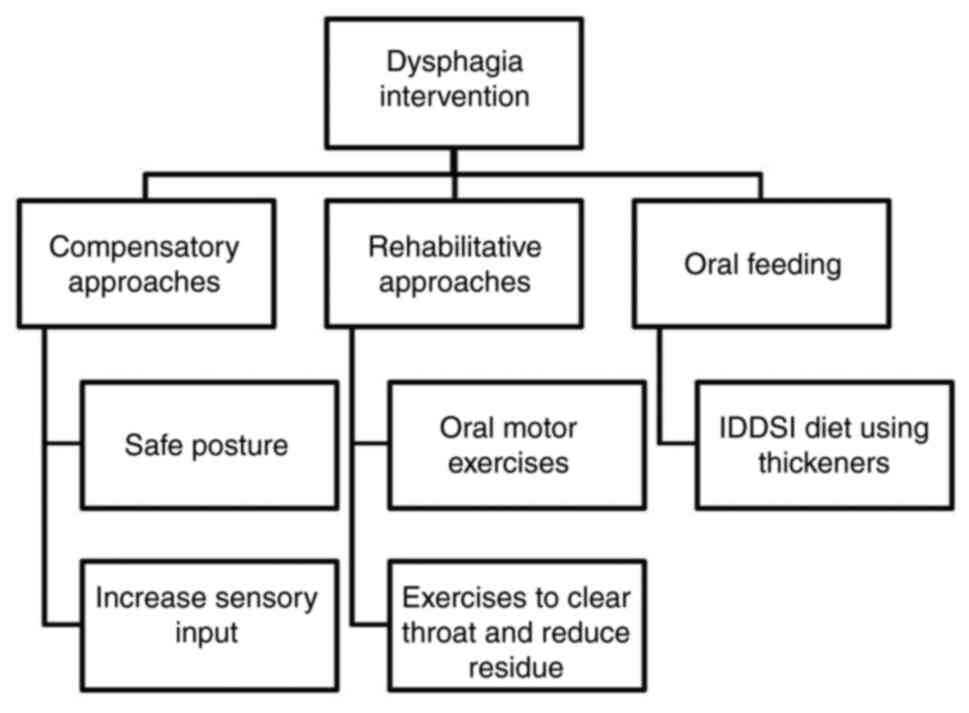
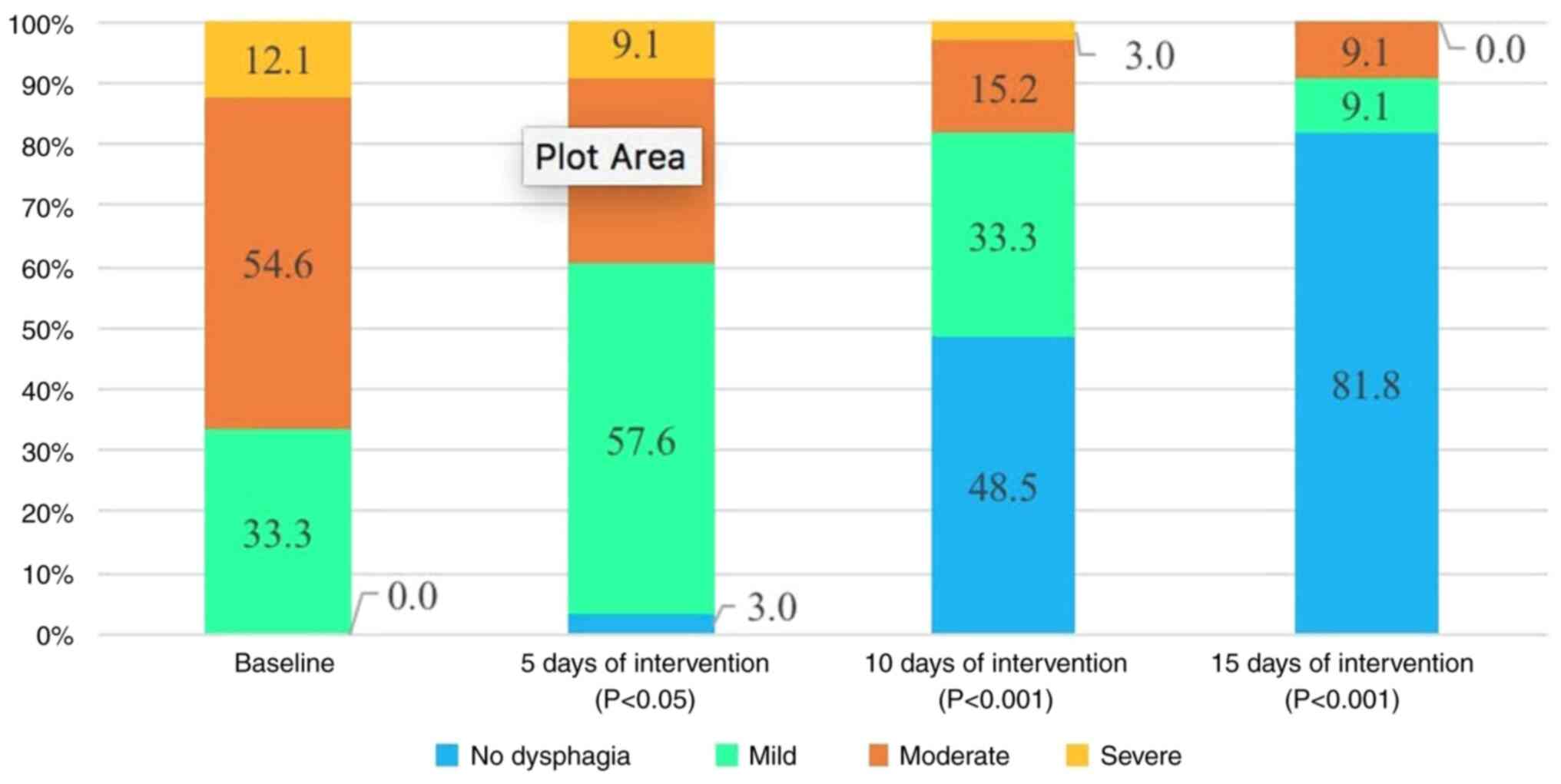
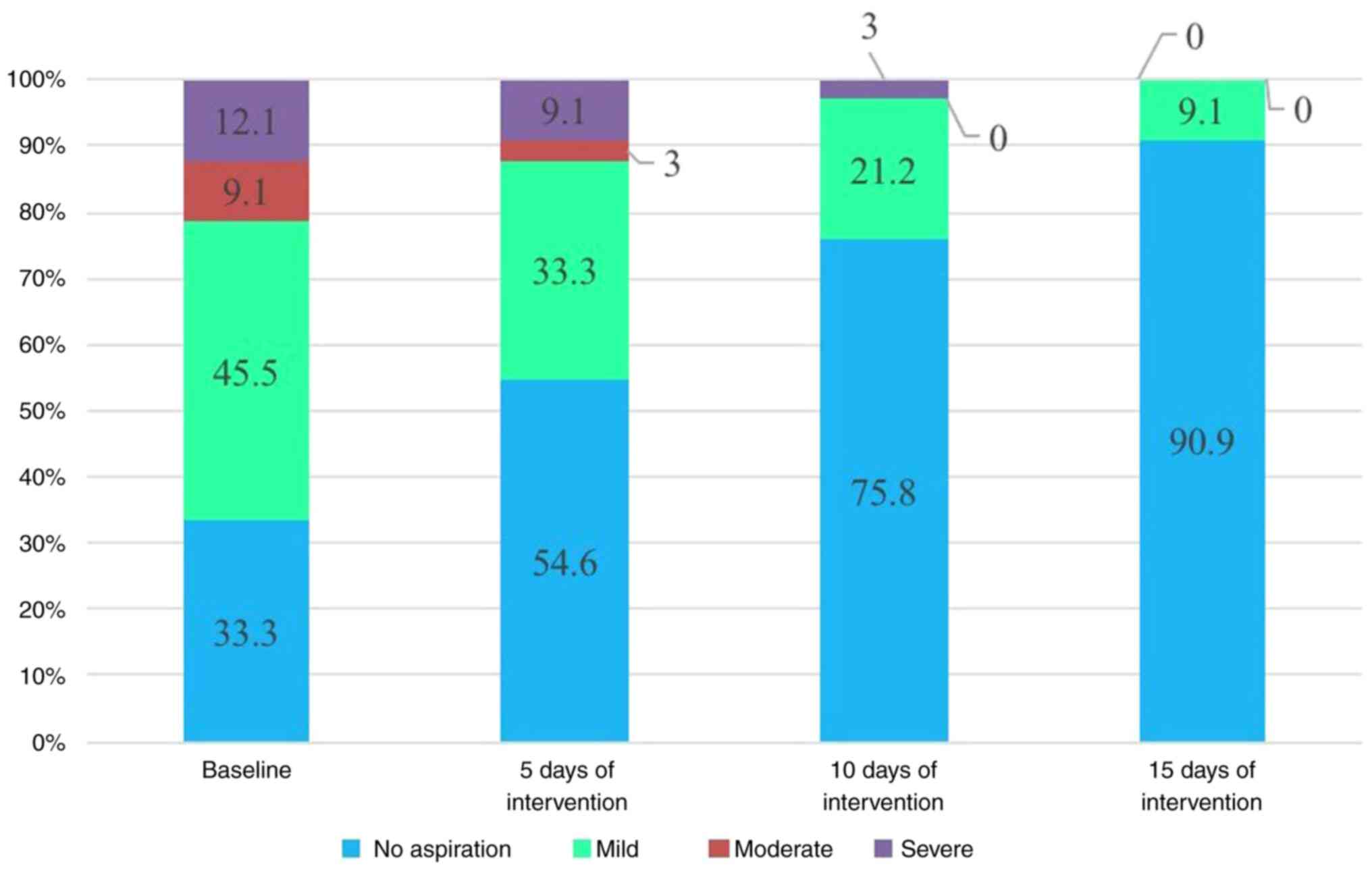
|
1
|
Krishnamurthi RV, Ikeda T and Feigin VL:
Global, regional and country-specific burden of ischaemic stroke,
intracerebral haemorrhage and subarachnoid haemorrhage: A
systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study 2017.
Neuroepidemiology. 54:171–179. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Carr C, Kahn L, Mathkour M, Biro E, Bui CJ
and Dumont AS: The shifting burden of neurosurgical disease:
Vietnam and the middle-income nations. Neurosurg Focus.
45(E12)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Takizawa C, Gemmell E, Kenworthy J and
Speyer R: A systematic review of the prevalence of oropharyngeal
dysphagia in stroke, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, head
injury, and pneumonia. Dysphagia. 31:434–441. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Vesey S: Dysphagia and quality of life. Br
J Community Nurs. 18:S14–19. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Newman R, Vilardell N, Clavé P and Speyer
R: Effect of bolus viscosity on the safety and efficacy of
swallowing and the kinematics of the swallow response in patients
with oropharyngeal dysphagia: White paper by the European society
for swallowing disorders (ESSD). Dysphagia. 31:232–249.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kuhlemeier KV, Palmer JB and Rosenberg D:
Effect of liquid bolus consistency and delivery method on
aspiration and pharyngeal retention in dysphagia patients.
Dysphagia. 16:119–122. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Clavé P, Arreola V, Romea M, Medina L,
Palomera E and Serra-Prat M: Accuracy of the volume-viscosity
swallow test for clinical screening of oropharyngeal dysphagia and
aspiration. Clin Nutr. 27:806–815. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Diniz PB, Vanin G, Xavier R and Parente
MA: Reduced incidence of aspiration with spoon-thick consistency in
stroke patients. Nutr Clin Pract. 24:414–418. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Rofes L, Arreola V and Clavé P: The
volume-viscosity swallow test for clinical screening of dysphagia
and aspiration. Nestle Nutr Inst Workshop Ser. 72:33–42.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jongprasitkul H and Kitisomprayoonkul W:
Effectiveness of conventional swallowing therapy in acute stroke
patients with Dysphagia. Rehabil Res Pract.
2020(2907293)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Mann G: MASA, the mann assessment of
swallowing ability. Vol. 1 New York, NY: Cengage Learning;
(2002).
|
|
12
|
Antonios N, Carnaby-Mann G, Crary M,
Miller L, Hubbard H, Hood K, Sambandam R, Xavier A and Silliman S:
Analysis of a physician tool for evaluating dysphagia on an
inpatient stroke unit: The modified mann assessment of swallowing
ability. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 19:49–57. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kwon S, Sim J, Park J, Jung Y, Cho KH, Min
K, Kim MY, Kim KM and Im SH: Assessment of aspiration risk using
the mann assessment of swallowing ability in brain-injured patients
with cognitive impairment. Front Neurol. 10(1264)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mann G, Hankey GJ and Cameron D:
Swallowing disorders following acute stroke: Prevalence and
diagnostic accuracy. Cerebrovasc Dis. 10:380–386. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Terré R and Mearin F: Oropharyngeal
dysphagia after the acute phase of stroke: Predictors of
aspiration. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 18:200–205. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Daniels SK, Brailey K, Priestly DH,
Herrington LR, Weisberg LA and Foundas AL: Aspiration in patients
with acute stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 79:14–19. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Warms T and Richards J: ‘Wet Voice’ as a
predictor of penetration and aspiration in oropharyngeal dysphagia.
Dysphagia. 15:84–88. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Murray J, Langmore SE, Ginsberg S and
Dostie A: The significance of accumulated oropharyngeal secretions
and swallowing frequency in predicting aspiration. Dysphagia.
11:99–103. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
McCullough GH, Rosenbek JC, Wertz RT,
McCoy S, Mann G and McCullough K: Utility of clinical swallowing
examination measures for detecting aspiration post-stroke. J Speech
Lang Hear Res. 48:1280–1293. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Palmer JB, Pelletier CA and Matsuo K:
Rehabilitation of patients with swallowing disorders. In: Braddom
R. L., Chan L., Harrast M. A. et al., Editors. Physical
Medicine and Rehabilitation. 4th. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders,
2011.
|
|
21
|
Lazarus CL, Logemann JA, Rademaker AW,
Kahrilas PJ, Pajak T, Lazar R and Halper A: Effects of bolus
volume, viscosity, and repeated swallows in nonstroke subjects and
stroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 74:1066–1070.
1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bülow M, Olsson R and Ekberg O:
Videomanometric analysis of supraglottic swallow, effortful
swallow, and chin tuck in patients with pharyngeal dysfunction.
Dysphagia. 16:190–195. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Shaker R, Easterling C, Kern M, Nitschke
T, Massey B, Daniels S, Grande B, Kazandjian M and Dikeman K:
Rehabilitation of swallowing by exercise in tube-fed patients with
pharyngeal dysphagia secondary to abnormal UES opening.
Gastroenterology. 122:1314–1321. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kwakkel G, Kollen B and Lindeman E:
Understanding the pattern of functional recovery after stroke:
Facts and theories. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 22:281–299.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|