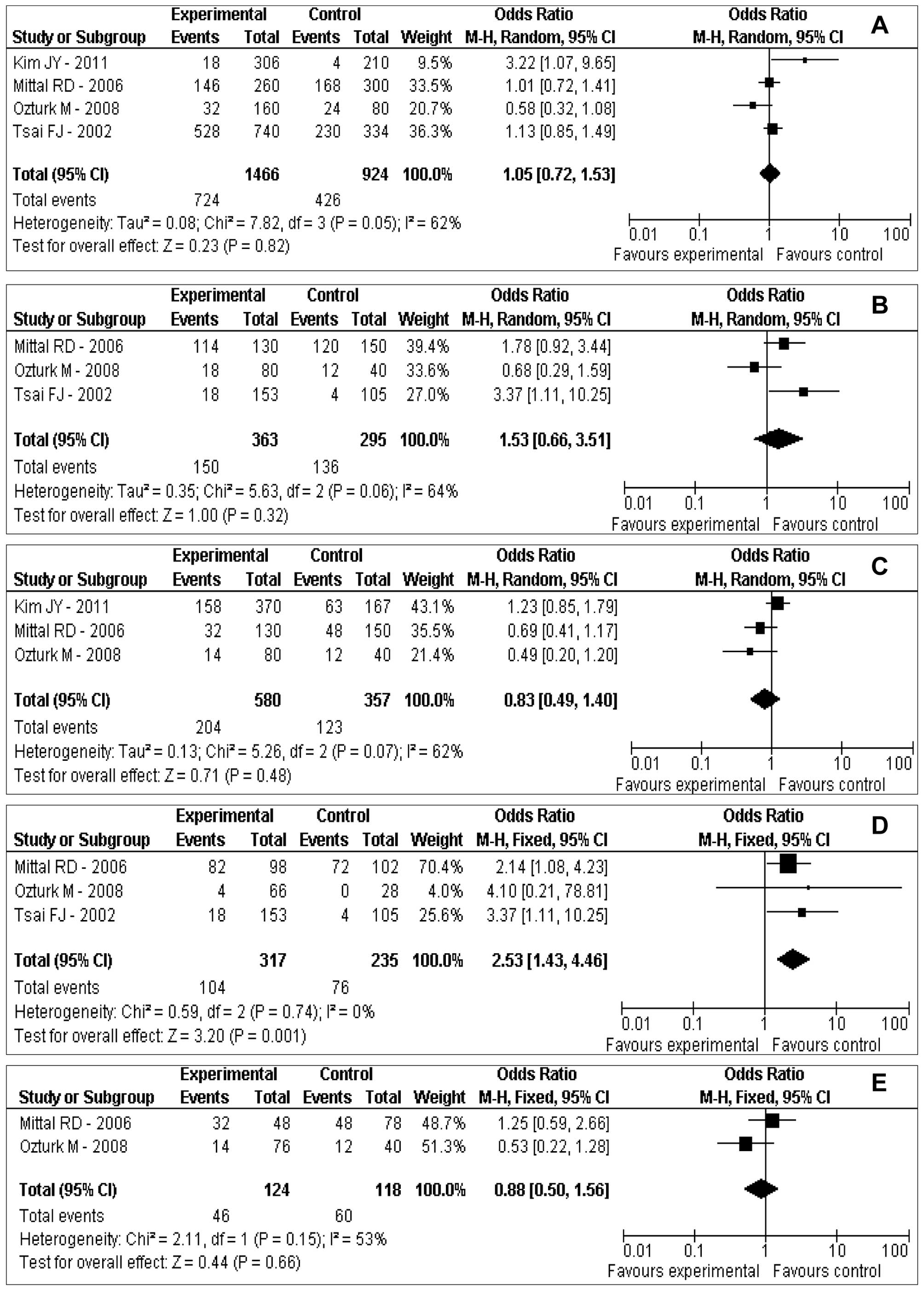
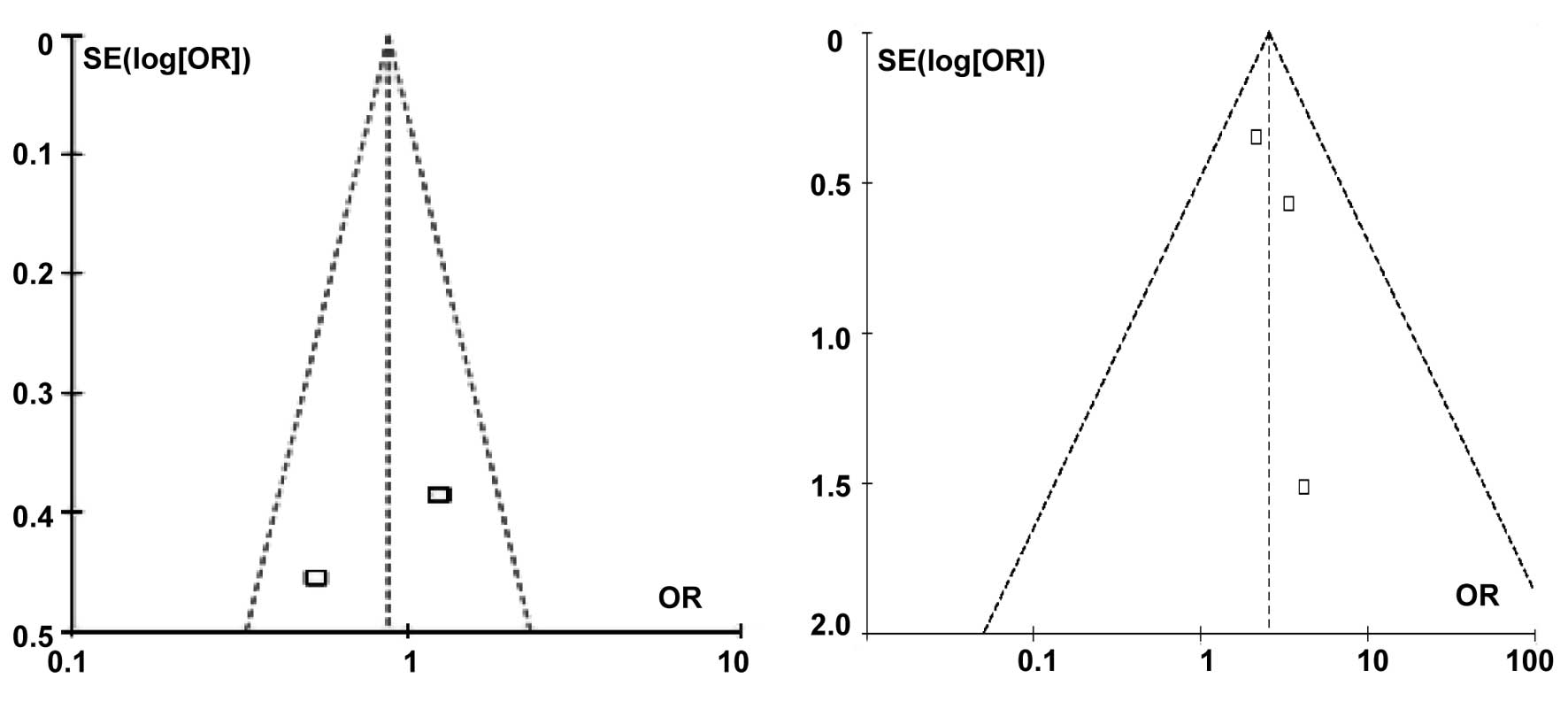
|
1
|
Johnson CM, Wilson DM, O’Fallon WM, Malek
RS and Kurland LT: Renal stone epidemiology: a 25-year study in
Rochester, Minnesota. Kidney Int. 16:624–631. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Caudarella R, Tonello L, Rizzoli E and
Vescini F: Predicting five-year recurrence rates of kidney stones:
an artificial neural network model. Arch Ital Urol Androl.
83:14–19. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Coe FL, Parks JH and Asplin JR: The
pathogenesis and treatment of kidney stones. N Engl J Med.
327:1141–1152. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Goodman HO, Brommage R, Assimos DG and
Holmes RP: Genes in idiopathic calcium oxalate stone disease. World
J Urol. 15:186–194. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wagner SN, Atkinson MJ, Wagner C, Höfler
H, Schmitt M and Wilhelm O: Sites of urokinase-type plasminogen
activator expression and distribution of its receptor in the normal
human kidney. Histochem Cell Biol. 105:53–60. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kitching AR, Holdsworth SR, Ploplis VA, et
al: Plasminogen and plasminogen activators protect against renal
injury in crescentic glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 185:963–968.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
du Toit PJ, van Aswegen CH, Steyn PL, Pols
A and du Plessis DJ: Effects of bacteria involved with the
pathogenesis of infection-induced urolithiasis on the urokinase and
sialidase (neuraminidase) activity. Urol Res. 20:393–397. 1992.
|
|
8
|
du Toit PJ, Van Aswegen CH, Steinmann CM,
Klue L and Du Plessis DJ: Does urokinase play a role in renal stone
formation? Med Hypotheses. 49:57–59. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Loder N: Genetic variations can point the
way to disease genes. Nature. 401:7341999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li D, Liu H, Yan L, Tang Y, Ren J and Xu
Z: Lack of association between hOGG1 Ser326Cys polymorphism and the
risk of bladder cancer: a meta-analysis. Urol Int. 88:88–94. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li D, Tian T, Guo C, et al: No association
of the MTHFR gene A1298C polymorphism with the risk of prostate
cancer: a meta-analysis. Exp Ther Med. 3:493–498. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gögebakan B, Igci YZ, Arslan A, et al:
Association between the T-593A and C6982T polymorphisms of the
osteopontin gene and risk of developing nephrolithiasis. Arch Med
Res. 41:442–448. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tripputi P, Blasi F, Verde P, Cannizzaro
LA, Emanuel BS and Croce CM: Human urokinase gene is located on the
long arm of chromosome 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 82:4448–4452.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Conne B, Berczy M and Belin D: Detection
of polymorphisms in the human urokinase-type plasminogen activator
gene. Thromb Haemost. 77:434–435. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shih CM, Kuo WH, Lin CW, et al:
Association of polymorphisms in the genes of the urokinase
plasminogen activation system with susceptibility to and severity
of non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 412:194–198. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mittal RD, Srivastava DS and Mishra DK: Is
urokinase gene 3′-UTR polymorphism associated with prostate cancer?
Cancer Biomark. 1:287–292. 2005.
|
|
17
|
Manchanda PK, Bid HK and Mittal RD:
Association of urokinase gene 3′-UTR T/C polymorphism with bladder
cancer. Urol Int. 77:81–84. 2006.
|
|
18
|
Tsai FJ, Lin CC, Lu HF, Chen HY and Chen
WC: Urokinase gene 3′-UTR T/C polymorphism is associated with
urolithiasis. Urology. 59:458–461. 2002.
|
|
19
|
Ozturk M, Kordan Y, Cangul H, et al:
Association of urokinase gene 3′-UTR T/C polymorphism with calcium
oxalate urolithiasis in children. Int Urol Nephrol. 40:563–568.
2008.
|
|
20
|
Mittal RD, Bid HK, Kumar A and Bhandari M:
Association of urokinase gene 3′-UTR polymorphism with calcium
oxalate nephrolithiasis. J Endourol. 20:157–160. 2006.
|
|
21
|
Kim JY, Kim YS, Chang IH, Kim TH and Kim
HR: Interleukin-1β, calcium-sensing receptor, and urokinase gene
polymorphisms in korean patients with urolithiasis. Korean J Urol.
52:340–344. 2011.
|
|
22
|
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ.
327:557–560. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee YH, Huang WC, Tsai JY, et al:
Epidemiological studies on the prevalence of upper urinary calculi
in Taiwan. Urol Int. 68:172–177. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
van Aswegen CH, Dirksen van Sckalckwyk JC,
du Toit PJ, Verster L, Franz RC and du Plessis DJ: The effect of
calcium and magnesium ions on urinary urokinase and sialidase
activity. Urol Res. 20:41–44. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang S, Wang X, Wu J, et al: Association
of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism and calcium urolithiasis in
the Chinese Han population. Urol Res. 40:277–284. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Klausner RD, Rouault TA and Harford JB:
Regulating the fate of mRNA: the control of cellular iron
metabolism. Cell. 72:19–28. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen K, Song F, Calin GA, Wei Q, Hao X and
Zhang W: Polymorphisms in microRNA targets: a gold mine for
molecular epidemiology. Carcinogenesis. 29:1306–1311. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ha M, Pang M, Agarwal V and Chen ZJ:
Interspecies regulation of microRNAs and their targets. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1779:735–742. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|