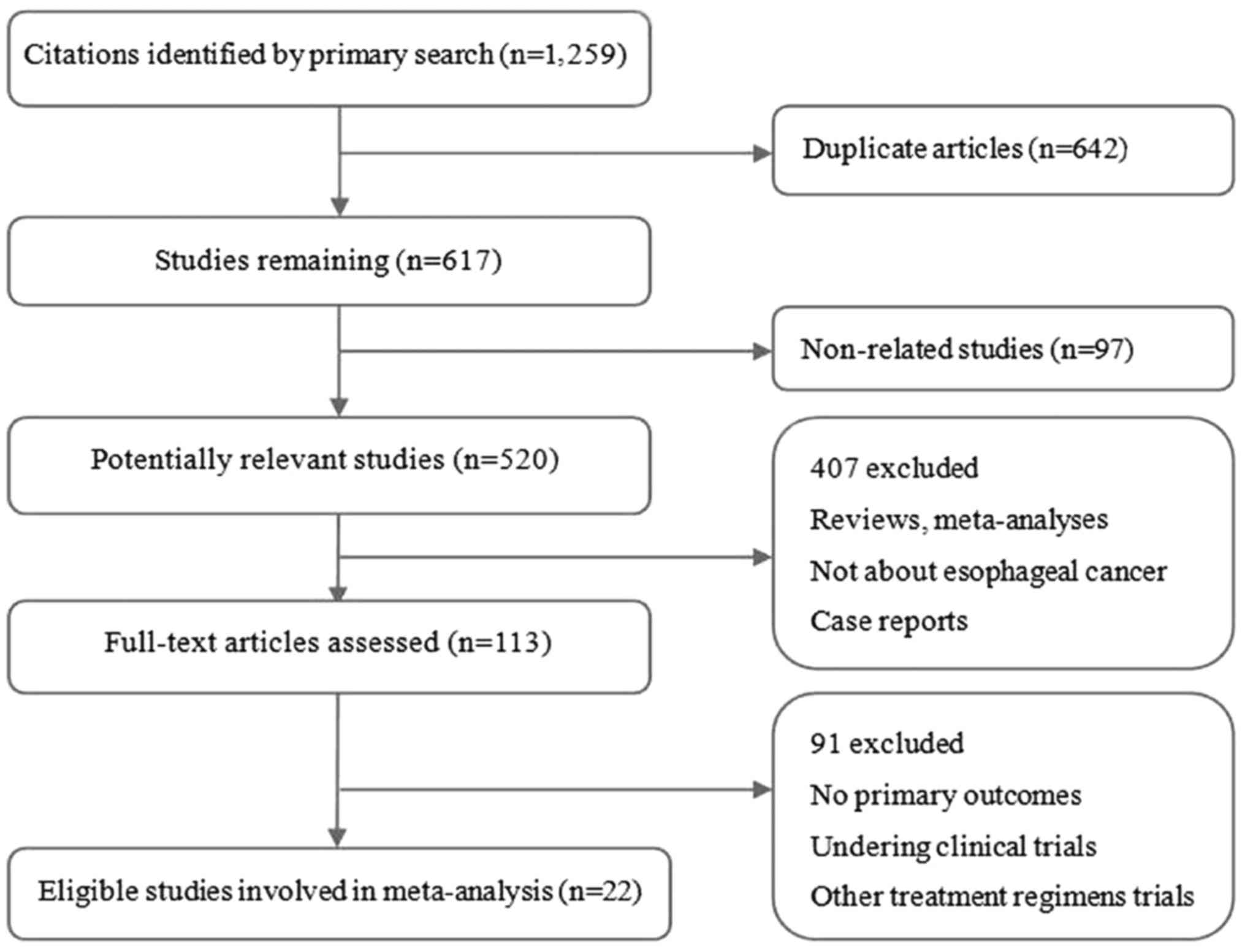
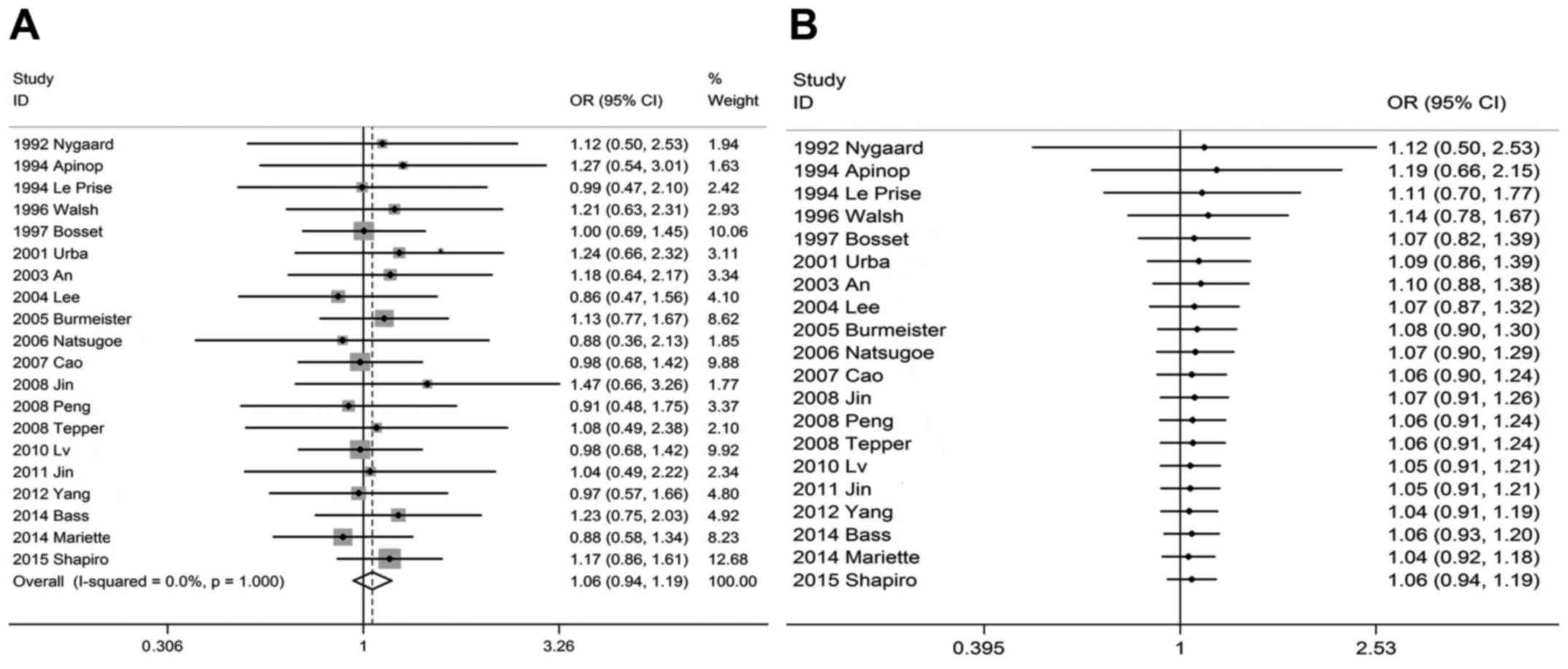
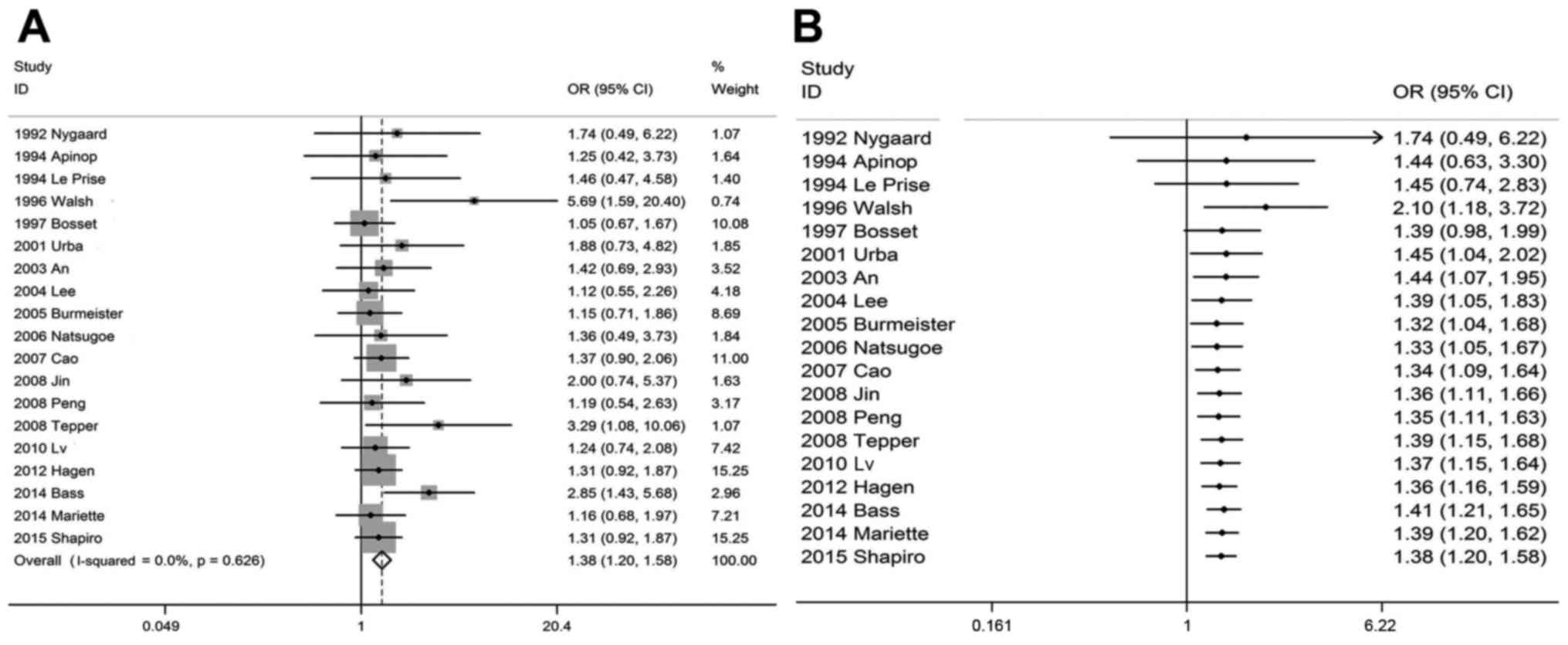
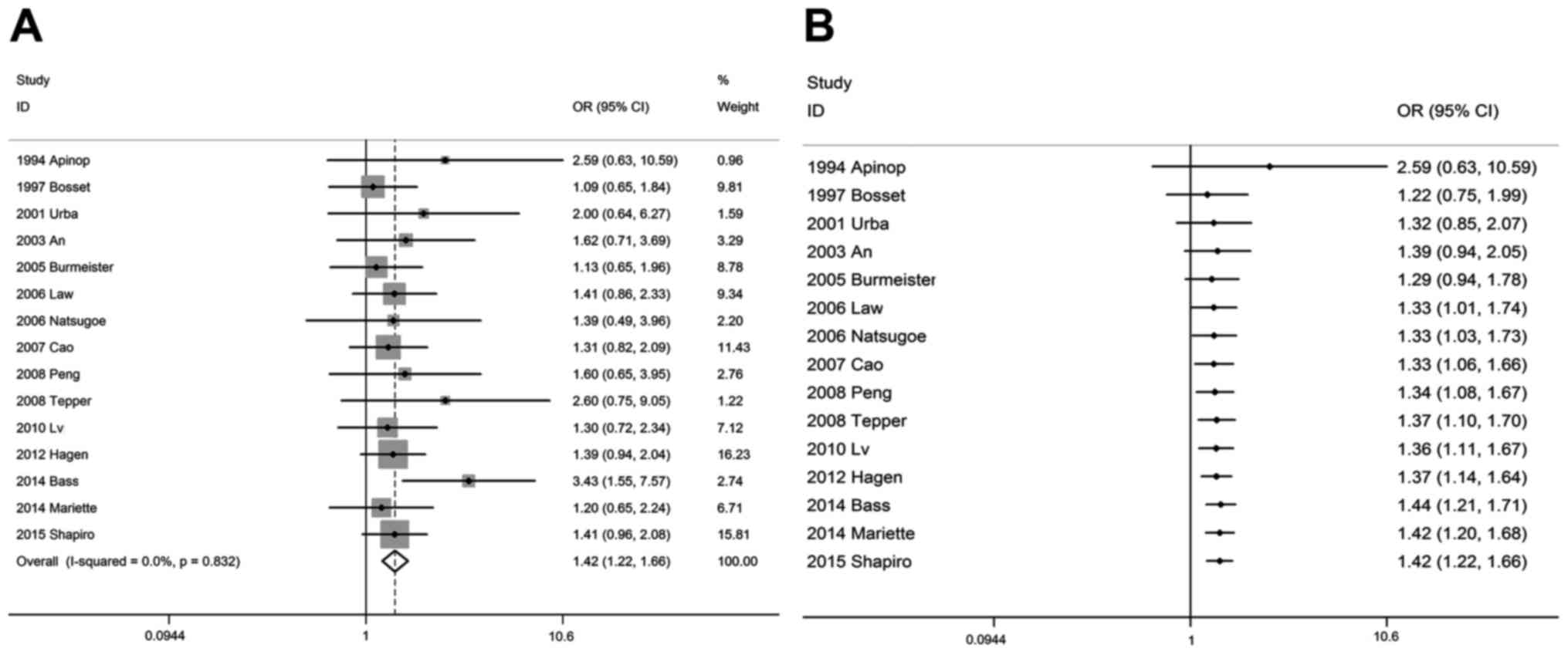
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM, Bray FI and Devesa SS: Cancer
burden in the year 2000. The global picture. Eur J Cancer. 37 Suppl
8:S4–S66. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Devesa SS, Blot WJ and Fraumeni JF Jr:
Changing patterns in the incidence of esophageal and gastric
carcinoma in the United States. Cancer. 83:2049–2053. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Song Y, Li L, Ou Y, Gao Z, Li E, Li X,
Zhang W, Wang J, Xu L, Zhou Y, et al: Identification of genomic
alterations in oesophageal squamous cell cancer. Nature. 509:91–95.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Funk EM and Witte J: Multimodal therapy
for esophageal adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 336:375–376, author
reply 375–376. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nygaard K, Hagen S, Hansen HS, Hatlevoll
R, Hultborn R, Jakobsen A, Mäntyla M, Modig H, Munck-Wikland E,
Rosengren B, et al: Pre-operative radiotherapy prolongs survival in
operable esophageal carcinoma: A randomized, multicenter study of
pre-operative radiotherapy and chemotherapy. The second
Scandinavian trial in esophageal cancer. World J Surg.
16:1104–1109, discussion 1110. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Apinop C, Puttisak P and Preecha N: A
prospective study of combined therapy in esophageal cancer.
Hepatogastroenterology. 41:391–393. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Le Prise E, Etienne PL, Meunier B, Maddern
G, Ben Hassel M, Gedouin D, Boutin D, Campion JP and Launois B: A
randomized study of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery
versus surgery for localized squamous cell carcinoma of the
esophagus. Cancer. 73:1779–1784. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Walsh TN, Noonan N, Hollywood D, Kelly A,
Keeling N and Hennessy TP: A comparison of multimodal therapy and
surgery for esophageal adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 335:462–467.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bosset JF, Gignoux M, Triboulet JP, Tiret
E, Mantion G, Elias D, Lozach P, Ollier JC, Pavy JJ, Mercier M, et
al: Chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery compared with surgery
alone in squamous-cell cancer of the esophagus. N Engl J Med.
337:161–167. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Urba SG, Orringer MB, Turrisi A,
Iannettoni M, Forastiere A and Strawderman M: Randomized trial of
preoperative chemoradiation versus surgery alone in patients with
locoregional esophageal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 19:305–313. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
An FS, Huang JQ, Xie YT, Chen SH and Rong
TH: A prospective study of combined chemoradiotherapy followed by
surgery in the treatment of esophageal carcinoma. Zhonghua Zhong
Liu Za Zhi. 25:376–379. 2003.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee JL, Park SI, Kim SB, Jung HY, Lee GH,
Kim JH, Song HY, Cho KJ, Kim WK, Lee JS, et al: A single
institutional phase III trial of preoperative chemotherapy with
hyperfractionation radiotherapy plus surgery versus surgery alone
for resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol.
15:947–954. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Burmeister BH, Smithers BM, Gebski V,
Fitzgerald L, Simes RJ, Devitt P, Ackland S, Gotley DC, Joseph D,
Millar J, et al Trans-Tasman Radiation Oncology Group, ;
Australasian Gastro-Intestinal Trials Group, : Surgery alone versus
chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery for resectable cancer of the
oesophagus: A randomised controlled phase III trial. Lancet Oncol.
6:659–668. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Natsugoe S, Okumura H, Matsumoto M,
Uchikado Y, Setoyama T, Yokomakura N, Ishigami S, Owaki T and Aikou
T: Randomized controlled study on preoperative chemoradiotherapy
followed by surgery versus surgery alone for esophageal squamous
cell cancer in a single institution. Dis Esophagus. 19:468–472.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cao XF, He XT, Ji L, Xiao J and Lv J:
Effects of neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy on pathological staging
and prognosis for locally advanced esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 22:477–481. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jin MG, Jiang SC and Chen ZW: Clinical
trial of preoperative concurrent chemoradiation followed by surgery
versus surgery alone for advanced esophageal carcinoma. China J
Cancer Prev Treat. 15:1815–1817. 2008.
|
|
19
|
Peng L, Xie TP, Han YT, et al: Randomized
controlled study on preoperative concurrent chemoradiotherapy
versus surgery alone for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumor
Chin. 28:620–622. 2008.
|
|
20
|
Tepper J, Krasna MJ, Niedzwiecki D, Hollis
D, Reed CE, Goldberg R, Kiel K, Willett C, Sugarbaker D and Mayer
R: Phase III trial of trimodality therapy with cisplatin,
fluorouracil, radiotherapy, and surgery compared with surgery alone
for esophageal cancer: CALGB 9781. J Clin Oncol. 26:1086–1092.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lv J, Cao XF, Zhu B, Ji L, Tao L and Wang
DD: Long-term efficacy of perioperative chemoradiotherapy on
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
16:1649–1654. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jin FL, Zu-Liang HU and Hai-Feng MA:
Treatment effect of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy followed by
surgery versus surgery alone in local advanced esophageal
carcinoma. Shiyong Zhongliu Zazhi. 26:523–526. 2011.
|
|
23
|
Yang H, Jh FU, Liu MZ, et al: A
multi-centered randomized controlled study of neo-adjuvant
chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery versus surgery alone for
locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus: an interim
analysis). Natl Med J Chin (Chin). 92:1028–1032. 2006.(In
Chinese).
|
|
24
|
Bass GA, Furlong H, O'Sullivan KE,
Hennessy TP and Walsh TN: Chemoradiotherapy, with adjuvant surgery
for local control, confers a durable survival advantage in
adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the oesophagus. Eur J
Cancer. 50:1065–1075. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mariette C, Dahan L, Mornex F, Maillard E,
Thomas PA, Meunier B, Boige V, Pezet D, Robb WB, Le Brun-Ly V, et
al: Surgery alone versus chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery for
stage I and II esophageal cancer: Final analysis of randomized
controlled phase III trial FFCD 9901. J Clin Oncol. 32:2416–2422.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shapiro J, van Lanschot JJB, Hulshof MCCM,
van Hagen P, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Wijnhoven BPL, van Laarhoven
HWM, Nieuwenhuijzen GAP, Hospers GAP, Bonenkamp JJ, et al CROSS
study group, : Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery versus
surgery alone for oesophageal or junctional cancer (CROSS):
Long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol.
16:1090–1098. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
van Hagen P, Hulshof MC, van Lanschot JJ,
Steyerberg EW, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Wijnhoven BP, Richel DJ,
Nieuwenhuijzen GA, Hospers GA, Bonenkamp JJ, et al CROSS Group, :
Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer.
N Engl J Med. 366:2074–2084. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Law S, Kwong DL, Wong KH, Kwok KF and Wong
J: The effects of neoadjuvant chemoradiation on pTNM staging and
its prognostic significance in esophageal cancer. J Gastrointest
Surg. 10:1301–1311. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sjoquist KM, Burmeister BH, Smithers BM,
Zalcberg JR, Simes RJ, Barbour A and Gebski V; Australasian
Gastro-Intestinal Trials Group, : Survival after neoadjuvant
chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy for resectable oesophageal
carcinoma: An updated meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 12:681–692.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gluud LL and Krag A: Banding ligation
versus beta-blockers for primary prevention in oesophageal varices
in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 8:CD0045442012.
|
|
31
|
Huang TC, Hsu CH, Lin CC and Tu YK:
Systematic review and network meta-analysis: Neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy for locoregional esophageal cancer. Jpn J Clin
Oncol. 45:1023–1028. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wijnhoven BP, van Lanschot JJ, Tilanus HW,
Steyerberg EW and van der Gaast A: Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy
for esophageal cancer: A review of meta-analyses. World J Surg.
33:2606–2614. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Baum ML, Anish DS, Chalmers TC, Sacks HS,
Smith H Jr and Fagerstrom RM: A survey of clinical trials of
antibiotic prophylaxis in colon surgery: Evidence against further
use of no-treatment controls. N Engl J Med. 305:795–799. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lau J, Antman EM, Jimenez-Silva J,
Kupelnick B, Mosteller F and Chalmers TC: Cumulative meta-analysis
of therapeutic trials for myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med.
327:248–254. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jin HL, Zhu H, Ling TS, Zhang HJ and Shi
RH: Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for resectable esophageal
carcinoma: A meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 15:5983–5991.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu SL, Yang H, Zhang P, Zhang L, Zhao L,
Luo LL, Fu JH, Liu MZ and Xi M: Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy with
cisplatin plus vinorelbine versus cisplatin plus fluorouracil for
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A matched case-control study.
Radiother Oncol. 116:262–268. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wolf M, Zehentmayr F, Niyazi M, Ganswindt
U, Haimerl W, Schmidt M, Hölzel D and Belka C: Long-term outcome of
mitomycin C- and 5-FU-based primary radiochemotherapy for
esophageal cancer. Strahlenther Onkol. 186:374–381. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|