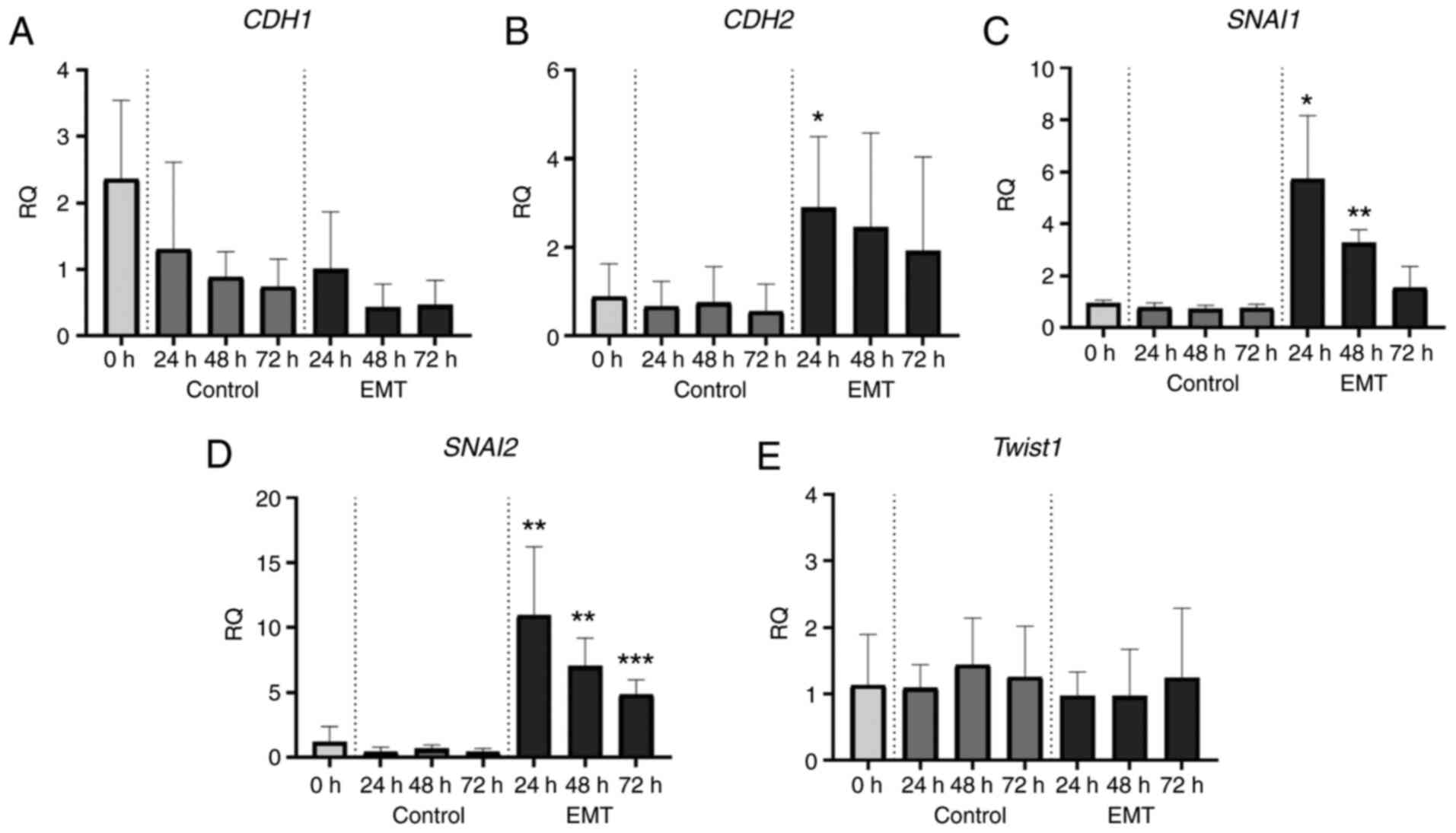
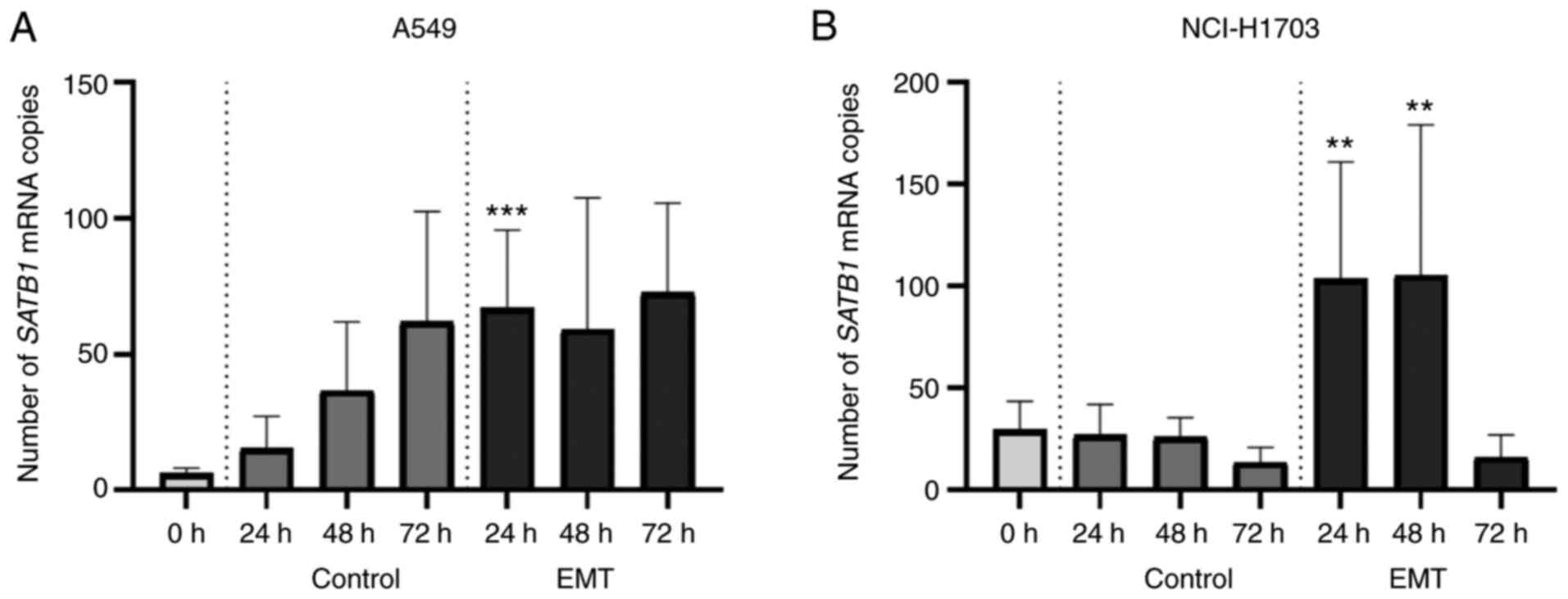
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Colombet M, Mery
L, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Soerjomataram I and Bray F: Global Cancer
Observatory: Cancer Today. Int Agency Res Cancer. 2018 https://publications.iarc.fr/Databases/Iarc-Cancerbases/Cancer-Today-Powered-By-GLOBOCAN-2018--2018December
62019 12 06;
|
|
2
|
Zappa C and Mousa SA: Non-small cell lung
cancer: Current treatment and future advances. Transl Lung Cancer
Res. 5:288–300. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Burke AP, Marx A
and Nicholson AG: Introduction to The 2015 World Health
Organization Classification of tumours of the lung, pleura, thymus
and heart. J Thorac Oncol. 10:1240–1242. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Perlikos F, Harrington KJ and Syrigos KN:
Key molecular mechanisms in lung cancer invasion and metastasis: A
comprehensive review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 87:1–11. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tamura T, Kurishima K, Nakazawa K,
Kagahashi K, Ishikawa H, Satoh H and Hizawa N: Specific organ
metastases and survival in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer.
Mol Clin Oncol. 3:217–221. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Milovanovic IS, Stjepanovic M and Mitrovic
D: Distribution patterns of the metastases of the lung carcinoma in
relation to histological type of the primary tumor: An autopsy
study. Ann Thorac Med. 12:191–198. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hsu F, De Caluwe A, Anderson D, Nichol A,
Toriumi T and Ho C: Patterns of spread and prognostic implications
of lung cancer metastasis in an era of driver mutations. Curr
Oncol. 24:228–233. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Miller D,
Brest A, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Mariotto A, Lewis DR, et al:
SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2017. https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2017April
15–2020
|
|
9
|
Diepenbruck M and Christofori G:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis: Yes, no,
maybe? Curr Opin Cell Biol. 43:7–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang X, Liang X, Zheng M and Tang Y:
Cellular phenotype plasticity in cancer dormancy and metastasis.
Front Oncol. 8:5052018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
De Craene B and Berx G: Regulatory
networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat
Rev Cancer. 13:97–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Y and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer: Complexity and
opportunities. Front Med. 12:361–373. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Santamaria PG, Moreno-Bueno G, Portillo F
and Cano A: EMT: Present and future in clinical oncology. Mol
Oncol. 11:718–738. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Singh M, Yelle N, Venugopal C and Singh
SK: EMT: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol Ther.
182:80–94. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pastushenko I and Blanpain C: EMT
transition states during tumor progression and metastasis. Trends
Cell Biol. 29:212–226. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Frixen UH, Behrens J, Sachs M, Eberle G,
Voss B, Warda A, Löchner D and Birchmeier W: E-cadherin-mediated
cell-cell adhesion prevents invasiveness of human carcinoma cells.
J Cell Biol. 113:173–185. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nagathihalli NS, Massion PP, Gonzalez AL,
Lu P and Datta PK: Smoking induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition in non-small cell lung cancer through HDAC-mediated
downregulation of E-cadherin. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:2362–2372. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mahmood MQ, Walters EH, Shukla SD, Weston
S, Muller HK, Ward C and Sohal SS: β-catenin, Twist and Snail:
Transcriptional regulation of EMT in smokers and COPD, and relation
to airflow obstruction. Sci Rep. 7:108322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu X, Chen L, Liu L and Niu X:
EMT-Mediated Acquired EGFR-TKI resistance in NSCLC: Mechanisms and
strategies. Front Oncol. 9:10442019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tulchinsky E, Demidov O, Kriajevska M,
Barlev NA and Imyanitov E: EMT: A mechanism for escape from
EGFR-targeted therapy in lung cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev
Cancer. 1871:29–39. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bronte G, Bravaccini S, Bronte E, Burgio
MA, Rolfo C, Delmonte A and Crinò L: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition in the context of epidermal growth factor receptor
inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc.
93:1735–1746. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li M, Yang J, Zhou W, Ren Y, Wang X, Chen
H, Zhang J, Chen J, Sun Y, Cui L, et al: Activation of an
AKT/FOXM1/STMN1 pathway drives resistance to tyrosine kinase
inhibitors in lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 117:974–983. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Santamaría PG, Moreno-Bueno G and Cano A:
Contribution of epithelial plasticity to therapy resistance. J Clin
Med. 8:6762019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liang SQ, Marti TM, Dorn P, Froment L,
Hall SR, Berezowska S, Kocher G, Schmid RA and Peng RW: Blocking
the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition pathway abrogates
resistance to anti-folate chemotherapy in lung cancer. Cell Death
Dis. 6:e18242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zheng HC: The molecular mechanisms of
chemoresistance in cancers. Oncotarget. 8:59950–59964. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fischer KR, Durrans A, Lee S, Sheng J, Li
F, Wong ST, Choi H, El Rayes T, Ryu S, Troeger J, et al:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung
metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance. Nature. 527:472–476.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kohwi-Shigematsu T, Kohwi Y, Takahashi K,
Richards HW, Ayers SD, Han HJ and Cai S: SATB1-mediated functional
packaging of chromatin into loops. Methods. 58:243–254. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Galande S, Purbey PK, Notani D and Kumar
PP: The third dimension of gene regulation: Organization of dynamic
chromatin loopscape by SATB1. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 17:408–414.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kohwi-Shigematsu T, Poterlowicz K,
Ordinario E, Han HJ, Botchkarev VA and Kohwi Y: Genome organizing
function of SATB1 in tumor progression. Semin Cancer Biol.
23:72–79. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fessing MY, Mardaryev AN, Gdula MR, Sharov
AA, Sharova TY, Rapisarda V, Gordon KB, Smorodchenko AD,
Poterlowicz K, Ferone G, et al: p63 regulates Satb1 to control
tissue-specific chromatin remodeling during development of the
epidermis. J Cell Biol. 194:825–839. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pavan Kumar P, Purbey PK, Sinha CK, Notani
D, Limaye A, Jayani RS and Galande S: Phosphorylation of SATB1, a
global gene regulator, acts as a molecular switch regulating its
transcriptional activity in vivo. Mol Cell. 22:231–243. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Purbey PK, Singh S, Notani D, Kumar PP,
Limaye AS and Galande S: Acetylation-dependent interaction of SATB1
and CtBP1 mediates transcriptional repression by SATB1. Mol Cell
Biol. 29:1321–1337. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nagpal N, Ahmad HM, Molparia B and
Kulshreshtha R: MicroRNA-191, an estrogen-responsive microRNA,
functions as an oncogenic regulator in human breast cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 34:1889–1899. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Brown CY, Dayan S, Wong SW, Kaczmarek A,
Hope CM, Pederson SM, Arnet V, Goodall GJ, Russell D, Sadlon TJ and
Barry SC: FOXP3 and miR-155 cooperate to control the invasive
potential of human breast cancer cells by down regulating ZEB2
independently of ZEB1. Oncotarget. 9:27708–27727. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li QQ, Chen ZQ, Cao XX, Xu JD, Xu JW, Chen
YY, Wang WJ, Chen Q, Tang F, Liu XP and Xu ZD: Involvement of
NF-κB/miR-448 regulatory feedback loop in chemotherapy-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells. Cell
Death Differ. 18:16–25. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
McInnes N, Sadlon TJ, Brown CY, Pederson
S, Beyer M, Schultze JL, McColl S, Goodall GJ and Barry SC: FOXP3
and FOXP3-regulated microRNAs suppress SATB1 in breast cancer
cells. Oncogene. 31:1045–1054. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pan X, Li D, Huo J, Kong F, Yang H and Ma
X: LINC01016 promotes the malignant phenotype of endometrial cancer
cells by regulating the miR-302a-3p/miR-3130-3p/NFYA/SATB1 axis.
Cell Death Dis. 9:3032018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lopes-Ramos CM, Habr-Gama A, Quevedo Bde
S, Felício NM, Bettoni F, Koyama FC, Asprino PF, Galante PA,
Gama-Rodrigues J, Camargo AA, et al: Overexpression of miR-21-5p as
a predictive marker for complete tumor regression to neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer patients. BMC Med Genomics.
7:682014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kowalczyk AE, Krazinski BE, Godlewski J,
Grzegrzolka J, Kiewisz J, Kwiatkowski P, Sliwinska-Jewsiewicka A,
Dziegiel P and Kmiec Z: SATB1 is Down-regulated in clear cell renal
cell carcinoma and correlates with miR-21-5p overexpression and
poor prognosis. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 13:209–217.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Alvarez JD, Yasui DH, Niida H, Joh T, Loh
DY and Kohwi-Shigematsu T: The MAR-binding protein SATB1
orchestrates temporal and spatial expression of multiple genes
during T-cell development. Genes Dev. 14:521–535. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Savarese F, Dávila A, Nechanitzky R, De La
Rosa-Velazquez I, Pereira CF, Engelke R, Takahashi K, Jenuwein T,
Kohwi-Shigematsu T, Fisher AG and Grosschedl R: Satb1 and Satb2
regulate embryonic stem cell differentiation and Nanog expression.
Genes Dev. 23:2625–2638. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Han HJ, Russo J, Kohwi Y and
Kohwi-Shigematsu T: SATB1 reprogrammes gene expression to promote
breast tumour growth and metastasis. Nature. 452:187–193. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nodin B, Johannesson H, Wangefjord S,
O'Connor DP, Lindquist KE, Uhlén M, Jirström K and Eberhard J:
Molecular correlates and prognostic significance of SATB1
expression in colorectal cancer. Diagn Pathol. 7:1152012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shukla S, Sharma H, Abbas A, MacLennan GT,
Fu P, Danielpour D and Gupta S: Upregulation of SATB1 is associated
with prostate cancer aggressiveness and disease progression. PLoS
One. 8:e535272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tu W, Luo M, Wang Z, Yan W, Xia Y, Deng H,
He J, Han P and Tian D: Upregulation of SATB1 promotes tumor growth
and metastasis in liver cancer. Liver Int. 32:1064–1078. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Han B, Luan L, Xu Z and Wu B: Expression
and biological roles of SATB1 in human bladder cancer. Tumor Biol.
34:2943–2949. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Nodin B, Hedner C, Uhlén M and Jirström K:
Expression of the global regulator SATB1 is an independent factor
of poor prognosis in high grade epithelial ovarian cancer. J
Ovarian Res. 5:242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang S, Zeng J, Xiao R, Xu G, Liu G, Xiong
D, Ye Y, Chen B, Wang H, Luo Q and Huang Z: Poor prognosis and
SATB1 overexpression in solid tumors: A meta-analysis. Cancer Manag
Res. 10:1471–1478. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sun Z, Zhang C, Zou X, Jiang G, Xu Z, Li W
and Xie H: Special AT-rich sequence-binding protein-1 participates
in the maintenance of breast cancer stem cells through regulation
of the Notch signaling pathway and expression of Snail1 and Twist1.
Mol Med Rep. 11:3235–3242. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lv JH, Wang F, Shen MH, Wang X and Zhou
XJ: SATB1 expression is correlated with β-catenin associated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol
Ther. 17:254–261. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Frömberg A, Rabe M and Aigner A: Multiple
effects of the special AT-rich binding protein 1 (SATB1) in colon
carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 135:2537–2546. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Mao L, Yang C, Wang J, Li W, Wen R, Chen J
and Zheng J: SATB1 is overexpressed in metastatic prostate cancer
and promotes prostate cancer cell growth and invasion. J Transl
Med. 11:1112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Mao LJ, Zhang J, Liu N, Fan L, Yang DR,
Xue BX, Shan YX and Zheng JN: Oncolytic virus carrying shRNA
targeting SATB1 inhibits prostate cancer growth and metastasis.
Tumor Biol. 36:9073–9081. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Qi H, Fu X, Li Y, Pang X, Chen S, Zhu X,
Li F and Tan W: SATB1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and metastasis in prostate cancer. Oncol Lett. 13:2577–2582. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wan F, Cheng C, Wang Z, Xiao X, Zeng H,
Xing S, Chen X, Wang J, Li S, Zhang Y, et al: SATB1 overexpression
regulates the development and progression in bladder cancer through
EMT. PLoS One. 10:e01175182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Baguma-Nibasheka M, Angka HE, Inanlou MR
and Kablar B: Microarray analysis of Myf5-/-:MyoD-/-hypoplastic
mouse lungs reveals a profile of genes involved in pneumocyte
differentiation. Histol Histopathol. 22:483–495. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Selinger CI, Cooper WA, Al-Sohaily S,
Mladenova DN, Pangon L, Kennedy CW, McCaughan BC, Stirzaker C and
Kohonen-Corish MR: Loss of special AT-rich binding protein 1
expression is a marker of poor survival in lung cancer. J Thorac
Oncol. 6:1179–1189. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Glatzel-Plucinska N, Piotrowska A,
Grzegrzolka J, Olbromski M, Rzechonek A, Dziegiel P and
Podhorska-Okolow M: SATB1 level correlates with Ki-67 expression
and is a positive prognostic factor in non-small cell lung
carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 38:723–736. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Huang B, Zhou H, Wang S, Lang XP and Wang
X: Effect of silencing SATB1 on proliferation, invasion and
apoptosis of A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Oncol Lett.
12:3818–3824. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Huang B, Zhou H, Wang X and Liu Z:
Silencing SATB1 with siRNA inhibits the proliferation and invasion
of small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 13:82013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Detterbeck FC, Boffa DJ and Tanoue LT: The
new lung cancer staging system. Chest. 136:260–271. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Tuffaha MSA: Phenotypic and Genotypic
Diagnosis of Malignancies: An Immunohistochemical and Molecular
Approach. 1st edition. Wiley-VCH; 2008, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Mogilner A and Keren K: The shape of
motile cells. Curr Biol. 19:R762–R771. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Glatzel-Plucinska N, Piotrowska A,
Dziegiel P and Podhorska-Okołów M: The role of SATB1 in tumour
progression and metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 20:41562019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zhang J, Zhang B, Zhang X, Sun Y, Wei X,
McNutt MA, Lu S, Liu Y, Zhang D, Wang M, et al: SATB1 expression is
associated with biologic behavior in colorectal carcinoma in vitro
and in vivo. PLoS One. 8:e479022013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Mansour MA, Hyodo T, Akter KA, Kokuryo T,
Uehara K, Nagino M and Senga T: SATB1 and SATB2 play opposing roles
in c-Myc expression and progression of colorectal cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:4993–5006. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhang Y, Tian X, Ji H, Guan X, Xu W, Dong
B, Zhao M, Wei M, Ye C, Sun Y, et al: Expression of SATB1 promotes
the growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer. PLoS One.
9:e1004132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Loh CY, Chai JY, Tang TF, Wong WF, Sethi
G, Shanmugam MK, Chong PP and Looi CY: The E-Cadherin and
N-Cadherin switch in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition:
Signaling, therapeutic implications, and challenges. Cells.
8:11182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Berx G and van Roy F: Involvement of
members of the cadherin superfamily in cancer. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 1:a0031292009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Bae GY, Choi SJ, Lee JS, Jo J, Lee J, Kim
J and Cha HJ: Loss of E-cadherin activates EGFR-MEK/ERK signaling,
which promotes invasion via the ZEB1/MMP2 axis in non-small cell
lung cancer. Oncotarget. 4:2512–2522. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Onder TT, Gupta PB, Mani SA, Yang J,
Lander ES and Weinberg RA: Loss of E-Cadherin promotes metastasis
via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways. Cancer Res.
68:3645–3654. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kase S, Sugio K, Yamazaki K, Okamoto T,
Yano T and Sugimachi K: Expression of E-cadherin and beta-catenin
in human non-small cell lung cancer and the clinical significance.
Clin Cancer Res. 6:4789–4796. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Bremnes RM, Veve R, Gabrielson E, Hirsch
FR, Baron A, Bemis L, Gemmill RM, Drabkin HA and Franklin WA:
High-throughput tissue microarray analysis used to evaluate biology
and prognostic significance of the E-cadherin pathway in
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 20:2417–2428. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Yan B, Zhang W, Jiang LY, Qin WX and Wang
X: Reduced E-Cadherin expression is a prognostic biomarker of
non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis based on 2395 subjects.
Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:4352–4356. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Lee YC, Wu CT, Chen CS and Chang YL:
E-Cadherin expression in surgically-resected non-small cell lung
cancers-A clinicopathological study. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
48:294–299. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Grigoras ML, Arghirescu TS, Folescu R,
Talpoş IC, Gîndac CM, Zamfir CL, Cornianu M, Anghel MD and Levai
CM: Expression of E-cadherin in lung carcinoma, other than those
with small cells (NSCLC). Rom J Morphol Embryol. 58:1317–1325.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Myong NH: Reduced expression of E-cadherin
in human non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Res Treat. 36:56–61.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Wu Y, Liu HB, Ding M, Liu JN, Zhan P, Fu
XS and Lu G: The impact of E-cadherin expression on non-small cell
lung cancer survival: A meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep. 39:9621–9628.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yang YL, Chen MW and Xian L: Prognostic
and clinicopathological significance of downregulated E-cadherin
expression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 9:e997632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Mrozik KM, Blaschuk OW, Cheong CM,
Zannettino ACW and Vandyke K: N-cadherin in cancer metastasis, its
emerging role in haematological malignancies and potential as a
therapeutic target in cancer. BMC Cancer. 18:9392018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Luo Y, Yu T, Zhang Q, Fu Q, Hu Y, Xiang M,
Peng H, Zheng T, Lu L and Shi H: Upregulated N-cadherin expression
is associated with poor prognosis in epithelial-derived solid
tumours: A meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Invest. 48:e129032018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Hui L, Zhang S, Dong X, Tian D, Cui Z and
Qiu X: Prognostic significance of twist and N-cadherin expression
in NSCLC. PLoS One. 8:e621712013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Sun H, Liu M, Wu X, Yang C, Zhang Y, Xu Z,
Gao K and Wang F: Overexpression of N-cadherin and β-catenin
correlates with poor prognosis in patients with nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 13:1725–1730. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Ozaki-Honda Y, Seki S, Fujiwara M,
Matsuura M, Fujita S, Ikeda H, Umeda M, Ayuse T and Ikeda T:
Prognostic prediction of oral squamous cell carcinoma by E-Cadherin
and N-Cadherin expression in overall cells in tumor nests or tumor
cells at the invasive front. Cancer Microenviron. 10:87–94. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Merikallio H, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T,
Pääkkö P, Mäkitaro R, Riitta K, Salo S, Salo T, Harju T and Soini
Y: Snail promotes an invasive phenotype in lung carcinoma. Respir
Res. 13:1042012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Alves CC, Carneiro F, Hoefler H and Becker
KF: Role of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulator Slug in
primary human cancers. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 14:3035–3050.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Zhao Z, Rahman MA, Chen ZG and Shin DM:
Multiple biological functions of Twist1 in various cancers.
Oncotarget. 8:20380–20393. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Zhang P, Hu P, Shen H, Yu J, Liu Q and Du
J: Prognostic role of Twist or Snail in various carcinomas: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Invest.
44:1072–1094. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Huang C, Zhang P, Zhang D and Weng X: The
prognostic implication of slug in all tumour patients-a systematic
meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Invest. 46:398–407. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Yanagawa J, Walser TC, Zhu LX, Hong L,
Fishbein MC, Mah V, Chia D, Goodglick L, Elashoff DA, Luo J, et al:
Snail promotes CXCR2 ligand-dependent tumor progression in
non-small cell lung carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:6820–6829. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Liu CW, Li CH, Peng YJ, Cheng YW, Chen HW,
Liao PL, Kang JJ and Yeng MH: Snail regulates Nanog status during
the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Smad1/Akt/GSK3β
signaling pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget.
5:3880–3894. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Jiang W, Pang XG, Wang Q, Shen YX, Chen XK
and Xi JJ: Prognostic role of Twist, Slug, and Foxc2 expression in
stage i non-small-cell lung cancer after curative resection. Clin
Lung Cancer. 13:280–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Abd El-Rehim DM, Abd-Elghany MI and Nazmy
MH: Integrin-Linked kinase, Snail and multidrug resistance protein
1: Three concordant players in the progression of non-small cell
lung cancer. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 27:129–137. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Muqbil I, Wu J, Aboukameel A, Mohammad RM
and Azmi AS: Snail nuclear transport: The gateways regulating
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition? Semin Cancer Biol. 27:39–45.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Shih JY and Yang PC: The EMT regulator
slug and lung carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 32:1299–1304. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Merikallio H, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen TT,
Pääkkö P, Mäkitaro R, Kaarteenaho R, Lehtonen S, Salo S, Salo T,
Harju T and Soini Y: Slug is associated with poor survival in
squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:5846–5854. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Hung PF, Hong TM, Chang CC, Hung CL, Hsu
YL, Chang YL, Wu CT, Chang GC, Chan NL, Yu SL, et al:
Hypoxia-induced Slug SUMOylation enhances lung cancer metastasis. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:52019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Li M, Zhang X, Xu X, Wu J, Hu K, Guo X and
Zhang P: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of Twist
overexpression in NSCLC. Oncotarget. 9:14642–14651. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Zeng J, Zhan P, Wu G, Yang W, Liang W, Lv
T and Song Y: Prognostic value of twist in lung cancer: Systematic
review and meta-analysis. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 4:236–241.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Shi Y, Wu H, Zhang M, Ding L, Meng F and
Fan X: Expression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related
proteins and their clinical significance in lung adenocarcinoma.
Diagn Pathol. 8:892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Pallier K, Cessot A, Côté JF, Just PA,
Cazes A, Fabre E, Danel C, Riquet M, Devouassoux-Shisheboran M,
Ansieau S, et al: TWIST1 a new determinant of epithelial to
mesenchymal transition in EGFR mutated lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS
One. 7:e299542012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Barutçu O, Kara M, Muratlı A, Güçlü O and
Dereköy S: Clinical significance of Ki-67, c-erbB-2 and E-cadherin
expressions in open partial laryngectomy patients. Kulak Burun
Bogaz Ihtis Derg. 26:283–292. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
González-Rodilla I, Aller L, Llorca J,
Muñoz AB, Verna V, Estévez J and Schneider J: The E-Cadherin
expression vs. tumor cell proliferation paradox in endometrial
cancer. Anticancer Res. 33:5091–5095. 2013.
|