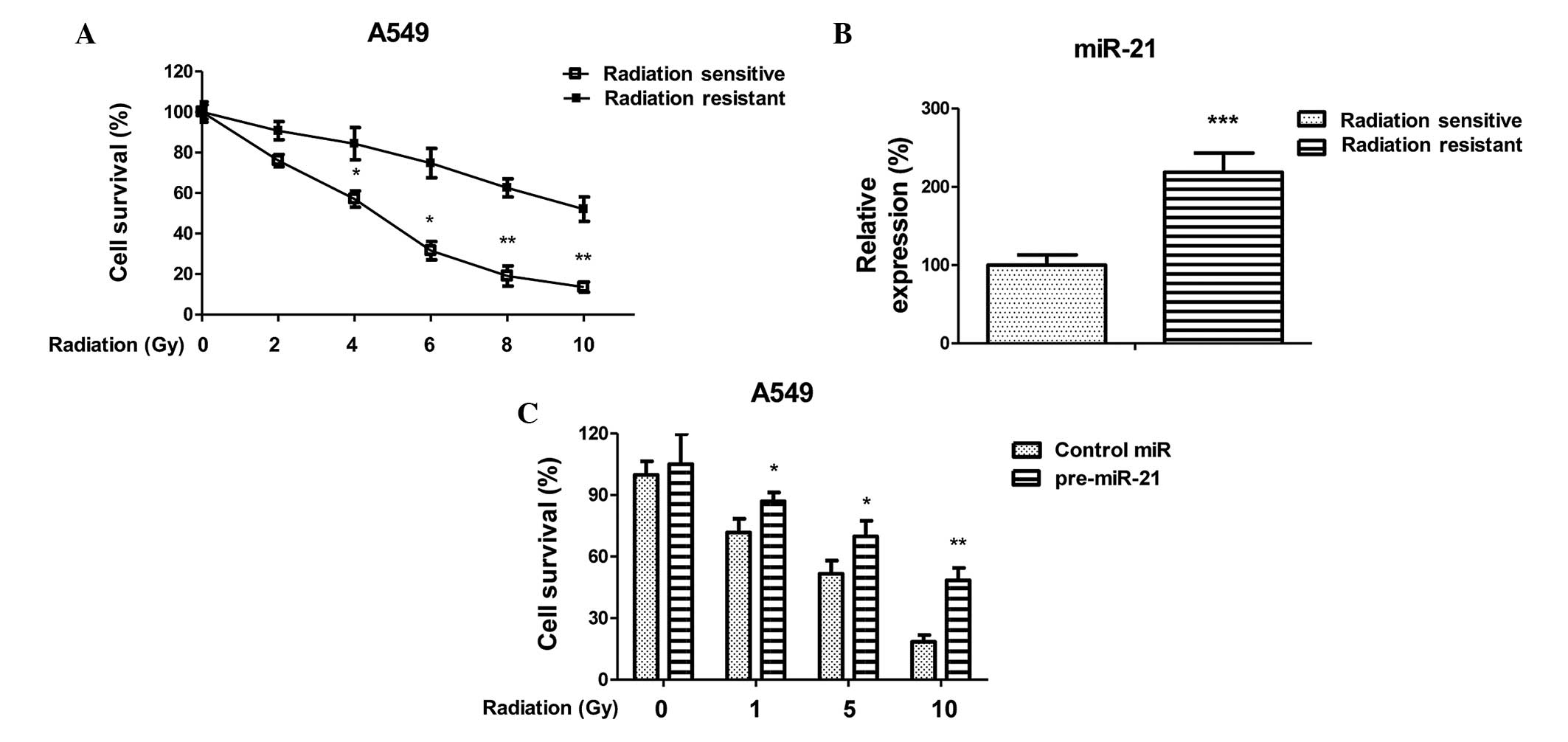
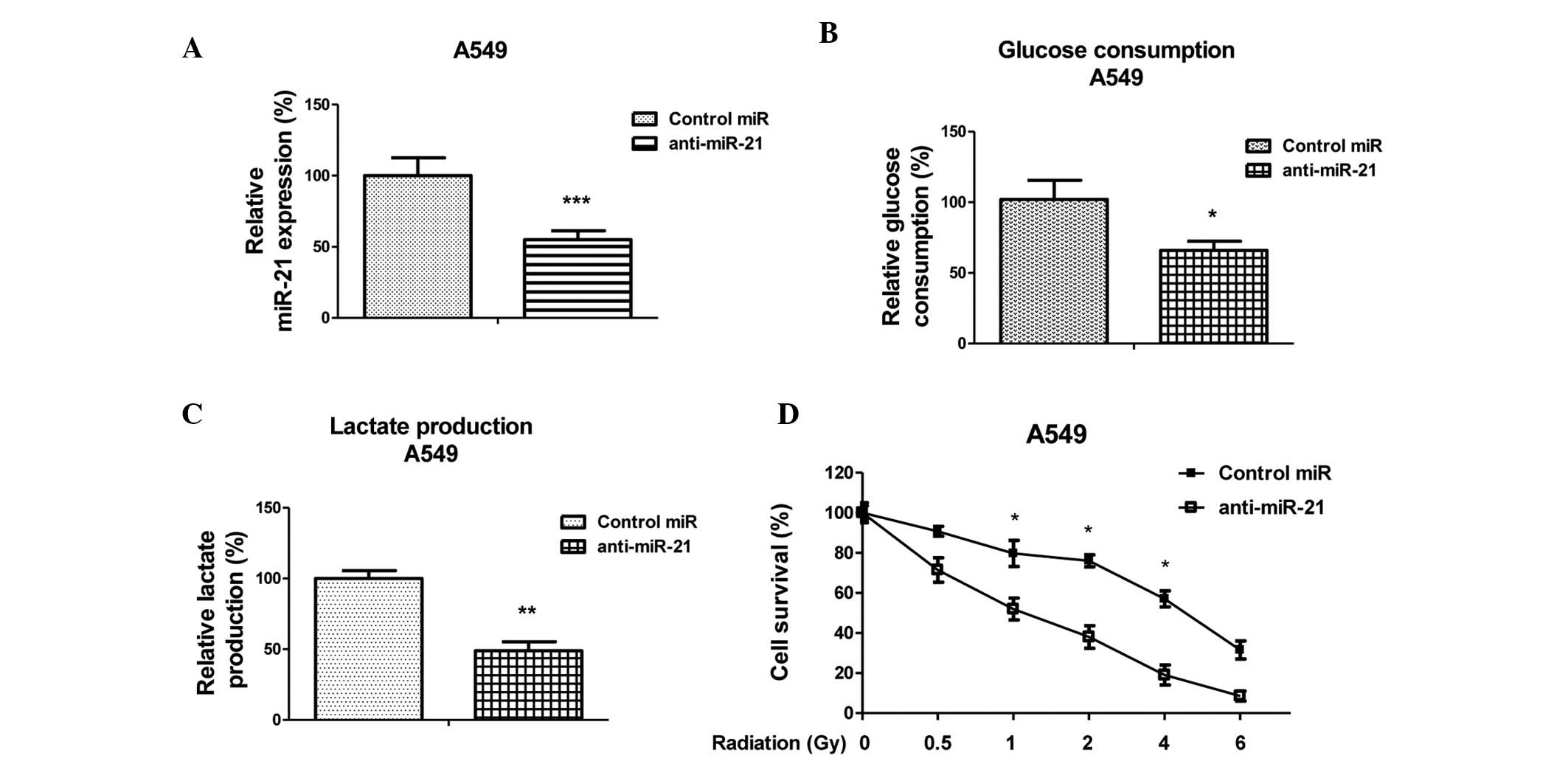
|
1
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brodersen P and Voinnet O: Revisiting the
principles of microRNA target recognition and mode of action. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:141–148. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ameres SL and Zamore PD: Diversifying
microRNA sequence and function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:475–488.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jansson MD and Lund AH: MicroRNA and
cancer. Mol Oncol. 6:590–610. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sicard F, Gayral M, Lulka H, Buscail L and
Cordelier P: Targeting miR-21 for the therapy of pancreatic cancer.
Mol Ther. 21:986–994. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A,
Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M,
et al: MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ma Y, Xia H, Liu Y and Li M: Silencing
miR-21 sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells to ionizing
radiation through inhibition of PI3K/Akt. Biomed Res Int.
2014:6178682014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pineau P, Volinia S, McJunkin K, Marchio
A, Battiston C, Terris B, Mazzaferro V, Lowe SW, Croce CM and
Dejean A: miR-221 overexpression contributes to liver
tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:264–269. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Chan SH, Wu CW, Li AF, Chi CW and Lin WC:
miR-21 microRNA expression in human gastric carcinomas and its
clinical association. Anticancer Res. 28:907–911. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iorio MV, Visone R, Di Leva G, Donati V,
Petrocca F, Casalini P, Taccioli C, Volinia S, Liu CG, Alder H, et
al: MicroRNA signatures in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
67:8699–8707. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yao T and Lin Z: MiR-21 is involved in
cervical squamous cell tumorigenesis and regulates CCL20. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1822:248–260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kanaan Z, Rai SN, Eichenberger MR, Roberts
H, Keskey B, Pan J and Galandiuk S: Plasma miR-21: A potential
diagnostic marker of colorectal cancer. Ann Surg. 256:544–551.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM and Kosik KS:
MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells.
Cancer Res. 65:6029–6033. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fu C, Dong W, Wang Z, Li H, Qin Q and Li
B: The expression of miR-21 and miR-375 predict prognosis of
esophageal cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 446:1197–1203. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Folini M, Gandellini P, Longoni N, Profumo
V, Callari M, Pennati M, Colecchia M, Supino R, Veneroni S,
Salvioni R, et al: miR-21: An oncomir on strike in prostate cancer.
Mol Cancer. 9:122010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xie Z, Cao L and Zhang J: miR-21 modulates
paclitaxel sensitivity and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression
in human ovarian cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 6:795–800.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fang J, Zhou SH, Fan J and Yan SX: Roles
of glucose transporter-1 and the phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway in cancer radioresistance
(review). Mol Med Rep. 11:1573–1581. 2015.
|
|
18
|
Shimura T, Noma N, Sano Y, Ochiai Y,
Oikawa T, Fukumoto M and Kunugita N: AKT-mediated enhanced aerobic
glycolysis causes acquired radioresistance by human tumor cells.
Radiother Oncol. 112:302–307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang XC, Wang W, Zhang ZB, Zhao J, Tan XG
and Luo JC: Overexpression of miRNA-21 promotes
radiation-resistance of non-small cell lung cancer. Radiat Oncol.
8:1462013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC and Thompson
CB: Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of
cell proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ganapathy-Kanniappan S and Geschwind JF:
Tumor glycolysis as a target for cancer therapy: Progress and
prospects. Mol Cancer. 12:1522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Young A, Berry R, Holloway AF, Blackburn
NB, Dickinson JL, Skala M, Phillips JL and Brettingham-Moore KH:
RNA-seq profiling of a radiation-resistant and radiation sensitive
prostate cancer cell line highlights opposing regulation of DNA
repair and targets for radiosensitization. BMC Cancer. 14:8082014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lu H, Forbes RA and Verma A:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activation by aerobic glycolysis
implicates the Warburg effect in carcinogenesis. J Biol Chem.
277:23111–23115. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Azzam EI, Jay-Gerin JP and Pain D:
Ionizing radiation-induced metabolic oxidative stress and prolonged
cell injury. Cancer Lett. 327:48–60. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Le A, Cooper CR, Gouw AM, Dinavahi R,
Maitra A, Deck LM, Royer RE, Vander Jagt DL, Semenza GL and Dang
CV: Inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase A induces oxidative stress
and inhibits tumor progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:2037–2042. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liang G, Li G, Wang Y, Lei W and Xiao Z:
Aberrant miRNA expression response to UV irradiation in human liver
cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 9:904–910. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Harada H, Inoue M, Itasaka S, Hirota K,
Morinibu A, Shinomiya K, Zeng L, Ou G, Zhu Y, Yoshimura M, et al:
Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity
and translocate towards tumour blood vessels. Nat Commun.
3:7832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|