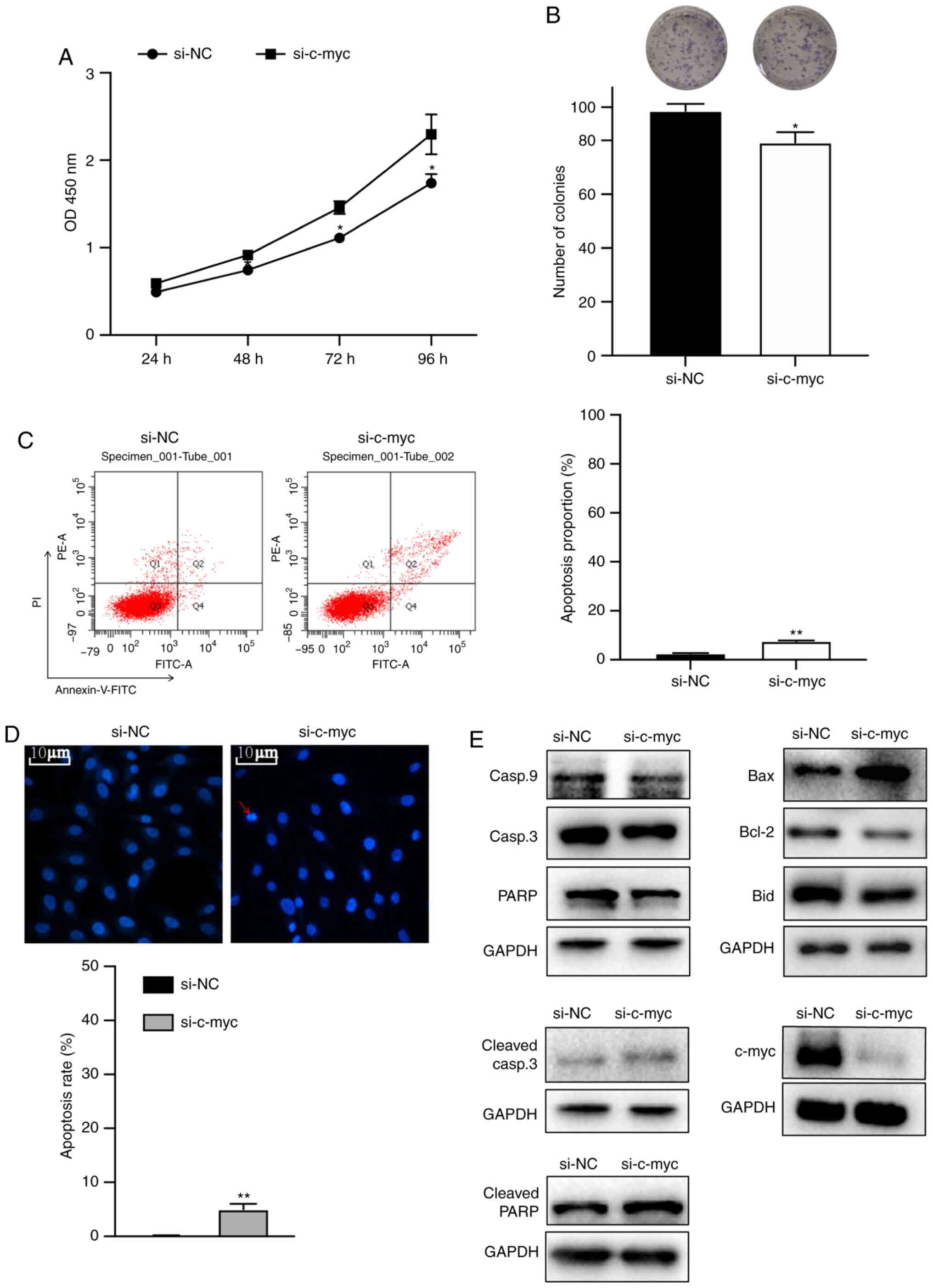
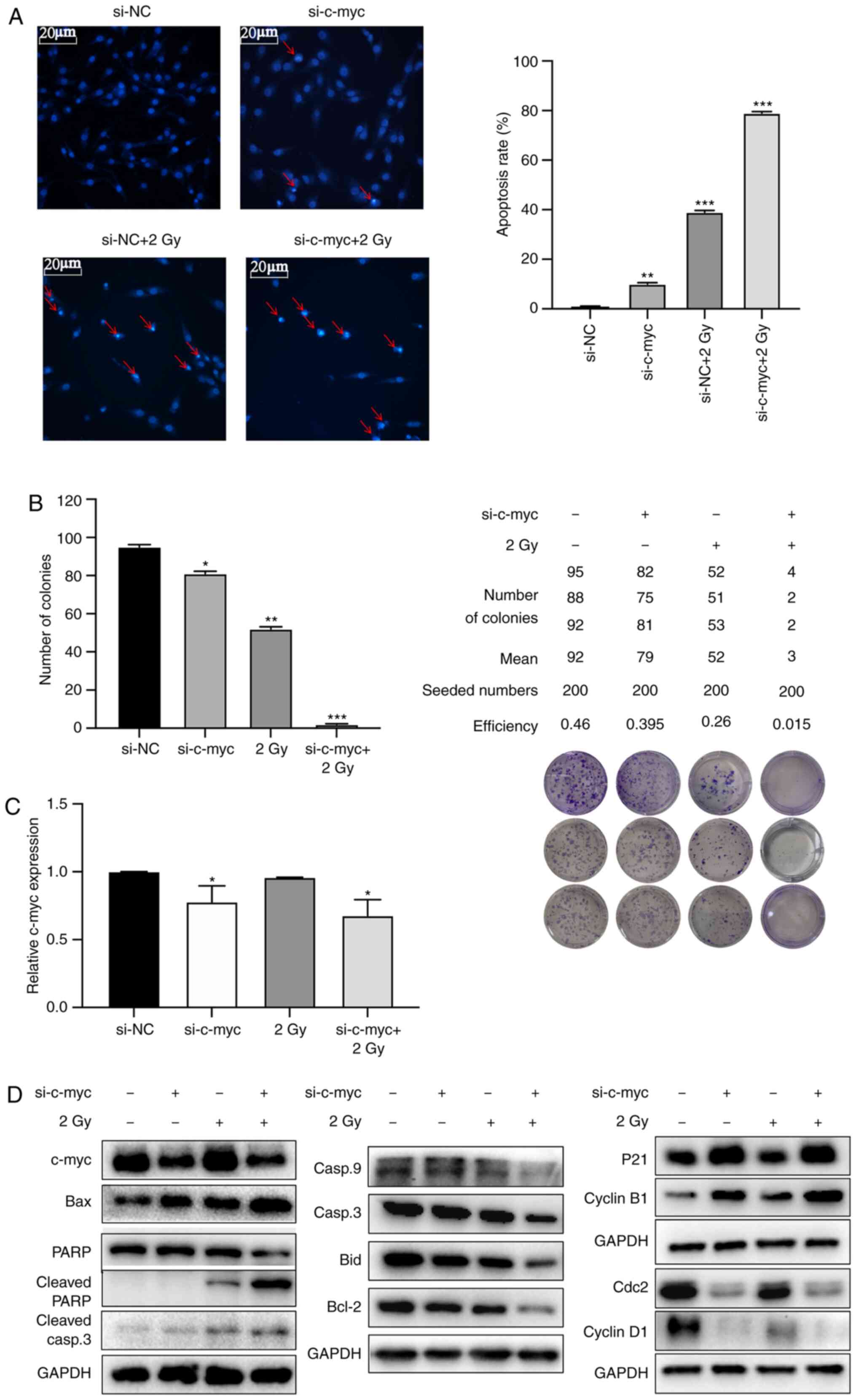
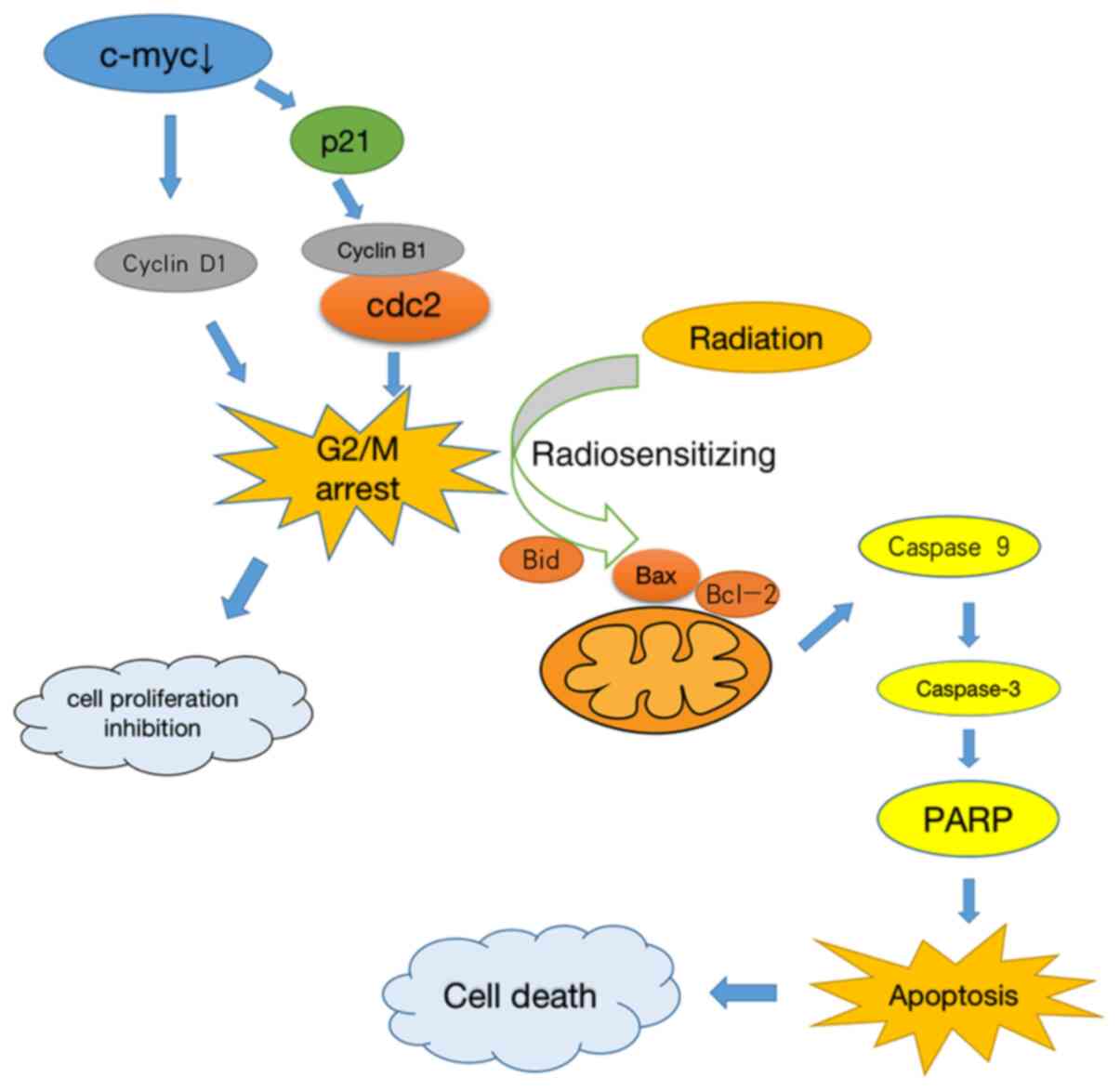
|
1
|
Kansara M, Teng MW, Smyth MJ and Thomas
DM: Translational biology of osteosarcoma. Nat Rev Cancer.
14:722–735. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kager L, Tamamyan G and Bielack S: Novel
insights and therapeutic interventions for pediatric osteosarcoma.
Future Oncol. 13:357–368. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kelleher FC and O'Sullivan H: Monocytes,
macrophages, and osteoclasts in osteosarcoma. J Adolesc Young Adult
Oncol. 6:396–405. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ferrari S, Mercuri M and Bacci G: Comment
on ‘Prognostic factors in high-grade osteosarcoma of the
extremities or trunk: An analysis of 1,702 patients treated on
neoadjuvant Cooperative Osteosarcoma Study Group protocols’. J Clin
Oncol. 20:2910–2911. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bishop MW, Janeway KA and Gorlick R:
Future directions in the treatment of osteosarcoma. Curr Opin
Pediatr. 28:26–33. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bugris V, Harmat V, Ferenc G, Brockhauser
S, Carmichael I and Garman EF: Radiation-damage investigation of a
DNA 16-mer. J Synchrotron Radiat. 26:998–1009. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li QC, Xu H, Wang X, Wang T and Wu J:
miR-34a increases cisplatin sensitivity of osteosarcoma cells in
vitro through up-regulation of c-Myc and Bim signal. Cancer
Biomark. 21:135–144. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Macaeva E, Saeys Y, Tabury K, Janssen A,
Michaux A, Benotmane MA, De Vos WH, Baatout S and Quintens R:
Radiation-induced alternative transcription and splicing events and
their applicability to practical biodosimetry. Sci Rep.
6:192512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cruse MJ, Kucharik CJ and Norman JM: Using
a simple apparatus to measure direct and diffuse photosynthetically
active radiation at remote locations. PLoS One. 10:e01156332015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li S, Hu T, Yuan T, Cheng D and Yang Q:
Nucleoside diphosphate kinase B promotes osteosarcoma proliferation
through c-Myc. Cancer Biol Ther. 19:565–572. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Machak GN, Tkachev SI, Solovyev YN,
Sinyukov PA, Ivanov SM, Kochergina NV, Ryjkov AD, Tepliakov VV,
Bokhian BY and Glebovskaya VV: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy and local
radiotherapy for high-grade osteosarcoma of the extremities. Mayo
Clin Proc. 78:147–155. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cartee L, Vrana JA, Wang Z, Park JS,
Birrer M, Fisher PB, Grant S and Dent P: Inhibition of the mitogen
activated protein kinase pathway potentiates radiation-induced cell
killing via cell cycle arrest at the G2/M transition and
independently of increased signaling by the JNK/c-Jun pathway. Int
J Oncol. 16:413–422. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Noh HJ, Koh DI, Lee KO, Jeon BN, Kim MK,
Snead ML and Hur MW: Role of MIZ-1 in AMELX gene expression.
Biochem Biophys Rep. 8:340–345. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bédard M, Maltais L, Montagne M and
Lavigne P: Miz-1 and Max compete to engage c-Myc: Implication for
the mechanism of inhibition of c-Myc transcriptional activity by
Miz-1. Proteins. 85:199–206. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Licchesi JD, Van Neste L, Tiwari VK, Cope
L, Lin X, Baylin SB and Herman JG: Transcriptional regulation of
Wnt inhibitory factor-1 by Miz-1/c-Myc. Oncogene. 29:5923–5934.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Concin N, Stimpfl M, Zeillinger C, Wolff
U, Hefler L, Sedlak J, Leodolter S and Zeillinger R: Role of p53 in
G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in response to
gamma-irradiation in ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Int J Oncol.
22:51–57. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Suen DF, Norris KL and Youle RJ:
Mitochondrial dynamics and apoptosis. Genes Dev. 22:1577–1590.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen BJ, Wu YL, Tanaka Y and Zhang W:
Small molecules targeting c-Myc oncogene: Promising Anti-cancer
therapeutics. Int J Biol Sci. 10:1084–1096. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee JA, Paik EK, Seo J, Kim DH, Lim JS,
Yoo JY and Kim MS: Radiotherapy and gemcitabine-docetaxel
chemotherapy in children and adolescents with unresectable
recurrent or refractory osteosarcoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 46:138–143.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya
SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi BVSK and
Varambally S: UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene
expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 19:649–658. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Unni KK and Dahlin DC: Osteosarcoma:
Pathology and classification. Semin Roentgenol. 24:143–152. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim E, Kim MS, Lee KH, Sai S, Jeong YK,
Koh JS and Kong CB: Effect of low- and high-linear energy transfer
radiation on in vitro and orthotopic in vivo models
of osteosarcoma by activation of caspase-3 and −9. Int J Oncol.
51:1124–1134. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Miyata H, Doki Y, Yamamoto H, Kishi K,
Takemoto H, Fujiwara Y, Yasuda T, Yano M, Inoue M, Shiozaki H, et
al: Overexpression of CDC25B overrides radiation-induced G2-M
arrest and results in increased apoptosis in esophageal cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 61:3188–3193. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fei H, Zhou Y, Li R, Yang M, Ma J and Wang
F: HBXIP, a binding protein of HBx, regulates maintenance of the
G2/M phase checkpoint induced by DNA damage and enhances
sensitivity to doxorubicin-induced cytotoxicity. Cell Cycle.
16:468–476. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li YX, Weber-Johnson K, Sun LQ, Paschoud
N, Mirimanoff RO and Coucke PA: Effect of pentoxifylline on
radiation-induced G2-phase delay and radiosensitivity of human
colon and cervical cancer cells. Radiat Res. 149:338–342. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cui F, Hou J, Huang C, Sun X, Zeng Y,
Cheng H, Wang H and Li C: C-Myc regulates radiation-induced G2/M
cell cycle arrest and cell death in human cervical cancer cells. J
Obstet Gynaecol Res. 43:729–735. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang Y, Xue K, Li Z, Zheng W, Dong W, Song
J, Sun S, Ma T and Li W: c-Myc regulates the CDK1/cyclin B1
dependent-G2/M cell cycle progression by histone H4 acetylation in
Raji cells. Int J Mol Med. 41:3366–3378. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shang Y: LncRNA THOR acts as a
retinoblastoma promoter through enhancing the combination of c-myc
mRNA and IGF2BP1 protein. Biomed Pharmacother. 106:1243–1249. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A,
Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork
P, et al: STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with
increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide
experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D607–D613. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Group NP: Translocations involving c-myc
and c-myc function. Oncogene. 20:5595–5610. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Androutsopoulos V and Spandidos D:
Anticancer pyridines induce G2/M arrest and apoptosis via p53 and
JNK upregulation in liver and breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
39:519–524. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nurse P: Universal control mechanism
regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 344:503–508. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Charrier-Savournin FB, Château MT, Gire V,
Sedivy J, Piette J and Dulic V: p21-mediated nuclear retention of
Cyclin B1-Cdk1 in response to Genotoxic Stress. Molr Biol Cell.
15:3965–3976. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Dang C: MYC on the path to cancer. Cell.
149:22–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang H, Zhang C and Wu D: Activation of
insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor regulates the
radiation-induced lung cancer cell apoptosis. Immunobiology.
220:1136–1140. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Speidel D: Transcription-independent p53
apoptosis: An alternative route to death. Trends in Cell Biology.
20:14–24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen W, Liu Q, Fu B, Liu K and Jiang W:
Overexpression of GRIM-19 accelerates radiation-induced
osteosarcoma cells apoptosis by p53 stabilization. Life Sci.
208:232–238. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|