|
1
|
Schnekenburger M and Diederich M:
Epigenetics offer new horizons for colorectal cancer prevention.
Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep. 8:66–81. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Glade MJ: Food, nutrition, and the
prevention of cancer: a global perspective. American Institute for
Cancer Research/World Cancer Research Fund, American Institute for
Cancer Research, 1997. Nutrition. 15:523–526. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Potter JD: Colorectal cancer: molecules
and populations. J Natl Cancer Inst. 91:916–932. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jasperson KW, Tuohy TM, Neklason DW and
Burt RW: Hereditary and familial colon cancer. Gastroenterology.
138:2044–2058. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Burt RW: Colon cancer screening.
Gastroenterology. 119:837–853. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lichtenstein P, Holm NV, Verkasalo PK,
Iliadou A, Kaprio J, Koskenvuo M, Pukkala E, Skytthe A and Hemminki
K: Environmental and heritable factors in the causation of cancer -
analyses of cohorts of twins from Sweden, Denmark, and Finland. N
Engl J Med. 343:78–85. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Vasudevan S, Tong Y and Steitz JA:
Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate
translation. Science. 318:1931–1934. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Loktionov A: Common gene polymorphisms,
cancer progression and prognosis. Cancer Lett. 208:1–33. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Duan R, Pak C and Jin P: Single nucleotide
polymorphism associated with mature miR-125a alters the processing
of pri-miRNA. Hum Mol Genet. 16:1124–1131. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zeng Y and Cullen BR: Sequence
requirements for micro RNA processing and function in human cells.
RNA. 9:112–123. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hoffman AE, Zheng T, Yi C, Leaderer D,
Weidhaas J, Slack F, Zhang Y, Paranjape T and Zhu Y: microRNA
miR-196a-2 and breast cancer: a genetic and epigenetic association
study and functional analysis. Cancer Res. 69:5970–5977. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu Z, Chen J, Tian T, Zhou X, Gu H, Xu L,
Zeng Y, Miao R, Jin G, Ma H, et al: Genetic variants of miRNA
sequences and non-small cell lung cancer survival. J Clin Invest.
118:2600–2608. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
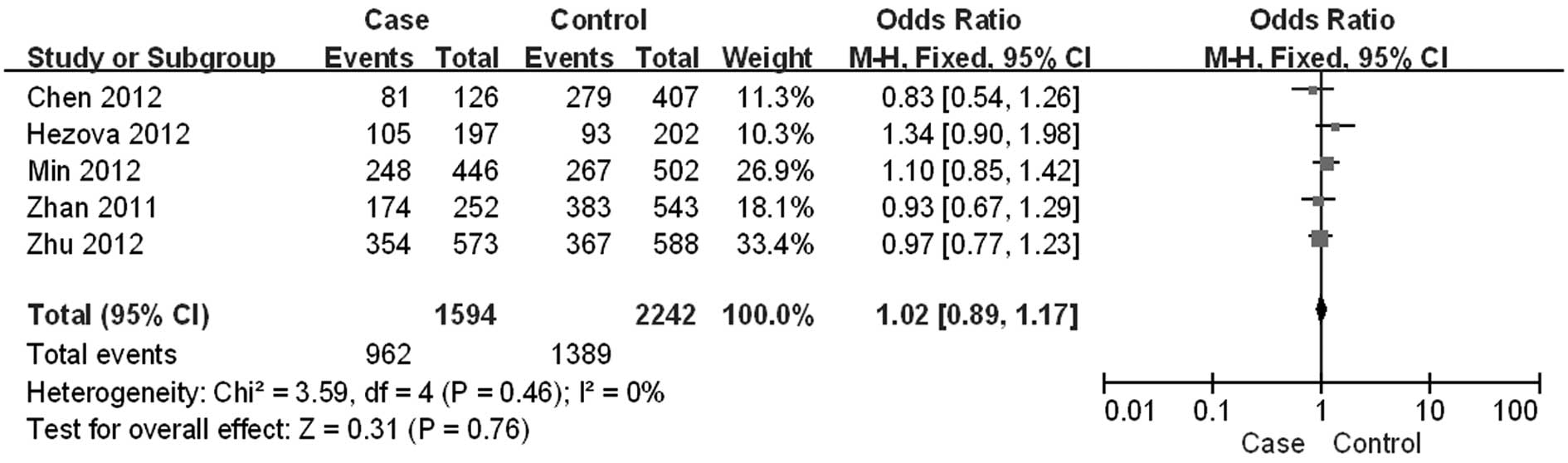
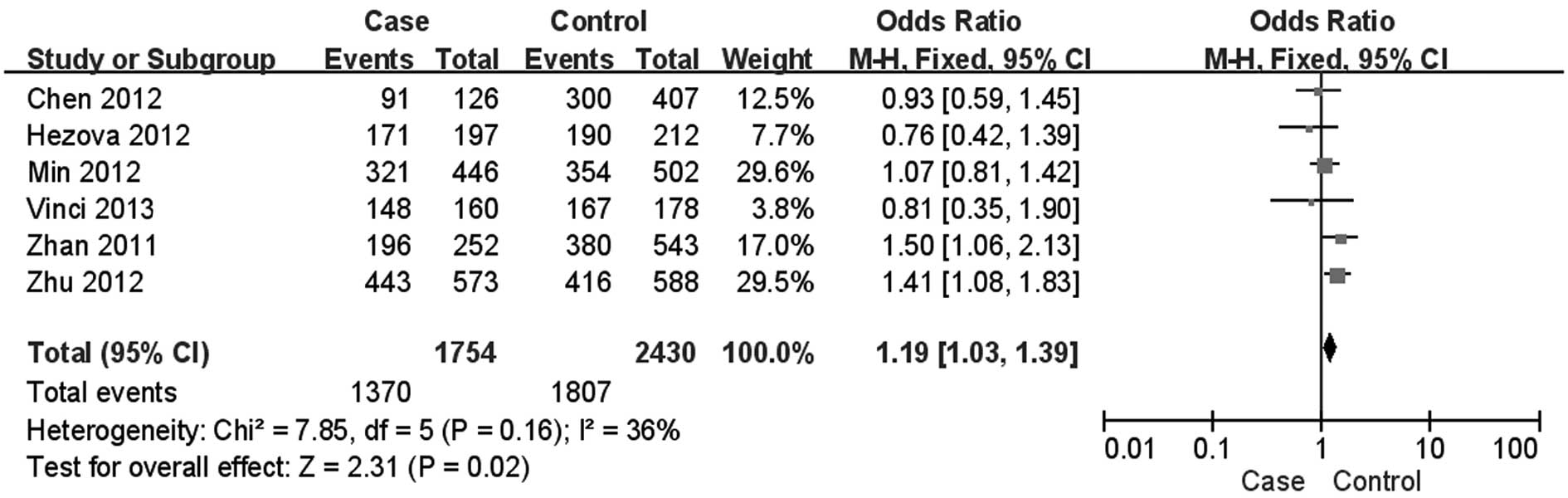
Zhan JF, Chen LH, Chen ZX, Yuan YW, Xie
GZ, Sun AM and Liu Y: A functional variant in microRNA-196a2 is
associated with susceptibility of colorectal cancer in a Chinese
population. Arch Med Res. 42:144–148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schimanski CC: High miR-196a levels
promote the oncogenic phenotype of colorectal cancer cells. World J
Gastroenterol. 15:2089–2096. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen H, Sun LY, Chen LL, Zheng HQ and
Zhang QF: A variant in microRNA-196a2 is not associated with
susceptibility to and progression of colorectal cancer in Chinese.
Intern Med J. 42:e115–e119. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hezova R, Kovarikova A, Bienertova-Vasku
J, Sachlova M, Redova M, Vasku A, Svoboda M, Radova L, Kiss I,
Vyzula R and Slaby O: Evaluation of SNPs in miR-196-a2, miR-27a and
miR-146a as risk factors of colorectal cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 18:2827–2831. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Min KT, Kim JW, Jeon YJ, Jang MJ, Chong
SY, Oh D and Kim NK: Association of the miR-146aC>G, 149C>T,
196a2C>T, and 499A>G polymorphisms with colorectal cancer in
the Korean population. Mol Carcinog. 51(Suppl 1): E65–E73.
2012.
|
|
20
|
Vinci S, Gelmini S, Mancini I, Malentacchi
F, Pazzagli M, Beltrami C, Pinzani P and Orlando C: Genetic and
epigenetic factors in regulation of microRNA in colorectal cancers.
Methods. 59:138–146. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhu L, Chu H, Gu D, Ma L, Shi D, Zhong D,
Tong N, Zhang Z and Wang M: A functional polymorphism in
miRNA-196a2 is associated with colorectal cancer risk in a Chinese
population. DNA Cell Biol. 31:350–354. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lau J, Ioannidis JP and Schmid CH:
Quantitative synthesis in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med.
127:820–826. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mantel N and Haenszel W: Statistical
aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of
disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 22:719–748. 1959.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
DerSimonian R and Laird N: Meta-analysis
in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 7:177–188. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
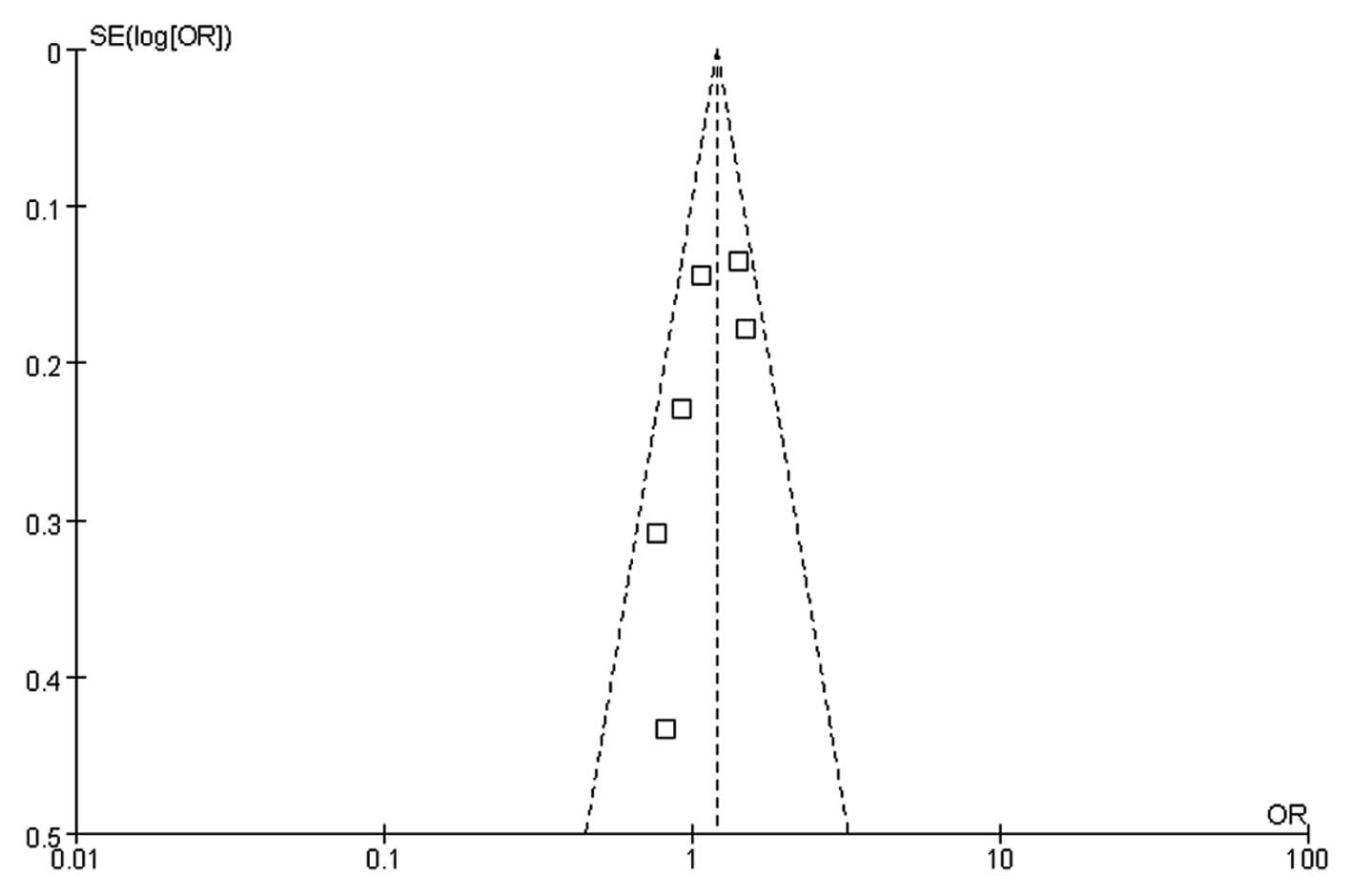
Begg CB and Mazumdar M: Operating
characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias.
Biometrics. 50:1088–1101. 1994. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang P, Xie S, Cui A, Zhang Y and Jiang B:
miR-196a2 polymorphisms and susceptibility to cancer: A
meta-analysis involving 24,697 subjects. Exp Ther Med. 3:324–330.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang F, Ma YL, Zhang P, Yang JJ, Chen HQ,
Liu ZH, Peng JY, Zhou YK and Qin HL: A genetic variant in
microRNA-196a2 is associated with increased cancer risk: a
meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep. 39:269–275. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chu H, Wang M, Shi D, Ma L and Zhang Z,
Tong N, Huo X, Wang W, Luo D, Gao Y and Zhang Z: Hsa-miR-196a2
Rs11614913 polymorphism contributes to cancer susceptibility:
evidence from 15 case-control studies. PLoS One. 6:e181082011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xu W, Xu J, Liu S, Chen B, Wang X, Li Y,
Qian Y, Zhao W and Wu J: Effects of common polymorphisms rs11614913
in miR-196a2 and rs2910164 in miR-146a on cancer susceptibility: a
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 6:e204712011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qiu LX, Wang Y, Xia ZG, Xi B, Mao C, Wang
JL, Wang BY, Lv FF, Wu XH and Hu LQ: miR-196a2 C allele is a
low-penetrant risk factor for cancer development. Cytokine.
56:589–592. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang J, Wang Q, Liu H, Shao N, Tan B,
Zhang G, Wang K, Jia Y, Ma W, Wang N and Cheng Y: The association
of miR-146a rs2910164 and miR-196a2 rs11614913 polymorphisms with
cancer risk: a meta-analysis of 32 studies. Mutagenesis.
27:779–788. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tian T, Xu Y, Dai J, Wu J, Shen H and Hu
Z: Functional polymorphisms in two pre-microRNAs and cancer risk: a
meta-analysis. Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet. 1:358–366.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gao LB, Bai P, Pan XM, Jia J, Li LJ, Liang
WB, Tang M, Zhang LS, Wei YG and Zhang L: The association between
two polymorphisms in pre-miRNAs and breast cancer risk: a
meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 125:571–574. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Z, Cao Y, Jiang C, Yang G, Wu J and
Ding Y: Lack of association of two common polymorphisms rs2910164
and rs11614913 with susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma: a
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 7:e400392012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guo J, Jin M, Zhang M and Chen K: A
genetic variant in miR-196a2 increased digestive system cancer
risks: a meta-analysis of 15 case-control studies. PLoS One.
7:e305852012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zambirinis CP, Theodoropoulos G and
Gazouli M: Undefined familial colorectal cancer. World J
Gastrointest Oncol. 1:12–20. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Burt R: Inheritance of colorectal cancer.
Drug Discov Today Dis Mech. 4:293–300. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Patel SG and Ahnen DJ: Familial colon
cancer syndromes: an update of a rapidly evolving field. Curr
Gastroenterol Rep. 14:428–438. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|