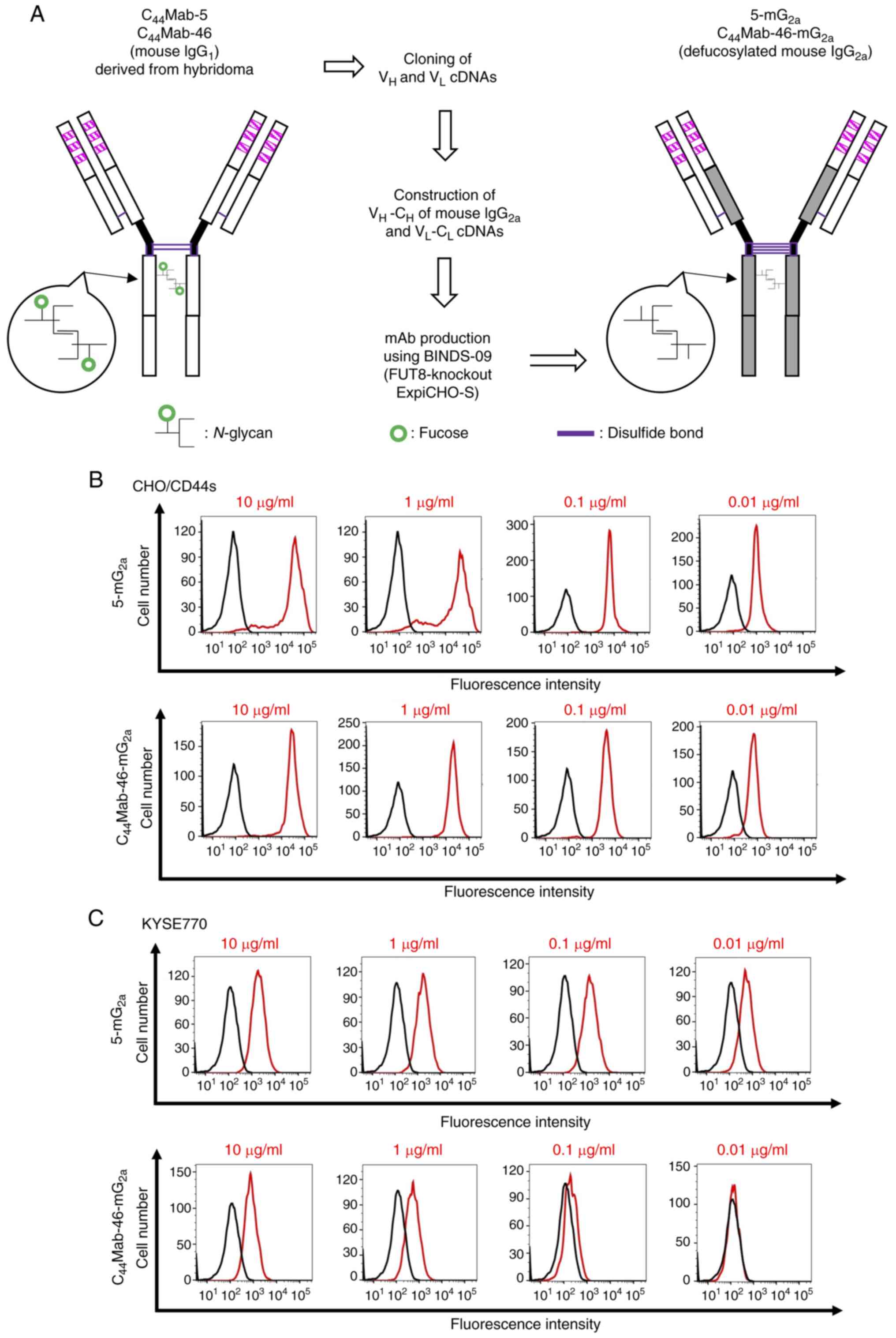
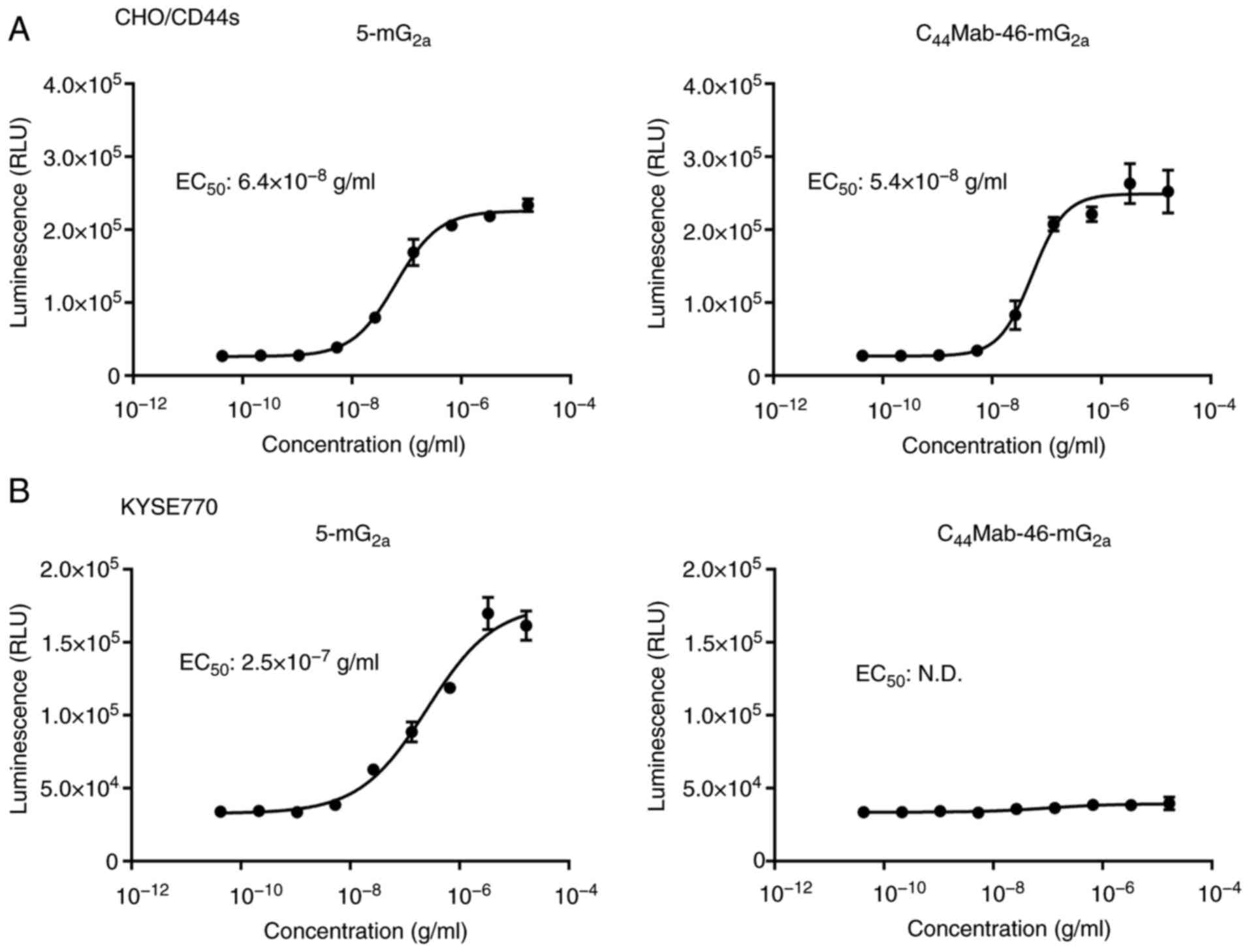
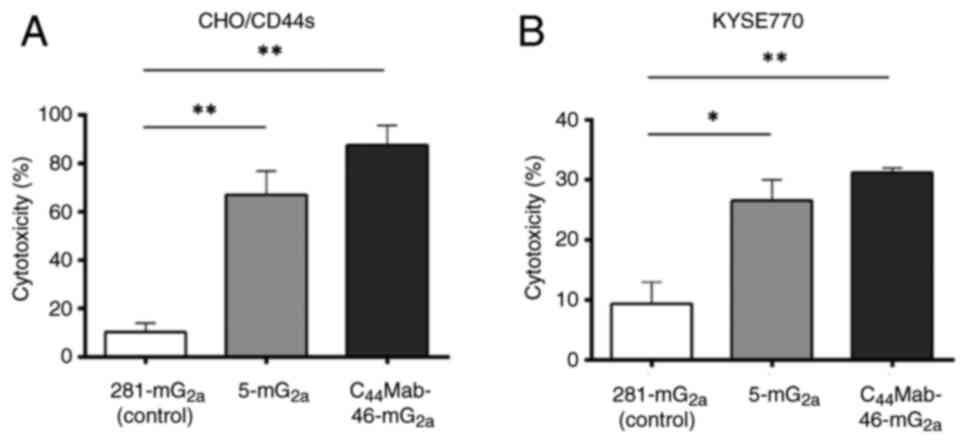
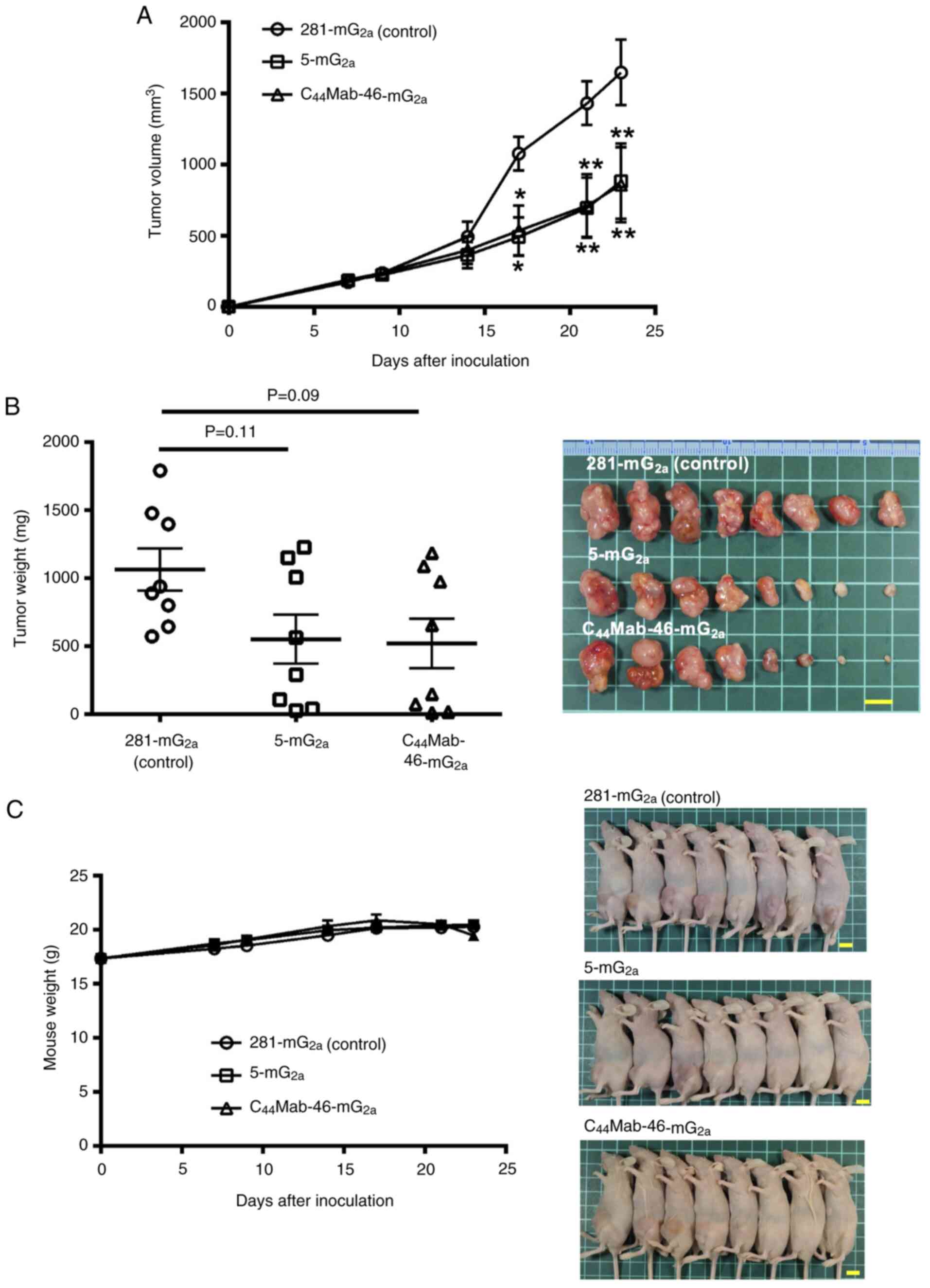
|
1
|
Ponta H, Sherman L and Herrlich PA: CD44:
From adhesion molecules to signalling regulators. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 4:33–45. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zöller M: CD44: Can a cancer-initiating
cell profit from an abundantly expressed molecule? Nat Rev Cancer.
11:254–267. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Prochazka L, Tesarik R and Turanek J:
Regulation of alternative splicing of CD44 in cancer. Cell Signal.
26:2234–2239. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guo Q, Yang C and Gao F: The state of CD44
activation in cancer progression and therapeutic targeting. FEBS J.
289:7970–7986. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zöller M: CD44, hyaluronan, the
hematopoietic stem cell, and leukemia-initiating cells. Front
Immunol. 6:2352015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hassn Mesrati M, Syafruddin SE, Mohtar MA
and Syahir A: CD44: A multifunctional mediator of cancer
progression. Biomolecules. 11:18502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cirillo N: The hyaluronan/CD44 axis: A
double-edged sword in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 24:158122023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Y, Wu T, Lu D, Zhen J and Zhang L:
CD44 overexpression related to lymph node metastasis and poor
prognosis of pancreatic cancer. Int J Biol Markers. 33:308–313.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tao Y, Li H, Huang R, Mo D, Zeng T, Fang M
and Li M: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of cancer
stem cell markers in ovarian cancer patients: Evidence from 52
studies. Cell Physiol Biochem. 46:1716–1726. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li L, Hao X, Qin J, Tang W, He F, Smith A,
Zhang M, Simeone DM, Qiao XT, Chen ZN, et al: Antibody against
CD44s inhibits pancreatic tumor initiation and postradiation
recurrence in mice. Gastroenterology. 146:1108–1118. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang S, Wu CC, Fecteau JF, Cui B, Chen L,
Zhang L, Wu R, Rassenti L, Lao F, Weigand S and Kipps TJ: Targeting
chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells with a humanized monoclonal
antibody specific for CD44. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:6127–6132.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vey N, Delaunay J, Martinelli G, Fiedler
W, Raffoux E, Prebet T, Gomez-Roca C, Papayannidis C, Kebenko M,
Paschka P, et al: Phase I clinical study of RG7356, an anti-CD44
humanized antibody, in patients with acute myeloid leukemia.
Oncotarget. 7:32532–32542. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Menke-van der Houven van Oordt CW,
Gomez-Roca C, van Herpen C, Coveler AL, Mahalingam D, Verheul HM,
van der Graaf WT, Christen R, Rüttinger D, Weigand S, et al:
First-in-human phase I clinical trial of RG7356, an anti-CD44
humanized antibody, in patients with advanced, CD44-expressing
solid tumors. Oncotarget. 7:80046–80058. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Todaro M, Gaggianesi M, Catalano V,
Benfante A, Iovino F, Biffoni M, Apuzzo T, Sperduti I, Volpe S,
Cocorullo G, et al: CD44v6 is a marker of constitutive and
reprogrammed cancer stem cells driving colon cancer metastasis.
Cell Stem Cell. 14:342–356. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Verel I, Heider KH, Siegmund M, Ostermann
E, Patzelt E, Sproll M, Snow GB, Adolf GR and van Dongen GA: Tumor
targeting properties of monoclonal antibodies with different
affinity for target antigen CD44V6 in nude mice bearing
head-and-neck cancer xenografts. Int J Cancer. 99:396–402. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Orian-Rousseau V and Ponta H: Perspectives
of CD44 targeting therapies. Arch Toxicol. 89:3–14. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tijink BM, Buter J, de Bree R, Giaccone G,
Lang MS, Staab A, Leemans CR and van Dongen GA: A phase I dose
escalation study with anti-CD44v6 bivatuzumab mertansine in
patients with incurable squamous cell carcinoma of the head and
neck or esophagus. Clin Cancer Res. 12:6064–6072. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Riechelmann H, Sauter A, Golze W, Hanft G,
Schroen C, Hoermann K, Erhardt T and Gronau S: Phase I trial with
the CD44v6-targeting immunoconjugate bivatuzumab mertansine in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 44:823–829. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Casucci M, Nicolis di Robilant B, Falcone
L, Camisa B, Norelli M, Genovese P, Gentner B, Gullotta F, Ponzoni
M, Bernardi M, et al: CD44v6-targeted T cells mediate potent
antitumor effects against acute myeloid leukemia and multiple
myeloma. Blood. 122:3461–3472. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Porcellini S, Asperti C, Corna S, Cicoria
E, Valtolina V, Stornaiuolo A, Valentinis B, Bordignon C and
Traversari C: CAR T cells redirected to CD44v6 control tumor growth
in lung and ovary adenocarcinoma bearing mice. Front Immunol.
11:992020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamada S, Itai S, Nakamura T, Yanaka M,
Kaneko MK and Kato Y: Detection of high CD44 expression in oral
cancers using the novel monoclonal antibody, C44Mab-5.
Biochem Biophys Rep. 14:64–68. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Goto N, Suzuki H, Tanaka T, Asano T,
Kaneko MK and Kato Y: Development of a novel Anti-CD44 monoclonal
antibody for multiple applications against esophageal squamous cell
carcinomas. Int J Mol Sci. 23:55352022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Takei J, Asano T, Suzuki H, Kaneko MK and
Kato Y: Epitope mapping of the anti-CD44 monoclonal antibody
(C44Mab-46) using alanine-scanning mutagenesis and surface plasmon
resonance. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 40:219–226. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Asano T, Kaneko MK, Takei J, Tateyama N
and Kato Y: Epitope mapping of the anti-CD44 monoclonal antibody
(C44Mab-46) using the REMAP method. Monoclon Antib
Immunodiagn Immunother. 40:156–161. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Asano T, Kaneko MK and Kato Y: Development
of a novel epitope mapping system: RIEDL insertion for epitope
mapping method. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 40:162–167.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Suzuki H, Kitamura K, Goto N, Ishikawa K,
Ouchida T, Tanaka T, Kaneko MK and Kato Y: A Novel anti-CD44
variant 3 monoclonal antibody C44Mab-6 was established
for multiple applications. Int J Mol Sci. 24:84112023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Suzuki H, Tanaka T, Goto N, Kaneko MK and
Kato Y: Development of a novel anti-CD44 variant 4 monoclonal
antibody C44Mab-108 for immunohistochemistry. Curr
Issues Mol Biol. 45:1875–1888. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kudo Y, Suzuki H, Tanaka T, Kaneko MK and
Kato Y: Development of a novel Anti-CD44 variant 5 monoclonal
antibody C44Mab-3 for multiple applications against
pancreatic carcinomas. Antibodies (Basel). 12:312023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ejima R, Suzuki H, Tanaka T, Asano T,
Kaneko MK and Kato Y: Development of a novel Anti-CD44 variant 6
monoclonal antibody C44Mab-9 for multiple applications
against colorectal carcinomas. Int J Mol Sci. 24:40072023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Suzuki H, Ozawa K, Tanaka T, Kaneko MK and
Kato Y: Development of a novel anti-CD44 variant 7/8 monoclonal
antibody, C44Mab-34, for multiple applications against
oral carcinomas. Biomedicines. 11:10992023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tawara M, Suzuki H, Goto N, Tanaka T,
Kaneko MK and Kato Y: A novel anti-CD44 variant 9 monoclonal
antibody C44Mab-1 was developed for immunohistochemical
analyses against colorectal cancers. Curr Issues Mol Biol.
45:3658–3673. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ishikawa K, Suzuki H, Kaneko MK and Kato
Y: Establishment of a novel anti-CD44 variant 10 monoclonal
antibody C44Mab-18 for immunohistochemical analysis
against oral squamous cell carcinomas. Curr Issues Mol Biol.
45:5248–5262. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li G, Suzuki H, Ohishi T, Asano T, Tanaka
T, Yanaka M, Nakamura T, Yoshikawa T, Kawada M, Kaneko MK and Kato
Y: Antitumor activities of a defucosylated anti-EpCAM monoclonal
antibody in colorectal carcinoma xenograft models. Int J Mol Med.
51:182023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nanamiya R, Suzuki H, Takei J, Li G, Goto
N, Harada H, Saito M, Tanaka T, Asano T, Kaneko MK and Kato Y:
Development of monoclonal antibody 281-mG2a-f against
golden hamster podoplanin. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother.
41:311–319. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Queiroz AL, Dantas E, Ramsamooj S, Murthy
A, Ahmed M, Zunica ERM, Liang RJ, Murphy J, Holman CD, Bare CJ, et
al: Blocking ActRIIB and restoring appetite reverses cachexia and
improves survival in mice with lung cancer. Nat Commun.
13:46332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yamada S, Kaneko MK, Nakamura T, Ichii O,
Konnai S and Kato Y: Development of mPMab-1, a mouse-rat chimeric
antibody against mouse podoplanin. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn
Immunother. 36:77–79. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Garvin D, Stecha P, Gilden J, Wang J,
Grailer J, Hartnett J, Fan F, Cong M and Cheng ZJ: Determining ADCC
activity of antibody-based therapeutic molecules using two
bioluminescent reporter-based bioassays. Curr Protoc. 1:e2962021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Takei J, Kaneko MK, Ohishi T, Hosono H,
Nakamura T, Yanaka M, Sano M, Asano T, Sayama Y, Kawada M, et al: A
defucosylated anti-CD44 monoclonal antibody 5-mG2a-f exerts
antitumor effects in mouse xenograft models of oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 44:1949–1960. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Birzele F, Voss E, Nopora A, Honold K,
Heil F, Lohmann S, Verheul H, Le Tourneau C, Delord JP, van Herpen
C, et al: CD44 isoform status predicts response to treatment with
anti-CD44 antibody in cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res.
21:2753–2762. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Golay J and Taylor RP: The role of
complement in the mechanism of action of therapeutic anti-cancer
mAbs. Antibodies (Basel). 9:582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Reis ES, Mastellos DC, Ricklin D,
Mantovani A and Lambris JD: Complement in cancer: Untangling an
intricate relationship. Nat Rev Immunol. 18:5–18. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Galon J and Bruni D: Approaches to treat
immune hot, altered and cold tumours with combination
immunotherapies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 18:197–218. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hiemstra IH, Santegoets KCM, Janmaat ML,
De Goeij BECG, Ten Hagen W, van Dooremalen S, Boross P, van den
Brakel J, Bosgra S, Andringa G, et al: Preclinical anti-tumour
activity of HexaBody-CD38, a next-generation CD38 antibody with
superior complement-dependent cytotoxic activity. EBioMedicine.
93:1046632023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
de Jong RN, Beurskens FJ, Verploegen S,
Strumane K, van Kampen MD, Voorhorst M, Horstman W, Engelberts PJ,
Oostindie SC, Wang G, et al: A novel platform for the potentiation
of therapeutic antibodies based on antigen-dependent formation of
IgG hexamers at the cell surface. PLoS Biol. 14:e10023442016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Schmudde I, Laumonnier Y and Köhl J:
Anaphylatoxins coordinate innate and adaptive immune responses in
allergic asthma. Semin Immunol. 25:2–11. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Carroll MC and Isenman DE: Regulation of
humoral immunity by complement. Immunity. 37:199–207. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gogia P, Ashraf H, Bhasin S and Xu Y:
Antibody-drug conjugates: A review of approved drugs and their
clinical level of evidence. Cancers (Basel). 15:38862023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Arimori T, Mihara E, Suzuki H, Ohishi T,
Tanaka T, Kaneko MK, Takagi J and Kato Y: Locally misfolded HER2
expressed on cancer cells is a promising target for development of
cancer-specific antibodies. Structure. 32:536–549.e5. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kaneko MK, Suzuki H and Kato Y:
Establishment of a novel cancer-specific anti-HER2
monoclonal antibody H2Mab-250/H2CasMab-2 for
breast cancers. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 43:35–43.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kaneko MK, Suzuki H, Ohishi T, Nakamura T,
Tanaka T and Kato Y: A cancer-specific monoclonal antibody against
HER2 exerts antitumor activities in human breast cancer xenograft
models. Int J Mol Sci. 25:19412024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lodewijk I, Dueñas M, Paramio JM and Rubio
C: CD44v6, STn & O-GD2: Promising tumor associated antigens
paving the way for new targeted cancer therapies. Front Immunol.
14:12726812023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Aasted MKM, Groen AC, Keane JT, Dabelsteen
S, Tan E, Schnabel J, Liu F, Lewis HS, Theodoropulos C, Posey AD
and Wandall HH: Targeting solid cancers with a cancer-specific
monoclonal antibody to surface expressed aberrantly O-glycosylated
proteins. Mol Cancer Ther. 22:1204–1214. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|