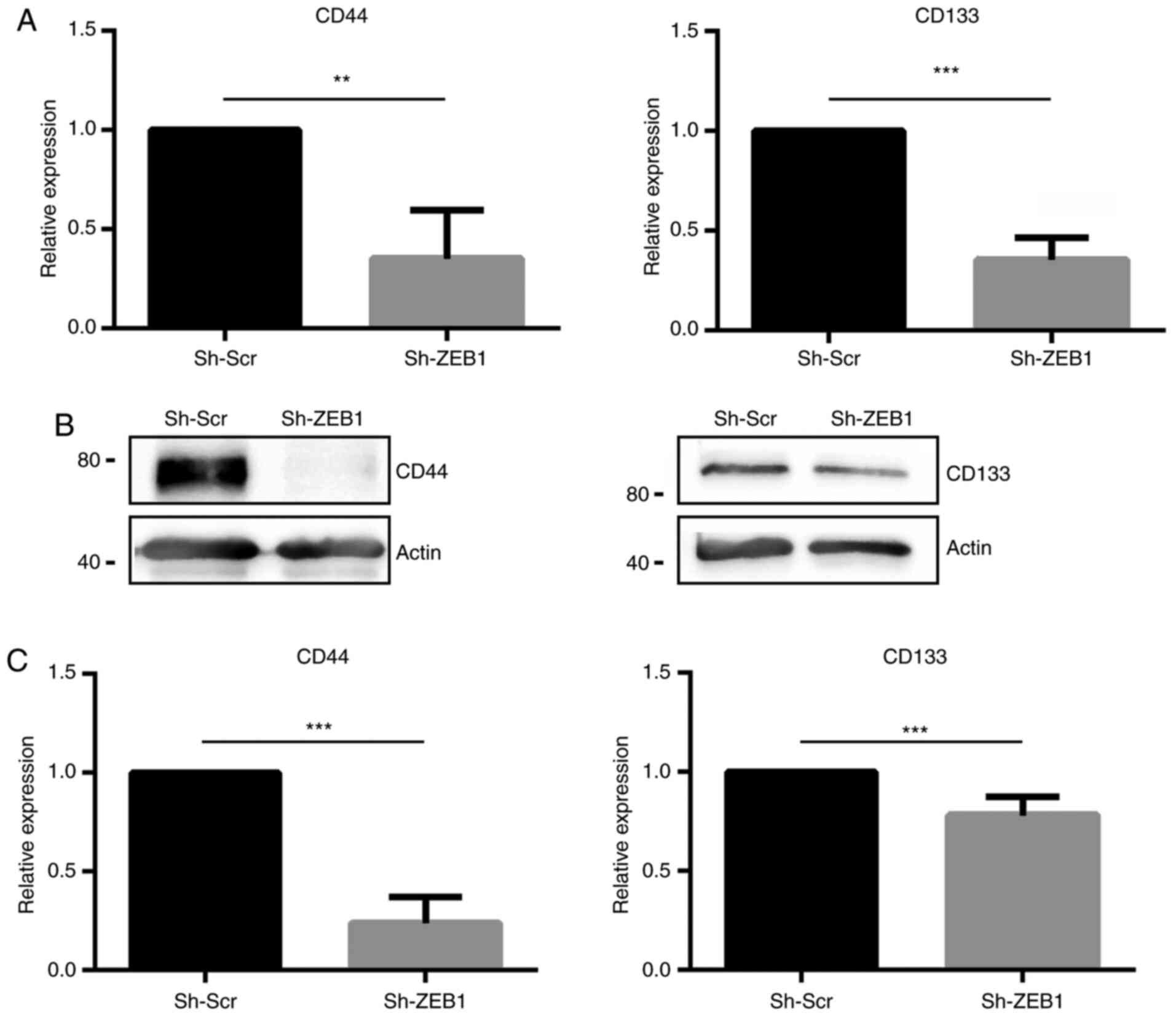
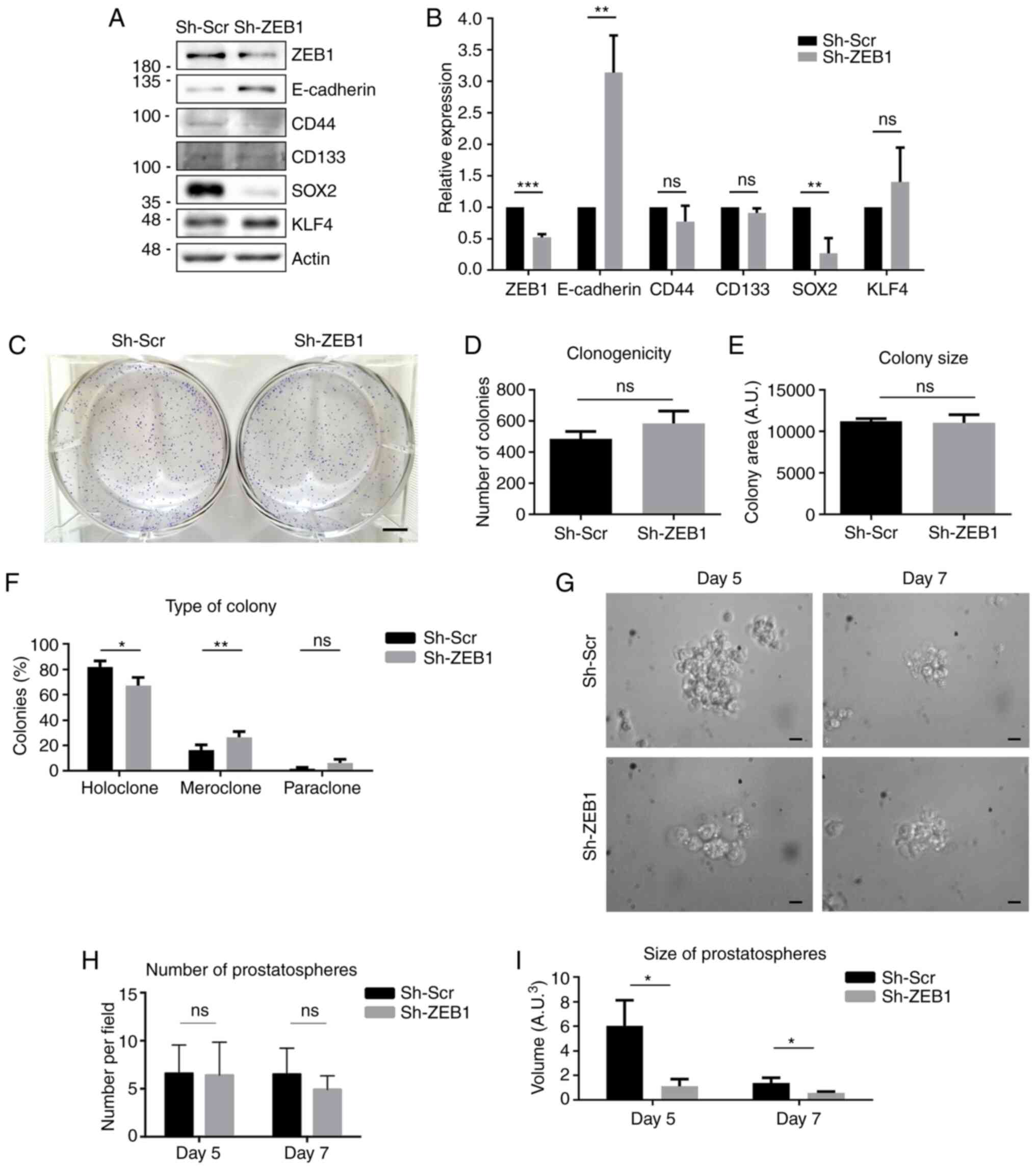
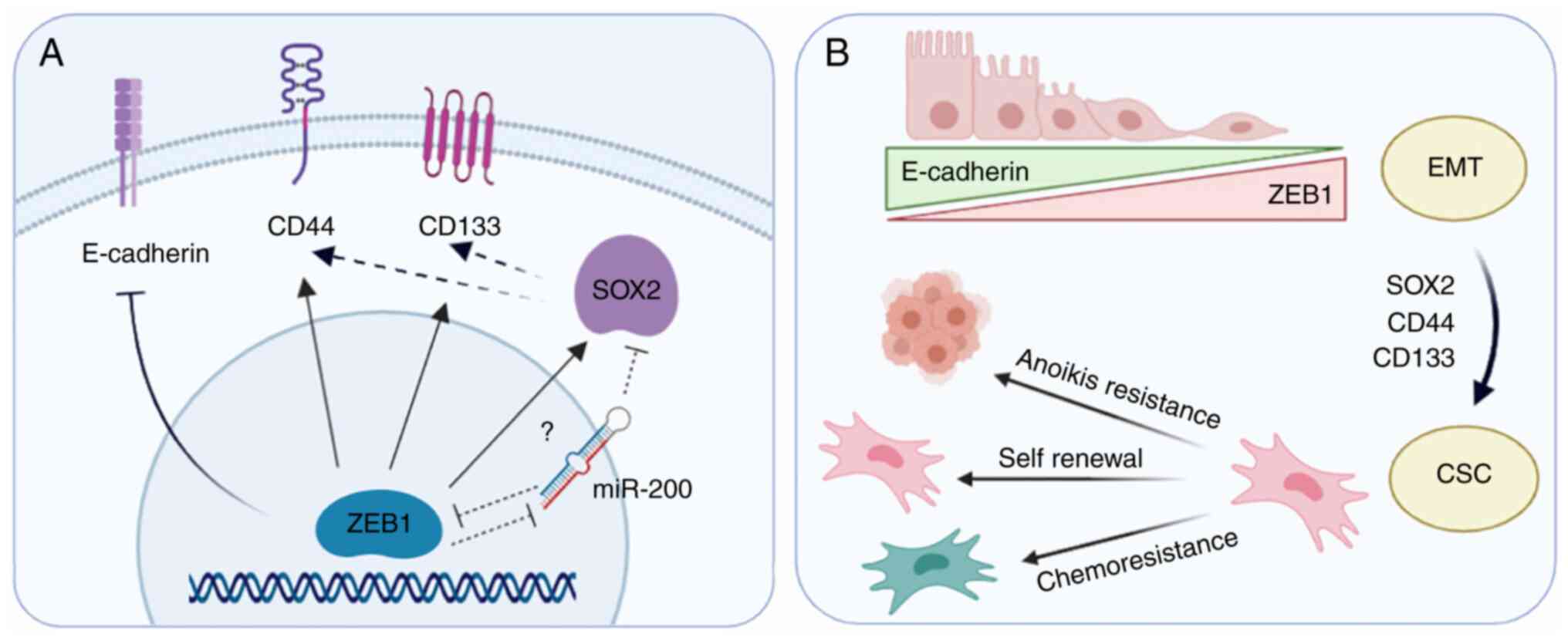
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in
185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fakhrejahani F, Madan RA and Dahut WL:
Management options for biochemically recurrent prostate cancer.
Curr Treat Options Oncol. 18:262017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang K, Ruan H, Xu T, Liu L, Liu D, Yang
H, Zhang X and Chen K: Recent advances on the progressive mechanism
and therapy in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Onco Targets
Ther. 11:3167–3178. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Briers E,
Cumberbatch MG, De Santis M, Fossati N, Gross T, Henry AM, Joniau
S, et al: EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1:
Screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent. Eur
Urol. 71:618–629. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cornford P, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Briers E,
De Santis M, Gross T, Henry AM, Joniau S, Lam TB, Mason MD, et al:
EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: Treatment of
relapsing, metastatic, and castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Eur Urol. 71:630–642. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chandrasekar T, Yang J, Gao A and Evans
CP: Mechanisms of resistance in castration-resistant prostate
cancer (CRPC). Transl Androl Urol. 4:365–380. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yun EJ, Lo UG and Hsieh JT: The evolving
landscape of prostate cancer stem cell: Therapeutic implications
and future challenges. Asian J Urol. 3:203–210. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen X, Li Q, Liu X, Liu C, Liu R, Rycaj
K, Zhang D, Liu B, Jeter C, Calhoun-Davis T, et al: Defining a
population of stem-like human prostate cancer cells that can
generate and propagate castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 22:4505–4516. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Deng Q and Tang DG: Androgen receptor and
prostate cancer stem cells: Biological mechanisms and clinical
implications. Endocr Relat Cancer. 22:T209–T220. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Di Zazzo E, Galasso G, Giovannelli P, Di
Donato M, Di Santi A, Cernera G, Rossi V, Abbondanza C, Moncharmont
B, Sinisi AA, et al: Prostate cancer stem cells: The role of
androgen and estrogen receptors. Oncotarget. 7:193–208. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ojo D, Lin X, Wong N, Gu Y and Tang D:
Prostate cancer stem-like cells contribute to the development of
castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancers (Basel). 7:2290–2308.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Peitzsch C, Tyutyunnykova A, Pantel K and
Dubrovska A: Cancer stem cells: The root of tumor recurrence and
metastases. Semin Cancer Biol. 44:10–24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tsao T, Beretov J, Ni J, Bai X, Bucci J,
Graham P and Li Y: Cancer stem cells in prostate cancer
radioresistance. Cancer Lett. 465:94–104. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Contreras HR, López-Moncada F and
Castellón EA: Cancer stem cell and mesenchymal cell cooperative
actions in metastasis progression and hormone resistance in
prostate cancer: Potential role of androgen and
gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptors. Int J Oncol.
56:1075–1082. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Castellón EA, Valenzuela R, Lillo J,
Castillo V, Contreras HR, Gallegos I, Mercado A and Huidobro C:
Molecular signature of cancer stem cells isolated from prostate
carcinoma and expression of stem markers in different Gleason
grades and metastasis. Biol Res. 45:294–305. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Castillo V, Valenzuela R, Huidobro C,
Contreras HR and Castellon EA: Functional characteristics of cancer
stem cells and their role in drug resistance of prostate cancer.
Int J Oncol. 45:985–994. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Carnero A, Garcia-Mayea Y, Mir C, Lorente
J, Rubio IT and LLeonart ME: The cancer stem-cell signaling network
and resistance to therapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 49:25–36. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Najafi M, Mortezaee K and Majidpoor J:
Cancer stem cell (CSC) resistance drivers. Life Sci.
234:1167812019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Steinbichler TB, Dudás J, Skvortsov S,
Ganswindt U, Riechelmann H and Skvortsova II: Therapy resistance
mediated by cancer stem cells. Semin Cancer Biol. 53:156–167. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mitra A, Mishra L and Li S: EMT, CTCs and
CSCs in tumor relapse and drug-resistance. Oncotarget.
6:10699–10710. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Leão R, Domingos C, Figueiredo A, Hamilton
R, Tabori U and Castelo-Branco P: Cancer stem cells in prostate
cancer: Implications for targeted therapy. Urol Int. 99:125–136.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Packer JR and Maitland NJ: The molecular
and cellular origin of human prostate cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1863:1238–1260. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun Y, Wang BE, Leong KG, Yue P, Li L,
Jhunjhunwala S, Chen D, Seo K, Modrusan Z, Gao WQ, et al: Androgen
deprivation causes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the
prostate: Implications for androgen-deprivation therapy. Cancer
Res. 72:527–36. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kuşoğlu A and Biray Avcı Ç: Cancer stem
cells: A brief review of the current status. Gene. 681:80–85. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Adamowicz J, Pakravan K, Bakhshinejad B,
Drewa T and Babashah S: Prostate cancer stem cells: From theory to
practice. Scand J Urol. 51:95–106. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lan L, Luo Y, Cui D, Shi BY, Deng W, Huo
LL, Chen HL, Zhang GY and Deng LL: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition triggers cancer stem cell generation in human thyroid
cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 43:113–120. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Eun K, Ham SW and Kim H: Cancer stem cell
heterogeneity: Origin and new perspectives on CSC targeting. BMB
Rep. 50:117–125. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nieto MA, Huang RYYJ, Jackson RAA and
Thiery JPP: EMT: 2016. Cell. 166:21–45. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gonzalez DM and Medici D: Signaling
mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci Signal.
7:re82014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang J, Tian XJ and Xing J: Signal
Transduction Pathways of EMT Induced by TGF-β, SHH, and WNT and
Their Crosstalks. J Clin Med. 5:412016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sánchez-Tilló E, Liu Y, De Barrios O,
Siles L, Fanlo L, Cuatrecasas M, Darling DS, Dean DC, Castells A
and Postigo A: EMT-activating transcription factors in cancer:
Beyond EMT and tumor invasiveness. Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:3429–3456.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Goossens S, Vandamme N, Van Vlierberghe P
and Berx G: EMT transcription factors in cancer development
re-evaluated: Beyond EMT and MET. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer.
1868:584–591. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang P, Sun Y and Ma L: ZEB1: At the
crossroads of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, metastasis and
therapy resistance. Cell Cycle. 14:481–487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lazarova D and Bordonaro M: ZEB1 mediates
drug resistance and EMT in p300-deficient CRC. J Cancer.
8:1453–1459. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang P, Wei Y, Wang L, Debeb BG, Yuan Y,
Zhang J, Yuan J, Wang M, Chen D, Sun Y, et al: ATM-mediated
stabilization of ZEB1 promotes DNA damage response and
radioresistance through CHK1. Nat Cell Biol. 16:864–875. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guo C, Ma J, Deng G, Qu Y, Yin L, Li Y,
Han Y, Cai C, Shen H and Zeng S: ZEB1 promotes oxaliplatin
resistance through the induction of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in colon cancer cells. J Cancer. 8:3555–3566. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Orellana-serradell O, Herrera D, Castellón
EA and Contreras HR: The transcription factor ZEB1 promotes
chemoresistance in prostate cancer cell lines. Asian J Androl.
21:460–467. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Orellana-Serradell O, Herrera D, Castellón
EA and Contreras HR: The transcription factor ZEB1 promotes an
aggressive phenotype in prostate cancer cell lines. Asian J Androl.
20:294–299. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Farfán N, Ocarez N, Castellón EA, Mejía N,
de Herreros AG and Contreras HR: The transcriptional factor ZEB1
represses Syndecan 1 expression in prostate cancer. Sci Rep.
8:114672018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Stone KR, Mickey DD, Wunderli H, Mickey GH
and Paulson DF: Isolation of a human prostate carcinoma cell line
(DU 145). Int J Cancer. 21:274–281. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Horoszewicz JS, Leong SS, Kawinski E, Karr
JP, Rosenthal H, Chu TM, Mirand EA and Murphy GP: LNCaP model of
human prostatic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 43:1809–1818.
1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Krasnov GS, Kudryavtseva AV, Snezhkina AV,
Lakunina VA, Beniaminov AD, Melnikova NV and Dmitriev AA:
Pan-cancer analysis of TCGA data revealed promising reference genes
for qPCR normalization. Front Genet. 10:972019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Barrandon Y and Green H: Three clonal
types of keratinocyte with different capacities for multiplication.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 84:2302–2306. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Acikgoz E, Guven U, Duzagac F, Uslu R,
Kara M, Soner BC and Oktem G: Enhanced G2/M arrest, caspase related
apoptosis and reduced E-cadherin dependent intercellular adhesion
by trabectedin in prostate cancer stem cells. PLoS One.
10:e01410902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang S: Anchorage-independent growth of
prostate cancer stem cells. Methods Mol Biol. 568:151–160. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sobel RE and Sadar MD: Cell lines used in
prostate cancer research: A compendium of old and new lines-Part 1.
J Urol. 173:342–359. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yu Z, Pestellc TG, Lisantic MP and Pestell
RG: Cancer Stem Cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:2144–2151. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Johnston MD, Maini PK, Jonathan Chapman S,
Edwards CM and Bodmer WF: On the proportion of cancer stem cells in
a tumour. J Theor Biol. 266:708–711. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Collins AT, Berry PA, Hyde C, Stower MJ
and Maitland NJ: Prospective identification of tumorigenic prostate
cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 65:10946–10951. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ajani JA, Song S, Hochster HS and
Steinberg IB: Cancer stem cells: The promise and the potential.
Semin Oncol. 42 (Suppl 1):S3–S17. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jolly MK and Celià-Terrassa T: Dynamics of
phenotypic heterogeneity during EMT and stemness in cancer
progression. J Clin Med. 8:15422019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hanrahan K, O'Neill A, Prencipe M, Bugler
J, Murphy L, Fabre A, Puhr M, Culig Z, Murphy K and Watson RW: The
role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition drivers ZEB1 and ZEB2 in
mediating docetaxel-resistant prostate cancer. Mol Oncol.
11:251–265. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Krebs AM, Mitschke J, Lasierra Losada M,
Schmalhofer O, Boerries M, Busch H, Boettcher M, Mougiakakos D,
Reichardt W, Bronsert P, et al: The EMT-activator Zeb1 is a key
factor for cell plasticity and promotes metastasis in pancreatic
cancer. Nat Cell Biol. 19:518–529. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhang S and Cui W: Sox2, a key factor in
the regulation of pluripotency and neural differentiation. World J
Stem Cells. 6:305–311. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Adachi K, Suemori H, Yasuda SY, Nakatsuji
N and Kawase E: Role of SOX2 in maintaining pluripotency of human
embryonic stem cells. Genes Cells. 15:455–470. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ghaleb AM and Yang VW: Krüppel-like factor
4 (KLF4): What we currently know. Gene. 611:27–137. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhang P, Andrianakos R, Yang Y, Liu C and
Lu W: Kruppel-like factor 4 (Klf4) prevents embryonic stem (ES)
cell differentiation by regulating Nanog gene expression. J Biol
Chem. 285:9180–9189. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
An Z, Liu P, Zheng J, Si C, Li T, Chen Y,
Ma T, Zhang MQ, Zhou Q and Ding S: Sox2 and Klf4 as the functional
core in pluripotency induction without exogenous Oct4. Cell Rep.
29:1986–2000,e8. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Mamun MA, Mannoor K, Cao J, Qadri F and
Song X: SOX2 in cancer stemness: Tumor malignancy and therapeutic
potentials. J Mol Cell Biol. 12:85–98. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Russo MV, Esposito S, Tupone MG, Manzoli
L, Airoldi I, Pompa P, Cindolo L, Schips L, Sorrentino C and Di
Carlo E: SOX2 boosts major tumor progression genes in prostate
cancer and is a functional biomarker of lymph node metastasis.
Oncotarget. 7:12372–12385. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Mu P, Zhang Z, Benelli M, Karthaus WR,
Hoover E, Chen CC, Wongvipat J, Ku SY, Gao D, Cao Z, et al: SOX2
promotes lineage plasticity and antiandrogen resistance in TP53-and
RB1-deficient prostate cancer. Science. 355:84–88. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Liu X, Qiao B, Zhao T, Hu F, Lam AK and
Tao Q: Sox2 promotes tumor aggressiveness and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tongue squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 42:1418–1426. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Gao H, Teng C, Huang W, Peng J and Wang C:
SOX2 promotes the epithelial to mesenchymal transition of
esophageal squamous cells by modulating slug expression through the
activation of STAT3/HIF-α signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 16:21643–21657.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Herreros-Villanueva M, Zhang JS, Koenig A,
Abel EV, Smyrk TC, Bamlet WR, de Narvajas AA, Gomez TS, Simeone DM,
Bujanda L, et al: SOX2 promotes dedifferentiation and imparts stem
cell-like features to pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogenesis.
2:e612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Srinivasan D, Senbanjo L, Majumdar S,
Franklin RB and Chellaiah MA: Androgen receptor expression reduces
stemness characteristics of prostate cancer cells (PC3) by
repression of CD44 and SOX2. J Cell Biochem. 120:2413–2428. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Zhou W, Lv R, Qi W, Wu D, Xu Y, Liu W, Mou
Y and Wang L: Snail contributes to the maintenance of stem
cell-like phenotype cells in human pancreatic cancer. PLoS One.
9:e874092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Deep G, Jain AK, Ramteke A, Ting H,
Vijendra KC, Gangar SC, Agarwal C and Agarwal R: SNAI1 is critical
for the aggressiveness of prostate cancer cells with low
E-cadherin. Mol Cancer. 13:372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Celià-terrassa T, Meca-cortés Ó, Mateo F,
Martínez de Paz A, Rubio N, Arnal-Estapé A, Ell BJ, Bermudo R, Díaz
A, Guerra-Rebollo M, et al: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition can
suppress major attributes of human epithelial. J Clin Invest.
122:1849–1868. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Anose BM and Sanders MM: Androgen receptor
regulates transcription of the ZEB1 transcription factor. Int J
Endocrinol. 2011:9039182011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Mooney SM, Parsana P, Hernandez JR, Liu X,
Verdone JE, Torga G, Harberg CA and Pienta KJ: The presence of
androgen receptor elements regulates ZEB1 expression in the absence
of androgen receptor. J Cell Biochem. 116:115–23. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Chaffer CL, Marjanovic ND, Lee T, Bell G,
Kleer CG, Reinhardt F, D'Alessio AC, Young RA and Weinberg RA:
Poised chromatin at the ZEB1 promoter enables breast cancer cell
plasticity and enhances tumorigenicity. Cell. 154:61–74. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhou C, Jiang H, Zhang Z, Zhang G, Wang H,
Zhang Q, Sun P, Xiang R and Yang S: ZEB1 confers stem cell-like
properties in breast cancer by targeting neurogenin-3. Oncotarget.
8:54388–54401. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Yu Z and Pestell RG: MicroRNAs and Cancer
Stem Cells. MicroRNAs in Cancer Translational Research. William
C.S.C: Springer; pp. 373–398. 2011, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Brabletz S, Bajdak K, Meidhof S, Burk U,
Niedermann G, Firat E, Wellner U, Dimmler A, Faller G, Schubert J
and Brabletz T: The ZEB1/miR-200 feedback loop controls Notch
signalling in cancer cells. EMBO J. 30:770–782. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Tan L, Sui X, Deng H and Ding M: Holoclone
forming cells from pancreatic cancer cells enrich tumor initiating
cells and represent a novel model for study of cancer stem cells.
PLoS One. 6:e233832011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhang L, Jiao M, Li L, Wu D, Wu K, Li X,
Zhu G, Dang Q, Wang X, Hsieh JT and He D: Tumorspheres derived from
prostate cancer cells possess chemoresistant and cancer stem cell
properties. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:675–686. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Knaack H, Lenk L, Philipp LM, Miarka L,
Rahn S, Viol F, Hauser C, Egberts JH, Gundlach JP, Will O, et al:
Liver metastasis of pancreatic cancer: The hepatic microenvironment
impacts differentiation and self-renewal capacity of pancreatic
ductal epithelial cells. Oncotarget. 9:31771–31786. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Sohn HM, Kim B, Park M, Ko YJ, Moon YH,
Sun JM, Jeong BC, Kim YW and Lim W: Effect of CD133 overexpression
on bone metastasis in prostate cancer cell line LNCaP. Oncol Lett.
18:1189–1198. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Bisson I and Prowse DM: WNT signaling
regulates self-renewal and differentiation of prostate cancer cells
with stem cell characteristics. Cell Res. 19:683–697. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Chen B, Zhu Z, Li L, Ye W, Zeng J, Gao J,
Wang S, Zhang L and Huang Z: Effect of overexpression of oct4 and
sox2 genes on the biological and oncological characteristics of
gastric cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther. 12:4667–4682. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Kanwal R, Shukla S, Walker E and Gupta S:
Acquisition of tumorigenic potential and therapeutic resistance in
CD133+ subpopulation of prostate cancer cells exhibiting stem-cell
like characteristics. Cancer Lett. 430:25–33. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Hoofd C, Wang X, Lam S, Jenkins C, Wood B,
Giambra V and Weng AP: CD44 promotes chemoresistance in T-ALL by
increased drug efflux. Exp Hematol. 44:166–171.e17. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|