|
1
|
Noone AM, Cronin KA, Altekruse SF,
Howlader N, Lewis DR, Petkov VI and Penberthy L: Cancer incidence
and survival trends by subtype using data from the surveillance
epidemiology and end results program, 1992–2013. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 26:632–641. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rainusso N, Wang LL and Yustein JT: The
adolescent and young adult with cancer: State of the Art-bone
tumors. Curr Oncol Rep. 15:296–307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ottaviani G and Jaffe N: The epidemiology
of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 152:3–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bishop MW, Janeway KA and Gorlick R:
Future directions in the treatment of osteosarcoma. Curr Opin
Pediatr. 28:26–33. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
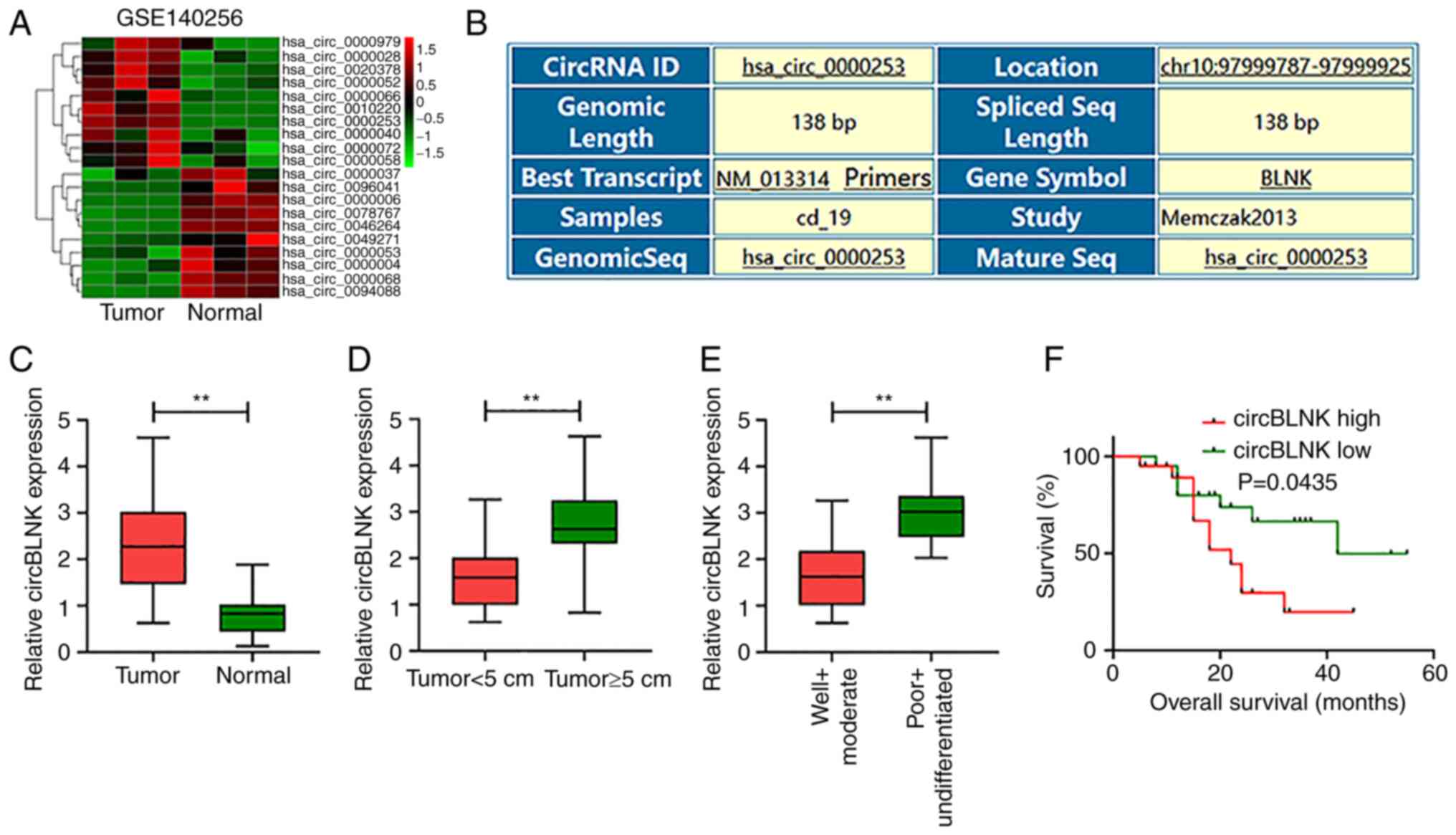
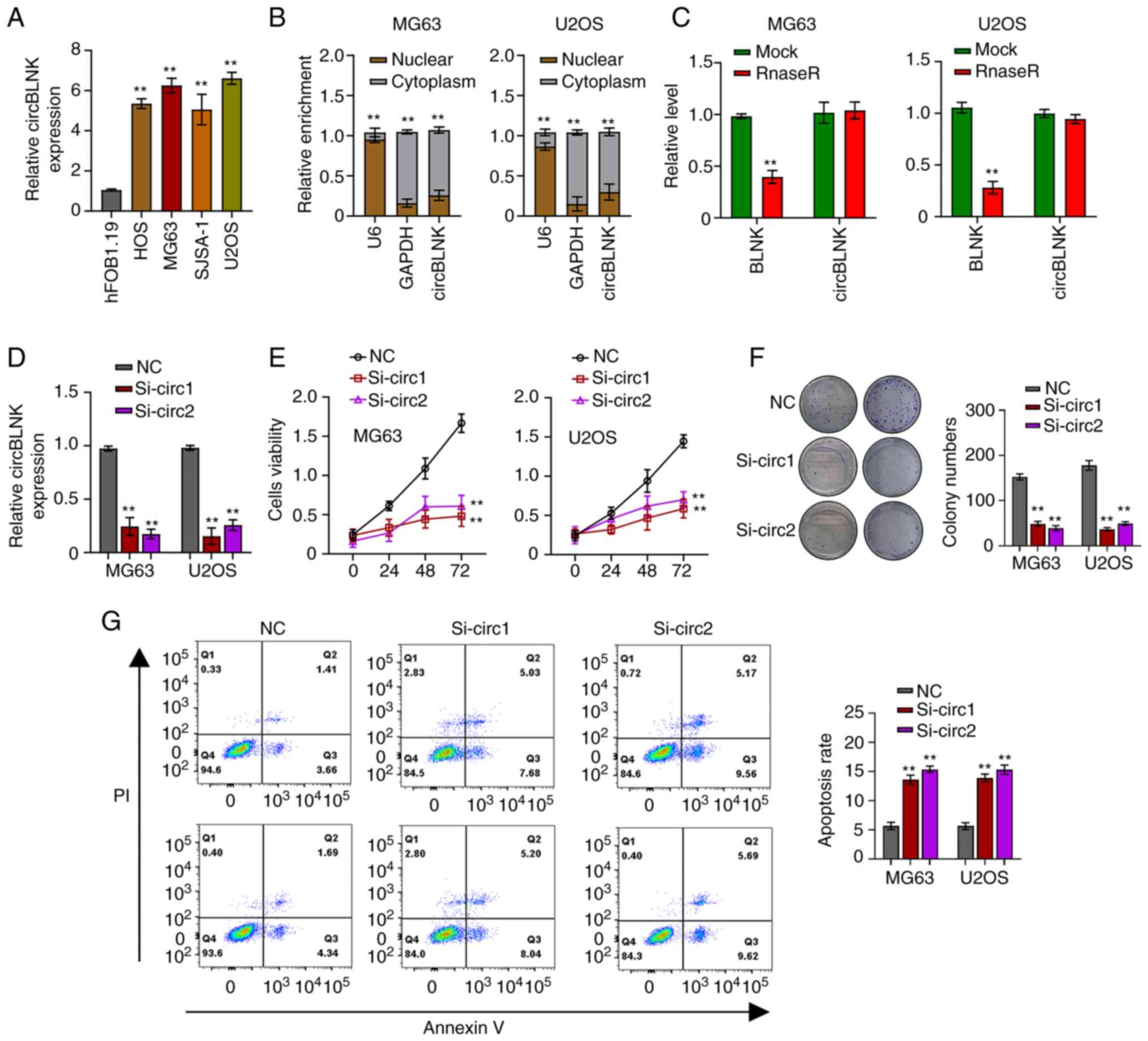
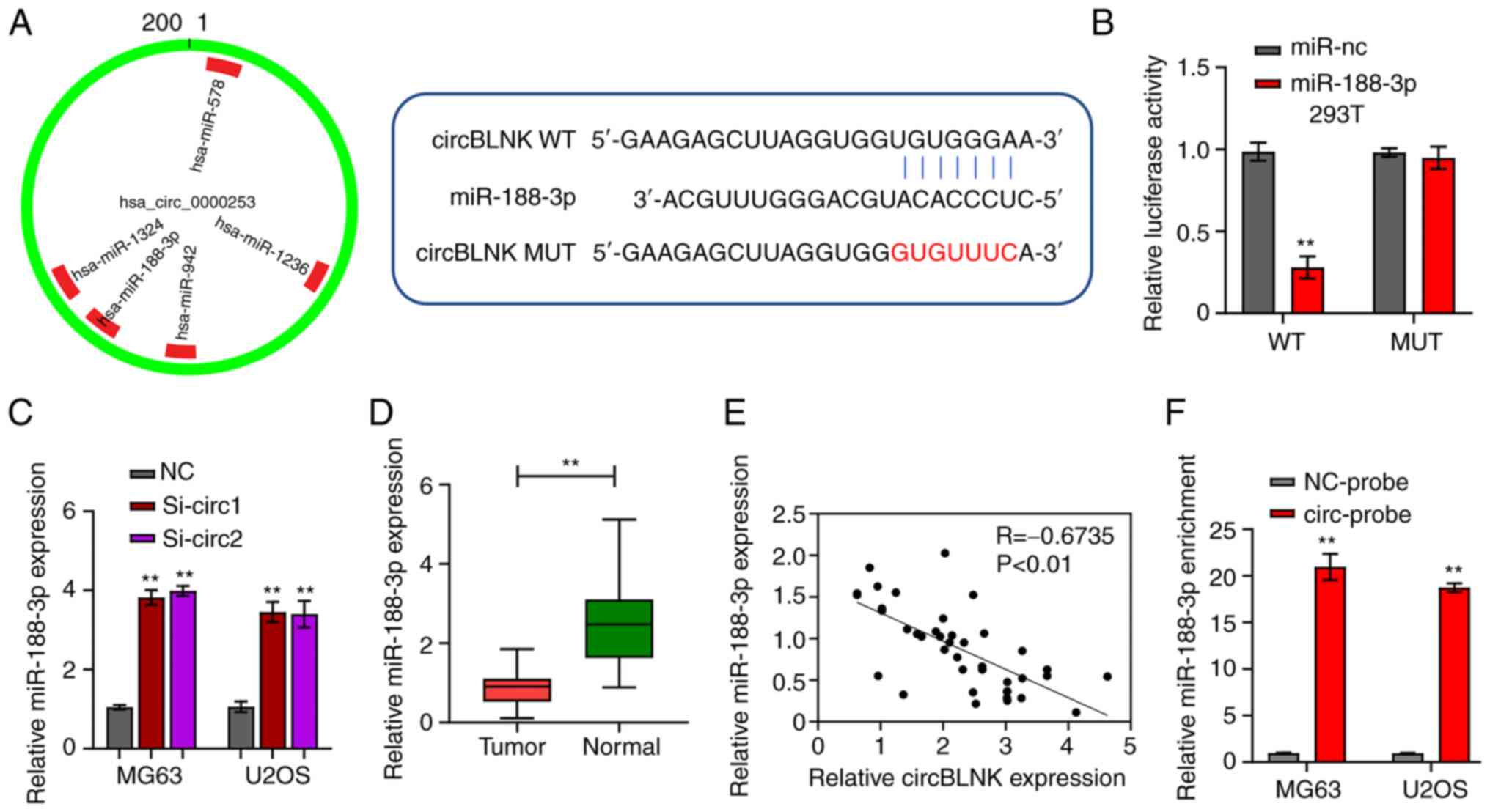
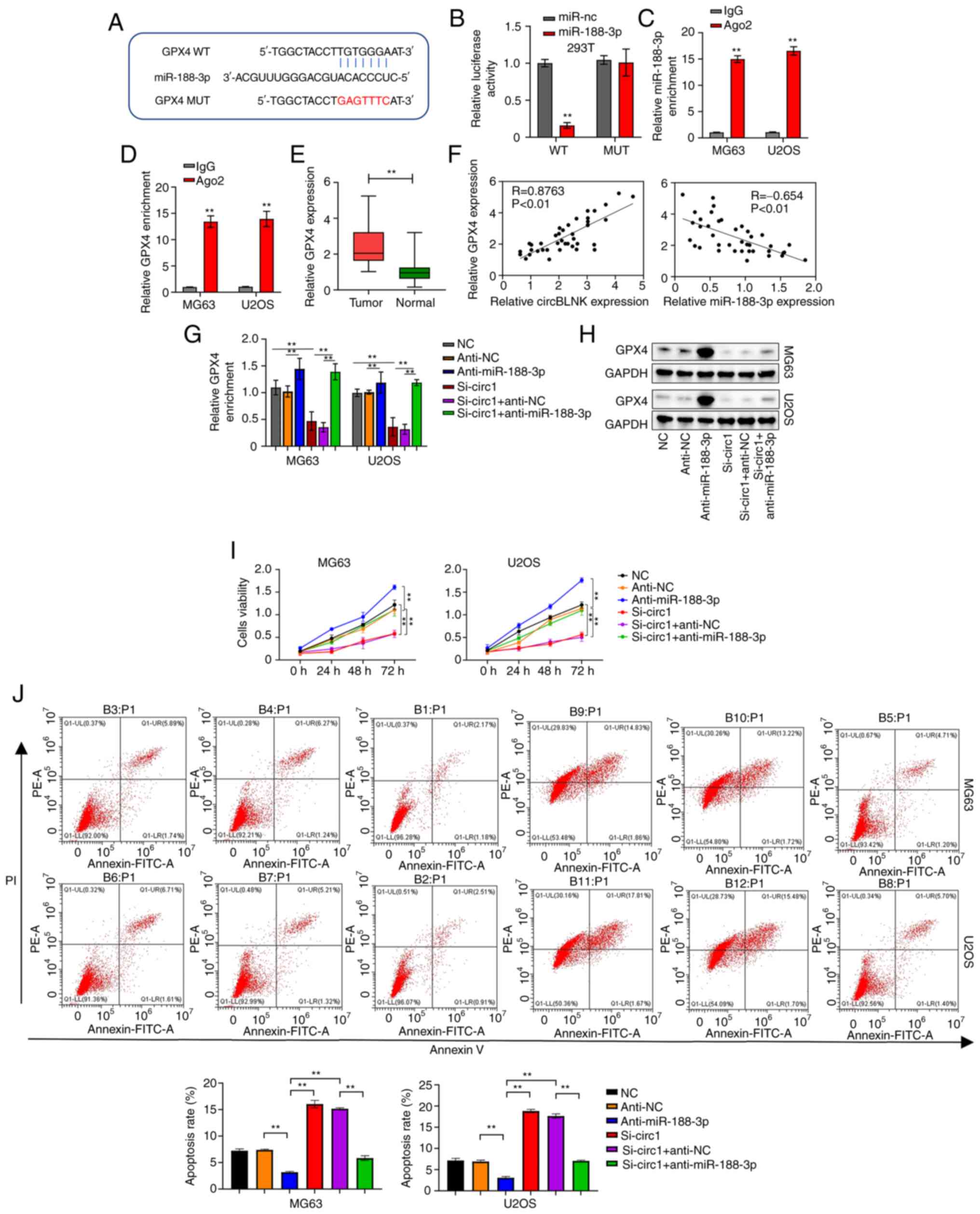
|
Otoukesh B, Boddouhi B, Moghtadaei M,
Kaghazian P and Kaghazian M: Novel molecular insights and new
therapeutic strategies in osteosarcoma. Cancer Cell Int.
18:1582018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bielack SS, Kempf-Bielack B, Delling G,
Exner GU, Flege S, Helmke K, Kotz R, Salzer-Kuntschik M, Werner M,
Winkelmann W, et al: Prognostic factors in high-grade osteosarcoma
of the extremities or trunk: An analysis of 1,702 patients treated
on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. J
Clin Oncol. 20:776–790. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW,
Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB and Kjems J: The biogenesis, biology and
characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 20:675–691. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li J, Sun D, Pu W, Wang J and Peng Y:
Circular RNAs in cancer: Biogenesis, function, and clinical
significance. Trends Cancer. 6:319–336. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu Z, Liu F, Wang F, Yang X and Guo W:
CircZNF609 promotes cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and
glycolysis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through regulating HRAS via
miR-338-3p. Mol Cell Biochem. 476:175–186. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fan C, Qu H, Xiong F, Tang Y, Tang T,
Zhang L, Mo Y, Li X, Guo C, Zhang S, et al: CircARHGAP12 promotes
nasopharyngeal carcinoma migration and invasion via ezrin-mediated
cytoskeletal remodeling. Cancer Lett. 496:41–56. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang L, Tong X, Zhou Z, Wang S, Lei Z,
Zhang T, Liu Z, Zeng Y, Li C, Zhao J, et al: Circular RNA
hsa_circ_0008305 (circPTK2) inhibits TGF-β-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by controlling
TIF1γ in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer. 17:1402018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li C, Tian Y, Liang Y and Li Q: Retraction
note to: Circ_0008035 contributes to cell proliferation and
inhibits apoptosis and ferroptosis in gastric cancer via
miR-599/EIF4A1 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 21:4162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li ZQ, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Lu C, Ding QL, Ren
R, Cheng BB and Lou LX: CircRNA_103801 accelerates proliferation of
osteosarcoma cells by sponging miR-338-3p and regulating
HIF-1/Rap1/PI3K-Akt pathway. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents.
35:1021–1028. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gong G, Han Z, Wang W, Xu Q and Zhang J:
Silencing hsa_circRNA_0008035 exerted repressive function on
osteosarcoma cell growth and migration by upregulating
microRNA-375. Cell Cycle. 19:2139–2147. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu DY, Li Z, Zhang K, Jiao N, Lu DG, Zhou
DW, Meng YB and Sun L: Circular RNA CircMTO1 suppressed
proliferation and metastasis of osteosarcoma through miR-630/KLF6
axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 25:86–93. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thomson DW and Dinger ME: Endogenous
microRNA sponges: Evidence and controversy. Nat Rev Genet.
17:272–283. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng S, Jiang F, Ge D, Tang J, Chen H,
Yang J, Yao Y, Yan J, Qiu J, Yin Z, et al: LncRNA
SNHG3/miRNA-151a-3p/RAB22A axis regulates invasion and migration of
osteosarcoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 112:1086952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang W, Li JZ, Tai QY, Tang JJ, Huang YH
and Gao SB: LncRNA DANCR regulates osteosarcoma migration and
invasion by targeting miR-149/MSI2 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
24:6551–6560. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu M, Zhang YY, Wang HF and Yang GS: The
expression and function of miRNA-106 in pediatric osteosarcoma. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:715–722. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Luo Z, Fan Y, Liu X, Liu S, Kong X, Ding
Z, Li Y and Wei L: MiR-188-3p and miR-133b suppress cell
proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma via
post-transcriptional suppression of NDRG1. Technol Cancer Res
Treat. 20:153303382110330742021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pei J, Zhang S, Yang X, Han C, Pan Y, Li
J, Wang Z, Sun C and Zhang J: Long non-coding RNA RP11-283G6.5
confines breast cancer development through modulating
miR-188-3p/TMED3/Wnt/β-catenin signalling. RNA Biol. 18 (Suppl
1):S287–S302. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Pei J, Zhang J, Yang X, Wu Z, Sun C, Wang
Z and Wang B: TMED3 promotes cell proliferation and motility in
breast cancer and is negatively modulated by miR-188-3p. Cancer
Cell Int. 19:752019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Seiler A, Schneider M, Förster H, Roth S,
Wirth EK, Culmsee C, Plesnila N, Kremmer E, Rådmark O, Wurst W, et
al: Glutathione peroxidase 4 senses and translates oxidative stress
into 12/15-lipoxygenase dependent- and AIF-mediated cell death.
Cell Metab. 8:237–248. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME,
Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, Cheah JH, Clemons PA, Shamji
AF, Clish CB, et al: Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by
GPX4. Cell. 156:317–331. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir
H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, Fulda S, Gascón S, Hatzios SK,
Kagan VE, et al: Ferroptosis: A regulated cell death nexus linking
metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 171:273–285. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu Z, Chen L, Wang C, Zhang L and Xu W:
MicroRNA-1287-5p promotes ferroptosis of osteosarcoma cells through
inhibiting GPX4. Free Radic Res. 55:1119–1129. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu Q and Wang K: The induction of
ferroptosis by impairing STAT3/Nrf2/GPx4 signaling enhances the
sensitivity of osteosarcoma cells to cisplatin. Cell Biol Int.
43:1245–1256. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Issue Information-declaration of Helsinki.
J Bone Miner Res. 34:BM i–BM ii. 2019.
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zheng X, Huang M, Xing L, Yang R, Wang X,
Jiang R, Zhang L and Chen J: The circRNA circSEPT9 mediated by E2F1
and EIF4A3 facilitates the carcinogenesis and development of
triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 19:732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu L, Duan J, Li M, Zhou C and Wang Q:
Circ_0000253 promotes the progression of osteosarcoma via the
miR-1236-3p/SP1 axis. J Pharm Pharmacol. 75:227–235. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Meng S, Zhou H, Feng Z, Xu Z, Tang Y, Li P
and Wu M: CircRNA: Functions and properties of a novel potential
biomarker for cancer. Mol Cancer. 16:942017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang D, Yang S, Wang H, Wang J, Zhang Q,
Zhou S, He Y, Zhang H, Deng F, Xu H, et al: The progress of
circular RNAs in various tumors. Am J Transl Res. 10:1571–1582.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang Y, Yujiao W, Fang W, Linhui Y, Ziqi
G, Zhichen W, Zirui W and Shengwang W: The roles of miRNA, lncRNA
and circRNA in the development of osteoporosis. Biological Res.
53:402020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Patop IL, Wüst S and Kadener S: Past,
present, and future of circRNAs. EMBO J. 38:e1008362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen Z, Xu W, Zhang D, Chu J, Shen S, Ma
Y, Wang Q, Liu G, Yao T, Huang Y, et al: circCAMSAP1 promotes
osteosarcoma progression and metastasis by sponging miR-145-5p and
regulating FLI1 expression. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 23:1120–1135.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Guan K, Liu S, Duan K, Zhang X, Liu H, Xu
B, Wang X and Jin X: Hsa_circ_0008259 modulates miR-21-5p and PDCD4
expression to restrain osteosarcoma progression. Aging (Albany NY).
13:25484–25495. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lin E, Liu S, Xiang W, Zhang H and Xie C:
CircEIF4G2 Promotes Tumorigenesis and Progression of Osteosarcoma
by Sponging miR-218. Biomed Res Int. 2020:83869362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Meng L, Jiang YP, Zhu J and Li B:
MiR-188-3p/GPR26 modulation functions as a potential regulator in
manipulating glioma cell properties. Neurol Res. 42:222–227. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pichler M, Stiegelbauer V,
Vychytilova-Faltejskova P, Ivan C, Ling H, Winter E, Zhang X,
Goblirsch M, Wulf-Goldenberg A, Ohtsuka M, et al: Genome-Wide miRNA
analysis identifies miR-188-3p as a novel prognostic marker and
molecular factor involved in colorectal carcinogenesis. Clin Cancer
Res. 23:1323–1333. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gao F, Han J, Wang Y, Jia L, Luo W and
Zeng Y: Circ_0109291 promotes cisplatin resistance of oral squamous
cell carcinoma by sponging miR-188-3p to increase ABCB1 expression.
Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 37:233–245. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Saliminejad K, Khorram Khorshid HR,
Soleymani Fard S and Ghaffari SH: An overview of microRNAs:
Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell
Physiol. 234:5451–5465. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hassannia B, Vandenabeele P and Vanden
Berghe T: Targeting ferroptosis to iron out cancer. Cancer Cell.
35:830–849. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G and Tang D:
Broadening horizons: The role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 18:280–296. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liang C, Zhang X, Yang M and Dong X:
Recent progress in ferroptosis inducers for cancer therapy. Adv
Mater. 31:e19041972019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sun X, Ou Z, Chen R, Niu X, Chen D, Kang R
and Tang D: Activation of the p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway protects
against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology.
63:173–184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lei T, Qian H, Lei P and Hu Y:
Ferroptosis-related gene signature associates with immunity and
predicts prognosis accurately in patients with osteosarcoma. Cancer
Sci. 112:4785–4798. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Luo Y, Gao X, Zou L, Lei M, Feng J and Hu
Z: Bavachin induces ferroptosis through the STAT3/P53/SLC7A11 axis
in osteosarcoma cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021:17834852021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|