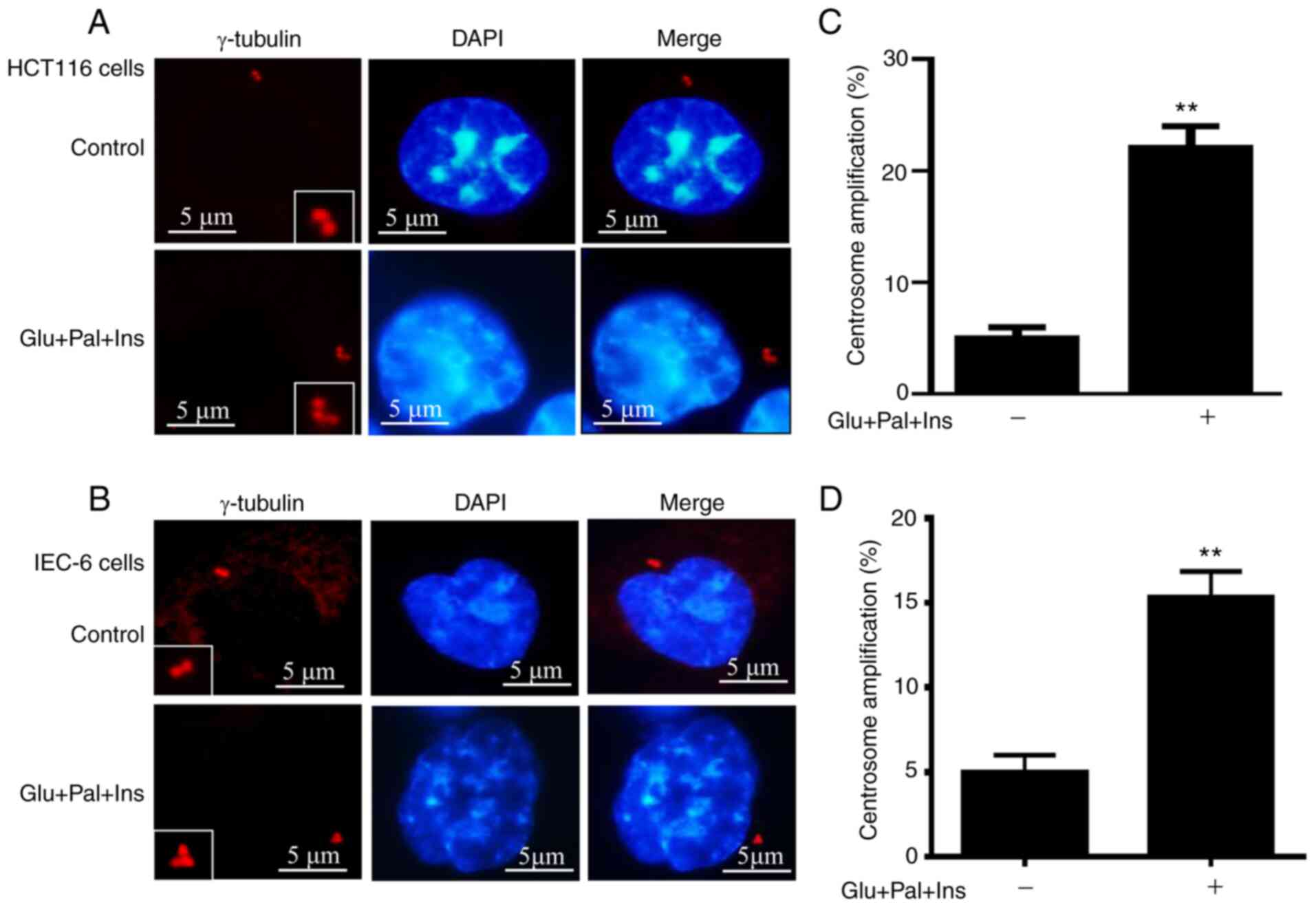
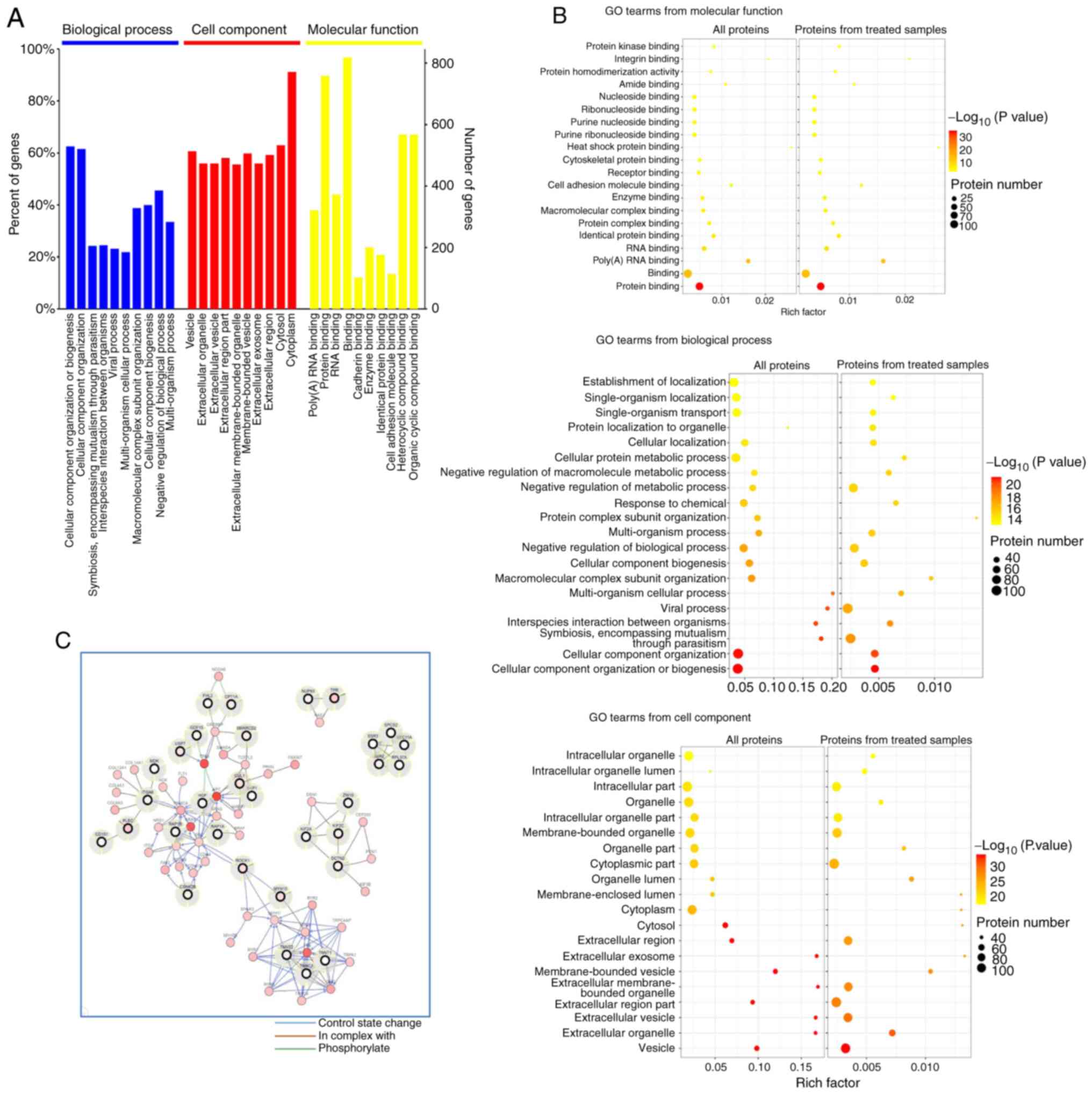
|
1
|
Zheng Y, Ley SH and Hu FB: Global
aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its
complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 14:88–98. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bommer C, Heesemann E, Sagalova V,
Manne-Goehler J, Atun R, Barnighausen T and Vollmer S: The global
economic burden of diabetes in adults aged 20–79 years: A
cost-of-illness study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 5:423–430. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nazir MA, AlGhamdi L, AlKadi M, AlBeajan
N, AlRashoudi L and AlHussan M: The burden of diabetes, its oral
complications and their prevention and management. Open Access
Maced J Med Sci. 6:1545–1553. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
World Health Organization: Fact sheets.
http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetesJune
29–2019
|
|
5
|
Dall TM, Yang W, Gillespie K, Mocarski M,
Byrne E, Cintina I, Beronja K, Semilla AP, Iacobucci W and Hogan
PF: The economic burden of elevated blood glucose levels in 2017:
Diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes, gestational diabetes mellitus,
and prediabetes. Diabetes Care. 42:1661–1668. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang P, Lu YC, Wang J, Wang L, Yu H, Li
YF, Kong A, Chan J and Lee S: Type 2 diabetes promotes cell
centrosome amplification via AKT-ROS-dependent signalling of ROCK1
and 14-3-3σ. Cell Physiol Biochem. 47:356–367. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Giovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC,
Bergenstal RM, Gapstur SM, Habel LA, Pollak M, Regensteiner JG and
Yee D: Diabetes and cancer: A consensus report. Diabetes Care.
33:1674–1685. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhu B, Wu X, Wu B, Pei D, Zhang L and Wei
L: The relationship between diabetes and colorectal cancer
prognosis: A meta-analysis based on the cohort studies. PLoS One.
12:e01760682017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, You X, Liu H, Xu M, Dang Q, Yang
L, Huang J and Shi W: High KIF2A expression predicts unfavorable
prognosis in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol.
96:1485–1491. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Landman GW, Ubink-Veltmaat LJ, Kleefstra
N, Kollen BJ and Bilo HJ: Increased cancer mortality in type 2
diabetes (ZODIAC-3). Anticancer Res. 28:1373–1375. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
D'Assoro AB, Lingle WL and Salisbury JL:
Centrosome amplification and the development of cancer. Oncogene.
21:6146–6153. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Basto R, Brunk K, Vinadogrova T, Peel N,
Franz A, Khodjakov A and Raff JW: Centrosome amplification can
initiate tumorigenesis in flies. Cell. 133:1032–1042. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li J, Xuan JW, Khatamianfar V, Valiyeva F,
Moussa M, Sadek A, Yang BB, Dong BJ, Huang YR and Gao WQ: SKA1
over-expression promotes centriole over-duplication, centrosome
amplification and prostate tumourigenesis. J Pathol. 234:178–189.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fan G, Sun L, Shan P, Zhang X, Huan J,
Zhang X, Li D, Wang T, Wei T, Zhang X, et al: Loss of KLF14
triggers centrosome amplification and tumorigenesis. Nat Commun.
6:84502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Levine MS, Bakker B, Boeckx B, Moyett J,
Lu J, Vitre B, Spierings DC, Lansdorp PM, Cleveland DW, Lambrechts
D, et al: Centrosome amplification is sufficient to promote
spontaneous tumorigenesis in mammals. Dev Cell. 40:313–322.e5.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dionne LK, Shim K, Hoshi M, Cheng T, Wang
J, Marthiens V, Knoten A, Basto R, Jain S and Mahjoub MR:
Centrosome amplification disrupts renal development and causes
cystogenesis. J Cell Biol. 217:2485–2501. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Godinho SA, Picone R, Burute M, Dagher R,
Su Y, Leung CT, Polyak K, Brugge JS, Théry M and Pellman D:
Oncogene-like induction of cellular invasion from centrosome
amplification. Nature. 510:167–171. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee SC and Chan JC: Evidence for DNA
damage as a biological link between diabetes and cancer. Chin Med J
(Engl). 128:1543–1548. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dodson H, Bourke E, Jeffers LJ, Vagnarelli
P, Sonoda E, Takeda S, Earnshaw WC, Merdes A and Morrison C:
Centrosome amplification induced by DNA damage occurs during a
prolonged G2 phase and involves ATM. EMBO J. 23:3864–3873. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
He QJ, Wang P, Liu Q, Wu Q, Li YF, Wang J
and Lee SC: Secreted Wnt6 mediates diabetes-associated centrosome
amplification via its receptor FZD4. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
318:C48–C62. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hartmann S, Ridley AJ and Lutz S: The
function of Rho-associated kinases ROCK1 and ROCK2 in the
pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease. Front Pharmacol. 6:2762015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liang H, Zhang C, Guan H, Liu J and Cui Y:
LncRNA DANCR promotes cervical cancer progression by upregulating
ROCK1 via sponging miR-335-5p. J Cell Physiol. 234:7266–7278. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tsai NP and Wei LN: RhoA/ROCK1 signaling
regulates stress granule formation and apoptosis. Cell Signal.
22:668–675. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen S, Liu Z, Lu S and Hu B: EPEL
promotes the migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by
upregulating ROCK1. Oncol Lett. 17:3133–3140. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zucchini C, Martinelli M, De Sanctis P,
Rodia MT, Mattei G, Ugolini G, Montroni I, Ghignone F and Solmi R:
Possible gender-related modulation by the ROCK1 gene in colorectal
cancer susceptibility. Pathobiology. 82:252–258. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Akagi EM, Lavorato-Rocha AM, Maia Bde M,
Rodrigues IS, Carvalho KC, Stiepcich MM, Baiocchi G, Sato-Kuwabara
Y, Rogatto SR, Soares FA and Rocha RM: ROCK1 as a novel prognostic
marker in vulvar cancer. BMC Cancer. 14:8222014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Beeharry N, Lowe JE, Hernandez AR,
Chambers JA, Fucassi F, Cragg PJ, Green MH and Green IC: Linoleic
acid and antioxidants protect against DNA damage and apoptosis
induced by palmitic acid. Mutat Res. 530:27–33. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chan N and Lim TM: Cytoplasmic
nucleophosmin has elevated T199 phosphorylation upon which G2/M
phase progression is dependent. Sci Rep. 5:117772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nunes P, Ernandez T, Roth I, Qiao X,
Strebel D, Bouley R, Charollais A, Ramadori P, Foti M, Meda P, et
al: Hypertonic stress promotes autophagy and microtubule-dependent
autophagosomal clusters. Autophagy. 9:550–567. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu M, Li XX, Chen Y, Pitzer AL, Zhang Y
and Li PL: Enhancement of dynein-mediated autophagosome trafficking
and autophagy maturation by ROS in mouse coronary arterial
myocytes. J Cell Mol Med. 18:2165–2175. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Braathen GJ, Høyer H, Busk ØL, Tveten K,
Skjelbred CF and Russell MB: Variants in the genes DCTN2, DNAH10,
LRIG3, and MYO1A are associated with intermediate
charcot-marie-tooth disease in a Norwegian family. Acta Neurol
Scand. 134:67–75. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bransfield KL, Askham JM, Leek JP,
Robinson PA and Mighell AJ: Phenotypic changes associated with
DYNACTIN-2 (DCTN2) over expression characterise SJSA-1 osteosarcoma
cells. Mol Carcinog. 45:157–163. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fischer U, Keller A, Leidinger P,
Deutscher S, Heisel S, Urbschat S, Lenhof HP and Meese E: A
different view on DNA amplifications indicates frequent, highly
complex, and stable amplicons on 12q13-21 in glioma. Mol Cancer
Res. 6:576–584. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Q, Wang X, Liang Q, Wang S, Liao X,
Li D and Pan F: Prognostic value of dynactin mRNA expression in
cutaneous melanoma. Med Sci Monit. 24:3752–3763. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang S, Wang Q, Zhang X, Liao X, Wang G,
Yu L, Zhang W, Zhou Q, Hu S and Yuan W: Distinct prognostic value
of dynactin subunit 4 (DCTN4) and diagnostic value of DCTN1, DCTN2,
and DCTN4 in colon adenocarcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 10:5807–5824.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Han X, Hou S and Yang A: Correlation
between IGFs-related proteins expression and incidence of
colorectal cancer in diabetic patients and related mechanisms. Med
Sci Monit. 22:848–854. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Marthiens V, Rujano MA, Pennetier C,
Tessier S, Paul-Gilloteaux P and Basto R: Centrosome amplification
causes microcephaly. Nat Cell Biol. 15:731–740. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mahjoub MR and Stearns T: Supernumerary
centrosomes nucleate extra cilia and compromise primary cilium
signaling. Curr Biol. 22:1628–1634. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Otto EA, Hurd TW, Airik R, Chaki M, Zhou
W, Stoetzel C, Patil SB, Levy S, Ghosh AK, Murga-Zamalloa CA, et
al: Candidate exome capture identifies mutation of SDCCAG8 as the
cause of a retinal-renal ciliopathy. Nat Genet. 42:840–850. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|