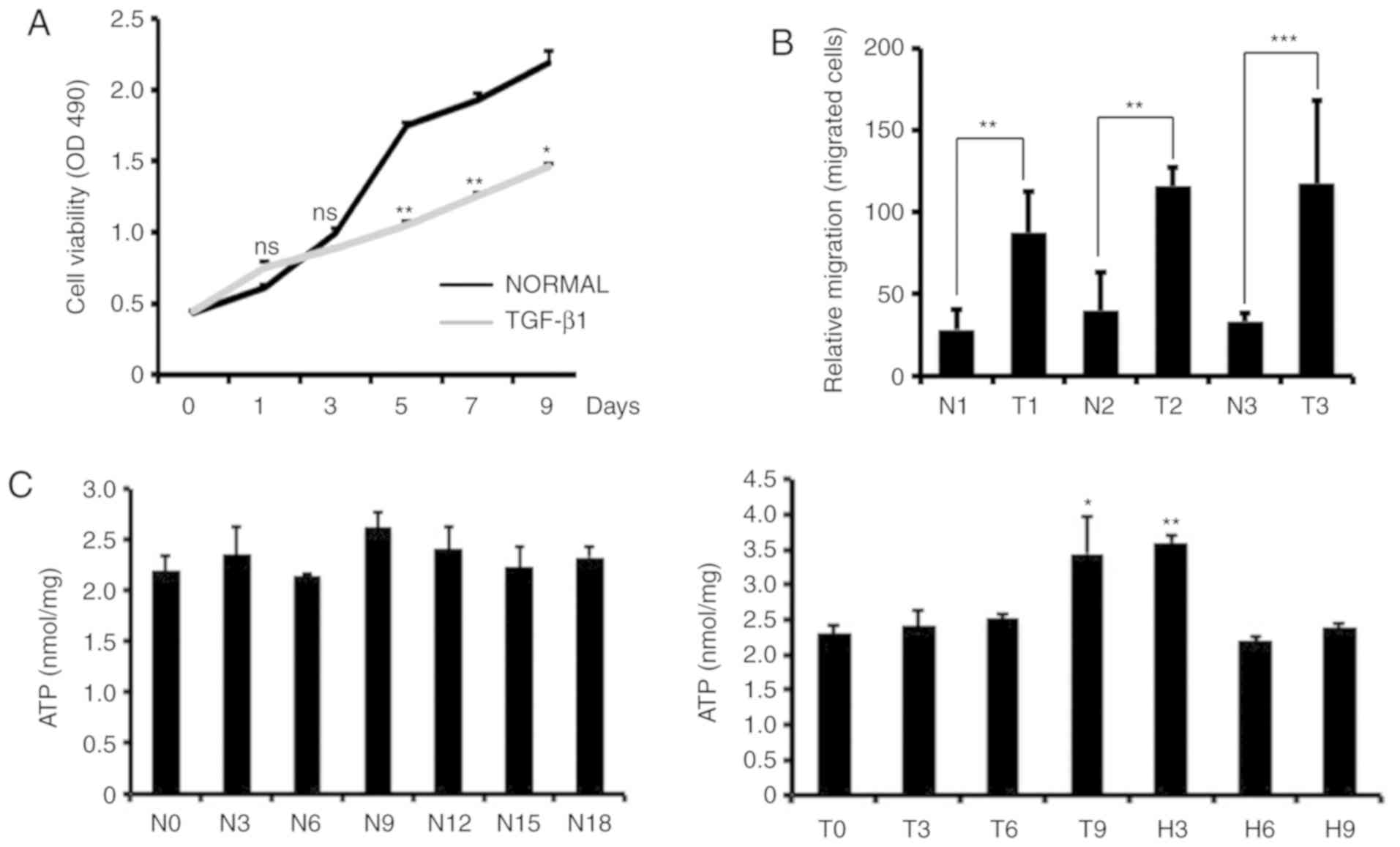
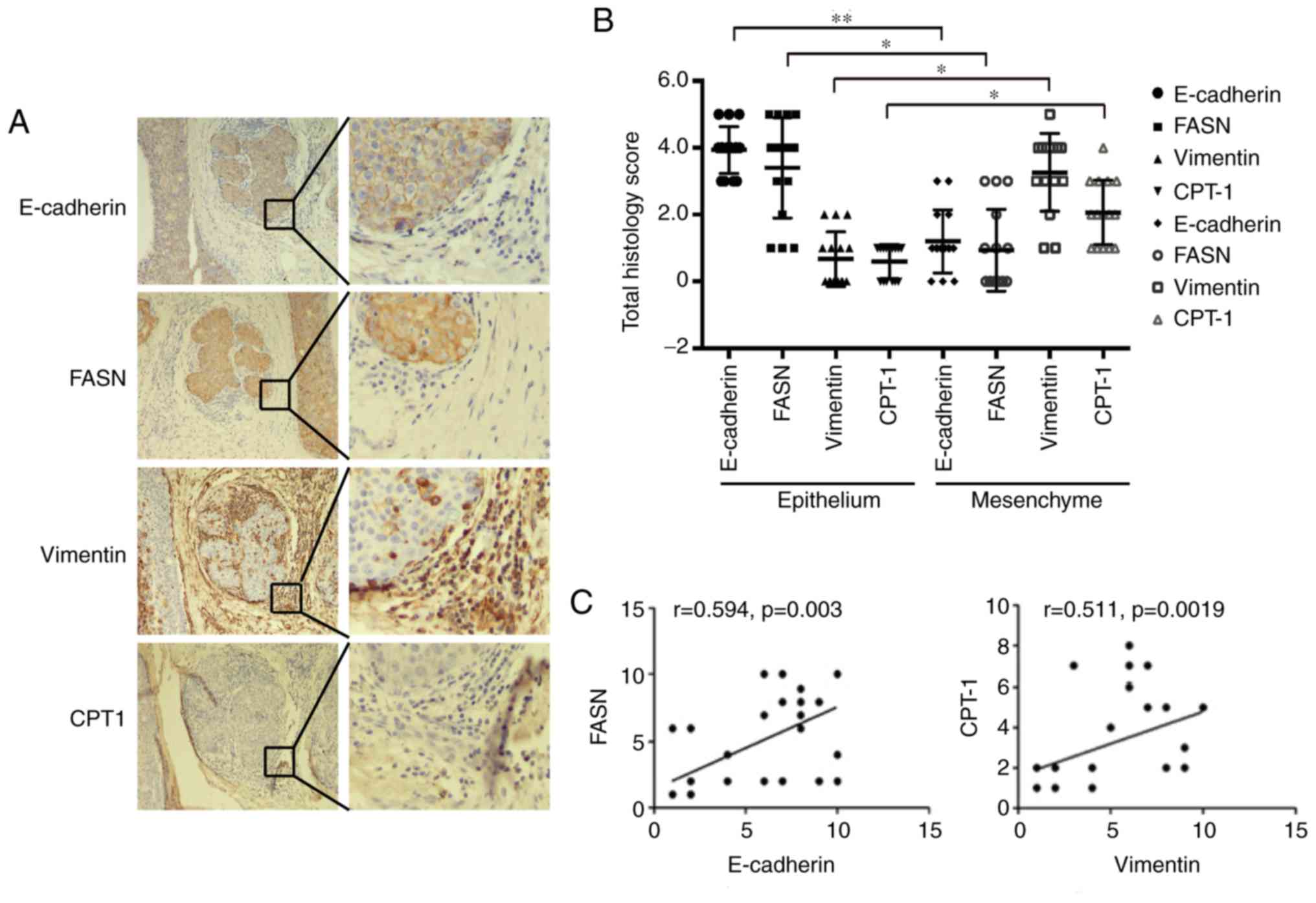
|
1
|
Anastasiadi Z, Lianos GD, Ignatiadou E,
Harissis HV and Mitsis M: Breast cancer in young women: An
overview. Updates Surg. 69:313–317. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Medeiros B and Allan AL: Molecular
mechanisms of breast cancer metastasis to the lung: Clinical and
experimental perspectives. Int J Mol Sc. 20:22722019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Siegel PM, Bos PD, Shu
W, Giri DD, Viale A, Olshen AB, Gerald WL and Massagué J: Genes
that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature. 436:518–524.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hu J, Li G, Zhang P, Zhuang X and Hu G: A
CD44v+ subpopulation of breast cancer stem-like cells
with enhanced lung metastasis capacity. Cell Death Dis.
8:e26792017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu X, Yan Q, Wang Y and Dong X: NTN4 is
associated with breast cancer metastasis via regulation of
EMT-related biomarkers. Oncol Rep. 37:449–457. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pastushenko I, Brisebarre A, Sifrim A,
Fioramonti M, Revenco T, Boumahdi S, Van Keymeulen A, Brown D,
Moers V, Lemaire S, et al: Identification of the tumour transition
states occurring during EMT. Nature. 556:463–468. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nieto MA, Huang RY, Jackson RA and Thiery
JP: EMT: 2016. Cell. 166:21–45. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ungefroren H, Witte D and Lehnert H: The
role of small GTPases of the Rho/Rac family in TGF-β-induced EMT
and cell motility in cancer. Dev Dyn. 247:451–461. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu FL, Mo EP, Yang L, Du J, Wang HS,
Zhang H, Kurihara H, Xu J and Cai SH: Autophagy is involved in
TGF-β1-induced protective mechanisms and formation of
cancer-associated fibroblasts phenotype in tumor microenvironment.
Oncotarget. 7:4122–4141. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang R and Zong X: Aberrant cancer
metabolism in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer
metastasis: Mechanisms in cancer progression. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 115:13–22. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen XL, Lei L, Hong LL and Ling ZQ:
Potential role of NDRG2 in reprogramming cancer metabolism and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Histol Histopathol.
33:655–663. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tan TZ, Miow QH, Miki Y, Noda T, Mori S,
Huang RY and Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition spectrum
quantification and its efficacy in deciphering survival and drug
responses of cancer patients. EMBO Mol Med. 6:1279–1293. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Syed V: TGF-β Signaling in Cancer. J Cell
Biochem. 117:1279–1287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim I and He YY: Targeting the
AMP-activated protein kinase for cancer prevention and therapy.
Front Oncol. 3:1752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chiarugi P and Cirri P: Metabolic
exchanges within tumor microenvironment. Cancer Lett. 380:272–280.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gouirand V, Guillaumond F and Vasseur S:
Influence of the tumor microenvironment on cancer cells metabolic
reprogramming. Front Oncol. 8:1172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cheng S, Wang G, Wang Y, Cai L, Qian K, Ju
L, Liu X, Xiao Y and Wang X: Fatty acid oxidation inhibitor
etomoxir suppresses tumor progression and induces cell cycle arrest
via PPARγ-mediated pathway in bladder cancer. Clin Sci (Lond).
133:1745–1758. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen RR, Yung MMH, Xuan Y, Zhan S, Leung
LL, Liang RR, Leung THY, Yang H, Xu D, Sharma R, et al: Targeting
of lipid metabolism with a metabolic inhibitor cocktail eradicates
peritoneal metastases in ovarian cancer cells. Commun Biol.
2:2812019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li J, Condello S, Thomes-Pepin J, Ma X,
Xia Y, Hurley TD, Matei D and Cheng JX: Lipid desaturation is a
metabolic marker and therapeutic target of ovarian cancer stem
cells. Cell Stem Cell. 20:303–314.e5. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Klein M, Seeger P, Schuricht B, Alper SL
and Schwab A: Polarization of Na(+)/H(+) and Cl(−)/HCO (3)(−)
exchangers in migrating renal epithelial cells. J Gen Physiol.
115:599–608. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lagana A, Vadnais J, Le PU, Nguyen TN,
Laprade R, Nabi IR and Noël J: Regulation of the formation of tumor
cell pseudopodia by the Na(+)/H(+) exchanger NHE1. J Cell Sc.
113:3649–3662. 2000.
|
|
22
|
Fan FT, Shen CS, Tao L, Tian C, Liu ZG,
Zhu ZJ, Liu YP, Pei CS, Wu HY, Zhang L, et al: PKM2 regulates
hepatocellular carcinoma cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
migration upon EGFR activation. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:1961–1970. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Arseneault R, Chien A, Newington JT,
Rappon T, Harris R and Cumming RC: Attenuation of LDHA expression
in cancer cells leads to redox-dependent alterations in
cytoskeletal structure and cell migration. Cancer Lett.
338:255–266. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu X, Wang X, Zhang J, Lam EK, Shin VY,
Cheng AS, Yu J, Chan FK, Sung JJ and Jin HC: Warburg effect
revisited: An epigenetic link between glycolysis and gastric
carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 29:442–450. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang L, Hou Y, Yuan J, Tang S, Zhang H,
Zhu Q, Du YE, Zhou M, Wen S, Xu L, et al: Twist promotes
reprogramming of glucose metabolism in breast cancer cells through
PI3K/AKT and p53 signaling pathways. Oncotarget. 6:25755–25769.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hardie DG, Schaffer BE and Brunet A: AMPK:
An energy-sensing pathway with multiple inputs and outputs. Trends
Cell Biol. 26:190–201. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Carling D: AMPK signalling in health and
disease. Current opinion in cell biology. 45:31–37. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu Y, Sarkissyan M, McGhee E, Lee S and
Vadgama JV: Combined inhibition of glycolysis and AMPK induces
synergistic breast cancer cell killing. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
151:529–539. 2015.
|
|
29
|
Liu X, Chhipa RR, Nakano I and Dasgupta B:
The AMPK inhibitor compound C is a potent AMPK-independent
antiglioma agent. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:596–605. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mauro L, Naimo GD, Gelsomino L, Malivindi
R, Bruno L, Pellegrino M, Tarallo R, Memoli D, Weisz A, Panno ML
and Andò S: Uncoupling effects of estrogen receptor alpha on
LKB1/AMPK interaction upon adiponectin exposure in breast cancer.
FASEB J. 32:4343–4355. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|