Introduction
Most cases of leukemia are acute lymphoid, acute
myeloid leukemia or chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) (1). CML has been used as a model cancer
demonstrating the clinical benefit of targeted therapy and the
ability of molecular diagnosis and monitoring (2). Dr Janet Rowley determined that a
shortened chromosome 22 is formed after the mutual translocation
between chromosome 9 and 22; ABL1 gene on chromosome 9 is inserted
into the BCR region of chromosome 22; this translocation produces a
fusion oncoprotein, BCR-ABL1 (3).
The BCR-ABL chimeric gene is responsible for the production of
BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase (4).
Imatinib (IM) is a small molecule drug that competitively binds to
the ATP-binding site of BCR-ABL. This inhibits the
autophosphorylation of BCR-ABL, prevents its activation and blocks
its downstream signaling (5).
However, IM drug resistance and intolerance remain an issue in
certain individuals, contributing to recurrence after treatment
discontinuation (6). The N-Myc
downstream-regulated gene (NDRG) family, which has four members, is
functionally involved in multiple biological behaviors and can be
used as a biomarker for various types of diseases, including
prostate cancer, nervous system diseases and liver damage (7–9). NDRG2
plays an important role in cell proliferation, metastasis and
apoptosis (10). NDRG3 is
upregulated in tumor tissues (11–13).
NDRG3 and the flexible loop corresponding to helix α6 of NDRG2
responsible for tumor suppression have structural differences
leading to distinct roles, and this flexible loop region appears to
play a unique role in NDRG3-induced oncogenic progression (14). As a key genetic element of
lactate-dependent regulation, NDRG3 binds to lactate to maintain
tumor progression and promote angiogenesis via the Raf/Erk pathway
(15,16). At the same time, NDRG3 inhibits
hypoxia-induced apoptosis (12).
The role of a class of endogenous RNA molecules, microRNAs (miRNAs
or miRs), has received extensive attention in cell biology
(17,18). miRNAs are small non-coding RNAs that
inhibit gene expression by binding to the 3′ untranslated region
(UTR) of target mRNAs and are involved in biological behaviors such
as cell proliferation and migration; it has been reported that
miRNAs are involved in drug resistance (19–21).
NDRG3 is associated with drug resistance. The small nucleolar RNA
host gene 20/miR-140-5p/NDRG3 axis is implicated in resistance to
5-fluorouracil in gastric cancer cell lines; miR-31 inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) proliferation in vitro and
in vivo and sensitizes HCC cancer cells to adri-70
doxorubicin by regulating its target gene NDRG3 (22,23).
To the best of our knowledge, however, the role of NDRG3 in CML
imatinib resistance has not been studied.
The upregulation of the Wnt signaling pathway has
been implicated in tumorigenesis due to aberrant activation of
β-catenin signaling, which is involved in cell metastasis,
differentiation and drug resistance (24–26).
In the cytoplasm, free β-catenin is typically transient, recognized
by destruction complexes and rapidly targeted for degradation
(27). The destruction complex
contains the proteins glycogen synthase kinase 3β, adenomatous
polyposis coli, casein kinase 1 and axin (28). When the degradation complex of
β-catenin is converted into the active form, phosphorylated
β-catenin is ubiquitinated and transported to the proteasome for
degradation; when the degradation complex is inactive, β-catenin
accumulates, flows into the nucleus to form a transcriptional
complex with T cell-specific transcription factor/lymphoid
enhancer-binding factor and initiates the transcription of
downstream genes (29,30). β-catenin activates the transcription
of c-Myc and cyclinD1, which are involved in cell proliferation and
gene expression (27,31). Therefore, the present study
investigated the role of β-catenin in IM resistance in CML to
identify potential targets and mechanisms against drug
resistance.
Materials and methods
Clinical samples
Patient and normal control samples were obtained
from the Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University
(Shandong, China). Sample collection was performed from October
2021 to January 2022. All patients were diagnosed with CML by
pathology. The healthy controls had no physical disease or tumor.
Subject information is shown in Table
SI. The research protocol was approved by the Medical Ethics
Committee of Binzhou Medical University (approval no. 2020-10-06)
and the written informed consent of all subjects was obtained
before study.
Cell culture
The human CML cell line K562 (Shanghai Yaji
Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) was cultured in RPMI-1640 medium
supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (both Gibco; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin (Beyotime
Institute of Biotechnology) in a humid atmosphere containing 5%
CO2, 37°C. K562 is a cell line isolated from the bone
marrow of a 53-year-old patient with CML. We use K562 cells as the
maternal cell line. K562 cells were treated with imatinib (IM)
(Aladdin Industrial Corporation) to create the resistant K/G cells.
K/G cells were incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 in the
presence of 10 µM IM for at least three days before the start of
the experiment.
Lentiviral transduction
The lentiviral expression vector (pCDHNC or
pCDHNDRG3; KeyyBio Sciences) and second-generation lentiviral
packaging vectors (Addgene, Inc.) were transfected into 293T
(Shanghai Cell Bank, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China) cells at
37°C. The working solution (target plasmid: helper 1.0 plasmid:
helper2.0 plasmid=16:12:8 µg) was placed into a 1.5 ml Eppendorf
(EP) tube and 0.5 ml normal saline was added. At the same time, 10
µl VigoFect (Viglass Biotech) was added to another EP tube and
supplemented with 0.5 ml normal saline. The two solutions were
gently mixed and incubated for 15 min at 37°C, placed into a petri
dish and incubated at 37°C and 5% CO2. Duration of
transfection was 6 h. Six hours after transfection, the cells were
cultured in 1640 medium containing 10% serum. The virus supernatant
was collected after 24 h, 48h and 72 h. Cell debris was removed by
centrifugation at 4,000 g for 10 min at 4°C. K/G cells were
infected at an MOI of 20 with polybrene (Sigma Aldrich; Merck KGaA)
and lentiviral particles. Transfection was performed at a cell
density of 70–80% in six-well plates in a 37°C, 5% CO2
incubator. Infection efficiency was assessed by observing the
expression of GFP using a fluorescence microscope. After infected
with lentivirus for 6–8 h, the cells were replaced with 1640 medium
with 10% serum for culture. Follow-up experiments were carried out
after 24–48 h. Transduction into target cells can last 48–72 h. The
empty plasmid served as a negative control (NC). The plasmid
vectors were from GenePharma Company. The sequences were as
follows: NC forward, 5′-GTTCTCCGAACGTGTCACGT(T)-3′ and reverse,
5′-AACGTGACACGTTCGGAGAACTT-3′; small interfering (si)-NDRG3
forward, 5′-AGGAAGAGTTACAGGCCAATT-3′ and reverse,
5′-TTGGCCTGTAACTCTTCCT(T)-3′; si-β-catenin forward,
5′-TGGTTAATAAGGCTGCAGTTATTTCAAGAGAATAACTGCAGCCTTATTAACCTTTTTTC-3′
and reverse,
5′-TCGAGAAAAAAGGTTAATAAGGCTGCAGTTATTCTCTTGAAATAACTGCAGCCTTATTAACCA-3′;
miR-204-5p-mimic forward, 5′-TTCCCTTTGTCATCCTATGCCT-3′ and reverse,
5′-AGGCATAGGATGACAAAGGGAA(TT)-3′ and miR-204-5p- inhibitor,
5′-AGGCATAGGATGACAAAGGGAA(TT)-3′.
Cell Counting Kit (CCK)-8 assay
Following transfection, a bovine abalone counter was
used to count K562 and K/G cells. Cells were plated into 96-well
flat bottom plates at 2×103 cells/well with or without
16 µM IM treatment at 37°C, 24 h. After cells were cultured for 0,
24, 48 and 72 h at 37°C, the cell proliferation was determined
using the CCK-8 kit (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology).
K/G cells were plated into 96-well flat bottom
plates at 2×103 cells/well with or without IM (0, 1, 2,
4, 8, 16, 32, 64 and 128 µM) for 24 h at 37 °C. CCK-8 reagent was
added to the cultured cells for 2 h. The absorbance at 450 nm was
determined using a microplate reader (Multiskan FC; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.). The cell viability curve was constructed and the
half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was
obtained using GraphPad Prism 8 software (GraphPad Software,
Inc.).
Western blot analysis
Cell and tissue proteins were extracted using RIPA
(Beyotime Biotechnology). Protein concentration was detected by the
BCA kit and the protein loading was 10–40 µg. Proteins were
separated by using a 10% gel for polyacrylamide gel
electrophoresis, and transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride
membranes and blocked for 2 h with 5% skimmed milk at room
temperature. Then, proteins on the membrane were detected with
primary antibodies for 16–18 h at 4°C, including anti-β-catenin
(1:1,000; cat. no. bsm-33194M; BIOSS), anti-NDRG3 (1:750; cat. no.
BS62436; Bioworld Technology, Inc.), anti-c-Myc (1:6,000; ca. to.
10828-1-AP; Proteintech Group, Inc.), anti-MDR1 (1:1,000; ca. to.
13342S; Cell Signaling Technology), anti-LaminB1 (1:6,000;
cat.no.12987-I-AP; Proteintech Group, Inc.) and anti-GAPDH
(1:6,000; cat. no. BS65483M; Bioworld Technology, Inc.). After 2 h
of incubation with goat anti-rabbit IgG H&L HRP conjugate
secondary antibody (1:6,000; cat. no. BS13278; Bioworld Technology,
Inc.) at 4°C, protein bands were visualized using BeyoECL Plus
(Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology). Finally, the densitometric
analysis of the protein was performed using ImageJ software
(National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA).
Reverse transcriptionquantitative
(RTq)PCR
RNA was extracted from cells and tissues on ice
using TRIzol® reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc).
According to the manufacturer's protocol, reverse transcription of
RNA was performed to generate cDNA using PrimeScript RT Kit (Takara
Bio, Inc). Reagents for RT-qPCR (SYBR® Mix ExTaq™ II)
were obtained from Takara Bio, Inc. Thermocycling conditions were
as follows: Initial denaturation at 95°C for 2 min, followed by 40
cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 15 sec, annealing at 60°C for 30
sec and extension at 72°C for 30 sec.
5S rRNA was used as the internal reference gene of
miRNA. GAPDH was used as the internal reference gene of mRNA and
the 2−ΔΔCq method was used for normalization (32). Primers used for RT-qPCR are shown in
Tables SII and SIII. The analysis of clinical samples was
performed based on the change in cycle threshold (ΔCq) between the
target gene NDRG3 and housekeeping gene GAPDH using
2−ΔCq (33).
Flow cytometric analysis
Treated K/G cells were seeded into 6-well plates at
a density of 70–80% and cultured for 48 h at 37°C. Then, cells were
fixed with 70% ethanol for 12–16 h at 4°C and stained with
propidium iodide (PI/RNaseA, Nanjing KeyGen Biotech Co., Ltd.) for
30–60 min at room temperature. Cell cycle distribution was analyzed
using a BD Accuri™ C6 Plus Flow Cytometer (BD Biosciences) and
ModFitLT4.0 mapping (Verity Software House).
Luciferase activity assay
Based on the wild-type (wt) binding site between
miR-204-5p and NDRG3 (determined via Targetscan7.1;
targetscan.org/vert_71/), the mutant (mut) sequence fragment of
NDRG3 was designed. Luciferase reporter plasmids, including
NDRG3-3′-UTR-wt and NDRG3-3′-UTR-mut, were constructed by
GenePharma The sequences were as follows:
NC,5′-GTTCTCCGAACGTGTCACGT(T)-3′; miR-204-5p,
5′-TTCCCTTTGTCATCCTATGCCT-3′. The plasmid vectors were from
GenePharma Company. For dual-luciferase reporter assays, 293T cells
were transfected with miR-204-5p or NC and NDRG3-3′-UTR-wt or
NDRG3-3′-UTR-mut and incubated by using Lipofectamine
2000® reagent (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc) for 4–8 h. Duration between transfection and activity
measurement was 48 h. Then, cells were harvested and lysed on ice.
The luciferase activity was measured using a Dual-Glo®
Luciferase Assay System (Promega Corporation). Firefly luciferase
activity was normalized to Renilla luciferase activity.
Immunofluorescence
Sterilized cover slips were placed onto 24-well
plates. Gelatin-coated solution (400 µl, Sigma Aldrich, USA) was
added for 10 min at room temperature. Excess gelatin-coated
solution was aspirated and coverslips were air-dried for 15 min.
Dry cover slips were stored at room temperature until use. Treated
293T cells were seeded onto gelatin coverslips at a cell density of
50–60%, which were prewashed three times with Phosphate Buffered
Saline (PBS). The formaldehyde fixative (300–400 µl, 2–4%) was
added to each well and incubated for 20 min at room temperature.
Coverslips containing fixed cells were washed twice with 400 µl
PBS). Non-specific staining was blocked by the addition of 400 µl
fluids (1% BSA+0.2% TritonX-100, PBS) and incubated for 1 h at room
temperature. coverslips were then incubated with mouse
anti-β-catenin (1:100; cat. no. bsm-33194M; BIOSS) and anti-NDRG3
(1:100; cat. no. BS62436; Bioworld Technology, Inc.) at 37°C for 2
h. Alexa fluor conjugate secondary antibodies (1:100,
Donkey-anti-Rabbit IgG-Alexa fluor 594, cat. no. abs20021, absin
and 1:100, goat anti-mouse IgG H&L/Alexa Fluor 488, cat. no.
bs-0296G-AF488, BIOSS) were incubated at 37°C for 2 h and stained
with DAPI (10 µg/ml, Solarbio) for 5–10 min at room temperature.
Images were captured by confocal microscopy at 400X magnification.
The same microscope/software intensity parameters were used for
both groups.
Extraction of cytoplasmic and nuclear
protein
K/G cells were washed once with PBS and centrifuged
by using Legend Micro 17R centrifuge (Thermo Scientific) at 500 ×
g, 4°C for 2–3 min. The supernatant was aspirated and the pellet
was retained. A total of 200 µl cytosol protein extraction kit
(Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd)/20 µl cell
pellet (~2×106 cells) was added, placed on ice for 10
min after pipetting evenly and centrifuged at 12,000 g and 4°C for
10 min. The supernatant contained plasma protein. The remaining
precipitate was added to 50–100 µl nuclear protein extraction kit
(Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd). the procedure
used to extract plasma proteins was used to extract nucleoprotein;
the obtained supernatant contained nucleoprotein, which was used
for subsequent experiments.
Immunoprecipitation
According to the requirements of the reagent
manufacturer, the nuclear protein extraction kit (Beijing Solarbio
Science & Technology Co., Ltd) was used to extract the
nucleoprotein, and the cells in a 10 cm culture dish need 800-1,000
µl the lysate. and centrifuged at 12,000 g for 10 min at 4°C.
Nuclear extracts were incubated on a rotator with 8–10 µl
anti-β-catenin overnight at 4°C. The anti-β-catenin antibody was
used for protein blotting (1:100; cat. no. A19657; ABclonal Biotech
Co, Ltd). A total of ~10 µl protein A/G agarose beads (cat. no.
PR40025; Proteintech Group, Inc.) was added and the IgG control was
detected by western blotting. The washing buffer was Tris-Buffered
Saline and 0.1% Tween20 (TBST). The protein-antibody protein
A/G-agarose bead complexes were boiled to achieve separation.
Western blot verification was then carried out.
Animal model
A total of 40 female nude mice (weighing 18 g were
purchased from Jinan Pengyue Company (BALB/c-nu; age, 5 weeks) and
they were kept in a laminar airflow cabinet under specific
pathogen-free conditions with a controlled temperature (23±2°C),
12/12-h light/dark cycle and humidity (40–70%) with free access to
food and water. Nude mice were divided into experimental groups
(n=5/group) with different treatments (pLV-NC,
pLV-miR-204-5p-mimic; pLV-NC, pLV-miR-204-5p-inhibitor; pLV-NC,
pLV-si-NDRG3; pLV-NC + IM, pLV-si-NDRG3 + IM). A total of
~5×106 K/G cells was resuspended into 50 µl PBS mixed
with 50 µl Matrigel (BD Biosciences) and subcutaneously into the
back of nude mice. For IM treatment, 10 mice were intraperitoneally
injected with IM (50 mg/kg) after the tumor grew to the seventh
day. Injection once on the fourteenth day, and once on the
twenty-first day, a total of three times. The health and weight of
mice were monitored every day. Tumor volume was measured every 5
days. After 25 days, 40 mice were euthanized by injection of sodium
pentobarbital (150–200 mg/kg). The tumor tissue was excised,
photographed and stored for western blotting. Animal experiments
were reviewed and approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of
Binzhou Medical University (Yantai, China; approval no.
2020-10-06).
Intervention
Inhibitor of β-catenin-responsive transcription 14
is abbreviated as iCRT14 (MedChemExpress). K/G cells were
transfected, and the groups were NDRG3+DMSO (Solarbio) and
NDRG3+iCRT14. The concentration of iCRT14 was 1 mM (dissolved in
DMSO), added iCRT14 after transfection 24 hours, and the final
concentration was 25 µM. The experiment was performed after another
24 h.
miRNAs databases
Targetscan database (targetscan.org/vert_71/), miRdb
(mirdb.org/index.html), mirDIP (ophid.utoronto.ca/mirDIP/) and
miRWalk (mirwalk.umm.uni-heidelberg.de/) were used to screen miRNAs
targeting NDRG3.
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation.
One-way ANOVA and Student's t test were used to compare differences
between three and two groups, respectively. Tukey's post hoc test
was used following ANOVA. Unpaired t-tests were used. All
statistical tests were two-sided. P<0.05 was considered to
indicate a statistically significant difference. GraphPad Prism 8
software was used for all data analysis.
Results
Expression of NDRG3 is associated with
cell proliferation in CML
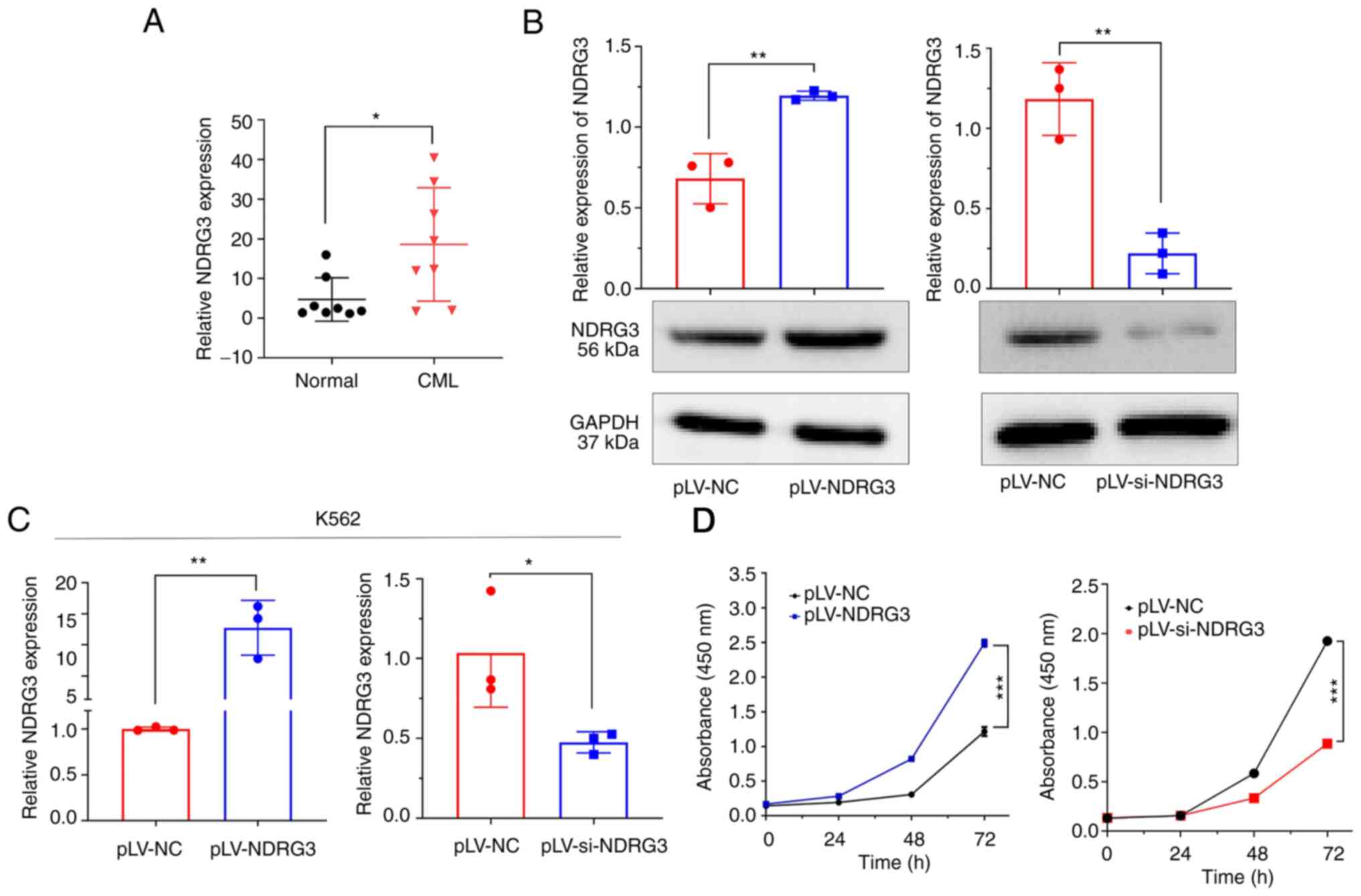
Expression of NDRG3 was assessed in patients with
CML and normal controls (both n=8) by RT-qPCR; NDRG3 was more
highly expressed in patients with CML (Fig. 1A). Next, the effects of
overexpression and knockdown of NDRG3 on mRNA and protein levels in
K562 cells were assessed by RT-qPCR and western blotting. NDRG3 was
successfully overexpressed and knocked down (Fig. 1B and C). IC50 in K562
cells was 0.2125 µM (Fig. S1).
CCK-8 assay confirmed that compared with the control, the
downregulation of NDRG3 significantly inhibited the proliferation
of K562 cells, whereas NDRG3 overexpression promoted the
proliferation of K562 cells (Fig.
1D).
NDRG3 promotes cell proliferation and
drug resistance in vitro and in vivo
Western blotting showed expression of NDRG3 in K/G
cells was higher than that in K562 cells, which suggested that
NDRG3 may be involved in drug resistance (Fig. 2A). NDRG3 knockdown group showed
significantly inhibited proliferation of K/G cells and NDRG3
knockdown + IM exhibited a notable inhibitory effect. The NDRG3
overexpression group promoted proliferation, but this was
attenuated when NDRG3 co-acts with IM (Figs. 2B and S2A and B). The cell cycle analysis
revealed that the NDRG3 knockdown group had a higher proportion of
G2/M phase cells compared with the control group (Fig. 2C). Growth curves showed that the
IC50 of IM was elevated in NDRG3-overexpressing cells
compared with untreated cells (Fig.
2D). The role of NDRG3 was verified by nude mouse xenograft
experiments (Fig. 2E). The tumor
growth curve showed the slowest growth in NDRG3 knockdown + IM
group (Fig. 2F). Knockdown of NDRG3
+ IM group had the smallest tumor weight (Fig. 2G and H). Finally, the pLV-si-NDRG3 +
IM group had the lowest NDRG3 protein expression in tumor tissue
(Fig. 2I). These results indicated
that NDRG3 promoted cellular IM resistance and proliferation in
vitro and in vivo.
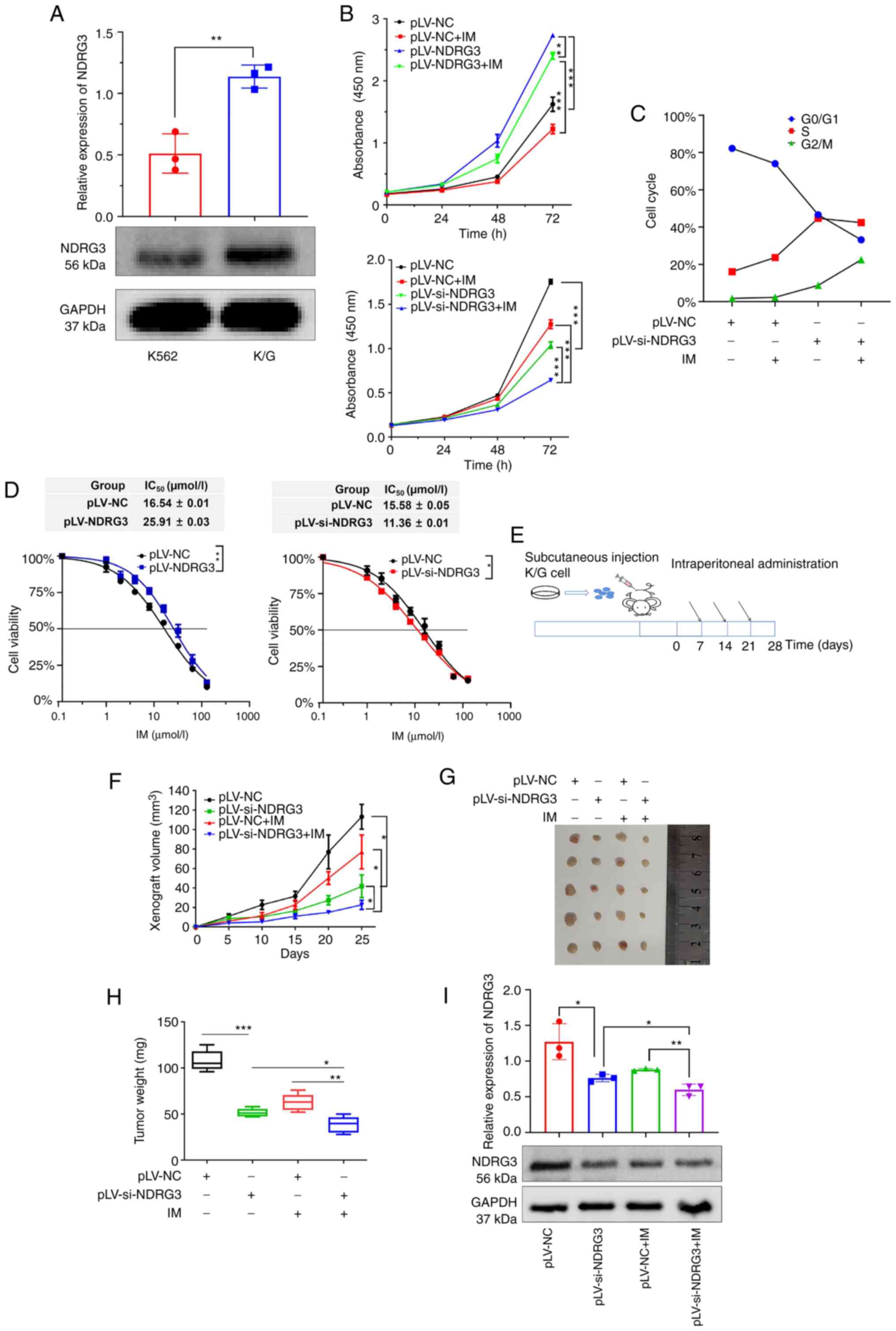 | Figure 2.NDRG3 promotes cell proliferation and
drug resistance in vitro and in vivo. (A) NDRG3
expression in K562 and K/G cells. (B) Cell proliferation after
NDRG3 and IM treatments at 0, 24, 48, and 72 h, as shown by the
CCK-8 assay. (C) Determination of cell cycle progression following
NDRG3 and IM treatment by flow cytometry. (D) Detection of IC50 by
CCK-8 assay after transfection of NDRG3. (E) Experimental timeline
of tumor-bearing nude mice. (F) Monitoring of tumor growth by using
tumor volume. (G) Representative images of tumor tissue. (H)
Monitoring of tumor growth by using tumor weight. (I) Expression of
NDRG3 protein in tumor tissues of nude mice shown by western
blotting. The histogram shows relative intensity of NDRG3 and
GAPDH. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001. NDRG3, N-Myc
downstream-regulated gene 3; CCK8, Cell Counting Kit8; IM,
imatinib; IC50, half-maximal inhibitory concentration;
NC, negative control; si, small interfering. |
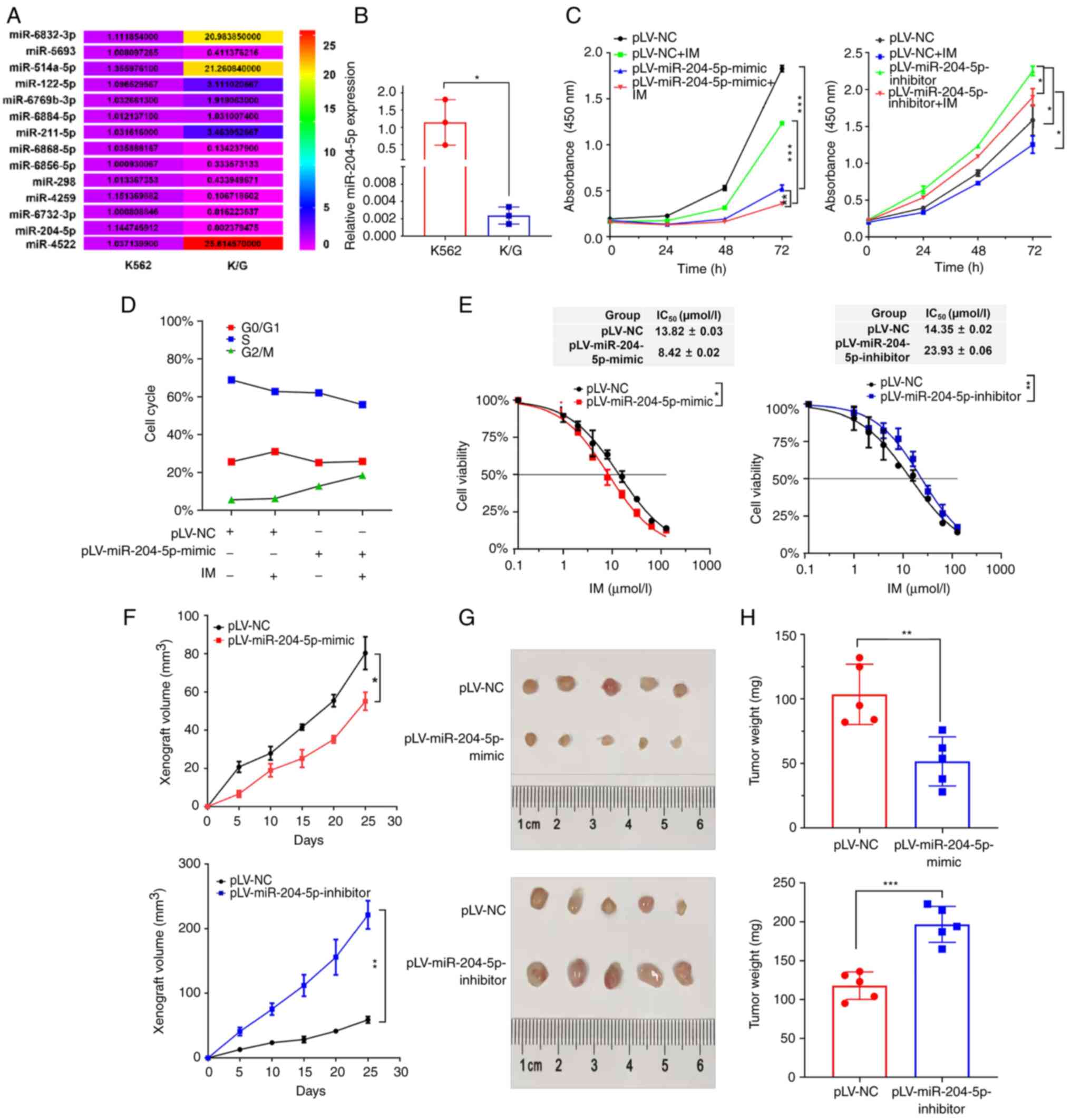
miR-204-5p suppresses cell
proliferation and drug resistance
To screen for miRNAs that may target NDRG3 and
participate in IM response, multiple databases were searched, which
identified 14 miRNAs (Fig. 3A).
miRNAs in K562 and K/G cell lines were analyzed by RT-qPCR;
miR-204-5p expression was lowest in K/G cells compared with K562
cells (Figs. S3A and B). The
proliferation of K/G cells in the IM, pLV-miR-204-5p-mimc and
pLV-miR-204-5p-mimic + IM groups was markedly decreased compared
with that in the pLV-nc group. Furthermore, pLV-miR-204-5p-mimic +
IM-treated cells exhibited a lower decrease in proliferation
compared with IM-treated cells. The miR-204-5p-inhibitor group
demonstrated that the cell proliferation was enhanced (Figs. 3C and S3B). The cell cycle assay indicated that
entry into G2/M phase was inhibited after overexpression of
miR-204-5p; this effect was stronger after combination with IM
(Fig. 3D). It was investigated
whether miR-204-5p-mimic increases IM sensitivity in CML cells.
IC50 of the miR-204-5p-mimic group was 8.422 µM in K/G
cells and IC50 of the miR-204-5p-inhibitor group was
23.93 µM (Fig. 3E).
The effect of miR-204-5p was verified in vivo
by tumor-bearing experiments in nude mice; compared with that in
the control group, tumor growth was slower in the miR-204-5p
overexpression group and faster in the miR-204-5p knockdown group
(Fig. 3F). Compared with the
control group, tumor weights of the overexpression and knockdown
groups were smaller and larger, respectively (Fig. 3G and H).
miR-204-5p targets NDRG3
To demonstrate that miR-204-5p targets NDRG3, wt and
mut NDRG3 3′-UTR regions were constructed (Fig. 4A). Dual-luciferase reporter gene
assay showed that miR-204-5p targeted the 3′-UTR of NDRG3 (Fig. 4B). miR-204-5p-mimic significantly
decreased NDRG3 protein levels in cells and tumor tissue (Fig. 4C and D). Cell proliferation
experiments showed that the inhibitory effect of miR-204-5p on cell
proliferation and drug resistance was alleviated following
co-transfection with miR-204-5p-mimic with NDRG3 (Fig. 4E and F). In summary, these results
suggested that miR-204-5p inhibited the expression of NDRG3 and
that NDRG3 overexpression abolished the effect of miR-204-5p.
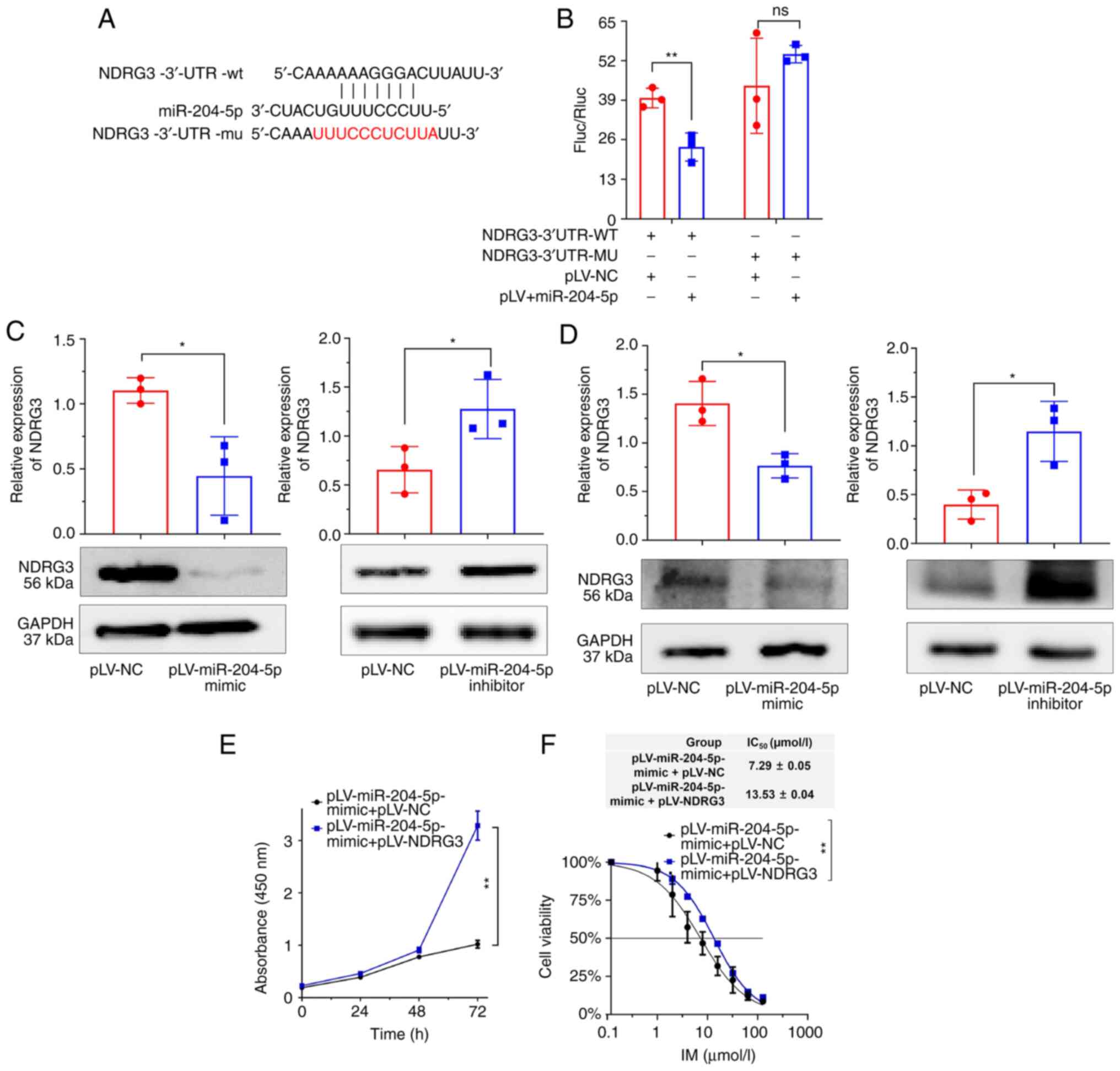 | Figure 4.miR-204-5p targets NDRG3. (A)
Sequence fragments of NDRG3-3′-UTR-wt and NDRG3′-UTR-mut. Positions
404–410 of the NDRG3-3′-UTR have a binding site for miR-204-5p.
Mutation at positions 404–414 of the NDRG3-3′-UTR. (B) Association
between miR-204-5p and NDRG3 validated by dual-luciferase reporter
gene analysis. (C) Western blot analysis of expression changes in
NDRG3 after miR-204-5p treatment in K/G cells. The histogram shows
relative intensity of NDRG3 and GAPDH. (D) NDRG3 of expression
changes in tumor tissue. The histogram shows relative intensity of
NDRG3 and GAPDH. (E) Cell viability and (F) IC50 after
co-transfection of miR-204-5p and NDRG3 assessed by Cell Counting
Kit-8 assay. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. NDRG3, N-Myc
downstream-regulated gene 3; IC50, half-maximal
inhibitory concentration; miR, microRNA; UTR, untranslated region;
wt, wild-type; mut, mutant; ns, not significant; Fluc, firefly
luciferase; Rluc, Renilla luciferase; NC, negative
control. |
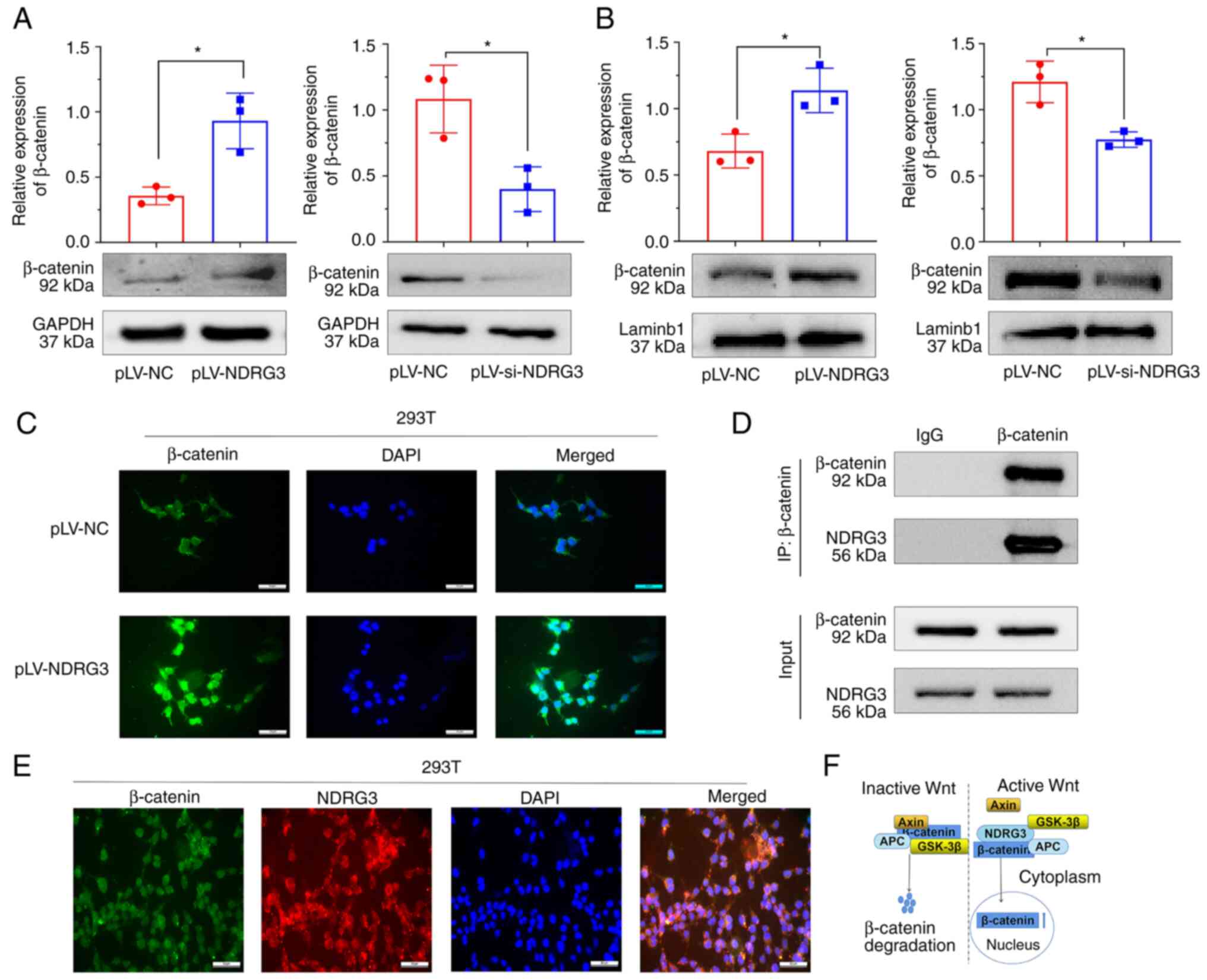
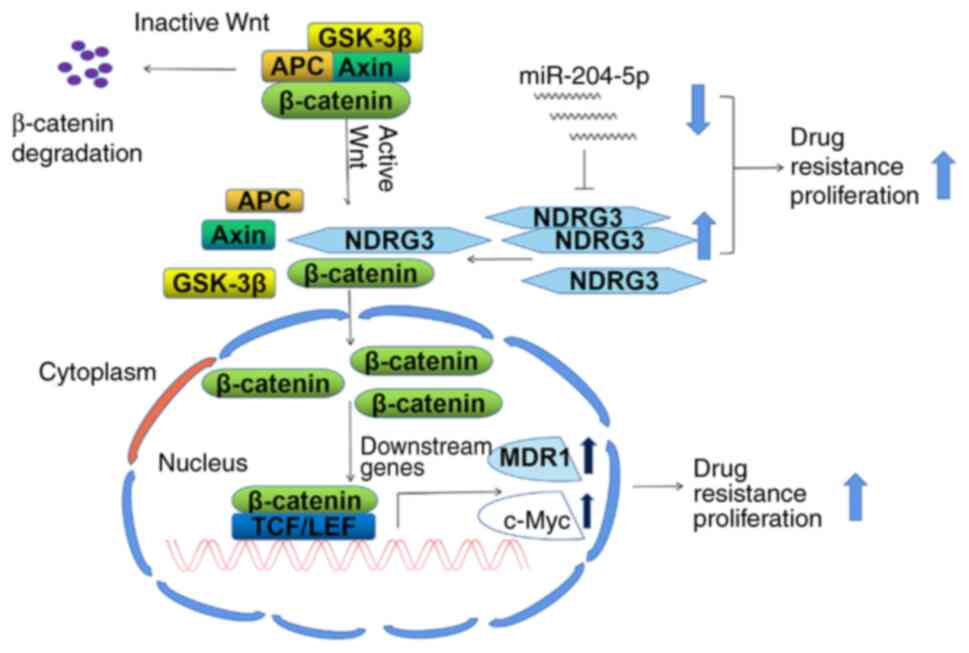
NDRG3 promotes accumulation of
β-catenin in the nucleus
The mechanism by which NDRG3 promoted drug
resistance in CML was investigated. Western blotting using whole
cell lysates showed that the expression of β-catenin was
significantly increased and decreased by NDRG3 overexpression and
downregulation, respectively (Fig.
5A). Western blot using nuclear extracts found that the
overexpression of NDRG3 further increased expression of β-catenin
in the nucleus (Fig. 5B). The
nucleus accumulation of β-catenin in 293T cells increased after
NDRG3 overexpression compared with controls (Fig. 5C). β-catenin was shown to be
co-expressed with NDRG3 by immunoprecipitation of nuclear extracts
(Fig. 5D). Immunofluorescence
staining showed that NDRG3 and β-catenin were co-localized in the
cytoplasm of 293T cells Fig. 5E).
The schematic diagram of β-catenin functioning was shown in
Fig. 5F. The mRNA levels of c-Myc
and MDR1 was increased, and the protein expression of c-Myc and
MDR1 was increased following overexpression of NDRG3 (Fig. S4A and B).
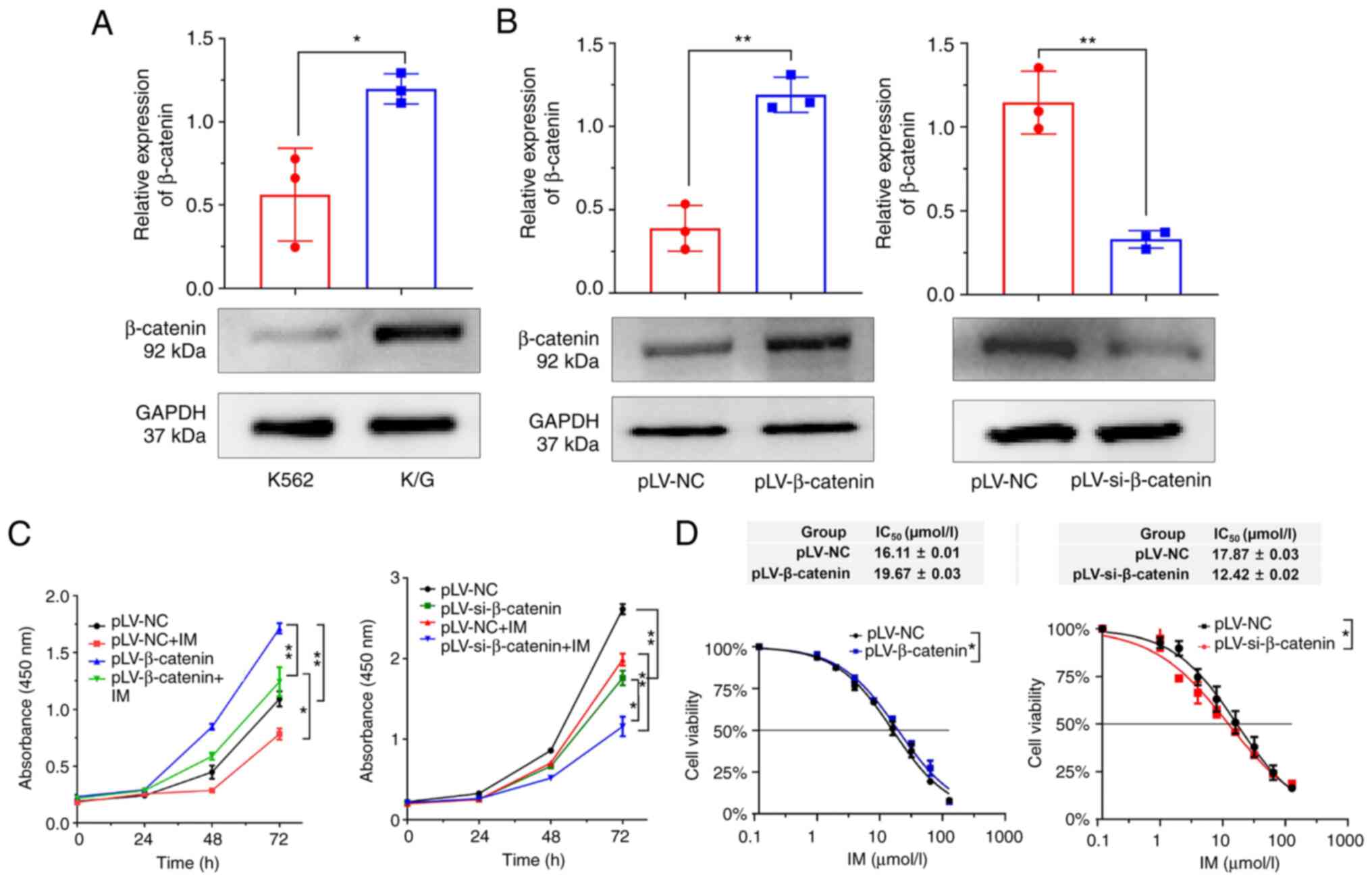
β-catenin enhances cell proliferation
and drug resistance
Expression of β-catenin in K/G cells was higher than
that in K562 cells (Fig. 6A).
β-catenin was successfully knocked down (Fig. S5) and the knockdown of β-catenin
enhanced the antitumor activity of IM, as shown by cell
proliferation experiments (Figs. 6B and
C). CCK-8 assay showed that β-catenin knockdown could decrease
IM resistance in CML cells (Fig.
6D). These results indicated that β-catenin was involved in
cell proliferation and drug resistance.
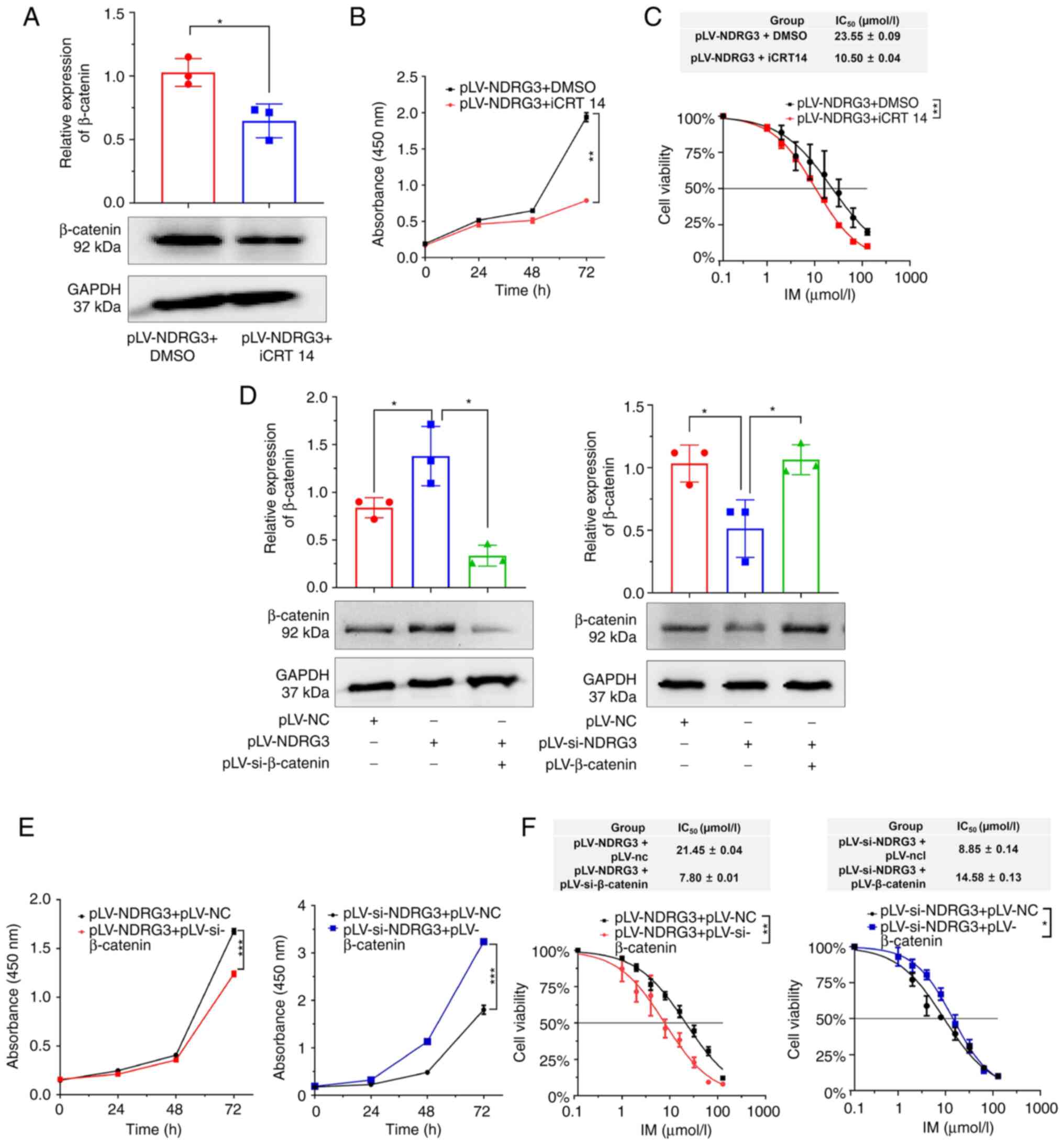
β-catenin reverses the effects of
NDRG3 on cell proliferation and drug resistance
To verify whether NDRG3 functions via the β-catenin
signaling pathway, iCRT14 was used. β-catenin was inhibited at the
protein level after adding the inhibitor (Fig. 7A). CCK-8 experiment found that the
inhibitor suppressed the ability of NDRG3 to promote cell
proliferation and IM resistance (Fig.
7B and C). In summary, the effect of NDRG3 on β-catenin was
weakened after adding the inhibitor. Western blot showed that the
expression of β-catenin protein decreased after the co-transfection
of pLV-NDRG3 and pLV-si-β-catenin (Fig.
7D). The inhibitory effect of β-catenin abolished the ability
of NDRG3 to promote cell proliferation and IC50 was
decreased following co-transfection of pLV-si-β-catenin and
pLV-NDRG3 (Fig. 7E and F).
β-catenin knockdown reversed the effect of NDRG3 on K/G cell
resistance. The potential mechanism is shown in Fig. 8. β-catenin is degraded when the Wnt
signaling pathway is inactive (34), but β-catenin will accumulate in the
nucleus under the action of NDRG3. As a result, it leads to
increased expression of downstream factors, including c-Myc and
MDR1, and initiates downstream biological behaviors such as cell
proliferation and drug resistance. miR-204-5p regulates the
expression of NDRG3.
Discussion
Previous studies have suggested that NDRG3 serves a
role in tumor growth in hepatocarcinogenesis and osteosarcoma
(23,35). However, NDRG3 plays a tumor
suppressor role in prostate cancer (7). Conflicting data may be attributed to
differences in the tumor microenvironment, tumor type or
experimental approaches (36). A
previous study demonstrated NDRG3 is a hypoxia-induced lactate
sensor and the lactate/NDRG3/Raf/ERK signaling pathway may underlie
hypoxia-associated physiological and pathophysiological responses
(12). The present results showed
that expression of NDRG3 in patients with CML was higher than that
in normal controls and promoted K562 cell proliferation. The
problem of drug resistance in cancer diagnosis and treatment is a
key obstacle to successful treatment (37). 7-Ketocholesterol is an oxidized
cholesterol derivative that improves vincristine and doxorubicin
cytotoxicity through a classical MDR-regulated mechanism in CML
(38). Vandetanib, an oral multiple
tyrosine kinase Inhibitor (TKI), inhibits acute myeloid leukemia
cells proliferation and overcomes IM resistance in CML by targeting
ephrin type-B receptor 4 (EPHB4) (39). In the present study, compared with
K562 cells, K/G cells exhibited greater IM resistance. NDRG3 was
highly expressed in IM-resistant cell lines. When NDRG3 was
overexpressed, the IC50 of K/G cells significantly
increased, which means that NDRG3 increased IM resistance. The
present data suggested that NDRG3 exerted a clear role in promoting
imatinib resistance. In other studies, it was found that there are
multiple ways to regulate drug resistance, such as drug action,
protein regulation, kinase stimulation and autophagy (40–43).
The aforementioned results showed that NDRG3 plays a role in CML
cell proliferation and drug resistance.
Gene expression is regulated by miRNAs. For example,
miR-483 directly targets NDRG2 to promote biological progression of
colorectal cancer cells (10).
miR-204-5p is an upstream factor of NDRG3. miR-204-5p inhibits cell
proliferation and invasion in liver cancer and acute myeloid
leukemia (44,45). miR-204-5p can promote drug
resistance in gastric cancer and melanoma (46,47).
The aforementioned studies show that miR-204-5p has different
expression and roles in different types of cancer. Here, miR-204-5p
inhibited cell proliferation and decreased drug resistance.
IC50 following co-transfection with NDRG3 and
miR-204-5p-mimic was 1.85 times higher than in cells transfected
only with miR-204-5p-mimic. Therefore, NDRG3 can reverse the
effects of miR-204-5p.
Grassi et al (48) demonstrated that the WNT/β-catenin
involvement is a key factor in drug resistance. β-catenin primarily
exerts its function in the nucleus as a downstream transcription
factor of Wnt signaling (49).
Wnt/β-catenin signaling is involved in NDRG3-mediated HCC
metastasis (37). When cells
receive Wnt signals, the degradation pathway is inhibited, leading
to stabilization and nuclear accumulation of β-catenin protein.
Nuclear β-catenin exerts further biological roles (50,51).
NDRG3 is primarily localized in the cytoplasm and is a key factor
required for drug resistance (52).
The present study found that NDRG3 and β-catenin can interact in
the cytoplasm. Wnt/β-catenin regulates the transcription of ABCB1
(β-catenin) in CML multidrug resistance (53). Addition of cholamine to
KBM5-mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC) co-culture restores the effect
of IM by abolishing MSC-mediated induction of β-catenin; inhibition
of β-catenin signaling in CML cells by chidamide and IM inhibits
proliferation of TKI-resistant cells and increases chemosensitivity
(54). The present findings
suggested that β-catenin was involved in drug resistance;
accumulation of β-catenin increased in the nucleus after
overexpression of NDRG3. Downstream factors of β-catenin promote
cell proliferation and drug resistance. The effect of NDRG3 was
alleviated after adding β-catenin inhibitor. In addition, the
effects of NDRG3 on cell proliferation were reversed by β-catenin.
IC50 after co-transfection with si-NDRG3 and β-catenin
overexpression was 1.64 times greater than in cells transfected
with si-NDRG3 alone. si-β-catenin affects NDRG3, thereby weakening
IM resistance of NDRG3.
A limitation of the present study is that certain
drug-resistant cells survive at high concentrations of IM, which
may hinder the recovery of patients with CML patients. An
additional limitation is that the formation of IM-resistant cells
is critical for overcoming CML relapse; further studies should be
performed at the single-cell level to obtain more detailed data and
determine the underlying mechanism. Immunofluorescence images with
higher magnification should be captured.
Future studies should investigate primary tumors in
a mouse model of leukemia. The mechanism by which NDRG3 affects
β-catenin needs further study. CML is a model disease with a long
history (55). Identifying and
understanding the biological characteristics of CML stem cells is a
key research field (56). The role
of NDRG3 in CML stem cells should be investigated in future. In
addition, it was hypothesized that K562 cells serve a role in IM
resistance; this should be investigated in the future.
In conclusion, the present study found that NDRG3
increased nuclear accumulation of β-catenin, thus increasing K/G
cell proliferation and enhancing drug resistance. Moreover,
miR-204-5p regulated NDRG3. The present study provides a basis for
alleviating drug resistance in CML.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by The Support Plan for Youth
Entrepreneurship and Technology of Colleges and Universities in
Shandong (grant no. 2019KJK014), The National Natural Science
Foundation of China (grant nos. 81800169 and 82002604), The
Shandong Science and Technology Committee (grant nos. ZR2019MH022,
ZR2020QH221 and ZR2020KH015), The Shandong Province Taishan Scholar
Project (grant no. ts201712067), The Foundation of Binzhou Medical
University (grant no. BY2021LCX04) and The Shandong Province Yantai
Science and Technology Project (grant no. 2022YD075).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
SX, YL, YS, XW and BY designed the study, performed
data analysis and revised the paper. XY and XL collected clinical
samples. XW and SR performed cell culture experiments. HS, YY, GS,
YL and PW analyzed and interpreted data. XW and YL confirm the
authenticity of all the raw data. All authors have read and
approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study protocol was approved by the
Animal Ethics Committee of Binzhou Medical University and the
Medical Ethics Committee of Binzhou Medical University (Yantai,
China) (approval number: 2020-10-06). The written informed consent
was obtained from all subjects.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Gale RP: Radiation and leukaemia: Which
leukaemias and what doses? Blood Rev. 58:1010172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Radich J, Yeung C and Wu D: New approaches
to molecular monitoring in CML (and other diseases). Blood.
134:1578–1584. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Berman E: How I treat chronic-phase
chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 139:3138–3147. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Navabi A, Akbari B, Abdalsamadi M and
Naseri S: The role of microRNAs in the development, progression and
drug resistance of chronic myeloid leukemia and their potential
clinical significance. Life Sci. 296:1204372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hershkovitz-Rokah O, Modai S,
Pasmanik-Chor M, Toren A, Shomron N, Raanani P, Shpilberg O and
Granot G: Restoration of miR-424 suppresses BCR-ABL activity and
sensitizes CML cells to imatinib treatment. Cancer Lett.
360:245–256. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zeng F, Peng Y, Qin Y, Wang J, Jiang G,
Feng W and Yuan Y: Wee1 promotes cell proliferation and imatinib
resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia via regulating DNA damage
repair dependent on ATM-γH2AX-MDC1. Cell Commun Signal. 20:1992022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee GY, Shin SH, Shin HW, Chun YS and Park
JW: NDRG3 lowers the metastatic potential in prostate cancer as a
feedback controller of hypoxia-inducible factors. Exp Mol Med.
50:1–13. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schonkeren SL, Massen M, van der Horst R,
Koch A, Vaes N and Melotte V: Nervous NDRGs: The N-myc
downstream-regulated gene family in the central and peripheral
nervous system. Neurogenetics. 20:173–186. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sohn HA, Lee DC, Park A, Kang M, Yoon BH,
Lee CH, Kim YH, Oh KJ, Kim CY, Park SH, et al: Glycogen storage
disease phenotypes accompanying the perturbation of the methionine
cycle in NDRG3-deficient mouse livers. Cells. 11:15362022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun X, Li K, Wang H, Xia Y, Meng P and
Leng X: MiR-483 promotes colorectal cancer cell biological
progression by directly targeting NDRG2 through regulation of the
PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. J Healthc Eng. 2022:45740272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li T, Sun R, Lu M, Chang J, Meng X and Wu
H: NDRG3 facilitates colorectal cancer metastasis through
activating Src phosphorylation. Onco Targets Ther. 11:2843–2852.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park KC, Lee DC and Yeom YI:
NDRG3-mediated lactate signaling in hypoxia. BMB Rep. 48:301–302.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu C, Hao X, Zhang S, Hu W, Li J, Sun J
and Zheng M: Characterization of the prognostic values of the NDRG
family in gastric cancer. Therap Adv Gastroenterol.
12:17562848198585072019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim KR, Kim KA, Park JS, Jang JY, Choi Y,
Lee HH, Lee DC, Park KC, Yeom YI, Kim HJ and Han BW: Structural and
biophysical analyses of human N-Myc Downstream-Regulated Gene 3
(NDRG3) protein. Biomolecules. 10:902020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee DC, Sohn HA, Park ZY, Oh S, Kang YK,
Lee KM, Kang M, Jang YJ, Yang SJ, Hong YK, et al: A lactate-induced
response to hypoxia. Cell. 161:595–609. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang J and Zhang Q: VHL and hypoxia
signaling: Beyond HIF in cancer. Biomedicines. 6:352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Si W, Shen J, Du C, Chen D, Gu X, Li C,
Yao M, Pan J, Cheng J, Jiang D, et al: A miR-20a/MAPK1/c-Myc
regulatory feedback loop regulates breast carcinogenesis and
chemoresistance. Cell Death Differ. 25:406–420. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hill M and Tran N: miRNA interplay:
Mechanisms and consequences in cancer. Dis Model Mech.
14:dmm0476622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu C, Fu H, Gao L, Wang L, Wang W, Li J,
Li Y, Dou L, Gao X, Luo X, et al: BCR-ABL/GATA1/miR-138 mini
circuitry contributes to the leukemogenesis of chronic myeloid
leukemia. Oncogene. 33:44–54. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Feng X, Zou B, Nan T, Zheng X, Zheng L,
Lan J, Chen W and Yu J: MiR-25 enhances autophagy and promotes
sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting
FBXW7. Int J Med Sci. 19:257–266. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yao S, Yin Y, Jin G, Li D, Li M, Hu Y,
Feng Y, Liu Y, Bian Z, Wang X, et al: Exosome-mediated delivery of
miR-204-5p inhibits tumor growth and chemoresistance. Cancer Med.
9:5989–5998. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu J, Shen J, Qiao X, Cao L, Yang Z, Ye H,
Xi C, Zhou Q, Wang P and Gong Z: SNHG20/miR-140-5p/NDRG3 axis
contributes to 5-fluorouracil resistance in gastric cancer. Oncol
Lett. 18:1337–1343. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Du Z, Niu S, Xu X and Xu Q:
MicroRNA31-NDRG3 regulation axes are essential for hepatocellular
carcinoma survival and drug resistance. Cancer Biomark. 19:221–230.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Paller AS: Wnt signaling in focal dermal
hypoplasia. Nat Genet. 39:820–821. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Z, Li Z and Ji H: Direct targeting of
β-catenin in the Wnt signaling pathway: Current progress and
perspectives. Med Res Rev. 41:2109–2129. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu Y, Zhuang H, Cao F, Li J, Guo Y, Zhang
J, Zhao Q and Liu Y: Shc3 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma
stemness and drug resistance by interacting with β-catenin to
inhibit its ubiquitin degradation pathway. Cell Death Dis.
12:2782021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Valenta T, Hausmann G and Basler K: The
many faces and functions of β-catenin. EMBO J. 31:2714–2736. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schunk SJ, Floege J, Fliser D and Speer T:
WNT-β-catenin signalling-a versatile player in kidney injury and
repair. Nat Rev Nephrol. 17:172–184. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu F, Yu C, Li F, Zuo Y, Wang Y, Yao L, Wu
C, Wang C and Ye L: Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cancers and targeted
therapies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:3072021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cui C, Zhou X, Zhang W, Qu Y and Ke X: Is
β-catenin a druggable target for cancer therapy? Trends Biochem
Sci. 43:623–634. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu J, Xiao Q, Xiao J, Niu C, Li Y, Zhang
X, Zhou Z, Shu G and Yin G: Wnt/β-catenin signalling: Function,
biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 7:32022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gao Y, Han T, Han C, Sun H, Yang X, Zhang
D and Ni X: Propofol regulates the TLR4/NF-κB pathway through
miRNA-155 to protect colorectal cancer intestinal barrier.
Inflammation. 44:2078–2090. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
McLoughlin R, Berthon BS, Rogers GB,
Baines KJ, Leong LE, Gibson PG, Williams EJ and Wood LG: Soluble
fibre supplementation with and without a probiotic in adults with
asthma: A 7-day randomised, double blind, three way cross-over
trial. EBioMedicine. 46:473–485. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Perugorria MJ, Olaizola P, Labiano I,
Esparza-Baquer A, Marzioni M, Marin JJ, Bujanda L and Banales JM:
Wnt-β-catenin signalling in liver development, health and disease.
Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:121–136. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ma W, Zhao X, Xue N, Gao Y and Xu Q: The
LINC01410/miR-122-5p/NDRG3 axis is involved in the proliferation
and migration of osteosarcoma cells. IUBMB Life. 73:705–717. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ma J, Liu S, Zhang W, Zhang F, Wang S, Wu
L, Yan R, Wu L, Wang C, Zha Z and Sun J: High expression of NDRG3
associates with positive lymph node metastasis and unfavourable
overall survival in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Pathology.
48:691–696. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shi J, Zheng H and Yuan L: High NDRG3
expression facilitates HCC metastasis by promoting nuclear
translocation of β-catenin. BMB Rep. 52:451–456. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rosa Fernandes L, Stern AC, Cavaglieri RC,
Nogueira FC, Domont G, Palmisano G and Bydlowski SP:
7-Ketocholesterol overcomes drug resistance in chronic myeloid
leukemia cell lines beyond MDR1 mechanism. J Proteomics. 151:12–23.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ma W, Zhu M, Wang B, Gong Z, Du X, Yang T,
Shi X, Dai B, Zhan Y, Zhang D, et al: Vandetanib drives growth
arrest and promotes sensitivity to imatinib in chronic myeloid
leukemia by targeting ephrin type-B receptor 4. Mol Oncol.
16:2747–2765. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nagata K, Kawakami T, Kurata Y, Kimura Y,
Suzuki Y, Nagata T, Sakuma Y, Miyagi Y and Hirano H: Augmentation
of multiple protein kinase activities associated with secondary
imatinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors as revealed
by quantitative phosphoproteome analysis. J Proteomics.
115:132–142. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Saha M and Sarkar A: Review on multiple
facets of drug resistance: A rising challenge in the 21st century.
J Xenobiot. 11:197–214. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sun X, Niu X, Chen R, He W, Chen D, Kang R
and Tang D: Metallothionein-1G facilitates sorafenib resistance
through inhibition of ferroptosis. Hepatology. 64:488–500. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang XY, Sun GB, Wang YJ and Yan F: Emodin
inhibits resistance to Imatinib by downregulation of Bcr-Abl and
STAT5 and allosteric inhibition in chronic myeloid leukemia cells.
Biol Pharm Bull. 43:1526–1533. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xue F and Che H: The long non-coding RNA
LOC285758 promotes invasion of acute myeloid leukemia cells by
down-regulating miR-204-5p. FEBS Open Bio. 10:734–743. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jiang G, Wen L, Zheng H, Jian Z and Deng
W: miR-204-5p targeting SIRT1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma
progression. Cell Biochem Funct. 34:505–510. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xiao YF, Li BS, Liu JJ, Wang SM, Liu J,
Yang H, Hu YY, Gong CL, Li JL and Yang SM: Role of lncSLCO1C1 in
gastric cancer progression and resistance to oxaliplatin therapy.
Clin Transl Med. 12:e6912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Díaz-Martínez M, Benito-Jardón L, Alonso
L, Koetz-Ploch L, Hernando E and Teixidó J: miR-204-5p and
miR-211-5p contribute to BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma.
Cancer Res. 78:1017–1030. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Grassi S, Palumbo S, Mariotti V, Liberati
D, Guerrini F, Ciabatti E, Salehzadeh S, Baratè C, Balducci S,
Ricci F, et al: The WNT pathway is relevant for the
BCR-ABL1-independent resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia. Front
Oncol. 9:5322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ding L, Chen Q, Chen K, Jiang Y, Li G,
Chen Q, Bai D, Gao D, Deng M, Zhang H and Xu B: Simvastatin
potentiates the cell-killing activity of imatinib in
imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells mainly through
PI3K/AKT pathway attenuation and Myc downregulation. Eur J
Pharmacol. 913:1746332021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu F, Kohlmeier S and Wang CY: Wnt
signaling and skeletal development. Cell Signal. 20:999–1009. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sinha A, Fan VB, Ramakrishnan AB,
Engelhardt N, Kennell J and Cadigan KM: Repression of Wnt/β-catenin
signaling by SOX9 and mastermind-like transcriptional coactivator
2. Sci Adv. 7:eabe08492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nakamura K, Kustatscher G, Alabert C, Hödl
M, Forne I, Völker-Albert M, Satpathy S, Beyer TE, Mailand N,
Choudhary C, et al: Proteome dynamics at broken replication forks
reveal a distinct ATM-directed repair response suppressing DNA
double-strand break ubiquitination. Mol Cell. 81:1084–1099.e6.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Huang Y, Yuan C, Liu Q and Wang L: KIF23
promotes autophagy-induced imatinib resistance in chronic myeloid
leukaemia through activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 49:1334–1341. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
He B, Wang Q, Liu X, Lu Z, Han J, Pan C,
Carter BZ, Liu Q, Xu N and Zhou H: A novel HDAC inhibitor chidamide
combined with imatinib synergistically targets tyrosine kinase
inhibitor resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 129:1103902020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Minciacchi VR, Kumar R and Krause DS:
Chronic myeloid leukemia: A model disease of the past, present and
future. Cells. 10:1172021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Houshmand M, Simonetti G, Circosta P,
Gaidano V, Cignetti A, Martinelli G, Saglio G and Gale RP: Chronic
myeloid leukemia stem cells. Leukemia. 33:1543–1556. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|