Introduction
An increased mean platelet volume (MPV) is an early
marker of platelet activation (1).
Larger platelets may be more readily stimulated to release chemical
mediators; therefore, larger platelets are recognized as being more
reactive compared to smaller ones (2). MPV has been found to be increased in
patients with various thromboembolic disorders (3, 4).
Several studies assessed the prognostic significance of platelet
count in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (5, 6).
Thrombocytosis was noted to predict a poor overall survival (OS).
Furthermore, a previous study demonstrated that a low MPV was
significantly associated with an inferior OS in patients with
advanced NSCLC (7). However, there
has been no analysis of the prognostic effect of MPV on patients
with resected NSCLC. The purpose of this study was to investigate
the effect of MPV on survival in patients with completely resected
NSCLC.
Materials and methods
Patient selection
We conducted a retrospective analysis of patients
diagnosed with NSCLC who underwent surgery at the Tazuke Kofukai
Medical Research Institute, Kitano Hospital, between January, 2007
and December, 2011. All the patients met the following criteria:
pathological confirmation of NSCLC; complete curative resection; no
preoperative treatment; no microscopic residual tumor; no history
of transplantation and/or immunosuppression; no evidence of
infection, such as pneumonia, prior to surgery; no treatment for
concomitant autoimmune diseases with immunosuppressive therapy; no
history of hematological malignancy, including malignant lymphoma
and leukemia; and availability of laboratory data and follow-up
information.
Sample collection and staging
A peripheral venous blood sample was collected from
each patient within a month prior to surgery. A blood test was
performed using a fully automated blood cell counting system.
Histological classification was performed according to the WHO
guidelines (8). Disease staging
was based on the 7th edition of the TNM classification of malignant
tumors (9). Study approval was
granted by the Ethics Committee of the Tazuke Kofukai Medical
Research Institute, Kitano Hospital.
Clinicopathological
characteristics
The following clinical characteristics were
retrieved from the available clinical records: age, gender, Eastern
Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status, smoking
history, pathological stage, pathological tumor status,
pathological lymph node status, pleural invasion, peripheral
platelet count and MPV.
Survival analysis
Disease-free survival (DFS) was measured from the
date of surgery until the date of disease recurrence or death, or
until the date the patient was last known to be disease-free. OS
was measured from the date of surgery until the date of death from
any cause or until the date on which the patient was last known to
be alive. We estimated DFS and OS employing the Kaplan-Meier
analysis (10). Differences
between survival curves were tested for statistical significance
using the two-tailed log-rank test. Univariate and multivariate
prognostic analyses were performed for OS and DFS outcomes using
the Cox proportional hazards model. Receiver operating
characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to determine the
optimal cut-off value for MPV; values with maximum joint
sensitivity and specificity were selected. Categorical variables
were compared using the χ2 test and continuous variables
were compared using the t-test. All the statistical analyses were
performed employing the R statistical software, version 2.13.1 (R
Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). All the
P-values are two-sided and P-values <0.05 were considered to
indicate statistically significant differences.
Results
Patients
Data from 373 patients diagnosed with NSCLC who
underwent surgery at our hospital between January, 2007 and
December, 2011 were reviewed from the hospitals database and 65
patients were excluded due to preoperative treatment (n=20),
incomplete resection (n=37) and history of hematological disorders
(n=8). Thus, 308 patients were finally included in this study. The
clinicopathological characteristics of the patients are summarized
in Table I. The patients included
164 men and 144 women, with a median age at the time of surgery of
69 years (range, 19–87 years). The median follow-up duration was
36.0 months (range, 1.0–77.4 months). A total of 64 patients
received postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy and 64 patients
experienced NSCLC recurrence. The 5-year DFS and OS rate of all 308
patients were 66.2% (pathological stage I, 76.5%; pathological
stage II, 39.6%; and pathological stage IIIA, 33.5%) and 80.5%
(pathological stage I, 85.1%; pathological stage II, 78.3%; and
pathological stage IIIA, 56.9%), respectively.
 | Table IAssociation between MPV and
clinicopathological factors. |
Table I
Association between MPV and
clinicopathological factors.
| MPV | |
|---|
|
| |
|---|
| Variables | <8.50 fl
(n=176) | ≥8.50 fl (n=132) | P-value |
|---|
| Age, years [median
(range)] | 69 (19–87) | 68 (37–85) |
0.414 |
| Gender
(male/female) | 98/78 | 66/66 |
0.357 |
| ECOG performance
status (0/1/2) | 170/4/2 | 127/4/1 |
0.924 |
| Smoking history
(never/ever) | 64/112 | 58/74 |
0.196 |
| Resected side
(right/left) | 101/75 | 79/53 |
0.726 |
| Surgical procedure
(pneumo/lob/seg) | 1/155/20 | 0/110/22 |
0.240 |
| Pathological stage
(I/II/IIIA) | 129/18/29 | 100/18/14 |
0.265 |
| Tumor status
(T1/T2/T3/T4) | 102/60/10/4 | 81/43/6/2 |
0.907 |
| Lymph node status
(N0/N1/N2) | 140/9/27 | 111/9/12 |
0.221 |
| Histology
(Ad/Sq/other) | 139/25/12 | 103/25/4 |
0.214 |
| Pleural invasion
(present/absent) | 57/119 | 29/103 |
0.054 |
| Postoperative
adjuvant chemotherapy | 42 | 22 |
0.156 |
| Recurrence of lung
cancer | 40 | 24 |
0.395 |
| Cause of death (lung
cancer/other/unknown) | 15/20/4 | 5/3/0 |
0.504 |
Optimal cut-off values for MPV and
association between MPV and clinicopathological factors
The ROC curve for MPV was used to determine the
cut-off values. The area under the curve for MPV was 0.641 [95%
confidence interval (CI): 0.562–0.719]. An MPV of 8.50 fl
corresponded to the maximum joint sensitivity and specificity on
the ROC curve (87.2% sensitivity and 44.1% specificity). The
associations between MPV and the clinicopathological factors in
this study population are shown in Table I. A low MPV was not found to be
significantly associated with any other clinicopathological
factor.
Evaluation of the prognostic effect of
MPV
The Kaplan-Meier analysis was performed to determine
whether MPV was associated with DFS and OS. The DFS was
significantly shorter in the group with a MPV of <8.50 fl
compared to that in the group with a MPV of ≥8.50 fl (P=0.011;
Fig. 1A). The 5-year DFS rate in
the <8.50 fl and ≥8.50 fl groups was 60.8 and 74.4%,
respectively. The OS in the group with a MPV of <8.50 fl was
significantly inferior to that in the group with a MPV of ≥8.50 fl
(P=0.001; Fig. 1B). The 5-year OS
rate in the two groups was 73.6 and 93.3%, respectively.
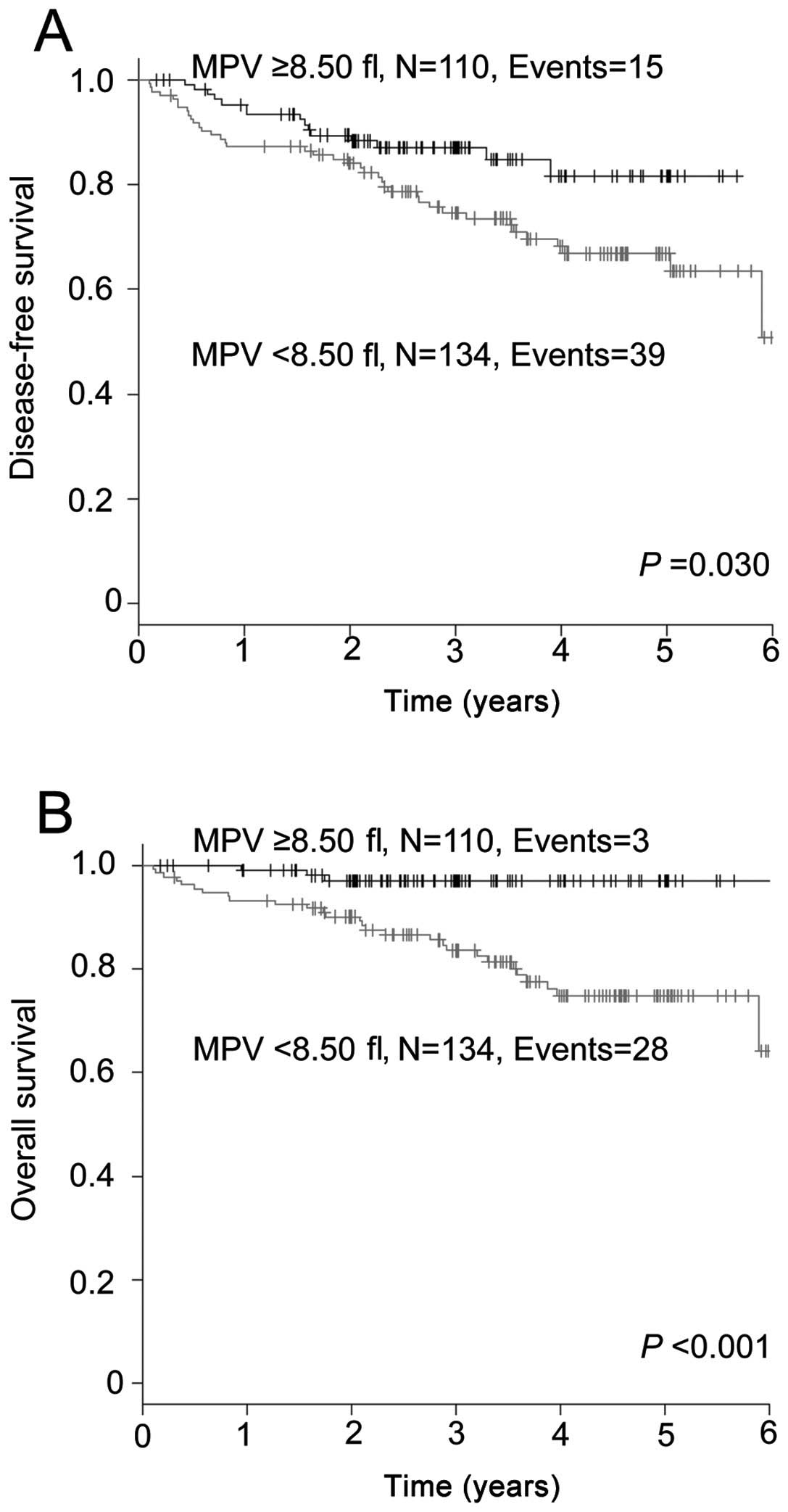
We also evaluated the effect of MPV on the prognosis
of the 244 patients who did not receive adjuvant chemotherapy,
employing the Kaplan-Meier analysis. The DFS of the group with a
MPV of <8.50 fl was significantly shorter compared to that in
the group with a MPV of ≥8.50 fl (P=0.030; Fig. 2A). The 5-year DFS rate in the
<8.50 and ≥8.50 fl groups was 66.8 and 81.6%, respectively. The
group with a MPV of <8.50 fl experienced a significantly
inferior OS compared to that in the group with a MPV of ≥8.50 fl
(P<0.001; Fig. 2B). The 5-year
OS rate in the two groups was 74.8 and 97.0%, respectively.
Univariate and multivariate analyses
of factors associated with prognosis
The univariate analysis identified seven significant
risk factors for DFS, namely age, gender, smoking history, tumor
status, lymph node status, histology and MPV (Table II). In the multivariate analysis,
a low MPV was shown to be a statistically significant independent
predictor of DFS, [hazard ratio (HR)=1.713; 95% CI: 1.070–2.742,
P=0.025]. The other independent prognostic factors were age
(HR=1.753; 95% CI: 1.127–2.727, P=0.013), tumor status (HR=1.716;
95% CI: 1.063–2.770, P=0.027) and lymph node status (HR=3.493; 95%
CI: 2.144–5.689, P<0.001).
 | Table IIPrognostic effect of
clinicopathological factors on disease-free survival in NSCLC. |
Table II
Prognostic effect of
clinicopathological factors on disease-free survival in NSCLC.
| Univariate
analysis | Multivariate
analysis |
|---|
|
|
|
|---|
| Variables | HR | 95% CI | P-value | HR | 95% CI | P-value |
|---|
| Age (years) | | | | | | |
| ≥70 |
1.756 |
1.148–2.684 |
0.009 |
1.753 |
1.127–2.727 |
0.013 |
| Gender | | | | | | |
| Male |
2.382 |
1.513–3.751 |
<0.001 |
1.789 |
0.954–3.354 |
0.070 |
| Smoking history | | | | | | |
| Ever |
2.001 |
1.258–3.184 |
0.003 |
1.357 |
0.691–2.665 |
0.375 |
| Tumor status | | | | | | |
|
T2/T3/T4 |
2.762 |
1.797–4.244 |
<0.001 |
1.716 |
1.063–2.770 |
0.027 |
| Lymph node
status | | | | | | |
|
N1/N2 |
4.096 |
2.667–6.289 |
<0.001 |
3.493 |
2.144–5.689 |
<0.001 |
| Histology | | | | | | |
|
Non-Ad |
1.916 |
1.209–3.037 |
0.006 |
0.773 |
0.445–1.343 |
0.361 |
| MPV | | | | | | |
| ≤8.50
fL |
1.813 |
1.138–2.888 |
0.012 |
1.713 |
1.070–2.742 |
0.025 |
As regards OS, the univariate analysis identified
seven significant risk factors, namely age, gender, smoking
history, tumor status, lymph node status, histology and MPV
(Table III). The multivariate
analysis identified low MPV as a statistically significant
independent prognostic factor of OS (HR=2.835; 95% CI: 1.304–6.163,
P=0.009). The other independent prognostic factors were age
(HR=4.466; 95% CI: 2.223–8.972, P<0.001) and lymph node status
(HR=3.654; 95% CI: 1.881–7.098, P<0.001).
 | Table IIIPrognostic effect of
clinicopathological factors on overall survival in NSCLC. |
Table III
Prognostic effect of
clinicopathological factors on overall survival in NSCLC.
| Univariate
analysis | Multivariate
analysis |
|---|
|
|
|
|---|
| Variables | HR | 95% CI | P-value | HR | 95% CI | P-value |
|---|
| Age (years) | | | | | | |
| ≥70 |
3.800 |
1.971–7.329 |
<0.001 |
4.466 |
2.223–8.972 |
<0.001 |
| Gender | | | | | | |
| Male |
2.820 |
1.462–5.438 |
0.002 |
2.197 |
0.822–5.874 |
0.117 |
| Smoking
history | | | | | | |
|
Ever |
2.419 |
1.231–4.755 |
0.010 |
1.376 |
0.484–3.918 |
0.550 |
| Tumor status | | | | | | |
|
T2/T3/T4 |
2.110 |
1.181–3.768 |
0.012 |
1.325 |
0.703–2.498 |
0.385 |
| Lymph node
status | | | | | | |
|
N1/N2 |
3.388 |
1.891–6.069 |
<0.001 |
3.654 |
1.881–7.098 |
<0.001 |
| Histology | | | | | | |
|
Non-Ad |
1.881 |
1.003–3.528 |
0.049 |
0.649 |
0.307–1.374 |
0.259 |
| MPV | | | | | | |
| ≤8.50
fl |
3.303 |
1.539–7.086 |
0.002 |
2.835 |
1.304–6.163 |
0.009 |
Discussion
In this study, we demonstrated that a low MPV was a
poor prognostic factor in patients with NSCLC who received curative
resection. A low MPV prior to the initiation of treatment was
reported to predict a poor prognosis in advanced NSCLC (7). To the best of our knowledge, this is
the first study to demonstrate the prognostic effect of MPV on DFS
and OS in patients with completely resected NSCLC.
MPV has been considered to reflect platelet
activity, as it was shown to be associated with platelet
aggregation (11), thromboxane B2
release (12) and increased
expression of the platelet adhesion molecule glycoprotein IIb/IIIa
(13). Several clinical studies
reported that an elevated MPV is associated with thromboembolic
diseases, such as myocardial infarction (3) or stroke (4). Recently, the association between MPV
and various types of cancer has attracted significant attention. A
significant decrease in MPV was demonstrated in various cancer
patients with metastasis to the bone marrow compared to control
subjects (14). In addition, MPV
was found to be decreased in patients with advanced NSCLC (9).
The association between coagulation and cancer may
be key to explaining the decrease in MPV. A recent report
demonstrated that lung cancer cell-derived microparticles bearing
P-selectin and tissue factor activate the circulating platelets,
leading to thrombus formation (15). Furthermore, tumor cells release
various soluble proinflammatory (i.e., tumor necrosis factor-α and
interleukin-1 β) and proangiogenic factors (i.e., vascular
endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor)
(16), which may stimulate the
prothrombotic properties of vascular cells. The tendency of larger
platelets to react to stimuli causes selective consumption of
larger platelets, with a resulting decrease in the MPV of
circulating platelets. Mutlu et al (17) analyzed MPV levels in patients with
various cancers and found a significant decrease in MPV levels at
the time of the thrombotic events compared to those at diagnosis.
In 241 patients (78.2%) of the population included in that study,
the MPV was below the normal limit, which may support the
hypothesis that MPV decreases in patients with NSCLC. Further
studies on the association between MPV and cancer-related
thrombosis are required.
The effect of platelets on the survival of patients
with cancer has been extensively investigated. Platelets have been
suggested to play an important role in cancer progression and
metastasis (18). A previous study
demonstrated that preliminarily activated platelets have
tumor-promoting properties (19).
Although the number of studies that have investigated the
biological association between MPV and cancer progression is
limited, recent clinical reports demonstrated the negative effect
of a low MPV on the prognosis of cancer patients. Riedl et
al (20) evaluated the data of
1,544 patients with various types of cancer and found that high MPV
values were associated not only with a decreased risk of venous
thromboembolism, but also with an improved patient survival. As for
advanced NSCLC, a low MPV prior to the treatment was shown to
predict a poor prognosis (7). The
present study also demonstrated the negative effect of a low MPV on
the DFS and OS of NSCLC patients who received complete resection,
even subtracting the effects of adjuvant chemotherapy, which
supports the findings of previous studies. However, these results
should be verified in a prospective study with a larger sample
size.
In this study, we demonstrated that a low MPV prior
to surgery was an independent unfavorable prognostic factor in
patients who underwent complete resection of NSCLC. MPV, available
in a routine complete blood count examination, may represent one of
the easiest measurements to be used as a prognostic marker
independent of tumor status or lymph node status in NSCLC.
Therefore, preoperative MPV may be a useful tool for selecting
optimal treatment strategies, including adjuvant chemotherapy. The
limitations of the present study include its retrospective design
and relatively short follow-up duration. Further investigations are
required to elucidate the precise mechanisms through which
circulating platelets affect the prognosis of patients with
NSCLC.
References
|
1
|
Thompson CB and Jakubowski JA: The
pathophysiology and clinical relevance of platelet heterogeneity.
Blood. 72:1–8. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thompson CB, Jakubowski JA, Quinn PG, et
al: Platelet size and age determine platelet function
independently. Blood. 63:1372–1375. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Martin JF, Bath PM and Burr ML: Influence
of platelet size on outcome after myocardial infarction. Lancet.
338:1409–1411. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tohgi H, Suzuki H, Tamura K, et al:
Platelet volume, aggregation, and adenosine triphosphate release in
cerebral thrombosis. Stroke. 22:17–21. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aoe K, Hiraki A, Ueoka H, et al:
Thrombocytosis as a useful prognostic indicator in patients with
lung cancer. Respiration. 71:170–173. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Maráz A, Furák J, Varga Z, et al:
Thrombocytosis has a negative prognostic value in lung cancer.
Anticancer Res. 33:1725–1730. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Inagaki N, Kibata K, Tamaki T, et al:
Prognostic impact of the mean platelet volume/platelet count ratio
in terms of survival in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung
Cancer. 83:97–101. 2014.
|
|
8
|
World Health Organization, . Tumours of
the lungTumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. Travis WD,
Bramvilla E, Muller-Hermelink HK and Harris CC: International
Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon: pp. 102004
|
|
9
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: International Union Against Cancer (UICC): TNM classification of
malignant tumours. 7th. John Willkey and Sons, Ltd.; UK: 2010
|
|
10
|
Kaplan E and Meier P: Nonparametric
estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc.
53:457–481. 1958. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Thompson CB, Eaton KA, Princiotta SM, et
al: Size dependent platelet subpopulations: relationship of
platelet volume to ultrastructure, enzymatic activity, and
function. Br J Haematol. 50:509–519. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jakubowski JA, Thompson CB, Vaillancourt
R, et al: Arachidonic acid metabolism by platelets of differing
size. Br J Haematol. 53:503–511. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Giles H, Smith RE and Martin JF: Platelet
glycoprotein IIb-IIIa and size are increased in acute myocardial
infarction. Eur J Clin Invest. 24:69–72. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Aksoy S, Kilickap S, Hayran M, et al:
Platelet size has diagnostic predictive value for bone marrow
metastasis in patients with solid tumors. Int J Lab Hematol.
30:214–219. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thomas GM, Panicot-Dubois L, Lacroix R, et
al: Cancer cell-derived microparticles bearing P-selectin
glycoprotein ligand 1 accelerate thrombus formation in vivo. J Exp
Med. 206:1913–1927. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Falanga A, Panova-Noeva M and Russo L:
Procoagulant mechanisms in tumour cells. Best Pract Res Clin
Haematol. 22:49–60. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mutlu H, Artis TA, Erden A and Akca Z:
Alteration in mean platelet volume and platicrit values in patients
with cancer that developed thrombosis. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost.
19:331–333. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nash GF, Turner LF, Scully MF, et al:
Platelets and cancer. Lancet Oncol. 3:425–430. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang W, Dang S, Hong T, et al: A
humanized single-chain antibody against beta 3 integrin inhibits
pulmonary metastasis by preferentially fragmenting activated
platelets in the tumor microenvironment. Blood. 120:2889–2898.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Riedl J, Kaider A, Reitter EM, et al:
Association of mean platelet volume with risk of venous
thromboembolism and mortality in patients with cancer. Results from
the Vienna Cancer and Thrombosis Study (CATS). Thromb Haemost.
111:670–678. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|