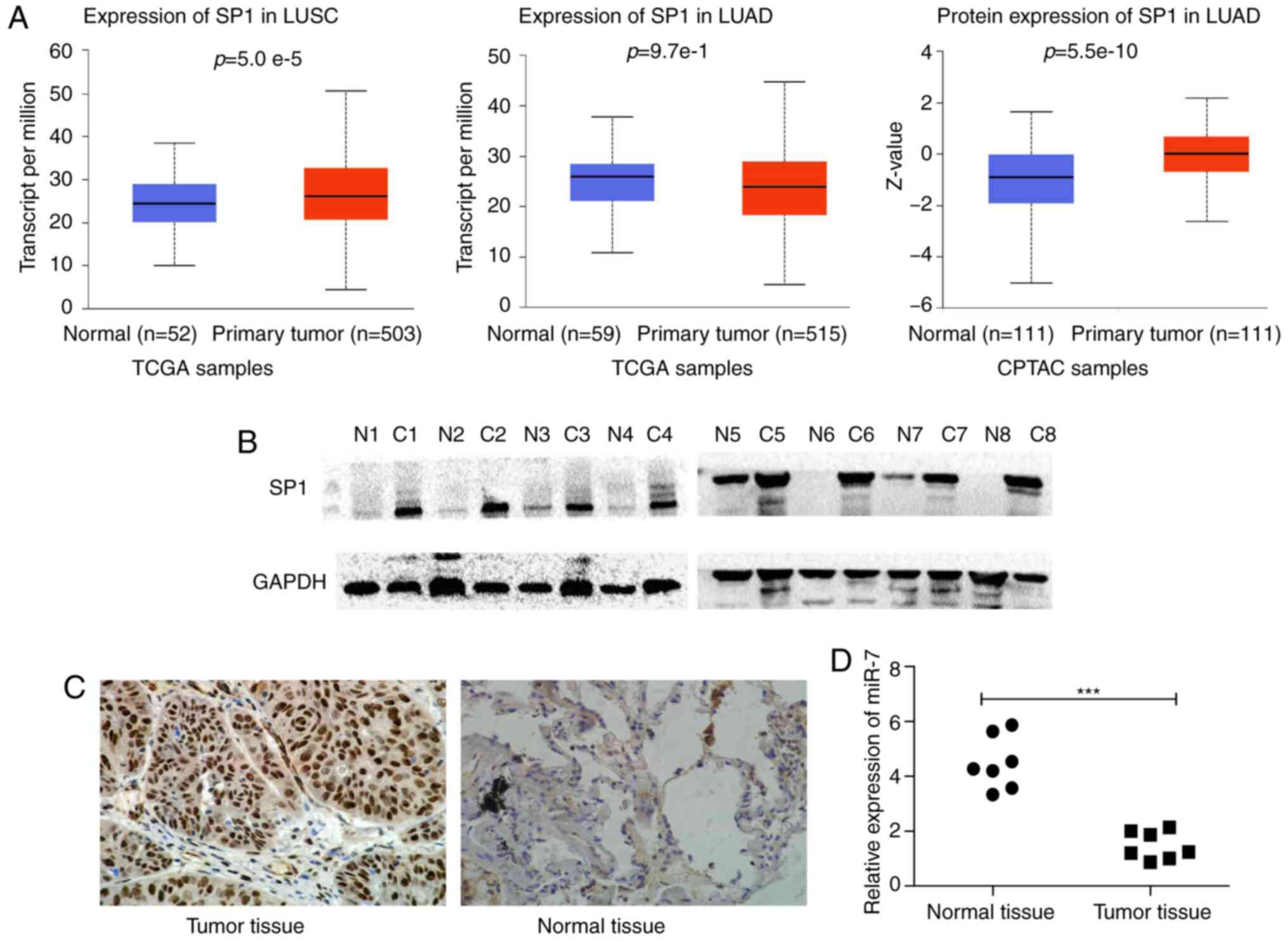
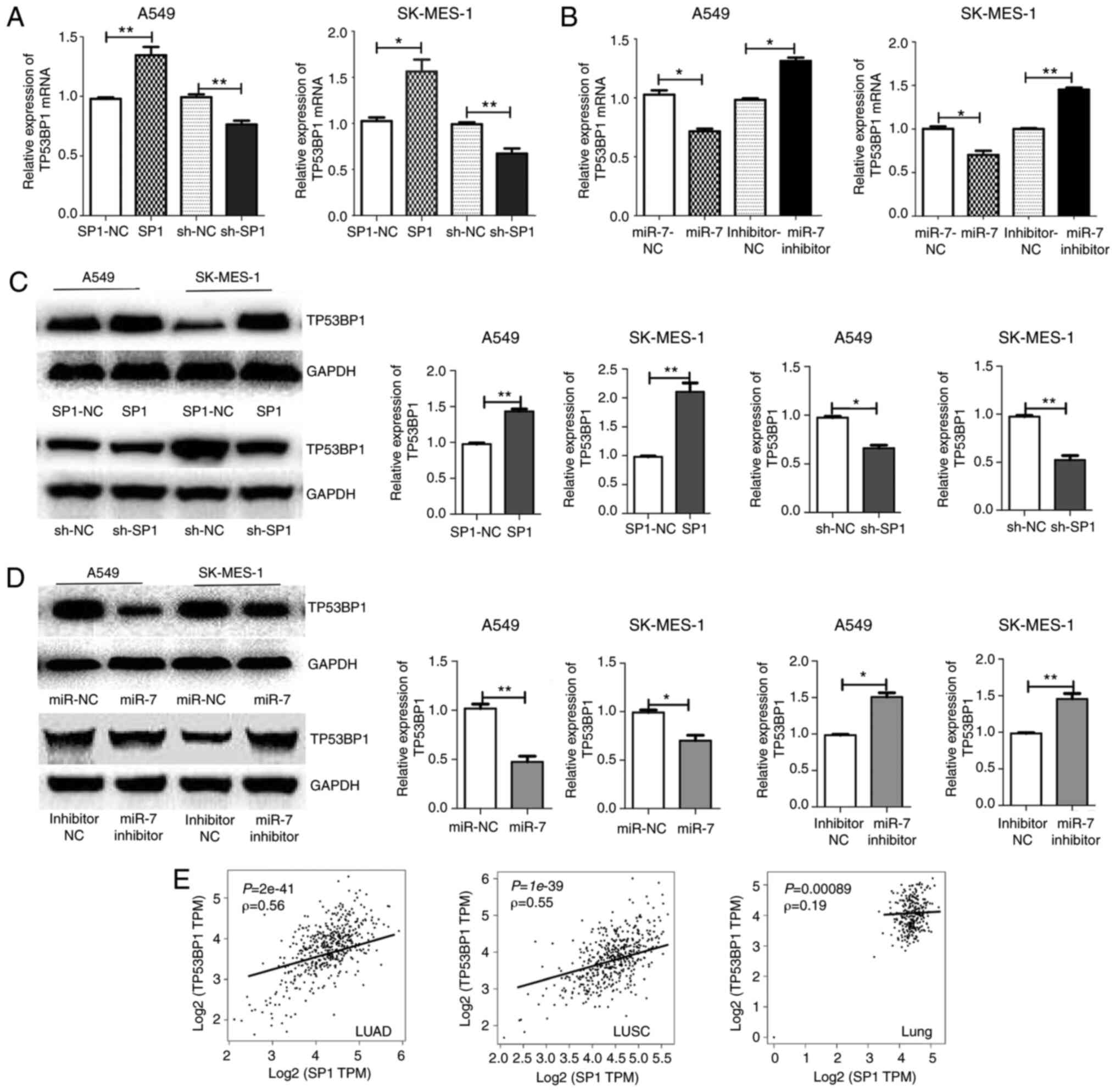
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Koh PK, Faivre-Finn C, Blackhall FH and De
Ruysscher D: Targeted agents in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC):
Clinical developments and rationale for the combination with
thoracic radiotherapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 38:626–640. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen K and Rajewsky N: The evolution of
gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Nat Rev
Genet. 8:93–103. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Redis RS, Berindan-Neagoe I, Pop VI and
Calin GA: Non-coding RNAs as theranostics in human cancers. J Cell
Biochem. 113:1451–1459. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cherni I and Weiss GJ: miRNAs in lung
cancer: Large roles for small players. Future Oncol. 7:1045–1055.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xiong S, Zheng Y, Jiang P, Liu R, Liu X,
Qian J, Gu J, Chang L, Ge D and Chu Y: PA28gamma emerges as a novel
functional target of tumour suppressor microRNA-7 in non-small-cell
lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 110:353–362. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Su C, Han Y, Zhang H, Li Y, Yi L, Wang X,
Zhou S, Yu D, Song X, Xiao N, et al: CiRS-7 targeting miR-7
modulates the progression of non-small cell lung cancer in a manner
dependent on NF-κB signalling. J Cell Mol Med. 22:3097–3107. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee KM, Choi EJ and Kim IA: microRNA-7
increases radiosensitivity of human cancer cells with activated
EGFR-associated signaling. Radiother Oncol. 101:171–176. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yano S, Kondo K, Yamaguchi M, Richmond G,
Hutchison M, Wakeling A, Averbuch S and Wadsworth P: Distribution
and function of EGFR in human tissue and the effect of EGFR
tyrosine kinase inhibition. Anticancer Res. 23:3639–3650.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Beishline K, Kelly CM, Olofsson BA, Koduri
S, Emrich J, Greenberg RA and Azizkhan-Clifford J: Sp1 facilitates
DNA double-strand break repair through a nontranscriptional
mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 32:3790–3799. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Olofsson BA, Kelly CM, Kim J, Hornsby SM
and Azizkhan-Clifford J: Phosphorylation of Sp1 in response to DNA
damage by ataxia telangiectasia-mutated kinase. Mol Cancer Res.
5:1319–1330. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Iwahori S, Yasui Y, Kudoh A, Sato Y,
Nakayama S, Murata T, Isomura H and Tsurumi T: Identification of
phosphorylation sites on transcription factor Sp1 in response to
DNA damage and its accumulation at damaged sites. Cell Signal.
20:1795–1803. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Luo J, Wang X, Xia Z, Yang L, Ding Z, Chen
S, Lai B and Zhang N: Transcriptional factor specificity protein 1
(SP1) promotes the proliferation of glioma cells by up-regulating
midkine (MDK). Mol Biol Cell. 26:430–439. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang WJ, Song MJ, Park EY, Lee JJ, Park
JH, Park K, Park JH and Kim HP: Transcription factors Sp1 and Sp3
regulate expression of human ABCG2 gene and chemoresistance
phenotype. Mol Cells. 36:368–375. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schultz LB, Chehab NH, Malikzay A and
Halazonetis TD: P53 binding protein 1 (53bp1) is an early
participant in the cellular response to DNA double-strand breaks. J
Cell Biol. 151:1381–1390. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rappold I, Iwabuchi K, Date T and Chen J:
Tumor suppressor p53 binding protein 1 (53BP1) is involved in DNA
damage-signaling pathways. J Cell Biol. 153:613–620. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang XX, Ma M, Sang MX, Zhang XY, Liu ZK,
Song H and Zhu SC: BMI-1 suppression increases the radiosensitivity
of oesophageal carcinoma via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncol
Rep. 39:667–678. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wingender E, Schoeps T, Haubrock M, Krull
M and Dönitz J: TFClass: Expanding the classification of human
transcription factors to their mammalian orthologs. Nucleic Acids
Res. 46:D343–D347. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kay FU, Kandathil A, Batra K, Saboo SS,
Abbara S and Rajiah P: Revisions to the tumor, node, metastasis
staging of lung cancer (8th edition): Rationale, radiologic
findings and clinical implications. World J Radiol. 9:269–279.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Travis WD: The 2015 WHO classification of
lung tumors. Pathologe. 35 (Suppl 2):1882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya
SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi BVSK and
Varambally S: UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene
expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 19:649–658. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:W98–W102.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen K and Rajewsky N: Natural selection
on human microRNA binding sites inferred from SNP data. Nat Genet.
38:1452–1456. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rehmsmeier M, Steffen P, Hochsmann M and
Giegerich R: Fast and effective prediction of microRNA/target
duplexes. RNA. 10:1507–1517. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS and
Sander C: The microRNA.org resource: Targets and expression.
Nucleic Acids Res. 36:D149–D153. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, van Dongen
S, Bateman A and Enright AJ: miRBase: MicroRNA sequences, targets
and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:D140–D144. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cui X, Xiao D, Cui Y and Wang X:
Exosomes-derived long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reduces laryngeal
cancer radiosensitivity by regulating microRNA-454-3p/E2F2 axis.
Onco Targets Ther. 12:10827–10839. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Du M, Wang J, Chen H, Wang S, Chen L, Xu
Y, Su F and Lu X: MicroRNA-200a suppresses migration and invasion
and enhances the radiosensitivity of NSCLC cells by inhibiting the
HGF/c-Met signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 41:1497–1508.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lin RK, Wu CY, Chang JW, Juan LJ, Hsu HS,
Chen CY, Lu YY, Tang YA, Yang YC, Yang PC and Wang YC:
Dysregulation of p53/Sp1 control leads to DNA methyltransferase-1
overexpression in lung cancer. Cancer Res. 70:5807–5817. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li BY, Luo Y, Zhao WS, Zhang L, Zhou HJ,
Zou YC and Zhang T: MicroRNA-210 negatively regulates the
radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep.
16:1401–1408. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yuan W, Xiaoyun H, Haifeng Q, Jing L,
Weixu H, Ruofan D, Jinjin Y and Zongji S: MicroRNA-218 enhances the
radiosensitivity of human cervical cancer via promoting radiation
induced apoptosis. Int J Med Sci. 11:691–696. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hu JL, He GY, Lan XL, Zeng ZC, Guan J,
Ding Y, Qian XL, Liao WT, Ding YQ and Liang L: Inhibition of
ATG12-mediated autophagy by miR-214 enhances radiosensitivity in
colorectal cancer. Oncogenesis. 7:162018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xia J, Cao T, Ma C, Shi Y, Sun Y, Wang ZP
and Ma J: miR-7 suppresses tumor progression by directly targeting
MAP3K9 in pancreatic cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 13:121–132.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yue K, Wang X, Wu Y, Zhou X, He Q and Duan
Y: microRNA-7 regulates cell growth, migration and invasion via
direct targeting of PAK1 in thyroid cancer. Mol Med Rep.
14:2127–2134. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhao X, Dou W, He L, Liang S, Tie J, Liu
C, Li T, Lu Y, Mo P, Shi Y, et al: MicroRNA-7 functions as an
anti-metastatic microRNA in gastric cancer by targeting
insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. Oncogene. 32:1363–1372.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chang WC and Hung JJ: Functional role of
post-translational modifications of Sp1 in tumorigenesis. J Biomed
Sci. 19:942012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu G, Ye Z, Zhao X and Ji Z: SP1-induced
up-regulation of lncRNA SNHG14 as a ceRNA promotes migration and
invasion of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by regulating N-WASP.
Am J Cancer Res. 7:2515–2525. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang L, Liu SK, Song L and Yao HR:
SP1-induced up-regulation of lncRNA LUCAT1 promotes proliferation,
migration and invasion of cervical cancer by sponging miR-181a.
Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47:556–564. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kang M, Xiao J, Wang J, Zhou P, Wei T,
Zhao T and Wang R: MiR-24 enhances radiosensitivity in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting SP1. Cancer Med. 5:1163–1173.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li R, Peng C, Zhang X, Wu Y, Pan S and
Xiao Y: Roles of Arf6 in cancer cell invasion, metastasis and
proliferation. Life Sci. 182:80–84. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yilmaz M and Christofori G: Mechanisms of
motility in metastasizing cells. Mol Cancer Res. 8:629–642. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Banyard J, Chung I, Migliozzi M, Phan DT,
Wilson AM, Zetter BR and Bielenberg DR: Identification of genes
regulating migration and invasion using a new model of metastatic
prostate cancer. BMC Cancer. 14:3872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Duan XM, Liu XN, Li YX, Cao YQ, Silayiding
A, Zhang RK and Wang JP: MicroRNA-498 promotes proliferation,
migration, and invasion of prostate cancer cells and decreases
radiation sensitivity by targeting PTEN. Kaohsiung J Med Sci.
35:659–671. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pordanjani SM and Hosseinimehr SJ: The
role of NF-κB inhibitors in cell response to radiation. Curr Med
Chem. 23:3951–3963. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yan J, Jiang Y, Lu J, Wu J and Zhang M:
Inhibiting of proliferation, migration, and invasion in lung cancer
induced by silencing interferon-induced transmembrane protein 1
(IFITM1). Biomed Res Int. 2019:90854352019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Scully R, Panday A, Elango R and Willis
NA: DNA double-strand break repair-pathway choice in somatic
mammalian cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:698–714. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Jeggo PA and Löbrich M: How cancer cells
hijack DNA double-strand break repair pathways to gain genomic
instability. Biochem J. 471:1–11. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Iwabuchi K, Li B, Massa HF, Trask BJ, Date
T and Fields S: Stimulation of p53-mediated transcriptional
activation by the p53-binding proteins, 53BP1 and 53BP2. J Biol
Chem. 273:26061–26068. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bunting SF, Callén E, Wong N, Chen HT,
Polato F, Gunn A, Bothmer A, Feldhahn N, Fernandez-Capetillo O, Cao
L, et al: 53BP1 inhibits homologous recombination in
Brca1-deficient cells by blocking resection of DNA breaks. Cell.
141:243–254. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lee JA, Suh DC, Kang JE, Kim MH, Park H,
Lee MN, Kim JM, Jeon BN, Roh HE, Yu MY, et al: Transcriptional
activity of Sp1 is regulated by molecular interactions between the
zinc finger DNA binding domain and the inhibitory domain with
corepressors, and this interaction is modulated by MEK. J Biol
Chem. 280:28061–28071. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|