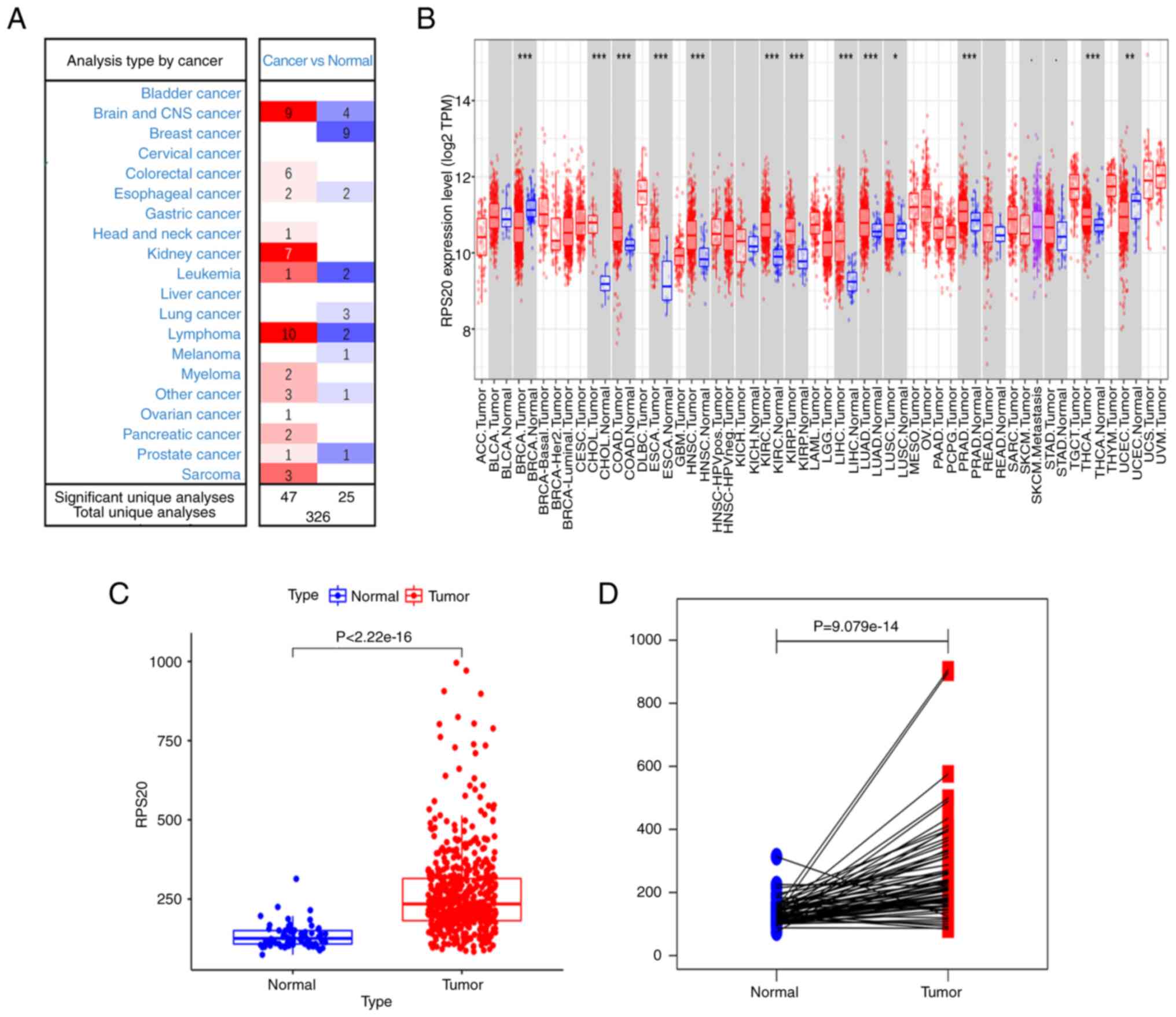
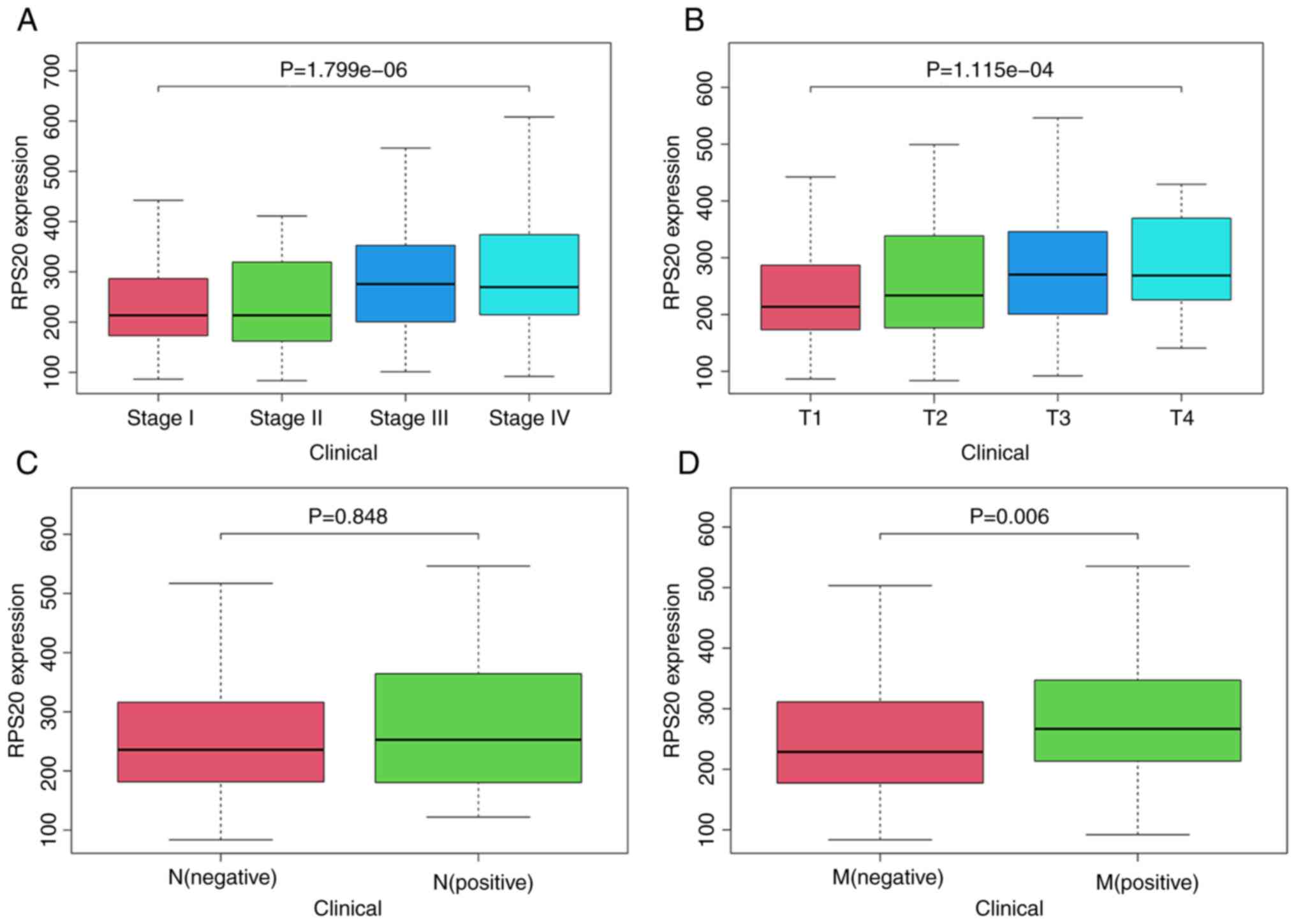
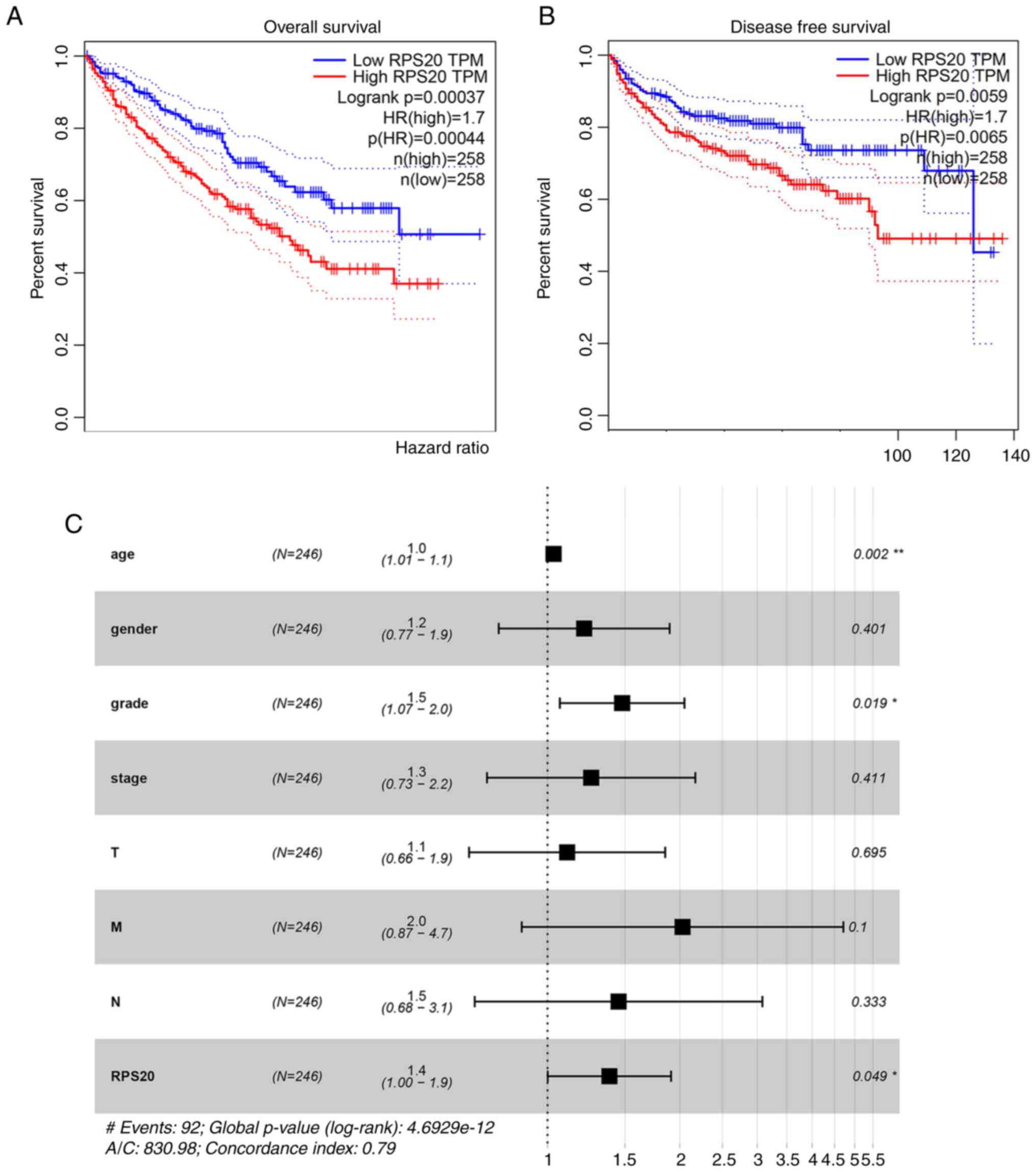
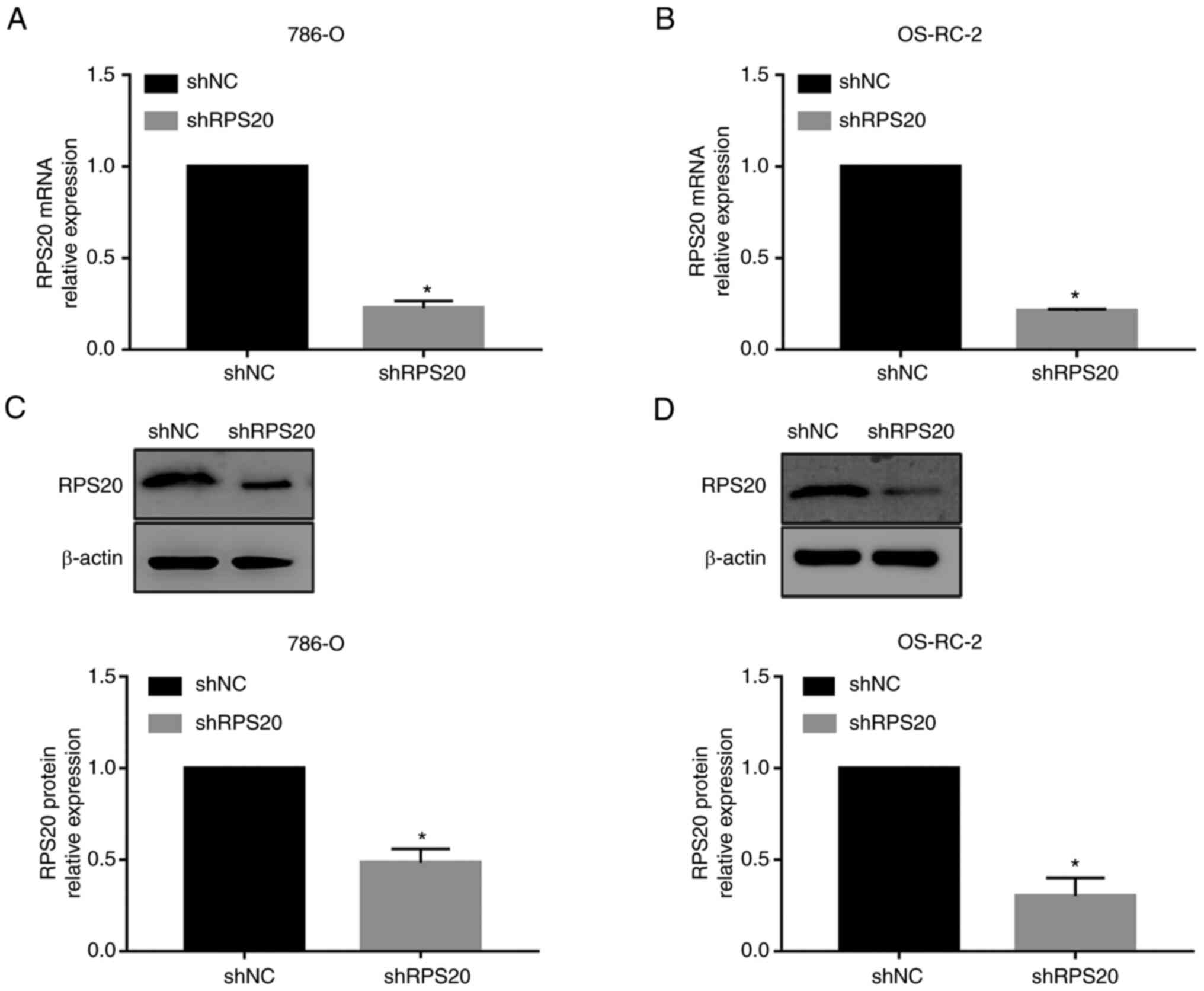
|
1
|
Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB,
Rowland JH, Yabroff KR, Alfano CM, Jemal A, Kramer JL and Siegel
RL: Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J
Clin. 69:363–385. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fernández-Pello S, Hofmann F, Tahbaz R,
Marconi L, Lam TB, Albiges L, Bensalah K, Canfield SE, Dabestani S,
Giles RH, et al: A systematic review and meta-analysis comparing
the effectiveness and adverse effects of different systemic
treatments for non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol.
71:426–436. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rhoades Smith KE and Bilen MA: A review of
papillary renal cell carcinoma and MET inhibitors. Kidney Cancer.
3:151–161. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen VJ, Hernandez-Meza G, Agrawal P,
Zhang CA, Xie L, Gong CL, Hoerner CR, Srinivas S, Oermann EK and
Fan AC: Time on therapy for at least three months correlates with
overall survival in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancers
(Basel). 11:10002019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gao C, Guo X, Xue A, Ruan Y, Wang H and
Gao X: High intratumoral expression of eIF4A1 promotes
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and predicts unfavorable
prognosis in gastric cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
52:310–319. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ruggero D and Pandolfi PP: Does the
ribosome translate cancer? Nat Rev Cancer. 3:179–192. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lindström MS: Emerging functions of
ribosomal proteins in gene-specific transcription and translation.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 379:167–170. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chu W, Presky DH, Swerlick RA and Burns
DK: Human ribosomal protein S20 cDNA sequence. Nucleic Acids Res.
21:16721993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
O'Donohue MF, Choesmel V, Faubladier M,
Fichant G and Gleizes PE: Functional dichotomy of ribosomal
proteins during the synthesis of mammalian 40S ribosomal subunits.
J Cell Biol. 190:853–866. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tai LR, Chou CW, Wu JY, Kirby R and Lin A:
Late-assembly of human ribosomal protein S20 in the cytoplasm is
essential for the functioning of the small subunit ribosome. Exp
Cell Res. 319:2947–2953. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ko JR, Wu JY, Kirby R, Li IF and Lin A:
Mapping the essential structures of human ribosomal protein L7 for
nuclear entry, ribosome assembly and function. FEBS Lett.
580:3804–3810. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen IJ, Wang IA, Tai LR and Lin A: The
role of expansion segment of human ribosomal protein L35 in nuclear
entry, translation activity, and endoplasmic reticulum docking.
Biochem Cell Biol. 86:271–277. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schmidt C, Lipsius E and Kruppa J: Nuclear
and nucleolar targeting of human ribosomal protein S6. Mol Biol
Cell. 6:1875–1885. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shu-Nu C, Lin CH and Lin A: An acidic
amino acid cluster regulates the nucleolar localization and
ribosome assembly of human ribosomal protein L22. FEBS Lett.
484:22–28. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Da Costa L, Tchernia G, Gascard P, Lo A,
Meerpohl J, Niemeyer C, Chasis JA, Fixler J and Mohandas N:
Nucleolar localization of RPS19 protein in normal cells and
mislocalization due to mutations in the nucleolar localization
signals in 2 Diamond-Blackfan anemia patients: Potential insights
into pathophysiology. Blood. 101:5039–5045. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Antoine M, Reimers K, Wirz W, Gressner AM,
Müller R and Kiefer P: Identification of an unconventional nuclear
localization signal in human ribosomal protein S2. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 335:146–153. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ferreira-Cerca S, Pöll G, Gleizes PE,
Tschochner H and Milkereit P: Roles of eukaryotic ribosomal
proteins in maturation and transport of pre-18S rRNA and ribosome
function. Mol Cell. 20:263–275. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rouquette J, Choesmel V and Gleizes PE:
Nuclear export and cytoplasmic processing of precursors to the 40S
ribosomal subunits in mammalian cells. EMBO J. 24:2862–2872. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y and Lu H: Signaling to p53:
Ribosomal proteins find their way. Cancer Cell. 16:369–377. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Boulon S, Westman BJ, Hutten S, Boisvert
FM and Lamond AI: The nucleolus under stress. Mol Cell. 40:216–227.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Y, Wolf GW, Bhat K, Jin A, Allio T,
Burkhart WA and Xiong Y: Ribosomal protein L11 negatively regulates
oncoprotein MDM2 and mediates a p53-dependent ribosomal-stress
checkpoint pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 23:8902–8912. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dai MS and Lu H: Inhibition of
MDM2-mediated p53 ubiquitination and degradation by ribosomal
protein L5. J Biol Chem. 279:44475–44482. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jin A, Itahana K, O'Keefe K and Zhang Y:
Inhibition of HDM2 and activation of p53 by ribosomal protein L23.
Mol Cell Biol. 24:7669–7680. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang Y, Wang J, Yuan Y, Zhang W, Guan W,
Wu Z, Jin C, Chen H, Zhang L, Yang X and He F: Negative regulation
of HDM2 to attenuate p53 degradation by ribosomal protein L26.
Nucleic Acids Res. 38:6544–6554. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen D, Zhang Z, Li M, Wang W, Li Y,
Rayburn ER, Hill DL, Wang H and Zhang R: Ribosomal protein S7 as a
novel modulator of p53-MDM2 interaction: Binding to MDM2,
stabilization of p53 protein, and activation of p53 function.
Oncogene. 26:5029–5037. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xiong X, Zhao Y, He H and Sun Y: Ribosomal
protein S27-like and S27 interplay with p53-MDM2 axis as a target,
a substrate and a regulator. Oncogene. 30:1798–1811. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun XX, DeVine T, Challagundla KB and Dai
MS: Interplay between ribosomal protein S27a and MDM2 protein in
p53 activation in response to ribosomal stress. J Biol Chem.
286:22730–22741. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Frum R, Busby SA, Ramamoorthy M, Deb S,
Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF and Deb SP: HDM2-binding partners:
Interaction with translation elongation factor EF1alpha. J Proteome
Res. 6:1410–1417. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Krishnan R, Boddapati N and Mahalingam S:
Interplay between human nucleolar GNL1 and RPS20 is critical to
modulate cell proliferation. Sci Rep. 8:114212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rhodes DR, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Mahavisno
V, Varambally R, Yu J, Briggs BB, Barrette TR, Anstet MJ,
Kincead-Beal C, Kulkarni P, et al: Oncomine 3.0: Genes, pathways,
and networks in a collection of 18,000 cancer gene expression
profiles. Neoplasia. 9:166–180. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lánczky A, Nagy Á, Bottai G, Munkácsy G,
Szabó A, Santarpia L and Győrffy B: miRpower: A web-tool to
validate survival-associated miRNAs utilizing expression data from
2178 breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 160:439–446.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:W98–W102.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zheng B, Mao JH, Qian L, Zhu H, Gu DH, Pan
XD, Yi F and Ji DM: Pre-clinical evaluation of AZD-2014, a novel
mTORC1/2 dual inhibitor, against renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett.
357:468–475. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wettersten HI, Aboud OA, Lara PN and Weiss
RH: Metabolic reprogramming in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat
Rev Nephrol. 13:410–419. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xie M, Ma T, Xue J, Ma H, Sun M, Zhang Z,
Liu M, Liu Y, Ju S, Wang Z and De W: The long intergenic
non-protein coding RNA 707 promotes proliferation and metastasis of
gastric cancer by interacting with mRNA stabilizing protein HuR.
Cancer Lett. 443:67–79. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dai MS, Sears R and Lu H: Feedback
regulation of c-Myc by ribosomal protein L11. Cell Cycle.
6:2735–2741. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Khanna N, Sen S, Sharma H and Singh N: S29
ribosomal protein induces apoptosis in H520 cells and sensitizes
them to chemotherapy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 304:26–35. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Warner JR and McIntosh KB: How common are
extraribosomal functions of ribosomal proteins? Mol Cell. 34:3–11.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Daftuar L, Zhu Y, Jacq X and Prives C:
Ribosomal proteins RPL37, RPS15 and RPS20 regulate the
Mdm2-p53-MdmX network. PLoS One. 8:e686672013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nieminen TT, O'Donohue MF, Wu Y, Lohi H,
Scherer SW, Paterson AD, Ellonen P, Abdel-Rahman WM, Valo S,
Mecklin JP, et al: Germline mutation of RPS20, encoding a ribosomal
protein, causes predisposition to hereditary nonpolyposis
colorectal carcinoma without DNA mismatch repair deficiency.
Gastroenterology. 147:595–598.e5. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li CX, Chen J, Xu ZG, Yiu WK and Lin YT:
The expression and prognostic value of RNA binding proteins in
clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Transl Cancer Res Dec.
9:7415–7431. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Uekita T and Sakai R: Roles of CUB
domain-containing protein 1 signaling in cancer invasion and
metastasis. Cancer Sci. 102:1943–1948. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Friedl P, Locker J, Sahai E and Segall JE:
Classifying collective cancer cell invasion. Nat Cell Biol.
14:777–783. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fan D, Liu Q, Wu F, Liu N, Qu H, Yuan Y,
Li Y, Gao H, Ge J, Xu Y, et al: Prognostic significance of
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway members in clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. PeerJ. 8:e92612020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Igaki T, Pagliarini RA and Xu T: Loss of
cell polarity drives tumor growth and invasion through JNK
activation in Drosophila. Curr Biol. 16:1139–1146. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen PN, Hsieh YS, Chiang CL, Chiou HL,
Yang SF and Chu SC: Silibinin inhibits invasion of oral cancer
cells by suppressing the MAPK pathway. J Dent Res. 85:220–225.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Reddy KB, Nabha SM and Atanaskova N: Role
of MAP kinase in tumor progression and invasion. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 22:395–403. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Toyoda H,
Takamatsu R, Yasuda E, Okuda S, Maeda A, Kaneoka Y, Yoshimi N,
Kumada T and Kozawa O: Heat shock protein 22 (HSPB8) reduces the
migra-tion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the
suppression of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1863:1629–1639. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang L, Fang Z, Gao P and Zheng J: GLUD1
suppresses renal tumorigenesis and development via inhibiting
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Front Oncol. 12:9755172022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|