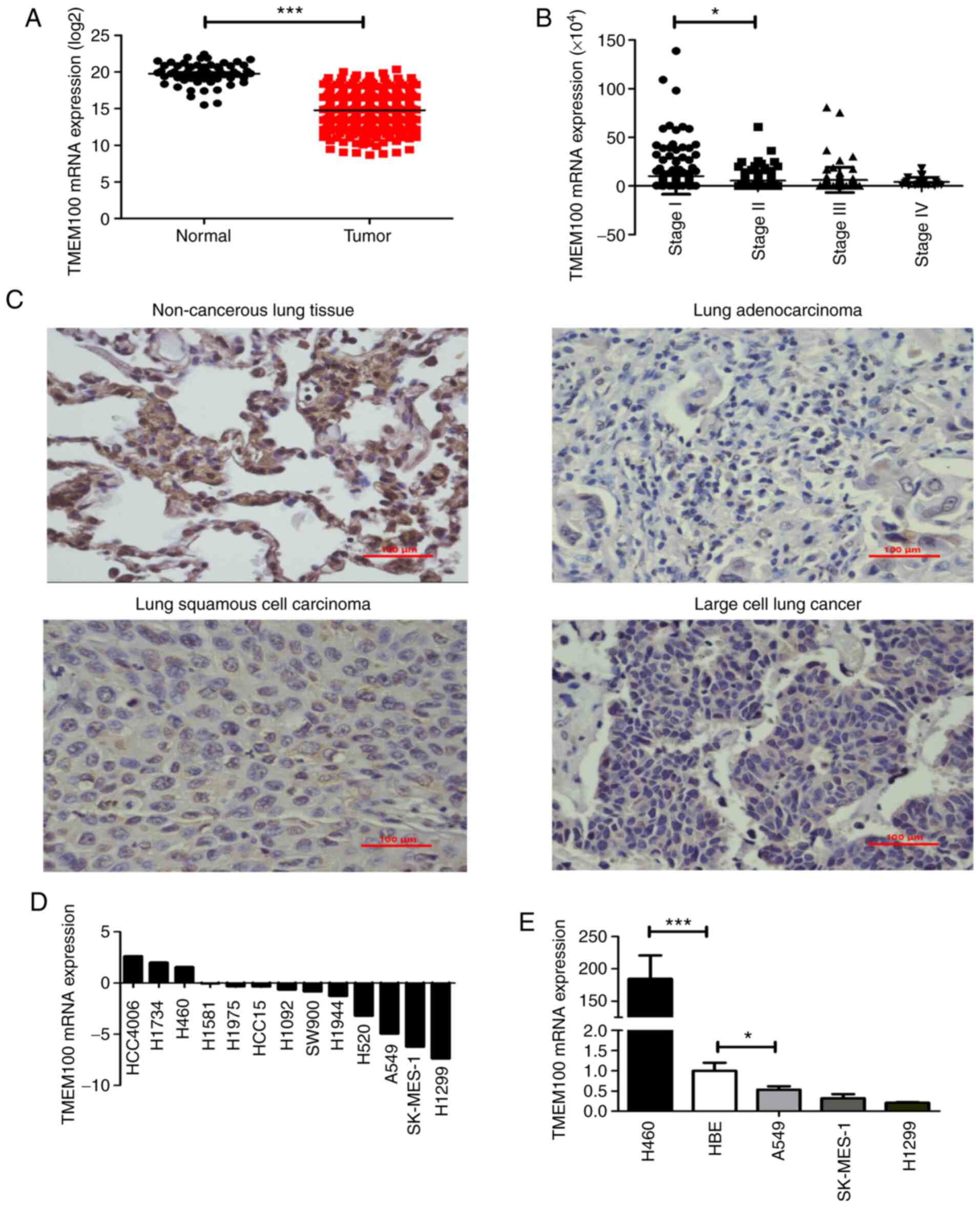
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Herbst RS, Heymach JV and Lippman SM: Lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 359:1367–1380. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lemjabbar-Alaoui H, Hassan OU, Yang YW and
Buchanan P: Lung cancer: Biology and treatment options. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1856:189–210. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D and Boshoff C:
The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature.
533:446–454. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kawai J, Shinagawa A, Shibata K, Yoshino
M, Itoh M, Ishii Y, Arakawa T, Hara A, Fukunishi Y, Konno H, et al:
Functional annotation of a full-length mouse cDNA collection.
Nature. 409:685–690. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Moon EN, Kim MJ, Ko KS, Kim YS, Seo J, Oh
SP and Lee YJ: Generation of mice with a conditional and reporter
allele for Tmem100. Genesis. 48:673–678. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Somekawa S, Imagawa K, Hayashi H, Sakabe
M, Ioka T, Sato GE, Inada K, Iwamoto T, Mori T, Uemura S, et al:
Tmem100, an ALK1 receptor signaling-dependent gene essential for
arterial endothelium differentiation and vascular morphogenesis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:12064–12069. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Moon EH, Kim YS, Seo J, Lee YJ and Oh SP:
Essential role for TMEM100 in vascular integrity but limited
contributions to the pathogenesis of hereditary haemorrhagic
telangiectasia. Cardiovasc Res. 105:353–360. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yamazaki T, Muramoto M, Okitsu O, Morikawa
N and Kita Y: Discovery of a novel neuroprotective compound,
AS1219164, by high-throughput chemical screening of a newly
identified apoptotic gene marker. Eur J Pharmacol. 669:7–14. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Eisenman ST, Gibbons SJ, Singh RD, Bernard
CE, Wu J, Sarr MG, Kendrick ML, Larson DW, Dozois EJ, Shen KR and
Farrugia G: Distribution of TMEM100 in the mouse and human
gastrointestinal tract-a novel marker of enteric nerves.
Neuroscience. 240:117–128. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Weng HJ, Patel KN, Jeske NA, Bierbower SM,
Zou W, Tiwari V, Zheng Q, Tang Z, Mo GC, Wang Y, et al: Tmem100 is
a regulator of TRPA1-TRPV1 complex and contributes to persistent
pain. Neuron. 85:833–846. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Frullanti E, Colombo F, Falvella FS,
Galvan A, Noci S, De Cecco L, Incarbone M, Alloisio M, Santambrogio
L, Nosotti M, et al: Association of lung adenocarcinoma clinical
stage with gene expression pattern in noninvolved lung tissue. Int
J Cancer. 131:E643–E648. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ou D, Yang H, Hua D, Xiao S and Yang L:
Novel roles of TMEM100: Inhibition metastasis and proliferation of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:17379–17390. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Han Z, Wang T, Han S, Chen Y, Chen T, Jia
Q, Li B, Li B, Wang J, Chen G, et al: Low-expression of TMEM100 is
associated with poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Am J
Transl Res. 9:2567–2578. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang ZJ, Chee CE, Huang S and Sinicrope
FA: The role of autophagy in cancer: Therapeutic implications. Mol
Cancer Ther. 10:1533–1541. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Arroyo DS, Gaviglio EA, Peralta Ramos JM,
Bussi C, Rodriguez-Galan MC and Iribarren P: Autophagy in
inflammation, infection, neurodegeneration and cancer. Int
Immunopharmacol. 18:55–65. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ding ZB, Shi YH, Zhou J, Qiu SJ, Xu Y, Dai
Z, Shi GM, Wang XY, Ke AW, Wu B and Fan J: Association of autophagy
defect with a malignant phenotype and poor prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 68:9167–9175. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang H, Zhang Y, Zhu X, Chen C, Zhang C,
Xia Y, Zhao Y, Andrisani O and Kong L: DEAD box protein 5 inhibits
liver tumorigenesis by stimulating autophagy via interaction with
p62/SQSTM1. Hepatology. 69:1046–1063. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guo JY, Teng X, Laddha SV, Ma S, Van
Nostrand SC, Yang Y, Khor S, Chan CS, Rabinowitz JD and White E:
Autophagy provides metabolic substrates to maintain energy charge
and nucleotide pools in Ras-driven lung cancer cells. Genes Dev.
30:1704–1717. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Strohecker AM, Guo JY, Karsli-Uzunbas G,
Price SM, Chen GJ, Mathew R, McMahon M and White E: Autophagy
sustains mitochondrial glutamine metabolism and growth of
BrafV600E-driven lung tumors. Cancer Discov. 3:1272–1285. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Poillet-Perez L, Xie X, Zhan L, Yang L,
Sharp DW, Hu ZS, Su X, Maganti A, Jiang C, Lu W, et al: Autophagy
maintains tumour growth through circulating arginine. Nature.
563:569–573. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang J, Liu Z, Hu T, Han L, Yu S, Yao Y,
Ruan Z, Tian T, Huang T, Wang M, et al: Nrf2 promotes progression
of non-small cell lung cancer through activating autophagy. Cell
Cycle. 16:1053–1062. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cai J, Li R, Xu X, Zhang L, Lian R, Fang
L, Huang Y, Feng X, Liu X, Li X, et al: CK1α suppresses lung tumour
growth by stabilizing PTEN and inducing autophagy. Nat Cell Biol.
20:465–478. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Karsli-Uzunbas G, Guo JY, Price S, Teng X,
Laddha SV, Khor S, Kalaany NY, Jacks T, Chan CS, Rabinowitz JD and
White E: Autophagy is required for glucose homeostasis and lung
tumor maintenance. Cancer Discov. 4:914–927. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rao S, Yang H, Penninger JM and Kroemer G:
Autophagy in non-small cell lung carcinogenesis: A positive
regulator of antitumor immunosurveillance. Autophagy. 10:529–531.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin
MJ, Abeliovich H, Acevedo Arozena A, Adachi H, Adams CM, Adams PD,
Adeli K, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays
for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy. 12:1–222. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fan S, Zhang B, Luan P, Gu B, Wan Q, Huang
X, Liao W and Liu J: PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K pathway is involved in
Aβ25-35-induced autophagy. Biomed Res Int. 2015:1610202015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hou X, Hu Z, Xu H, Xu J, Zhang S, Zhong Y,
He X and Wang N: Advanced glycation endproducts trigger autophagy
in cadiomyocyte via RAGE/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cardiovasc
Diabetol. 13:782014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dikic I, Johansen T and Kirkin V:
Selective autophagy in cancer development and therapy. Cancer Res.
70:3431–3434. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Janku F, McConkey DJ, Hong DS and Kurzrock
R: Autophagy as a target for anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 8:528–539. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Maheswari U, Ghosh K and Sadras SR:
Licarin A induces cell death by activation of autophagy and
apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Apoptosis.
23:210–225. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kimura S, Noda T and Yoshimori T:
Dissection of the autophagosome maturation process by a novel
reporter protein, tandem fluorescent-tagged LC3. Autophagy.
3:452–460. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
White E: The role for autophagy in cancer.
J Clin Invest. 125:42–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lavandero S, Chiong M, Rothermel BA and
Hill JA: Autophagy in cardiovascular biology. J Clin Invest.
125:55–64. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guo XL, Li D, Sun K, Wang J, Liu Y, Song
JR, Zhao QD, Zhang SS, Deng WJ, Zhao X, et al: Inhibition of
autophagy enhances anticancer effects of bevacizumab in
hepatocarcinoma. J Mol Med (Berl). 91:473–483. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang P, Zheng Z, Ling L, Yang X, Zhang N,
Wang X, Hu M, Xia Y, Ma Y, Yang H, et al: w09, a novel autophagy
enhancer, induces autophagy-dependent cell apoptosis via activation
of the EGFR-mediated RAS-RAF1-MAP2K-MAPK1/3 pathway. Autophagy.
13:1093–1112. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
White E: Deconvoluting the
context-dependent role for autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
12:401–410. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Abida WM and Gu W: p53-dependent and
p53-independent activation of autophagy by ARF. Cancer Res.
68:352–357. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Arico S, Petiot A, Bauvy C, Dubbelhuis PF,
Meijer AJ, Codogno P and Ogier-Denis E: The tumor suppressor PTEN
positively regulates macroautophagy by inhibiting the
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway. J Biol
Chem. 276:35243–35246. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu J, Wang X, Zheng M and Luan Q:
Lipopolysaccharide from Porphyromonas gingivalis promotes autophagy
of human gingival fibroblasts through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling
pathway. Life Sci. 211:133–139. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Qi HY, Qu XJ, Liu J, Hou KZ, Fan YB, Che
XF and Liu YP: Bufalin induces protective autophagy by Cbl-b
regulating mTOR and ERK signaling pathways in gastric cancer cells.
Cell Bio Int. 43:33–43. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sun PH, Zhu LM, Qiao MM, Zhang YP, Jiang
SH, Wu YL and Tu SP: The XAF1 tumor suppressor induces autophagic
cell death via upregulation of Beclin-1 and inhibition of Akt
pathway. Cancer Lett. 310:170–180. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li YC, He SM, He ZX, Li M, Yang Y, Pang
JX, Zhang X, Chow K, Zhou Q, Duan W, et al: Plumbagin induces
apoptotic and autophagic cell death through inhibition of the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 344:239–259. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Schuurbiers OC, Kaanders JH, van der
Heijden HF, Dekhuijzen RP, Oyen WJ and Bussink J: The PI3-K/AKT-
pathway and radiation resistance mechanisms in non-small cell lung
cancer. J Thorac oncol. 4:761–767. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cao L, Walker MP, Vaidya NK, Fu M, Kumar S
and Kumar A: Cocaine-mediated autophagy in astrocytes involves
sigma 1 receptor, PI3K, mTOR, Atg5/7, Beclin-1 and induces type II
programmed cell death. Mol Neurobiol. 53:4417–4430. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kaminskyy VO, Piskunova T, Zborovskaya IB,
Tchevkina EM and Zhivotovsky B: Suppression of basal autophagy
reduces lung cancer cell proliferation and enhances
caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis by stimulating ROS
formation. Autophagy. 8:1032–1044. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu G, Pei F, Yang F, Li L, Amin AD, Liu
S, Buchan JR and Cho WC: Role of autophagy and apoptosis in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 18:3672017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zhao Y, Li K, Zhao B and Su L: HSP90
inhibitor DPB induces autophagy and more effectively apoptosis in
A549 cells combined with autophagy inhibitors. In Vitro Cell Dev
Biol Anim. 55:349–354. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|