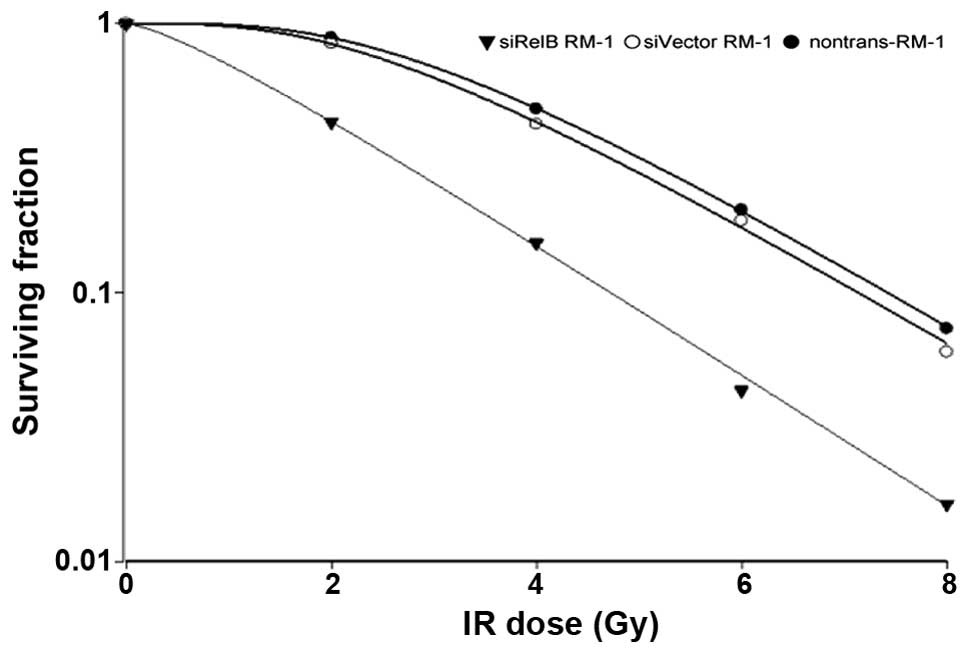
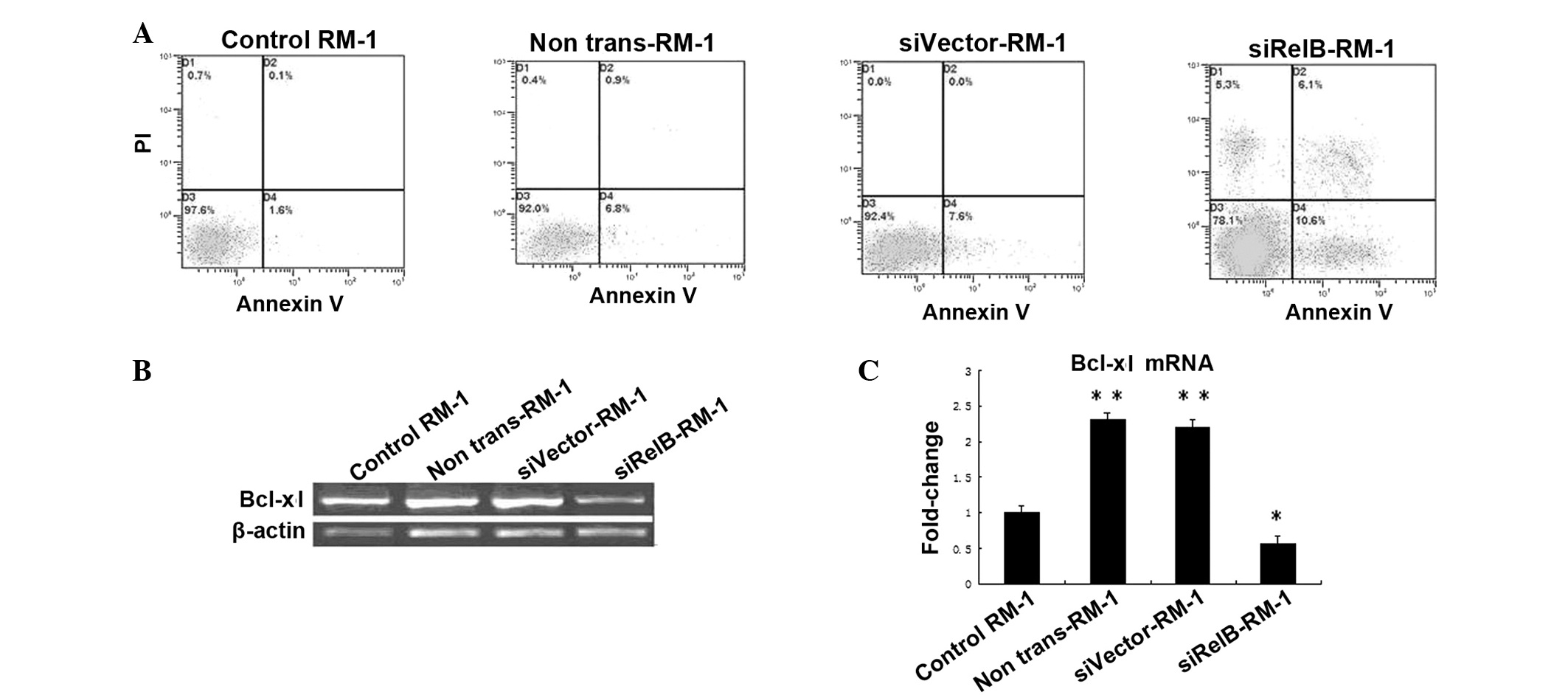
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic
and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:212–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xie BX, Zhang H, Yu L, et al: The
radiation response of androgen-refractory prostate cancer cell line
C4-2 derived from androgen-sensitive cell line LNCaP. Asian J
Androl. 12:405–414. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Alcorn S, Walker AJ, Gandhi N, et al:
Molecularly targeted agents as radiosensitizers in cancer therapy -
focus on prostate cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 14:14800–14832. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Holley AK, Xu Y, St Clair DK and St Clair
WH: RelB regulates manganese superoxide dismutase gene and
resistance to ionizing radiation of prostate cancer cells. Ann NY
Acad Sci. 1201:129–136. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu Y, Fang F, St Clair DK and St Clair WH:
Inverse relationship between PSA and IL-8 in prostate cancer: an
insight into a NF-κB-mediated mechanism. PLoS One.
7:e329052012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhu B, Yang LY, Zhao XK, et al: RNA
interference of RelB enhances the radiosensitivity of prostate
cancer cell line RM-1 in mice. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 18:595–599.
2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
7
|
Wong WW and Puthalakath H: Bcl-2 family
proteins: the sentinels of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway.
IUBMB Life. 60:390–397. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baud V and Karin M: Is NF-kappaB a good
target for cancer therapy? Hopes and pitfalls. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
8:33–40. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu Y, Fang F, Sun Y, et al: RelB-dependent
differential radiosensitization effect of STI571 on prostate cancer
cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:803–812. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ribeiro AM, Andrade S, Pinho F, et al:
Prostate cancer cell proliferation and angiogenesis in different
obese mice models. Int J Exp Pathol. 91:374–386. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu HC, Tao T and Liu XH: Construction and
identification of mouse RelB siRNA-expressing lentiviral vectors.
Sci Res Essays. 6:777–783. 2011.
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
13
|
Han RQ, Wu M, Chen WQ, et al: Analysis on
incidence and mortality of prostate cancer in China during
2003–2007. China Cancer. 21:805–811. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
14
|
Dass K, Ahmad A, Azmi AS, Sarkar SH and
Sarkar FH: Evolving role of uPA/uPAR system in human cancers.
Cancer Treat Rev. 34:122–136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang AL and Russell PJ: Paclitaxel
suppresses the growth of primary prostate tumours (RM-1) and
metastases in the lung in C57BL/6 mice. Cancer Lett. 233:185–191.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu Y, Fang F, St Clair DK, et al: SN52, a
novel nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor, blocks nuclear import of
RelB:p52 dimer and sensitizes prostate cancer cells to ionizing
radiation. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:2367–2376. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu Y, Fang F, St Clair DK, et al:
Suppression of RelB-mediated manganese superoxide dismutase
expression reveals a primary mechanism for radiosensitization
effect of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) in prostate cancer cells.
Mol Cancer Ther. 6:2048–2056. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Josson S, Xu Y, Fang F, et al: RelB
regulates manganese superoxide dismutase gene and resistance to
ionizing radiation of prostate cancer cells. Oncogene.
25:1554–1559. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Russo A, Terrasi M, Agnese V, et al:
Apoptosis: a relevant tool for anticancer therapy. Ann Oncol.
17(Suppl 7): vii115–vii123. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mineva ND, Rothstein TL, Meyers JA, et al:
CD40 ligand-mediated activation of the de novo RelB NF-kappaB
synthesis pathway in transformed B cells promotes rescue from
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 282:17475–17485. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Llambi F and Green DR: Apoptosis and
oncogenesis: give and take in the BCL-2 family. Curr Opin Genet
Dev. 21:12–20. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Strik H, Deininger M, Streffer J, et al:
BCL-2 family protein expression in initial and recurrent
glioblastomas: modulation by radiochemotherapy. J Neurol Neurosurg
Psychiatry. 67:763–768. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li JY, Li YY, Jin W, et al: ABT-737
reverses the acquired radioresistance of breast cancer cells by
targeting Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:1022012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang J, Sun M, Zhang A, et al:
Adenovirus-mediated siRNA targeting Bcl-xL inhibits proliferation,
reduces invasion and enhances radiosensitivity of human colorectal
cancer cells. World J Surg Oncol. 9:1172011. View Article : Google Scholar
|