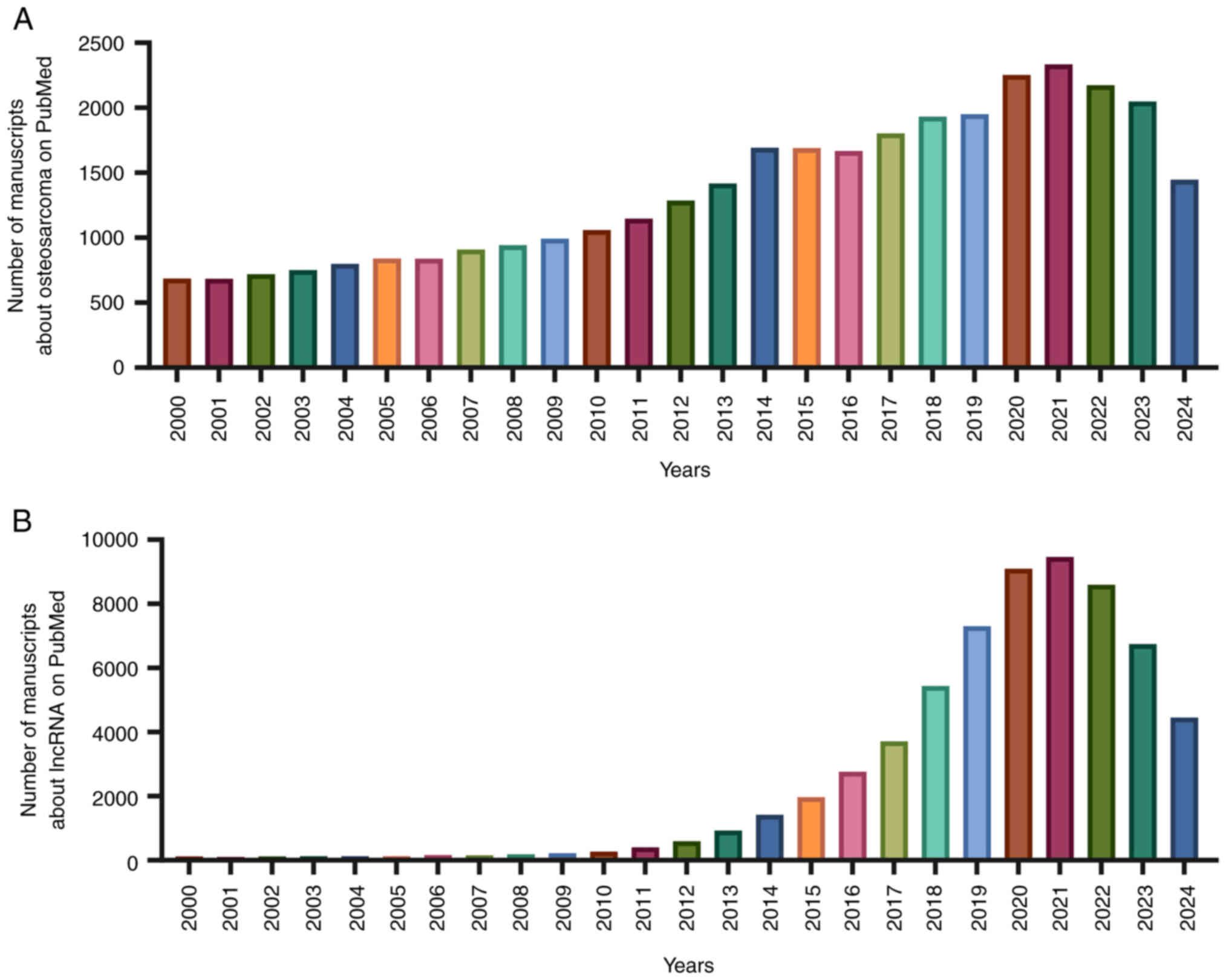
Introduction
Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most common primary
malignant bone tumor (1,2), and it substantially impacts bone
structure and function (3).
Research on OS has increased with continuous development of science
and technology. Using the key word ‘osteosarcoma’, relevant
articles were searched in PubMed (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) and it was observed
that the number of studies on OS has been increasing annually
between 2000 and 2021 (Fig. 1A).
Early detection and accurate staging of OS are critical in
predicting the clinical prognosis (4,5).
Currently, the early diagnosis of OS primarily relies on X-ray
imaging and local symptoms (6), and
there are no reliable biomarkers available, leading to untimely
diagnosis and a poor prognosis (7,8).
Therefore, specific molecular markers, such as long noncoding RNAs
(lncRNAs), are required in addition to understanding their
biological role. This may lead to the development of strategies
that block lncRNAs that promote tumor development while boosting
lncRNAs that inhibit tumor development.
lncRNAs are transcripts with a length of >200
nucleotides that do not exhibit protein-coding potential (9). As the most common type of noncoding
RNA (10,11), lncRNAs have attracted increasing
attention. Using the key word ‘lncRNA’, relevant articles were
searched in PubMed and it was observed that lncRNA research has
been increasing annually between 2000 and 2021 (Fig. 1B). The Human Genome Organisation
Gene Nomenclature Committee has suggested that lncRNAs should be
named based on their function when possible. For genes with unknown
function, if there is a closely related protein-coding gene, the
name of the lncRNA should begin with the name of the coding gene,
followed by a suffix indicating its target location, such as
antisense, intronic and opposite strand. Regarding the nomenclature
of long intergenic noncoding RNAs (lincRNAs), ‘linc’ is used as the
prefix and numbers as the suffix (12). In some physiological and
pathological processes, through regulation of the expression of
genes that promote or inhibit tumors, lncRNAs serve an essential
role in regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion,
metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (13). lncRNAs act by adsorbing microRNAs
(miRNAs/miRs), affecting the expression of downstream target genes
(14).
EMT is essential for tumor genesis and development
(15–18). Multiple studies have indicated that
successful tumor treatment can be achieved through EMT
intervention, which may also provide strategies for tumor
prevention (19–22). The level of EMT can be determined by
measuring the expression levels of a series of related proteins,
such as interstitial and epithelial markers (23–25).
The upregulation of EMT is manifested through the upregulation of
mesenchymal markers [Snail, Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1
(ZEB1), ZEB2, vimentin, N-cadherin and fibronectin] and the
downregulation of epithelial markers [E-cadherin and zonula
occludens-1 (ZO-1)]. The downregulation of EMT is manifested by the
downregulation of mesenchymal markers and the upregulation of
epithelial markers (23–25).
Using the key words ‘osteosarcoma’, ‘lncRNA’ and
‘EMT’, relevant articles were searched in PubMed and 93 articles
published between January 2015 and December 2023 were identified.
After further screening, 73 articles that met the review criteria
were selected and each article was examined independently. The
other 20 articles may be reviews or retrospective clinical studies
that only mentioned the aforementioned keywords, and were excluded.
Based on the relationship between lncRNAs and OS, lncRNAs were
divided into upregulated genes (promoting tumor development) and
downregulated genes (inhibiting tumor development). Based on their
putative biological effect on downstream genes, the lncRNAs were
further divided into two categories: Those affecting downstream
genes through adsorption of miRNAs and those affecting downstream
genes through other mechanisms. Finally, based on the lncRNA-naming
principle, lncRNAs were categorized as lncRNAs with known function,
antisense lncRNAs, lincRNAs and intronic lncRNAs.
There are numerous studies on OS, lncRNAs and EMT,
as well as the biological roles of lncRNA, and it is necessary to
summarize the findings of studies on lncRNA regulation of OS
occurrence and development through EMT, examine the underlying
regulatory mechanisms, and provide a novel theoretical basis and
targets for OS treatment. We hypothesized that the underlying
regulatory mechanism is a comprehensive, systematic network rather
than a single pathway.
lncRNAs promoting OS
By reviewing and organizing relevant articles on
lncRNAs and OS, it was revealed that most lncRNAs promote the EMT
process, leading to the occurrence and development of OS.
miRNA sponging
miRNAs induce gene silencing by binding to the mRNA
of target genes. lncRNAs regulate gene expression by competitively
binding to miRNAs. This process is known as the competing
endogenous RNA (ceRNA) mechanism. This section discusses how
lncRNAs promote the EMT process through the ceRNA mechanism,
resulting in OS progression.
lncRNAs with known functions
Some well-studied lncRNAs, including breast
cancer-related transcript 1 (BCRT1) and endogenous bornavirus-like
nucleoprotein three pseudogene (EBLN3P), are named based on their
known function. The present review discusses some lncRNAs with
known functions that promote the occurrence of OS through the ceRNA
mechanism.
In addition to inducing EMT, high expression levels
of BCRT1 promote OS progression and the cell cycle. Research has
indicated that high BCRT1 expression decreased the expression
levels of miR-1303 in MG-63 cells. Fibroblast growth factor 7
(FGF7) is a target gene of miR-1303 in OS cells (26). BCRT1 promotes OS cell reproduction
by regulating FGF7 expression, and promoting the process of EMT and
the secretion of inflammatory mediators (26).
A decrease in miR-200a-3p expression results in the
upregulation of its direct target gene O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT),
which further promotes EMT in OS cells. The expression of the
lncRNA EBLN3P is upregulated in OS. This lncRNA increases the
methotrexate resistance of OS cells by downregulating miR-200a-3p
expression, promoting EMT and increasing OGT expression (27).
Upregulation of the lncRNA HLA complex group 11
(HCG11) has been reported in OS tissues and cells. The cytoplasmic
lncRNA HCG11 increases the expression levels of MMP13 by adsorbing
miR-579. Downregulation of HCG11/MMP13 or upregulation of miR-579
suppresses EMT in OS cells (28).
Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript
1 (MALAT1) expression is upregulated in OS tissues and cells.
MALAT1 knockdown induces apoptosis while inhibiting the
proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT of OS cells. In OS
cells, MALAT1 knockdown upregulates the expression levels of
miR-590-3p. MALAT1 inhibits apoptosis, and induces the
proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT of OS cells by
inhibiting miR-590-3p expression (29).
MIR31 host gene expression is upregulated in OS
tissues and cells. In OS cells, its upregulation promotes the
expression of genes related to the proliferation and metastasis of
tumor cells that are downstream of miR-361, including vascular
endothelial-derived growth factor, Forkhead box M1 and Twist,
resulting in the upregulation of BCL2 and cyclin D1, and EMT
(30).
The lncRNA N-Myc downstream-regulated gene 1 (NDRG1)
is highly expressed in OS cells and tissues. NDRG1 aggravates OS
progression and activates the PI3K/AKT pathway by adsorbing
miR-96-5p. This is completed through EMT (31).
Nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) is
highly expressed in OS tissues and cells. Upregulation of NEAT1
promotes the proliferation, invasion and EMT of OS cells.
Furthermore, miR-186-5p is located downstream of NEAT1 in OS cells,
and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) is a downstream target
gene of miR-186-5p. NEAT1 inhibits the expression of
miR-186-5p/HIF-1α and serves a tumorigenic role in OS cells
(32).
Low expression of miR-483 has been noted in OS
tissues and cells. Upregulation of miR-483 suppresses the
expression of EMT-related markers in U2OS cells. miR-483 targets
the 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR) of STAT3, thereby inhibiting
its expression. NEAT1 increases the expression levels of STAT3,
which inhibits STAT1 expression, by adsorbing miR-483, and
increases the EMT of OS cells. NEAT1 knockdown disrupts the
mesenchymal-epithelial transition at the metastatic site of OS
(33).
Prostate-specific transcript 1 (PCGEM1) knockdown
inhibits the proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT of OS
cells. The lncRNA PCGEM1 is a direct target of miR-433-3p. Research
has demonstrated that OMA1 is a direct target gene of
miR-433-3p (34).
Upregulation of p53-upregulated regulator of p53
levels (PURPL) expression promotes the proliferation, migration,
invasion and EMT of MG-63 cells. PURPL is a regulator of miR-363
expression and is located upstream of miR-363. miR-363 serves a
tumor-suppressive role in OS cells by reducing the expression of
PDZ domain containing 2 (35).
Small nucleolar RNA host gene (SNHG)1 expression is
upregulated in OS tissues and cells. miR-577 acts as a ceRNA of
SNHG1 in OS cells. As a direct target gene of miR-577, Wnt family
member 2B (WNT2B) activates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and acts as a
carcinogenic factor in OS cells. SNHG1 overexpression promotes the
proliferation, migration, EMT and tumor growth of U2OS and MG63
cells (36).
High SNHG7 levels in patients with OS are associated
with a high Enneking stage, remote metastasis and shorter overall
survival time. Inhibiting SNHG7 expression can restore miR-34a
expression in MG63 and SaOS2 OS cells. SNHG7 knockout inhibits the
viability, migration, invasion and EMT of OS cells (37).
Compared with those in healthy tissues, SNHG10
levels in OS tissues are increased. SNHG10 can regulate the
expression of frizzled class receptor 3 (FZD3) by sponging
miR-182-5p. The SNHG10/miR-182-5p/FZD3 axis increases the transfer
into the nucleus and accumulation of β-catenin in the nucleus to
activate the Wnt signaling pathway. SNHG10 serves an important role
in accelerating the proliferation, invasion and EMT of OS cells
(38).
The expression levels of SNHG16 and integrin subunit
α6 (ITGA6) are increased in OS, while the expression levels of
miR-488 are decreased. miR-488 overexpression and SNHG16 knockdown
inhibit the migration, invasion and EMT of OS cells. Thus, the
effect of SNHG16 on the aforementioned processes depends on miR-488
and ITGA6 (39).
Taurine-upregulated gene 1 (TUG1) knockout inhibits
the proliferation, migration and invasion of OS cells, and induces
apoptosis. TUG1 regulates miR-144-3p expression through direct
binding. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) is negatively regulated
by miR-144-3p and positively regulated by TUG1. EZH2
overexpression partially weakens the inhibition of the migration
and EMT of OS cells induced by TUG1 knockdown or miR-144-3p
overexpression (40).
Urothelial carcinoma-associated 1 (UCA1) expression
is upregulated in OS tissues and cells. UCA1 increases the
expression of cAMP response element-binding protein 1 (CREB1) by
acting as a ceRNA of anti-miR-582. UCA1 promotes EMT through the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway mediated by CREB1, resulting in metastasis
(41).
Compared with matched adjacent nontumor tissues, X
inactive-specific transcript (XIST) was highly expressed in 30
pairs of OS tissues. XIST upregulation promotes the invasion,
migration and EMT phenotype of OS tissues, and decreases the
expression levels of the epithelial marker E-cadherin. However, the
interstitial markers fibronectin, Snail and vimentin are
upregulated by exogenous XIST (42). XIST downregulates miR-153 directly
through a sponging process. The mesenchymal marker snail family
transcriptional repressor 1 (SNAI1) is the direct target gene of
miR-153. Inhibition of XIST suppresses the EMT of OS cells induced
by H2O2. XIST promotes the invasion,
migration and EMT of OS cells induced by oxidative stress through
the miR-153/SNAI1 pathway (42).
XIST is highly expressed in OS tissues and cells,
whereas miR-758 expression is low. XIST overexpression and miR-758
inhibitor transfection in OS cells promote the migration, invasion
and EMT of tumor cells. By contrast, knockdown of XIST and miR-758
mimic transfection inhibits the aforementioned processes.
Furthermore, miR-758 regulates Rab16 expression. XIST promotes the
migration, invasion and EMT of OS cells by regulating the
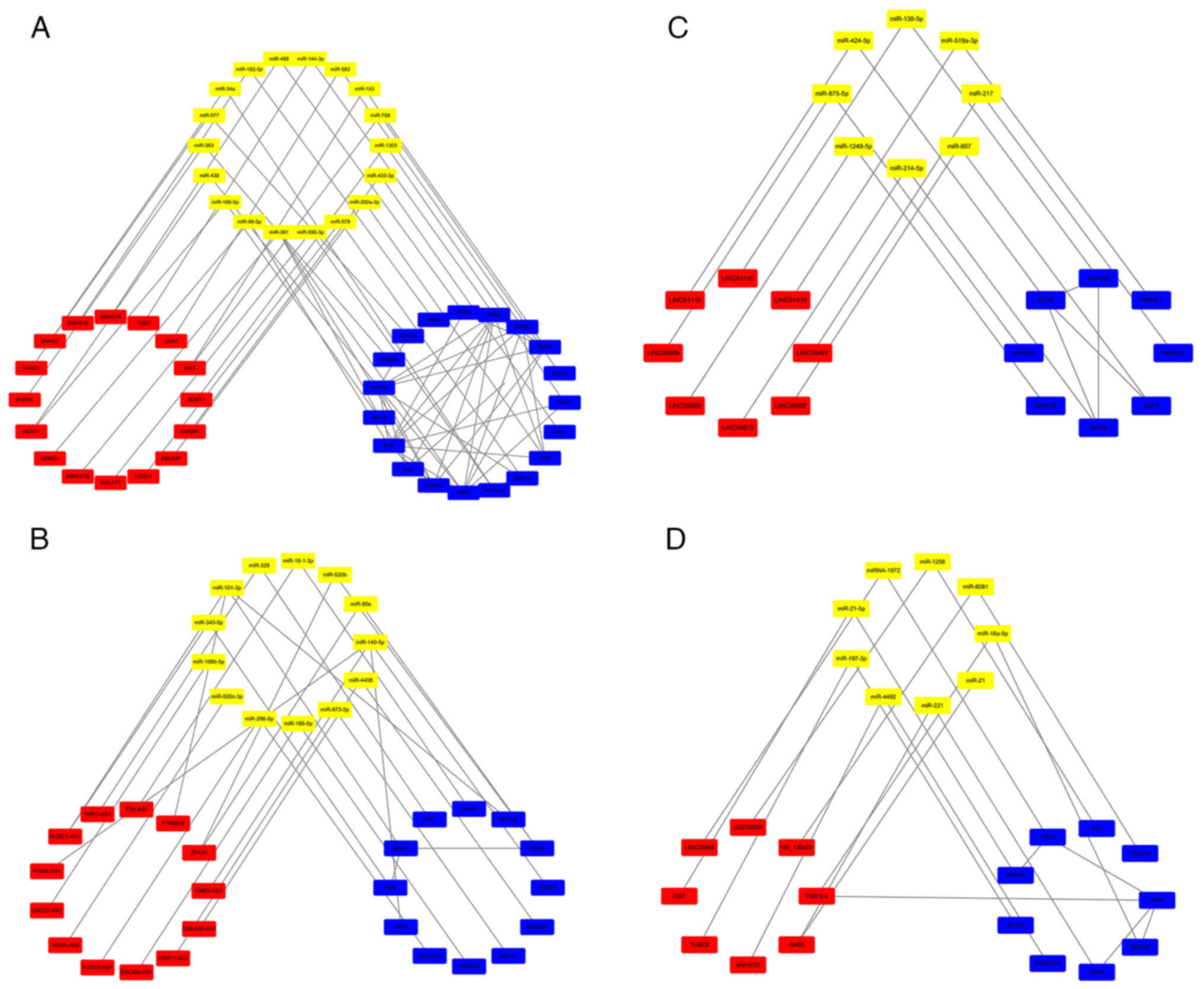
miR-758/Rab16 axis (43) (Table I; Fig.
2A).
 | Table I.lncRNAs with known functions acting
as miRNA sponges. |
Table I.
lncRNAs with known functions acting
as miRNA sponges.
| First author/s,
year | lncRNA | Relationship with
OS | Relationship with
EMT | Action
mechanism | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Han et al,
2021 | BCRT1 | Promotes the
proliferation and cell cycle of OS cells | Promotes EMT | Reduces the
expression levels of miR-1303; FGF7 is the target gene of
miR-1303 | (26) |
| Sun et al,
2022 | EBLN3P | Increases MTX
resistance of OS cells | Promotes EMT | Downregulates
miR-200a-3p, and then increases the expression levels of OGT | (27) |
| Wang et al,
2020 | HCG11 | Promotes the
progression of OS cells | Promotes EMT | Adsorbs miR-579 and
promotes MMP13 expression | (28) |
| Zhao et al,
2022 | MALAT1 | Inhibits the
apoptosis of OS cells, and promotes the proliferation, migration
and invasion of OS cells | Promotes EMT | Inhibition of
miR-590-3p expression in OS | (29) |
| Sun et al,
2019 | MIR31HG | Upregulated
expression in OS tissues and OS cell lines | Promotes EMT | Promotes downstream
target genes of MIR-361, including VEGF, FOXM1 and Twist | (30) |
| Wang et al,
2022 | NDRG1 | Aggravates the
progression of OS | Promotes EMT | Adsorbs miR-96-5p
and activates the PI3K/AKT pathway | (31) |
| Tan and Zhao,
2019 | NEAT1 | Promotes the
proliferation and invasion of OS cells | Promotes EMT | Inhibits the
miR-186-5p/HIF-1 α axis | (32) |
| Chen et al,
2021 | NEAT1 | Facilitates OS
metastasis | Promotes EMT | Adsorbs miR-483,
increases STAT3 expression and inhibits STAT1 expression | (33) |
| Li et al,
2023 | PCGEM1 | Promotes cell
proliferation, migration and invasion in OS | Promotes EMT | Directly binds with
miR-433-3p; OMA1 is the target gene of miR-433-3p | (34) |
| He et al,
2021 | PURPL | Promotes the
proliferation, migration and invasion of MG-63 cells | Promotes EMT | PURPL is the
upstream regulator of miR-363, which reduces PDZD2 expression | (35) |
| Jiang et al,
2018 | SNHG1 | Promotes the
proliferation, migration and tumor growth of U2OS and MG63
cells | Promotes EMT | miR-577 acts as the
ceRNA of SNHG1, WNT2B acts as the target of miR-577 and WNT2B
activates the Wnt/β-catenin axis | (36) |
| Deng et al,
2018 | SNHG7 | Improves the
viability, migration and invasion of MG63 and SaOS2 cells | Promotes EMT | Inhibition of
miR-34a expression | (37) |
| Zhu et al,
2020 | SNHG10 | Promotes OS growth
and invasion | Promotes EMT | Sponges miR-182-5p
to upregulate FZD3 levels, and promotes β-catenin transfer into the
nucleus and accumulation in the nucleus to maintain the activation
of Wnt signaling | (38) |
| Bu et al,
2021 | SNHG16 | Promotes the
migration and invasion of OS cells | Promotes EMT | Downregulates
miR-488 and upregulates ITGA6 | (39) |
| Cao et al,
2017 | TUG1 | Promotes OS cell
proliferation, migration and invasion, and inhibits cell
apoptosis | Promotes EMT | Directly combines
with miR-144-3p; EZH2 is negatively regulated by miR-144-3p | (40) |
| Ma et al,
2019 | UCA1 | Causes OS
metastasis | Promotes EMT | Increases CREB1
expression as an anti-miR-582 ceRNA, thus activating the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway | (41) |
| Wen et al,
2020 | XIST | Induces OS cell
invasion and migration | Promotes EMT | Directly
downregulates miR-153; SNAI1 is the direct target of miR-153 | (42) |
| Liu et al,
2021 | XIST | Promotes OS cell
migration and invasion | Promotes EMT | Inhibits the
miR-758/Rab16 axis | (43) |
A total of 16 lncRNAs with known functions that
promote the occurrence of OS through the ceRNA mechanism were
identified. NEAT1 and XIST were identified twice as
‘high-frequency’ lncRNAs. NEAT1 promotes EMT through the
miR-186-5p/HIF-1α and miR-483/STAT3 axes (32,33),
leading to OS progression. XIST promotes EMT through the
miR-153/SNAI1 and miR-758/Rab16 axes (42,43),
resulting in OS progression.
Antisense lncRNAs
Antisense lncRNAs are transcribed from opposite DNA
strands with protein-coding or noncoding functions that contribute
to the occurrence and development of OS and other tumors. The
present review discusses some antisense lncRNAs that promote the
occurrence of OS through the ceRNA mechanism.
Carbonyl reductase antisense RNA 1 (CBR3-AS1) is
highly expressed in OS cells, which can enhance the stemness, EMT
and proliferation of these cells (44). The lncRNA CBR3-AS1 adsorbs
miR-140-5p, recruits DEAD-box helicase 54, and induces the
expression of nuclear casein and cyclin-dependent kinase substrate
1, activating the mTOR signaling pathway (44).
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2B antisense RNA 1
(CDKN2B-AS1) is upregulated in OS tissues and cells. CDKN2B-AS1
knockout inhibits the proliferation, migration and EMT of OS cells.
CDKN2B-AS1 promotes OS progression by adsorbing miR-4458 and
enhancing MAP3K3 expression (45).
DEAD/H box protein 11 antisense RNA 1 (DDX11-AS1) is
highly expressed in OS cells. Decreased DDX11-AS1 expression
inhibits the proliferation, metastasis and EMT of OS cells.
DDX11-AS1 induces DDX11 expression in OS by sponging miR-873-5p.
DDX11-AS1 maintains DDX11 mRNA levels by binding to insulin-like
growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 in OS cells (46).
High expression levels of DSCAM antisense RNA 1
(DSCAM-AS1) have been reported in OS cell lines. Depletion of
DSCAM-AS1 inhibits the proliferation, migration and EMT of OS
cells. DSCAM-AS1 is primarily located in the cytoplasm of OS cells
and interacts with miR-186-5p. G protein-coupled receptor class C
group 5 member A (GPRC5A) is the downstream target of miR-186-5p.
GPRC5A is inversely regulated by miR-186-5p but is cooperatively
regulated by DSCAM-AS1, which induces GPRC5A expression in OS by
chelating miR-186-5p (47).
Increased expression of forkhead box D3 antisense
RNA 1 (FOXD3-AS1) is observed in OS tissues and cells. Decreased
expression of FOXD3-AS1 inhibits the migration, invasion and EMT of
OS cells. FOXD3-AS1 increases zinc finger CCHC-type containing 3
(ZCCHC3) by chelating miR-296-5p. Activated FOXD3-AS1 increases
ZCCHC3 expression by adsorbing miR-296-5p, which aggravates the
migration, invasion and EMT of OS cells (48).
HOXA-AS2 is upregulated in OS tissues. HOXA-AS2
induces the migration and invasion of OS cells by promoting EMT,
and inversely regulates miR-520c-3p expression in OS cells
(49).
LMCD1 antisense RNA 1 (LMCD1-AS1) and SP1 are highly
expressed in OS tissues and cells. Functionally, silencing of
LMCD1-AS1 inhibits the proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT
of OS cells. LMCD1-AS1 regulates the survival of OS cells by
targeting miR-106b-5p (50).
The lncRNA PGM5 antisense RNA 1 (PGM5-AS1) can
competitively bind to miR-140-5p to regulate fibrillin 1 (FBN1).
Furthermore, blocking PGM5-AS1 and FBN1 expression or increasing
miR-140-5p expression inhibits the migration, invasion and EMT of
OS cells (51).
The expression of RUSC1 antisense RNA 1 (RUSC1-AS1)
in U2OS and HOS cells is upregulated compared with that in hFOB1.19
cells. RUSC1-AS1 promotes the EMT of OS cells and directly binds to
the 3′-UTR of miR-340-5p to inhibit its expression and activate the
PI3K/AKT pathway (52).
RUSC1-AS1 and Notch1 are upregulated in OS
cells and tissues. RUSC1-AS1 knockdown suppresses the
proliferation, EMT, lung metastasis, migration and invasion of
MG-63 and Saos-2 cells. RUSC1-AS1 acts as a ceRNA. RUSC1-AS1
competitively adsorbs miR-101-3p and upregulates the expression
levels of Notch1, interfering with the malignant phenotype.
RUSC1-AS1 is a novel carcinogenic lncRNA expressed in OS. RUSC1-AS1
exerts its biological effect via the miR-101-3p-Notch1-Ras-ERK axis
(53).
TMPO antisense RNA 1 (TMPO-AS1) is upregulated in OS
cells. TMPO-AS1 binds to miR-329, which targets the E2F
transcription factor 1 (E2F1) gene. TMPO-AS1 regulates the EMT of
OS cells via the miR-329/E2F1 axis (54).
In OS cells, the expression levels of TTN-antisense
RNA 1 (TTN-AS1) and transcription factor activating enhancer
binding protein 4 (TFAP4) are upregulated, whereas those of
miR-16-1-3p are downregulated. Silencing of TTN-AS1 inhibits the
proliferation, migration, invasion and tumor growth of OS cells, as
well as the expression of N-cadherin and MMP-2 in these cells.
TTN-AS1 promotes the proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT of
OS cells by inhibiting the miR-16-1-3p/TFAP4 pathway (55).
Depletion of neuropilin and tolloid-like 2 (NETO2)
inhibits the proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT of OS
cells. NETO2 binds to and is negatively regulated by miR-101-3p,
which interacts with TYMS opposite-strand RNA in OS cells (56).
The lncRNA zinc finger antisense 1 (ZFAS1) is
upregulated in OS cells. Overexpression of ZFAS1 promotes the
proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT of OS cells, while
silencing of ZFAS1 has the opposite effect. With regard to its
mechanism, ZFAS1 acts as a sponge for miR-520b and miR-50e, while
upregulating the expression levels of Ras homolog C (RHOC)
(57) (Table II; Fig.
2B).
 | Table II.Antisense lncRNAs acting as miRNA
sponges. |
Table II.
Antisense lncRNAs acting as miRNA
sponges.
| First author/s,
year | lncRNA | Relationship with
OS | Relationship with
EMT | Action
mechanism | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Yao et al,
2022 | CBR3-AS1 | Promotes the
stemness of OS cells and the growth of OS | Promotes EMT | Adsorbs miR-140-5p
and recruits DDX54 to upregulate NUCKS1, thus activating the mTOR
pathway | (44) |
| Gui and Cao,
2020 | CDKN2B-AS1 | Promotes cell
proliferation and migration in OS | Promotes EMT | Adsorbs miR-4458
and enhances MAP3K3 expression | (45) |
| Zhang et al,
2020 | DDX11-AS1 | Promotes the
proliferation and metastasis of OS cells | Promotes EMT | Sponges miR-873-5p
to upregulate DDX11 expression; combines with IGF2BP2 to regulate
the mRNA stability of DDX11 | (46) |
| Ning and Bai,
2021 | DSCAM-AS1 | Promotes cell
proliferation and migration in OS | Promotes EMT | Chelates miR-186-5p
to enhance GPRC5A expression | (47) |
| Wang, 2021 | FOXD3-AS1 | Promotes cell
migration and invasion in OS | Promotes EMT | Adsorbs miR-296-5p
and increases ZCCHC3 expression | (48) |
| Wang et al,
2018 | HOXA-AS2 | Promotes OS cell
migration and invasion | Promotes EMT | Negative regulation
of miR-520c-3p expression | (49) |
| He et al,
2020 | LMCD1-AS1 | Promotes the
proliferation, migration and invasion of OS cells | Promotes EMT | Targets
miR-106b-5p | (50) |
| Liu et al,
2020 | PGM5-AS1 | Promotes the
migration and invasion of OS cells in vitro | Promotes EMT | Combines with
miR-140-5p to upregulate FBN1 expression | (51) |
| Tong et al,
2021 | RUSC1-AS1 | Upregulated in U2OS
and HOS cells compared with hFOB1.19 cells | Promotes EMT | Suppresses
miR-340-5p and activates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | (52) |
| Jiang et al,
2021 | RUSC1-AS1 | Enhances the
proliferation, growth, lung metas tasis, migration and invasion of
MG-63 and Saos-2 cells | Promotes EMT | Via
miR-101-3p-Notch1-Ras-ERK pathway | (53) |
| Liu et al,
2020 | TMPO-AS1 | Upregulated
expression in OS cells | Promotes EMT | Via the
miR-329/E2F1 axis | (54) |
| Meng et al,
2021 | TTN-AS1 | Promotes OS cell
proliferation, migration and invasion | Promotes EMT | Mediates the
miR-16-1-3p/TFAP4 axis | (55) |
| Zhang et al,
2022 | TYMSOS | Promotes OS cell
proliferation, migration and invasion | Promotes EMT | NETO2 is directly
targeted by miR-101-3p, which can be combined with TYMSOS | (56) |
| Liu et al,
2023 | ZFAS1 | Promotes the
proliferation, migration and invasion of OS cells | Promotes EMT | Serves as a sponge
for miR-520b and miR-50e, and upregulates RHOC | (57) |
A total of 14 studies of 13 antisense lncRNAs that
promote the occurrence of OS through the ceRNA mechanism were
identified. RUSC1-AS1 has been studied twice as a ‘high-frequency’
lncRNA. RUSC1-AS1 promotes EMT through the miR-340-5p/PI3K/AKT and
miR-101-3p-Notch1-Ras-ERK axes (52,53),
which results in OS progression.
lincRNAs
lincRNAs are RNAs that contribute to the occurrence
of various tumors, including OS. This section discusses some
lincRNAs that promote the occurrence of OS through the ceRNA
mechanism.
LINC00467 and high-mobility-group A1 (HMGA1) are
highly expressed in OS tissues and cells, whereas miR-217
expression is low. Knockout of LINC00467 or miR-217 mimics can
induce apoptosis, while inhibiting the proliferation, migration,
invasion and EMT of OS cells. LINC00467 directly targets miR-217,
whereas HMGA1 is the target of miR-217 (58). LINC00467 upregulates HMGA1
expression by targeting miR-217, and enhances the proliferation,
migration, invasion and EMT of OS cells (58).
LINC00607 promotes the proliferation, migration and
invasion of OS cells, as well as the migration and invasion of
endothelial cells, thereby simultaneously enhancing EMT. LINC00607
upregulates the expression levels of E2F6 through miR-607, which
promotes the proliferation of OS cells (59).
LINC00612 is highly expressed in metastatic OS
cells. LINC00612 upregulation regulates EMT by increasing the
expression levels of ZEB1, Snail and fibronectin 1, and decreasing
those of E-cadherin. LINC00612 overexpression upregulates SOX4
expression by inhibiting miR-214-5p (60).
LINC00665 is highly expressed in OS cells, and its
suppression inhibits the proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT
of OS cells. LINC00665 acts as a ceRNA to adsorb miR-1249-5p,
regulating WNT2B to activate the Wnt pathway, which induces
LINC00665 expression, forming a positive feedback loop (61).
LINC00909 expression is upregulated in OS cells and
tissues. LINC00909 induces EMT, while contributing to the ongoing
metastasis of OS tumors. LINC00909 adsorbs miR-875-5p to exert its
biological effect. Homeobox D9 (HOXD9) has been confirmed to be a
target gene of miR-875-5p. LINC00909 upregulates HOXD9 expression
by binding to miR-875-5p, induces EMT, and promotes the occurrence
and metastasis of OS tumors through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis
(62).
LINC01116 expression in MG-63/Dox cells is higher
than that in MG-63 cells. The inhibition of LINC01116 expression
impedes the viability, migration and invasion of these cells by
upregulating the expression levels of E-cadherin and downregulating
those of vimentin, thereby inhibiting EMT. LINC01116 inhibits HMGA2
expression by silencing EZH2-related miR-424-5p (63).
LINC01140 is expressed in OS cells, and its
silencing inhibits the proliferation, invasion and EMT of these
cells. LINC01140 adsorbs miR-139-5p, which inhibits the invasion,
proliferation and EMT of Saos2 and MG63 cells by targeting HOXA9.
Silencing of LINC01140 inhibits the invasion, proliferation and EMT
of OS cells via the miR-139-5p/HOXA9 pathway (64).
LINC01419 is highly expressed in OS tissues and
cells, and enhances the proliferation, metastasis and EMT of OS
cells. LINC01419 enhances the expression levels of p53 and DNA
damage-regulated gene 1 by inhibiting miR-519a-3p (65) (Table
III; Fig. 2C).
 | Table III.Long intergenic noncoding RNAs and
opposite strand lncRNAs acting as miRNA sponges. |
Table III.
Long intergenic noncoding RNAs and
opposite strand lncRNAs acting as miRNA sponges.
| First author/s,
year | lncRNA | Relationship with
OS | Relationship with
EMT | Action
mechanism | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Ma et al,
2020 | LINC00467 | Reduces OS cell
apoptosis, and promotes OS cell proliferation, migration and
invasion | Promotes EMT | Targets miR-217 and
upregulates HMGA1 | (58) |
| Zheng et al,
2020 | LINC00607 | Promotes OS
proliferation, migration and invasion | Promotes EMT | As a miR-607
sponge, upregulates E2F6 expression | (59) |
| Zhou et al,
2020 | LINC00612 | Upregulated in OS
cells and metastatic OS | Promotes EMT | Upregulates SOX4 by
inhibiting miR-214-5p | (60) |
| Bai et al,
2023 | LINC00665 | Promotes OS cell
proliferation, migration and invasion | Promotes EMT | Sponges miR-1249-5p
to regulate WNT2B to activate the Wnt pathway | (61) |
| Liu et al,
2022 | LINC00909 | Helps the
occurrence and metastasis of OS | Promotes EMT | By binding with
miR-875-5p, it upregulates HOXD9 expression and activates the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway | (62) |
| Li et al,
2021 | LINC01116 | Promotes cell
viability, migration and invasion in MG-63/Dox cells | Promotes EMT | Regulates HMGA2
expression by silencing EZH2-related miR-424-5p | (63) |
| Zhang and Chen,
2022 | LINC01140 | Promotes the
proliferation and invasion of OS cells | Promotes EMT | Targets the
miR-139-5p/HOXA9 axis | (64) |
| Gu et al,
2020 | LINC01419 | Accelerates OS cell
proliferation and movement | Promotes EMT | Enhances PDRG1
expression by miR-519a-3p sequestration | (65) |
A total of eight lincRNAs that promote the
occurrence of OS through the ceRNA mechanism were identified. No
‘high-frequency’ lncRNAs were detected.
miRNA sponging-independent
lncRNAs exert their biological effects not only
through ceRNA mechanisms but also through direct regulation of
downstream signaling pathways. This section discusses how lncRNAs
promote the EMT process through this mechanism, which results in OS
progression.
lncRNAs with known functions
Numerous lncRNAs are named based on their known
function. The present review discusses some lncRNAs with known
functions that promote the occurrence of OS by directly regulating
downstream signaling pathways.
lncRNA cancer susceptibility candidate 15 (CASC15)
expression is upregulated in OS tissues and cells. CASC15 activates
Wnt/β-catenin, which affects the cell cycle and promotes cell
proliferation (66). CASC15 causes
β-catenin to enter the nucleus through the Wnt signaling pathway,
which promotes the EMT of OS cells (66).
Colorectal neoplasia differentially expressed
(CRNDE) is highly expressed in OS tissues and cells. Overexpression
of CRNDE enhances the activity of Notch1 signaling in MG-63 cells
and promotes EMT (67).
Following CRNDE knockdown, the interstitial markers
N-cadherin, vimentin and Snail are downregulated, whereas the
epithelial markers E-cadherin and ZO-1 are upregulated. CRNDE
promotes the phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3β and the
activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway (68).
Compared with that in normal control cells, focally
amplified lncRNA on chromosome 1 (FAL1) is upregulated in human OS
tissues and cells. FAL1 knockdown inhibits the migration and
invasion of OS cells by inhibiting the EMT process (69).
lncRNA Ftx expression in OS tissues is higher than
that in adjacent nontumor tissues. Upregulated Ftx serves as a
biomarker for the progression and prognosis of OS, as Ftx promotes
tumor growth through the EMT mechanism. Ftx overexpression
decreases the expression levels of E-cadherin, and enhances those
of N-cadherin and Snail 1 (70).
Gastric cancer high expressed transcript 1 (GHET1)
levels are upregulated in OS tissues compared with those in normal
tissues. GHET1 knockout in MG-63 and U2OS cells inhibits the
proliferation, invasion, migration and EMT of OS cells (71).
Histocompatibility leukocyte antigen complex P5
expression is upregulated in OS cells, and its silencing suppresses
cell invasion and EMT (72).
Overexpression of Hox transcript antisense
intergenic RNA enhances the invasion and migration of MG63 and
Saos-2 cells. Furthermore, its overexpression induces EMT (73).
The expression of HOXA transcript at the distal tip
(HOTTIP) is markedly elevated in OS tissues and cells. Silencing of
HOTTIP inhibits the migration, invasion and EMT of tumor cells.
c-Myc upregulation increases HOTTIP expression, and HOTTIP promotes
the migration and invasion of OS cells by upregulating c-Myc
expression. HOTTIP and c-Myc constitute a positive feedback loop
that results in OS progression (74).
Downregulation of MALAT1 inhibits the proliferation,
migration, invasion and EMT of OS cells. This is related to the
17β-estradiol dose and not to estrogen receptor expression
(75).
Myc-induced lncRNA (MINCR) is expressed in OS
tissues and cells. The migration and invasion of Saos-2 OS cells
are decreased following MINCR knockout, and EMT is inhibited. MINCR
controls the growth and metastasis of OS via the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway (76).
Knockdown of the pseudogene Minato family member 2
(MSTO2P) results in the inhibition of the proliferation, invasion
and EMT of OS cells under hypoxic conditions. Programmed death
ligand 1 is a crucial receptor for MSTO2P in the regulation of OS
progression under hypoxic conditions (77).
NEAT1 levels are increased in OS tissues and cell
lines compared with normal tissues and cell lines. The ectopic
expression of NEAT1 also induces EMT. NEAT1 inhibits the expression
of E-cadherin through binding to the G9a-DNA methyltransferase
1-Snail compound (78).
Prostate cancer-associated transcript 1 (PCAT1) is
upregulated in OS tissues compared with nontumor tissues. High
levels of PCAT1 enhance the proliferation, invasion, migration and
EMT of MG-63 cells. PCAT1 knockout inhibits the proliferation,
invasion, migration and EMT of U2OS cells (79).
Plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 (PVT1)
expression is upregulated in OS. Knocking down PVT1 in vitro
can inhibit the proliferation, migration and invasion of OS cells.
Furthermore, PVT1 influences EMT in OS cells (80).
The levels of the lncRNA T-cell factor 7 (lnc-TCF7)
in OS tissues are increased compared with those in normal bone
tissues. lnc-TCF7 silencing inhibits tumor metastasis in OS by
inhibiting the EMT process (81).
Testis development-related 1 (TDRG1) expression is
upregulated in OS concomitantly with the upregulation of
phosphorylated (p-)PI3K and p-AKT levels. TDRG1 knockout inhibits
the proliferation, invasion, migration and EMT of OS cells, while
inducing apoptosis, whereas increased TDRG1 levels exert the
opposite effect. Inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling axis inhibits
the proliferation, invasion, migration and EMT of OS cells
(82).
Increased TNF and HNRNPL-related immunoregulatory
long non-coding RNA (THRIL) expression is associated with increased
TNF-α levels in OS tissues and serum. TNF-α signaling is increased
in OS cells, whereas THRIL knockout inhibits TNF-α signaling,
resulting in decreased viability, increased apoptosis, and reduced
invasion and EMT (83).
Silencing of human antigen R (HuR) reduces argonaute
2 (AGO2) expression. HuR enhances AGO2 expression, which is
mediated by the lncRNA XIST. AGO2 knockdown inhibits cell
proliferation, migration and EMT. Inhibition of the lncRNA XIST
reduces AGO2 expression (84)
(Table IV).
 | Table IV.lncRNAs with known function that do
not act as microRNA sponges. |
Table IV.
lncRNAs with known function that do
not act as microRNA sponges.
| First author/s,
year | lncRNA | Relationship with
OS | Relationship with
EMT | Action
mechanism | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Wang and Zhang,
2021 | CASC15 | Influences OS cell
cycle, thus promoting OS cell proliferation | Promotes EMT | Activation of the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway | (66) |
| Li et al,
2018 | CRNDE | Upregulated
expression in OS tissues and cell lines | Promotes EMT | Enhances Notch1
signal transduction activity | (67) |
| Ding et al,
2020 | CRNDE | High expression in
OS tissues and cell lines | Promotes EMT | Promotes GSK-3β
phosphorylation and activates the Wnt/β-catenin axis | (68) |
| Wang et al,
2018 | FAL1 | Promotes the
migration and invasion of OS cells | Promotes EMT | Reduces the level
of p21 and promotes GSK-3β phosphorylation | (69) |
| Li et al,
2018 | Ftx | Increased
expression in OS | Promotes EMT | Via the Snail
pathway | (70) |
| Yang et al,
2018 | GHET1 | Promotes MG-63 and
U2OS cell proliferation, invasion and migration | Promotes EMT | - | (71) |
| Zhao et al,
2019 | HCP5 | Induces OS cell
invasion | Promotes EMT | - | (72) |
| Wang et al,
2019 | HOTAIR | Promotes the
invasion and migration of MG63 and Saos-2 cells | Promotes EMT | - | (73) |
| Tang and Ji,
2019 | HOTTIP | Promotes OS cell
migration and invasion | Promotes EMT | Increases c-Myc
expression | (74) |
| Fang et al,
2015 | MALAT1 | Promotes OS cell
proliferation, migration and invasion | Promotes EMT | 17β-estradiol
dose-dependent and estrogen receptor-independent | (75) |
| Bai et al,
2022 | MINCR | Increases migration
and invasion of Saos-2 cells | Promotes EMT | Via the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway | (76) |
| Shi et al,
2020 | MSTO2P | Increases
proliferation and invasion of OS cells | Promotes EMT | PD-L1 is the key
effector | (77) |
| Li and Cheng,
2018 | NEAT1 | Increased
expression in OS tissues and cell lines | Promotes EMT | Inhibition of
E-cadherin expression by binding with G9a-DNMT1-Snail | (78) |
| Zhang et al,
2018 | PCAT1 | Enhances MG-63 cell
proliferation, invasion and migration | Promotes EMT | - | (79) |
| Xun et al,
2021 | PVT1 | Promotes the
proliferation, migration and invasion of OS cells | Promotes EMT | - | (80) |
| Gao et al,
2017 | lncTCF7 | Facilitates OS
metastasis | Promotes EMT | Increases MMP-2 and
MMP-9 expression | (81) |
| Huang et al,
2020 | TDRG1 | Promotes OS cell
proliferation, invasion and migration | Promotes EMT | Promotes the
PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | (82) |
| Xu et al,
2020 | THRIL | Increases the
viability of OS cells | Promotes EMT | Promotes TNF-α
expression | (83) |
| Liu et al,
2021 | XIST | Promotes cell
proliferation and migration in OS | Promotes EMT | Mediates the
increase of AGO2 expression | (84) |
A total of 19 studies of 18 lncRNAs with known
functions that promote the occurrence of OS by directly regulating
downstream signaling pathways were identified. CRNDE was described
twice as a ‘high-frequency’ lncRNA. CRNDE promotes EMT through
Notch1 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling (67,68),
which results in OS progression.
Antisense lncRNAs
Antisense lncRNAs are transcribed from opposite DNA
strands with protein-coding or noncoding properties. They serve an
important role in the occurrence and development of OS and other
tumors. The present review describes several antisense lncRNAs that
promote the occurrence of OS by directly regulating downstream
signaling pathways.
Actin filament-associated protein 1 antisense RNA 1
(AFAP1-AS1) is expressed in human OS tissues and cell lines.
AFAP1-AS1 knockout suppresses the proliferation, migration,
invasion, angiogenesis and EMT of OS cells (85). AFAP1-AS1 serves a carcinogenic role
in OS through the RHOC/Rho-associated coiled-coil containing
protein kinase 1/p38MAPK/twist family bHLH transcription factor 1
axis (85).
CDKN2B-AS1 is upregulated in OS tissues and cells.
CDKN2B-AS1 knockout in OS cells inhibits CDK4 and cyclin D1
expression, as well as EMT. This is evidenced by an increase in
E-cadherin levels, and a decrease in vimentin and N-cadherin levels
(86).
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 homeobox A antisense RNA
1 (HNF1A-AS1) is upregulated in human OS tissues and cells, and is
positively associated with distant metastasis and tumor stage.
HNF1A-AS1 knockout using small interfering RNA inhibits cell
proliferation and G1/S phase transition, simultaneously
inhibiting the migration and invasion of cells by obstructing the
EMT process (87).
Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox two antisense
RNA1 (ZEB2-AS1) is associated with tumor size, distant metastasis
and prognosis. ZEB2-AS1 knockout inhibits the migration, invasion
and EMT of tumor cells (88)
(Table V).
 | Table V.Antisense lncRNAs, long intergenic
noncoding RNAs and intronic lncRNAs not acting as microRNA
sponges. |
Table V.
Antisense lncRNAs, long intergenic
noncoding RNAs and intronic lncRNAs not acting as microRNA
sponges.
| First author/s,
year | lncRNA | Relationship with
OS | Relationship with
EMT | Action
mechanism | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Shi et al,
2019 | AFAP1-AS1 | Promotes OS cell
proliferation, migration, invasion and angiogenesis | Promotes EMT | Via the
RHOC/ROCK1/p38MAPK/Twist1 signaling pathway | (85) |
| Luo et al,
2020 | CDKN2B-AS1 | Upregulated in OS
tissues and cell lines | Promotes EMT | Promotes CDK4 and
cyclin D1 expression | (86) |
| Cai et al,
2017 | HNF1A-AS1 | Promotes OS cell
proliferation, G1/S phase transition, migration and
invasion | Promotes EMT | - | (87) |
| Yang et al,
2020 | ZEB2-AS1 | Promotes the
migration and invasion of OS cells in vitro | Promotes EMT | - | (88) |
| Jiang and Luo,
2020 | LINC01354 | Promotes the
invasion and infiltration of OS cells | Promotes EMT | Increases integrin
β1 expression | (89) |
| Xu et al,
2016 | SPRY4-IT1 | Promotes the
migration and invasion of OS cells | Promotes EMT | - | (90) |
A total of four antisense lncRNAs that promote the
occurrence of OS by directly regulating the downstream signaling
pathways involved were identified. No ‘high-frequency’ lncRNAs were
detected.
lincRNAs
lincRNAs can contribute to the development of
various tumors, including OS. The lincRNA LINC01354 promotes the
occurrence of OS by directly regulating downstream signaling
pathways (89). LINC01354 is highly
expressed in OS tissues, serum and cells (89). Upregulation of LINC01354 promotes
the invasion, EMT and integrin β1 expression of OS cells. However,
downregulation of LINC01354 suppresses the aforementioned processes
in OS cells. Furthermore, LINC01354 promotes EMT and invasion of OS
cells (89) (Table V).
Intronic lncRNAs
Intronic lncRNAs are located in the intronic region
of protein-coding genes and do not overlap with any exons in the
transcript. The lncRNA sprouty RTK signaling antagonist 4-intronic
transcript 1 (SPRY4-IT1) promotes the occurrence of OS by directly
regulating downstream signaling pathways (90). SPRY4-IT1 is upregulated in OS cells.
The promoting effect of SPRY4-IT1 on cell migration and invasion is
partially related to EMT (90)
(Table V).
lncRNAs inhibiting OS
As aforementioned, lncRNAs can promote the EMT
process, leading to the occurrence and development of OS. They can
also inhibit the occurrence and development of OS by suppressing
the EMT process.
miRNA sponge-dependent mechanism
This section describes how lncRNAs inhibit the EMT
process through the ceRNA mechanism to prevent the occurrence of
OS.
Compared with those in normal bone or hFOB1.19
cells, FER-1 family member 4 (FER1L4) levels in OS tissues and
cells are reduced (91).
Overexpression of FER1L4 promotes the expression of suppressor of
cytokine signaling by interacting with miR-18a-5p and inhibiting
EMT and PI3K/AKT pathways (91).
Compared with those in healthy volunteers (n=10),
the expression levels of growth arrest-specific transcript 5 (GAS5)
in patients with OS (n=24) were generally downregulated. Compared
with that of patients without lung metastasis (n=13), GAS5
expression in those with lung metastasis (n=11) was more
downregulated. GAS5 downregulation increases cell migration and
invasion, and upregulates EMT. This is demonstrated by the
downregulation of E-cadherin, and upregulation of vimentin, ZEB1
and ZEB2. The downregulation of GAS5 expression results in an
increase in miR-21 levels, and a decrease in the elevated miR-21
expression reverses the effect of GAS5 silencing (92).
As a ceRNA of miR-221, the lncRNA GAS5 inhibits the
proliferation and EMT of OS cells through the miR-221/ARHI axis
(93).
SNHG22 is downregulated in OS cells, and increased
SNHG22 expression suppresses OS progression. Furthermore, SNHG22
overexpression prevents the EMT of OS cells. SNHG22 interacts with
miR-4492 and upregulates NK-κB inhibitor-interacting Ras-like 2
(94).
Tumor suppressor candidate (TUSC)8 is downregulated
in OS tissues and cells. TUSC8 overexpression suppresses the
proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT of OS cells. TUSC8 acts
as a sponge to adsorb miR-197-3p, the target gene of which is EH
domain 2 (EHD2). As a ceRNA, TUSC8 inhibits the proliferation and
EMT of OS cells via the miR-197-3p/EHD2 pathway (95).
XIST maintains the expression levels of programmed
cell death 4 by blocking miR-21-5p expression, thus slowing the
progression of OS. XIST overexpression inhibits cell invasion and
migration by inhibiting the EMT process (96).
LINC00588 is downregulated in OS. Increased levels
of LINC00588 appear to suppress the proliferation, viability,
migration, invasion, endothelial cell function, EMT and tumor
growth of OS cells. This lincRNA serves a vital role in OS
progression by downregulating the levels of miRNA-1972, the target
gene of which is TP53 (97).
Compared with that in normal cells, LINC00691
expression is downregulated in OS cells. LINC00691 regulates ST5
levels by directly interacting with miR-1256. Excess LINC00691
expression suppresses the EMT process by upregulating E-cadherin
expression, and suppressing ZEB1, Snail and fibronectin expression
(98).
NR_136400 is downregulated in OS cells, which
promotes the EMT process by inhibiting E-cadherin expression, and
boosting ZEB1, Snail and fibronectin expression. NR_136400 binds to
miR-8081 and upregulates TUSC5 levels (99) (Table
VI; Fig. 2D).
 | Table VI.Antitumor lncRNAs acting as miRNA
sponges or via other mechanisms. |
Table VI.
Antitumor lncRNAs acting as miRNA
sponges or via other mechanisms.
| First author/s,
year | lncRNA | Relationship with
OS | Relationship with
EMT | Action
mechanism | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Ye et al,
2019 | FER1L4 | Reduction of FER1L4
in OS tissues and cell lines | Suppresses EMT | Promotes SOCS5 and
inhibits the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by downregulating
miR-18a-5p | (91) |
| Wang et al,
2021 | GAS5 | Reduces the
migration and invasion of U2OS cells | Suppresses EMT | Reduces miR-21
expression | (92) |
| Ye et al,
2017 | GAS5 | Inhibition of OS
cell proliferation and migration | Suppresses EMT | Via regulation of
the miR-221/ARHI pathway | (93) |
| Zheng et al,
2020 | SNHG22 | Inhibits the
progression of OS | Suppresses EMT | Directly interacts
with miR-4492 and upregulates NKIRAS2 expression | (94) |
| Fan et al,
2020 | TUSC8 | Inhibits the
proliferation, migration and invasion of OS cells | Suppresses EMT | Via the
miR-197-3p/EHD2 axis | (95) |
| Zhang and Xia,
2017 | XIST | Inhibition of OS
cell invasion and migration | Suppresses EMT | Blocks miR-21-5p to
maintain PDCD4 expression | (96) |
| Zhou et al,
2020 | LINC00588 | Inhibition of OS
cell proliferation, viability, migration, invasion, endothelial
cell function and tumor growth | Suppresses EMT | Downregulates
miRNA-1972 expression, while miRNA-1972 inhibits TP53
expression | (97) |
| Wan et al,
2020 | LINC00691 | Decreased levels in
OS cells | Suppresses EMT | Combines with
miR-1256 to regulate ST5 expression | (98) |
| Liu et al,
2020 | NR_136400 | Downregulated in OS
cells | Suppresses EMT | Combines with
miR-8081, and then upregulates TUSC5 expression | (99) |
| Ma et al,
2019 | FER1L4 | FER1L4 expression
is low in MG63 cells | Suppresses EMT | Via activation of
the PI3K/AKT pathway | (100) |
Due to a lack of studies on lncRNAs inhibiting OS
compared with those on lncRNAs promoting OS, lncRNAs were not
further classified based on the type of lncRNA. A total of 10
studies of eight lncRNAs that inhibit the occurrence of OS through
the ceRNA mechanism were identified, and GAS5 was identified twice
as a ‘high-frequency’ lncRNA. GAS5 inhibits EMT through miR-21 and
the miR-221/ARHI axis (92,93), leading to the prevention of OS.
miRNA sponge-independent
mechanism
This section describes how lncRNAs inhibit the EMT
process through this mechanism to prevent the occurrence of OS.
FER1L4 exhibits decreased expression in OS cells,
particularly MG63 cells. Increased FER1L4 expression inhibits the
EMT process, as evidenced by an increase in E-cadherin expression,
and a decrease in vimentin and fibronectin expression. FER1L4
serves an important role in preventing OS tumors by activating the
PI3K/AKT pathway (100) (Table VI; Fig.
2D).
A lncRNA, FER1L4, which inhibits the occurrence of
OS by directly regulating downstream signaling pathways, was
identified. Due to the lack of studies on lncRNAs inhibiting OS
compared with those on lncRNAs promoting OS, lncRNAs were not
further classified based on the type of lncRNA. Currently, there is
relatively little research in this area, although future studies
are warranted.
Discussion
By examining the literature on the relationship
between lncRNAs and EMT in OS, the present review indicated that
the developmental direction of EMT and OS is consistent. In other
words, enhancing EMT can promote the occurrence and progression of
OS, whereas inhibiting EMT has the opposite effect. Furthermore,
some lncRNAs promote the occurrence and progression of OS by
promoting the EMT process, whereas others exhibit opposite
biological effects.
Different lncRNAs regulate the EMT process through
various mechanisms to regulate the occurrence and progression of
OS. Of these, the most common and widely studied molecules are
lncRNAs that act as miRNA sponges to interact with downstream
molecules through the ceRNA mechanism. Furthermore, several lncRNAs
regulate the expression of downstream RNAs or proteins to fulfill
their biological roles by regulating signaling pathways.
For lncRNAs that promote the EMT process through the
ceRNA mechanism, the studies were reviewed by focusing on lncRNAs
with known functions, antisense lncRNAs and lincRNAs. For lncRNAs
that promote the EMT process through direct regulation of
downstream signaling pathways, the discussion was further divided
into four parts: lncRNAs with known functions, antisense lncRNAs,
lincRNAs and intronic lncRNAs. For lncRNAs that inhibit the EMT
process, the discussion was divided into two parts: lncRNAs
involved in ceRNA mechanisms and those directly participating in
the regulation of downstream signaling pathways.
Studies on lncRNAs are increasing. Previous research
has considered RNA molecules that cannot encode proteins as
ineffective; however, studies have indicated that these RNA
molecules can encode small open reading frame-derived peptides.
With the development of ribosome profiling, mass spectrometry and
sequencing technologies, increasing research on lncRNAs has
emerged. These findings are important for the development of
clinical diagnostic biomarkers, prognostic biomarkers and targeted
drugs (101–103). lncRNAs participate in the
occurrence and development of OS, other tumors and other nontumor
diseases through this mechanism (101–103). Only one lncRNA that regulates the
occurrence and development of OS by encoding a small peptide
(LINC00665) has been described. In OS, this lncRNA encodes an
18-amino acid-long peptide (LINC00665_18aa) that inhibits the
proliferation and migration of OS cells by suppressing CREB
(104). Since the EMT process was
not specified in the aforementioned study (104), this appears unrelated in the
context of the present review. However, the lncRNA was identified
in a study included in the present review (61). lncRNAs regulate the occurrence and
development of a disease through a complex network pathway rather
than a single pathway. Thus, based on the aforementioned studies
(61,104), lncRNAs likely regulate EMT by
encoding small peptides, thereby regulating the occurrence and
development of OS. This is expected to become a research focus in
future studies.
By studying and summarizing relevant articles,
evidence that lncRNAs regulate OS through the EMT process was
obtained. The vast majority of lncRNAs increase the occurrence of
OS by promoting the EMT process. Regarding the underlying
mechanism, most lncRNAs exert their biological effects of promoting
or inhibiting OS through miRNA-dependent pathways. Of these, MALAT1
(29,75), NEAT1 (32,33,78),
XIST (42,43,84,96)
and CDKN2B-AS1 (45,86) promote the EMT process, and the
occurrence and development of OS through the miRNA and non-miRNA
sponge methods. Notably, XIST enhances the EMT process to promote
the occurrence and development of OS (42,43,84).
XIST also inhibits the EMT process to suppress the occurrence and
development of OS (96). This will
be the focus of future research.
Conclusion
Based on the present review of the literature,
lncRNAs regulate the EMT process in OS in complex ways, thus
regulating its occurrence and development. Future studies should
focus on the identification of these lncRNAs and actively explore
their underlying mechanisms. This will become an innovative field
of study in OS and other tumor types. It will also provide a basis
for the early screening, prevention, diagnosis and treatment of
OS.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study received funding from the Liaoning Natural
Science Foundation Project (grant no. 2023-BS-035).
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors' contributions
YT contributed to the conception and design of the
study. ZL performed literature collection and review, tabulation
and drawing, and wrote and edited the manuscript. Data
authentication is not applicable. All authors have read and
approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Glossary
Abbreviations
Abbreviations:
|
OS
|
osteosarcoma
|
|
EMT
|
epithelial-mesenchymal transition
|
|
lncRNA
|
long noncoding RNA
|
|
lincRNA
|
long intergenic noncoding RNA
|
|
ZEB
|
zinc finger E-box binding homeobox
|
|
ZO-1
|
zonula occludens-1
|
|
ceRNA
|
competing endogenous RNA
|
|
3′-UTR
|
3′-untranslated region
|
|
BCRT1
|
breast cancer-related transcript
1
|
|
EBLN3P
|
endogenous bornavirus-like
nucleoprotein three pseudogene
|
|
FGF7
|
fibroblast growth factor 7
|
|
PCGEM1
|
prostate-specific transcript 1
|
|
OGT
|
O-GlcNAc transferase
|
|
HCG11
|
HLA complex group 11
|
|
MALAT1
|
metastasis-associated lung
adenocarcinoma transcript 1
|
|
NDRG1
|
N-Myc downstream-regulated gene 1
|
|
NEAT1
|
nuclear enriched abundant transcript
1
|
|
HIF-1α
|
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
|
|
PURPL
|
p53-upregulated regulator of p53
levels
|
|
SNHG
|
small nucleolar RNA host gene
|
|
ITGA6
|
integrin subunit α6
|
|
TUG1
|
taurine-upregulated gene 1
|
|
EZH2
|
enhancer of zeste homolog 2
|
|
XIST
|
X inactive-specific transcript
|
|
CBR3-AS1
|
carbonyl reductase antisense RNA
1
|
|
CDKN2B-AS1
|
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2B
antisense RNA 1
|
|
DDX11-AS1
|
DEAD/H box protein 11 antisense RNA
1
|
|
GPRC5A
|
G protein-coupled receptor class C
group 5 member A
|
|
FOXD3-AS1
|
forkhead box D3 antisense RNA 1
|
|
ZCCHC3
|
zinc finger CCHC-type containing
3
|
|
ZFAS1
|
zinc finger antisense 1
|
|
WNT2B
|
Wnt family member 2B
|
|
CASC15
|
cancer susceptibility candidate
15
|
|
CRNDE
|
colorectal neoplasia differentially
expressed
|
|
FAL1
|
focally amplified lncRNA on
chromosome 1
|
|
GHET1
|
gastric cancer high expressed
transcript 1
|
|
HOTTIP
|
HOXA transcript at the distal tip
|
|
MINCR
|
Myc-induced long noncoding RNA
|
|
MSTO2P
|
pseudogene Minato family member 2
|
|
PVT1
|
plasmacytoma variant translocation
1
|
|
lnc-TCF7
|
long non-coding RNA T-cell factor
7
|
|
TDRG1
|
testis development-related 1
|
|
AFAP1-AS1
|
actin filament-associated protein 1
antisense RNA 1
|
|
HNF1A-AS1
|
hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 homeobox
A antisense RNA 1
|
|
SPRY4-IT1
|
sprouty RTK signaling antagonist
4-intronic transcript 1
|
|
FER1L4
|
FER-1 family member 4
|
|
GAS5
|
growth arrest-specific transcript
5
|
|
TUSC
|
tumor suppressor candidate
|
References
|
1
|
Suehara Y, Alex D, Bowman A, Middha S,
Zehir A, Chakravarty D, Wang L, Jour G, Nafa K, Hayashi T, et al:
Clinical genomic sequencing of pediatric and adult osteosarcoma
reveals distinct molecular subsets with potentially targetable
alterations. Clin Cancer Res. 25:6346–6356. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Matsuoka K, Bakiri L, Wolff LI, Linder M,
Mikels-Vigdal A, Patiño-García A, Lecanda F, Hartmann C, Sibilia M
and Wagner EF: Wnt signaling and Loxl2 promote aggressive
osteosarcoma. Cell Res. 30:885–901. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gambera S, Abarrategi A, González-Camacho
F, Morales-Molina Á, Roma J, Alfranca A and García-Castro J: Clonal
dynamics in osteosarcoma defined by RGB marking. Nat Commun.
9:39942018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arvanitis C, Bendapudi PK, Tseng JR,
Gambhir SS and Felsher DW: (18)F and (18)FDG PET imaging of
osteosarcoma to non-invasively monitor in situ changes in cellular
proliferation and bone differentiation upon MYC inactivation.
Cancer Biol Ther. 7:1947–1951. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Asano N, Matsuzaki J, Ichikawa M, Kawauchi
J, Takizawa S, Aoki Y, Sakamoto H, Yoshida A, Kobayashi E, Tanzawa
Y, et al: A serum microRNA classifier for the diagnosis of sarcomas
of various histological subtypes. Nat Commun. 10:12992019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu H, Li P, Chen L, Jian C, Li Z and Yu
A: MicroRNAs as a novel class of diagnostic biomarkers for the
detection of osteosarcoma: A meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther.
10:5229–5236. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xia WK, Lin QF, Shen D, Liu ZL, Su J and
Mao WD: Clinical implication of long noncoding RNA 91H expression
profile in osteosarcoma patients. Onco Targets Ther. 9:4645–4652.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xiao-Long M, Kun-Peng Z and Chun-Lin Z:
Circular RNA circ_HIPK3 is down-regulated and suppresses cell
proliferation, migration and invasion in osteosarcoma. J Cancer.
9:1856–1862. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu C, Yang Z, Wu J, Zhang L, Lee S, Shin
DJ, Tran M and Wang L: Long noncoding RNA H19 interacts with
polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 to reprogram hepatic lipid
homeostasis. Hepatology. 67:1768–1783. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sztuba-Solinska J, Rausch JW, Smith R,
Miller JT, Whitby D and Le Grice SFJ: Kaposi's sarcoma-associated
herpesvirus polyadenylated nuclear RNA: A structural scaffold for
nuclear, cytoplasmic and viral proteins. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:6805–6821. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bester AC, Lee JD, Chavez A, Lee YR,
Nachmani D, Vora S, Victor J, Sauvageau M, Monteleone E, Rinn JL,
et al: An integrated genome-wide CRISPRa approach to functionalize
lncRNAs in drug resistance. Cell. 173:649–664.e20. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wright MW: A short guide to long
non-coding RNA gene nomenclature. Hum Genomics. 8:72014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu Y, Ding W, Yu W, Zhang Y, Ao X and
Wang J: Long non-coding RNAs: Biogenesis, functions, and clinical
significance in gastric cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 23:458–476.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu Y, Ao X, Wang Y, Li X and Wang J: Long
non-coding RNA in gastric cancer: Mechanisms and clinical
implications for drug resistance. Front Oncol. 12:8414112022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao H, Hao G, Sun Y, Li L and Wang Y: Long
noncoding RNA H19 mediated the chemosensitivity of breast cancer
cells via Wnt pathway and EMT process. Onco Targets Ther.
11:8001–8012. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Feng L, Wei W, Heng Z, Yantao H and Chunbo
W: Knockdown of REV7 inhibits breast cancer cell migration and
invasion. Oncol Res. 24:315–325. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ji M, Li Z, Lin Z and Chen L: Antitumor
activity of the novel HDAC inhibitor CUDC-101 combined with
gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 8:2402–2418.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhong G, Lin Y, Wang X, Wang K, Liu J and
Wei W: H19 knockdown suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis
by regulating miR-130a-3p/SATB1 in breast cancer cells. Onco
Targets Ther. 13:12501–12513. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
McFaline-Figueroa JL, Hill AJ, Qiu X,
Jackson D, Shendure J and Trapnell C: A pooled single-cell genetic
screen identifies regulatory checkpoints in the continuum of the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Nat Genet. 51:1389–1398.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu W and Kang Y: Epithelial-Mesenchymal
plasticity in cancer progression and metastasis. Dev Cell.
49:361–374. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Williams ED, Gao D, Redfern A and Thompson
EW: Controversies around epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in
cancer metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 19:716–732. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Latil M, Nassar D, Beck B, Boumahdi S,
Wang L, Brisebarre A, Dubois C, Nkusi E, Lenglez S, Checinska A, et
al: Cell-type-specific chromatin states differentially prime
squamous cell carcinoma tumor-initiating cells for epithelial to
mesenchymal transition. Cell Stem Cell. 20:191–204.e5. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun WW, Xu ZH, Lian P, Gao BL and Hu JA:
Characteristics of circulating tumor cells in organ metastases,
prognosis, and T lymphocyte mediated immune response. Onco Targets
Ther. 10:2413–2424. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen S, Shen J, Zhao J, Wang J, Shan T, Li
J, Xu M, Chen X, Liu Y and Cao G: Magnolol suppresses pancreatic
cancer development in vivo and in vitro via negatively regulating
TGF-β/Smad signaling. Front Oncol. 10:5976722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yoo YG, Christensen J and Huang LE: HIF-1α
confers aggressive malignant traits on human tumor cells
independent of its canonical transcriptional function. Cancer Res.
71:1244–1252. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Han G, Guo Q, Ma N, Bi W, Xu M, Jia J and
Wang W: LncRNA BCRT1 facilitates osteosarcoma progression via
regulating miR-1303/FGF7 axis. Aging. 13:15501–15510. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun MX, An HY, Sun YB, Sun YB and Bai B:
LncRNA EBLN3P attributes methotrexate resistance in osteosarcoma
cells through miR-200a-3p/O-GlcNAc transferase pathway. J Orthop
Surg Res. 17:5572022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang L, Zhou J, Zhang Y, Hu T and Sun Y:
Long non-coding RNA HCG11 aggravates osteosarcoma carcinogenesis
via regulating the microRNA-579/MMP13 axis. Int J Gen Med.
13:1685–1695. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao H, Wang Y, Hou W, Ding X and Wang W:
Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes cell proliferation, migration
and invasion by targeting miR-590-3p in osteosarcoma. Exp Ther Med.
24:6722022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun Y, Jia X, Wang M and Deng Y: Long
noncoding RNA MIR31HG abrogates the availability of tumor
suppressor microRNA-361 for the growth of osteosarcoma. Cancer
Manag Res. 11:8055–8064. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Z, Wei Y, Zhu H, Yu L, Zhu J, Han Q,
Liu Z, Huang J, Zhu Y, Fan G, et al: LncRNA NDRG1 aggravates
osteosarcoma progression and regulates the PI3K/AKT pathway by
sponging miR-96-5p. BMC Cancer. 22:7282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tan H and Zhao L: lncRNA nuclear-enriched
abundant transcript 1 promotes cell proliferation and invasion by
targeting miR-186-5p/HIF-1α in osteosarcoma. J Cell Biochem.
120:6502–6514. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen Y, Li J, Xiao JK, Xiao L, Xu BW and
Li C: The lncRNA NEAT1 promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by sponging miR-483
to upregulate STAT3 expression. Cancer Cell Int. 21:902021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li J, Zhang Y, Sun F, Zhang G, Pan XA and
Zhou Q: Long noncoding RNA PCGEM1 facilitates tumor growth and
metastasis of osteosarcoma by sponging miR-433-3p and targeting
OMA1. Orthop Surg. 15:1060–1071. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
He F, Ding G, Jiang W, Fan X and Zhu L:
Effect of tumor-associated macrophages on lncRNA
PURPL/miR-363/PDZD2 axis in osteosarcoma cells. Cell Death Discov.
7:3072021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jiang Z, Jiang C and Fang J: Up-regulated
lnc-SNHG1 contributes to osteosarcoma progression through
sequestration of miR-577 and activation of WNT2B/Wnt/β-catenin
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 495:238–245. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Deng Y, Zhao F, Zhang Z, Sun F and Wang M:
Long noncoding RNA SNHG7 promotes the tumor growth and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via regulation of miR-34a
signals in osteosarcoma. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 33:365–372.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhu S, Liu Y, Wang X, Wang J and Xi G:
lncRNA SNHG10 promotes the proliferation and invasion of
osteosarcoma via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
22:957–970. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bu J, Guo R, Xu XZ, Luo Y and Liu JF:
LncRNA SNHG16 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by
upregulating ITGA6 through miR-488 inhibition in osteosarcoma. J
Bone Oncol. 27:1003482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cao J, Han X, Qi X, Jin X and Li X: TUG1
promotes osteosarcoma tumorigenesis by upregulating EZH2 expression
via miR-144-3p. Int J Oncol. 51:1115–1123. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ma H, Su R, Feng H, Guo Y and Su G: Long
noncoding RNA UCA1 promotes osteosarcoma metastasis through
CREB1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and activating
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. J Bone Oncol. 16:1002282019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wen JF, Jiang YQ, Li C, Dai XK, Wu T and
Yin WZ: LncRNA-XIST promotes the oxidative stress-induced
migration, invasion, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of
osteosarcoma cancer cells through miR-153-SNAI1 axis. Cell Biol
Int. 44:1991–2001. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu W, Long Q, Zhang L, Zeng D, Hu B,
Zhang W, Liu S, Deng S and Chen L: Long non-coding RNA X-inactive
specific transcript promotes osteosarcoma metastasis via modulating
microRNA-758/Rab16. Ann Transl Med. 9:8412021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yao W, Hou J, Liu G, Wu F, Yan Q, Guo L
and Wang C: LncRNA CBR3-AS1 promotes osteosarcoma progression
through the network of miR-140-5p/DDX54-NUCKS1-mTOR signaling
pathway. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 25:189–200. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gui D and Cao H: Long non-coding RNA
CDKN2B-AS1 promotes osteosarcoma by increasing the expression of
MAP3K3 via sponging miR-4458. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim.
56:24–33. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang H, Lin J, Chen J, Gu W, Mao Y, Wang
H, Zhang Y and Liu W: DDX11-AS1 contributes to osteosarcoma
progression via stabilizing DDX11. Life Sci. 254:1173922020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ning Y and Bai Z: DSCAM-AS1 accelerates
cell proliferation and migration in osteosarcoma through
miR-186-5p/GPRC5A signaling. Cancer Biomark. 30:29–39. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang L: ELF1-activated FOXD3-AS1 promotes
the migration, invasion and EMT of osteosarcoma cells via sponging
miR-296-5p to upregulate ZCCHC3. J Bone Oncol. 26:1003352021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang Y, Zhang R, Cheng G, Xu R and Han X:
Long non-coding RNA HOXA-AS2 promotes migration and invasion by
acting as a ceRNA of miR-520c-3p in osteosarcoma cells. Cell Cycle.
17:1637–1648. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
He JW, Li DJ, Zhou JH, Zhu YL and Yu BQ:
SP1-mediated upregulation of lncRNA LMCD1-AS1 functions a ceRNA for
miR-106b-5p to facilitate osteosarcoma progression. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 526:670–677. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liu W, Liu P, Gao H, Wang X and Yan M:
Long non-coding RNA PGM5-AS1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, invasion and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by
impairing miR-140-5p-mediated FBN1 inhibition. Mol Oncol.
14:2660–2677. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tong CJ, Deng QC, Ou DJ, Long X, Liu H and
Huang K: LncRNA RUSC1-AS1 promotes osteosarcoma progression through
regulating the miR-340-5p and PI3K/AKT pathway. Aging (Albany NY).
13:20116–20130. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jiang R, Zhang Z, Zhong Z and Zhang C:
Long-non-coding RNA RUSC1-AS1 accelerates osteosarcoma development
by miR-101-3p-mediated Notch1 signalling pathway. J Bone Oncol.
30:1003822021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Liu X, Wang H, Tao GL, Chu TB, Wang YX and
Liu L: LncRNA-TMPO-AS1 promotes apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells by
targeting miR-329 and regulating E2F1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
24:11006–11015. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Meng X, Zhang Z, Chen L, Wang X, Zhang Q
and Liu S: Silencing of the long non-coding RNA TTN-AS1 attenuates
the malignant progression of osteosarcoma cells by regulating the
miR-16-1-3p/TFAP4 axis. Front Oncol. 11:6528352021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhang Z, Wang J, Zhang X, Ran B, Wen J and
Zhang H: TYMSOS-miR-101-3p-NETO2 axis promotes osteosarcoma
progression. Mol Cell Probes. 67:1018872022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liu X, Wang M, Zhang L and Huang L: LncRNA
ZFAS1 contributes to osteosarcoma progression via miR-520b and
miR-520e-mediated inhibition of RHOC signaling. Clinics (Sao
Paulo). 78:1001432023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ma HZ, Wang J, Shi J, Zhang W and Zhou DS:
LncRNA LINC00467 contributes to osteosarcoma growth and metastasis
through regulating HMGA1 by directly targeting miR-217. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 24:5933–5945. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zheng Y, Chen Z, Zhou Z, Xu X and Yang H:
Silencing of long non-coding RNA LINC00607 Prevents tumor
proliferation of osteosarcoma by acting as a sponge of miR-607 to
downregulate E2F6. Front Oncol. 10:5844522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhou Y, Li X and Yang H: LINC00612
functions as a ceRNA for miR-214-5p to promote the proliferation
and invasion of osteosarcoma in vitro and in vivo. Exp Cell Res.
392:1120122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Bai J, Zhang X, Jiang F, Shan H, Gao X, Bo
L and Zhang Y: A feedback loop of LINC00665 and the wnt signaling
pathway expedites osteosarcoma cell proliferation, invasion, and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Orthop Surg. 15:286–300. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Liu W, Zhang Q, Shen K, Li K, Chang J, Li
H, Duan A, Zhang S and Huang Y: Long noncoding RNA LINC00909
induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and contributes to
osteosarcoma tumorigenesis and metastasis. J Oncol.
2022:86609652022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Li R, Ruan Q, Zheng J, Zhang B and Yang H:
LINC01116 promotes doxorubicin resistance in osteosarcoma by
epigenetically silencing miR-424-5p and inducing
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Front Pharmacol. 12:6322062021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhang S and Chen R: LINC01140 regulates
osteosarcoma proliferation and invasion by targeting the
miR-139-5p/HOXA9 axis. Biochem Biophys Rep.
31:1013012022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Gu Z, Wu S, Wang J and Zhao S: Long
non-coding RNA LINC01419 mediates miR-519a-3p/PDRG1 axis to promote
cell progression in osteosarcoma. Cancer Cell Int. 20:1472020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wang H and Zhang P: lncRNA-CASC15 promotes
osteosarcoma proliferation and metastasis by regulating epithelial-
mesenchymal transition via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Oncol Rep. 45:762021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li Z, Tang Y, Xing W, Dong W and Wang Z:
LncRNA, CRNDE promotes osteosarcoma cell proliferation, invasion
and migration by regulating Notch1 signaling and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Exp Mol Pathol. 104:19–25. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ding Q, Mo F, Cai X, Zhang W, Wang J, Yang
S and Liu X: LncRNA CRNDE is activated by SP1 and promotes
osteosarcoma proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem.
121:3358–3371. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wang Y, Zhao Z, Zhang S, Li Z, Li D, Yang
S, Zhang H, Zeng X and Liu J: LncRNA FAL1 is a negative prognostic
biomarker and exhibits pro-oncogenic function in osteosarcoma. J
Cell Biochem. 119:8481–8489. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Li B, Ren P and Wang Z: Long non-coding
RNA Ftx promotes osteosarcoma progression via the epithelial to
mesenchymal transition mechanism and is associated with poor
prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
11:4503–4511. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Yang W, Shan Z, Zhou X, Peng L, Zhi C,
Chai J, Liu H, Yang J and Zhang Z: Knockdown of lncRNA GHET1
inhibits osteosarcoma cells proliferation, invasion, migration and
EMT in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biomark. 23:589–601. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zhao W and Li L: SP1-induced upregulation
of long non-coding RNA HCP5 promotes the development of
osteosarcoma. Pathol Res Pract. 215:439–445. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wang N, Meng X, Liu Y, Chen Y and Liang Q:
LPS promote osteosarcoma invasion and migration through
TLR4/HOTAIR. Gene. 680:1–8. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Tang Y and Ji F: lncRNA HOTTIP facilitates
osteosarcoma cell migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition by forming a positive feedback loop with c-Myc. Oncol
Lett. 18:1649–1656. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Fang D, Yang H, Lin J, Teng Y, Jiang Y,
Chen J and Li Y: 17β-estradiol regulates cell proliferation, colony
formation, migration, invasion and promotes apoptosis by
upregulating miR-9 and thus degrades MALAT-1 in osteosarcoma cell
MG-63 in an estrogen receptor-independent manner. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 457:500–506. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Bai S, Li Y, Wang Y, Zhou G, Liu C, Xiong
W and Chen J: Long non-coding RNA MINCR regulates the growth and
metastasis of human osteosarcoma cells via Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway. Acta Biochim Pol. 69:551–557. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Shi C, Huang CM, Wang B, Sun TF, Zhu AX
and Zhu YC: Pseudogene MSTO2P enhances hypoxia-induced osteosarcoma
malignancy by upregulating PD-L1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
530:673–679. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Li Y and Cheng C: Long noncoding RNA NEAT1
promotes the metastasis of osteosarcoma via interaction with the
G9a-DNMT1-Snail complex. Am J Cancer Res. 8:81–90. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Mao Y and Ma X: The
lncRNA PCAT1 is correlated with poor prognosis and promotes cell
proliferation, invasion, migration and EMT in osteosarcoma. Onco
Targets Ther. 11:629–638. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Xun C, Jiang D, Tian Z, Yunus A and Chen
J: Long noncoding RNA plasmacytoma variant translocation gene 1
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in osteosarcoma. J Clin
Lab Anal. 35:e235872021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Gao S, Guo J, Li F, Zhang K, Zhang Y,
Zhang Y, Zhang Y and Guo Y: Long non-coding RNA lncTCF7 predicts
poor prognosis and promotes tumor metastasis in osteosarcoma. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 10:10918–10925. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Huang Y, Xu YQ, Feng SY, Zhang X and Ni
JD: LncRNA TDRG1 promotes proliferation, invasion and
epithelial-mesenchymal transformation of osteosarcoma through
PI3K/AKT signal pathway. Cancer Manag Res. 12:4531–4540. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Xu B, Jin X, Yang T, Zhang Y, Liu S, Wu L,
Ying H and Wang Z: Upregulated lncRNA THRIL/TNF-α signals promote
cell growth and predict poor clinical outcomes of osteosarcoma.
Onco Targets Ther. 13:119–129. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Ma J, Xu X, Wang
Y, Zhou Z, Jiang D, Shen S, Ding Y, et al: Silencing of HuR
inhibits osteosarcoma cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition via
AGO2 in association with long non-coding RNA XIST. Front Oncol.
11:6019822021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Shi D, Wu F, Mu S, Hu B, Zhong B, Gao F,
Qing X, Liu J, Zhang Z and Shao Z: LncRNA AFAP1-AS1 promotes
tumorigenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of osteosarcoma
through RhoC/ROCK1/p38MAPK/Twist1 signaling pathway. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 38:3752019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Luo Y, Tao H, Jin L, Xiang W and Guo W:
CDKN2B-AS1 exerts oncogenic role in osteosarcoma by promoting cell
proliferation and epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cancer
Biother Radiopharm. 35:58–65. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Cai L, Lv J, Zhang Y, Li J, Wang Y and
Yang H: The lncRNA HNF1A-AS1 is a negative prognostic factor and
promotes tumorigenesis in osteosarcoma. J Cell Mol Med.
21:2654–2662. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Yang J, Zou Y, Wu J, Chen B, Luo C, Chen
X, Shen H and Luo L: The long noncoding RNA ZEB2-AS1 contributes to
proliferation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of
osteosarcoma. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 38:596–603.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Jiang Y and Luo Y: LINC01354 promotes
osteosarcoma cell invasion by up-regulating integrin β1. Arch Med
Res. 51:115–123. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Xu J, Ding R and Xu Y: Effects of long
non-coding RNA SPRY4-IT1 on osteosarcoma cell biological behavior.
Am J Transl Res. 8:5330–5337. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Ye F, Tian L, Zhou Q and Feng D: LncRNA
FER1L4 induces apoptosis and suppresses EMT and the activation of
PI3K/AKT pathway in osteosarcoma cells via inhibiting miR-18a-5p to
promote SOCS5. Gene. 721:1440932019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Wang Y, Ren X, Yuan Y and Yuan BS:
Downregulated lncRNA GAS5 and upregulated miR-21 lead to
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and lung metastasis of
osteosarcomas. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7076932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Ye K, Wang S, Zhang H, Han H, Ma B and Nan
W: Long noncoding RNA GAS5 suppresses cell growth and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in osteosarcoma by regulating the
miR-221/ARHI pathway. J Cell Biochem. 118:4772–4781. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Zheng HL, Yang RZ, Xu WN, Liu T, Chen PB,
Zheng XF, Li B, Jiang LS and Jiang SD: Characterization of LncRNA
SNHG22 as a protector of NKIRAS2 through miR-4492 binding in
osteosarcoma. Aging. 12:18571–18587. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Fan H, Liu T, Tian H and Zhang S: TUSC8
inhibits the development of osteosarcoma by sponging miR-197-3p and
targeting EHD2. Int J Mol Med. 46:1311–1320. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Zhang R and Xia T: Long non-coding RNA
XIST regulates PDCD4 expression by interacting with miR-21-5p and
inhibits osteosarcoma cell growth and metastasis. Int J Oncol.
51:1460–1470. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Zhou FC, Zhang YH, Liu HT, Song J and Shao
J: LncRNA LINC00588 suppresses the progression of osteosarcoma by
acting as a ceRNA for miRNA-1972. Front Pharmacol. 11:2552020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Wan D, Qu Y, Zhang L, Ai S and Cheng L:
The lncRNA LINC00691Functions as a ceRNA for miRNA-1256 to suppress
osteosarcoma by regulating the expression of ST5. Onco Targets
Ther. 13:13171–13181. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Liu L, Zheng M, Wang X, Gao Y and Gu Q:
LncRNA NR_136400 suppresses cell proliferation and invasion by
acting as a ceRNA of TUSC5 that is modulated by miR-8081 in
osteosarcoma. Front Pharmacol. 11:6412020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Ma L, Zhang L, Guo A, Liu LC, Yu F, Diao
N, Xu C and Wang D: Overexpression of FER1L4 promotes the apoptosis
and suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness
markers via activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in osteosarcoma
cells. Pathol Res Pract. 215:1524122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Tian H, Tang L, Yang Z, Xiang Y, Min Q,
Yin M, You H, Xiao Z and Shen J: Current understanding of
functional peptides encoded by lncRNA in cancer. Cancer Cell Int.
24:2522024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Yi Q, Feng J, Lan W, Shi H and Sun W and
Sun W: CircRNA and lncRNA-encoded peptide in diseases, an update
review. Mol Cancer. 23:2142024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Zhang Y: LncRNA-encoded peptides in
cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 17:662024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Pan J, Liu M, Duan X and Wang D: A short
peptide LINC00665_18aa encoded by lncRNA LINC00665 suppresses the
proliferation and migration of osteosarcoma cells through the
regulation of the CREB1/RPS6KA3 interaction. PLoS One.
18:e02864222023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|