|
1
|
Melian E: Radiation therapy in neurologic
disease. Handb Clin Neurol. 121:1181–1198. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
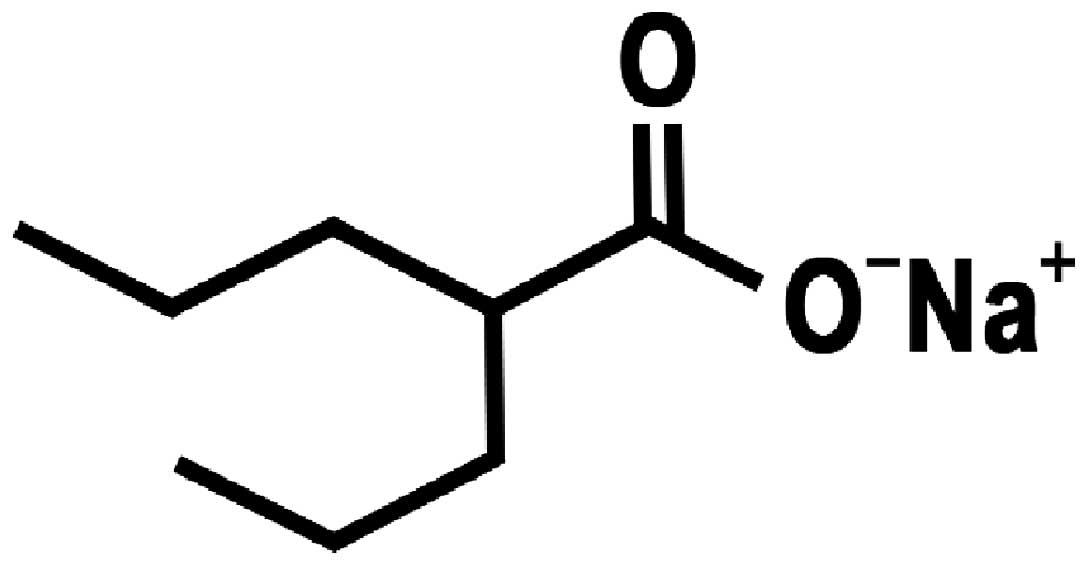
2
|
Wong CS and Van der Kogel AJ: Mechanisms
of radiation injury to the central nervous system: implications for
neuroprotection. Mol Interv. 4:273–284. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brown SL, Kolozsvary A, Liu J, Ryu S and
Kim JH: Histone deacetylase inhibitors protect against and mitigate
the lethality of total-body irradiation in mice. Radiat Res.
169:474–478. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chung YL, Lee MY and Pui NN: Epigenetic
therapy using the histone deacetylase inhibitor for increasing
therapeutic gain in oral cancer: prevention of radiation-induced
oral mucositis and inhibition of chemical-induced oral
carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 30:1387–1397. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wu X, Chen PS, Dallas S, et al: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors up-regulate astrocyte GDNF and BDNF gene
transcription and protect dopaminergic neurons. Int J
Neuropsychopharmacol. 11:1123–1134. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Purrucker JC, Fricke A, Ong MF, Rube C,
Rube CE and Mahlknecht U: HDAC inhibition radiosensitizes human
normal tissue cells and reduces DNA double-strand break repair
capacity. Oncol Rep. 23:263–269. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Peterson GM and Naunton M: Valproate: a
simple chemical with so much to offer. J Clin Pharm Ther.
30:417–421. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Phiel CJ, Zhang F, Huang EY, Guenther MG,
Lazar MA and Klein PS: Histone deacetylase is a direct target of
valproic acid, a potent anticonvulsant, mood stabilizer, and
teratogen. J Biol Chem. 276:36734–36741. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gӧttlicher M, Minucci S, Zhu P, et al:
Valproic acid defines a novel class of HDAC inhibitors inducing
differentiation of transformed cells. EMBO J. 20:6969–6978.
2001.
|
|
10
|
Marks PA, Miller T and Richon VM: Histone
deacetylases. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 3:344–351. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Camphausen K, Cerna D, Scott T, et al:
Enhancement of in vitro and in vivo tumor cell radiosensitivity by
valproic acid. Int J Cancer. 114:380–386. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chinnaiyan P, Cerna D, Burgan WE, Beam K,
Williams ES, Camphausen K and Tofilon PJ: Postradiation
sensitization of the histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid.
Clin Cancer Res. 14:5410–5415. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Van Nifterik KA, Van den Berg J, Slotman
BJ, Lafleur MV, Sminia P and Stalpers LJ: Valproic acid sensitizes
human glioma cells for temozolomide and γ-radiation. J Neurooncol.
107:61–67. 2012.
|
|
14
|
Zhou Y, Xu Y, Wang H, Niu J, Hou H and
Jiang Y: Histone deacetylase inhibitor, valproic acid,
radiosensitizes the C6 glioma cell line in vitro. Oncol
Lett. 7:203–208. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lai JS, Zhao C, Warsh JJ and Li PP:
Cytoprotection by lithium and valproate varies between cell types
and cellular stresses. Eur J Pharmacol. 539:18–26. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Castro LM, Gallant M and Niles LP: Novel
targets for valproic acid: up-regulation of melatonin receptors and
neurotrophic factors in C6 glioma cells. J Neurochem. 95:1227–1236.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mizumatsu S, Monje ML, Morhardt DR, Rola
R, Palmer TD and Fike JR: Extreme sensitivity of adult neurogenesis
to low doses of X-irradiation. Cancer Res. 63:4021–4027.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zabolotskii NN, Onishchenko LS and Galeev
IS: Mitochondrial megaconia and pleioconia in the rat brain as
possible adaptive reactions in conditions of lethal radiation and
radiomodified lesions. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 30:497–501. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yildirim O, Comoğlu S, Yardimci S, Akmansu
M, Bozkurt G and Sürücü S: Preserving effect of melatonin on the
levels of glutathione and malondialdehyde in rats exposed to
irradiation. Gen Physiol Biophys. 27:32–37. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yuan H, Gaber MW, Boyd K, Wilson CM, Kiani
MF and Merchant TE: Effects of fractionated radiation on the brain
vasculature in murine model: blood-brain barrier permeability,
astrocyte proliferation, and ultrastructural changes. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 66:860–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Cicciarello R, d'Avella D, Gagliardi ME,
et al: Time-related ultrastructural changes in an experimental
model of whole brain irradiation. Neurosurgery. 38:772–780. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vinchon-Petit S, Janet D, Jadaud E,
Feuvret L, Garcion E and Menei P: External irradiation models for
intracranial 9L glioma studies. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 29:1422010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Munshi A, Kurland JF, Nishikawa T, et al:
Histone deacetylase inhibitors radiosensitize human melanoma cells
by suppressing DNA repair activity. Clin Cancer Res. 11:4912–4922.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Blattmann C, Oertel S, Ehemann V, et al:
Enhancement of radiation response in osteosarcoma and
rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines by histone deacetylase inhibition. Int
J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 78:237–245. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stoilov L, Darroudi F, Meschini R, van der
Schans G, Mullenders LH and Nararajan AT: Inhibition of repair of
X-ray-induced DNA double-strand breaks in human lymphocytes exposed
to sodium butyrate. Int J Radiat Biol. 76:1485–1491. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chung YL, Wang AJ and Yao LF: Antitumor
histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress cutaneous radiation
syndrome: Implications for increasing therapeutic gain in cancer
radiotherapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 3:317–325. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li YQ, Jay V and Wong CS: Oligodendrocytes
in the adult rat spinal cord undergo radiation-induced apoptosis.
Cancer Res. 56:5417–5422. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chow BM, Li YQ and Wong CS:
Radiation-induced apoptosis in the adult central nervous system is
p53-dependent. Cell Death Differ. 7:712–720. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Atkinson SL, Li YQ and Wong CS: Apoptosis
and proliferation of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells in the
irradiated rodent spinal cord. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
62:535–544. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lu FG and Wong CS: Radiation-induced
apoptosis of oligodendrocytes and its association with increased
ceramide and down-regulated protein kinase B/Akt activity. Int J
Radiat Biol. 80:39–51. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vrdoljak E, Bill CA, Stephens LC, van der
Kogel AJ, Ang KK and Tofilon PJ: Radiation-induce apoptosis of
oligodendrocytes in vitro. Int J Radiat Biol. 62:475–480. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gu C, Casaccia-Bonnefil P, Srinivasan A
and Chao MV: Oligodendrocyte apoptosis mediated by caspase
activation. J Neurosci. 19:3043–3049. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lin HI, Lee YJ, Chen BF, et al:
Involvement of Bcl-2 family, cytochrome c and caspase 3 in
induction of apoptosis by beauvericin in human non-small cell lung
cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 230:248–259. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim DS, Jeon SE, Jeong YM, Kim SY, Kwon SB
and Park KC: Hydrogen peroxide is a mediator of indole-3-acetic
acid/horseradish peroxidise-induced apoptosis. FEBS Lett.
580:1439–1446. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zuliani T, Obriot H, Tual M, et al:
Variable Bax antigenicity is linked to keratinocyte position within
epidermal strata and UV-induced apoptosis. Exp Dermatol.
17:125–132. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Park SK, Kang H and Kwon CH:
Caspase-dependent cell death mediates potent cytotoxicity of
sulfide derivatives of 9-anilinoacridine. Anticancer Drugs.
19:381–389. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Soane L, Rus H, Niculescu F and Shin ML:
Inhibition of oligodendrocyte apoptosis by sublytic C5b-9 is
associated with enhanced synthesis of bcl-2 and mediated by
inhibition of caspase-3 activation. J Immunol. 163:6132–6138.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ferrer I: Role of caspases in ionizing
radiation-induced apoptosis in the developing cerebellum. J
Neurobiol. 41:549–558. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Michelin S, del Rosario Perez M, Dubner D
and Gisone P: Increased activity and involvement of caspase-3 in
radiation-induced apoptosis in neural cells precursors from
developing rat brain. Neurotoxicology. 25:387–398. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mathias S, Pena LA and Kolesnick RN:
Signal transduction of stress via ceramide. Biochem J. 335:465–480.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ferrer I: The effect of cycloheximide on
natural and X-ray-induced cell death in the developing cerebral
cortex. Brain Res. 588:351–357. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Brush J, Lipnick SL, Phillips T, Sitko J,
McDonald JT and McBride WH: Molecular mechanisms of late normal
tissue injury. Semin Radiat Oncol. 17:121–130. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li YQ, Guo YP, Jay V, Stewart PA and Wong
CS: Time course of radiation-induced apoptosis in the adult rat
spinal cord. Radiother Oncol. 39:35–42. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li YQ and Wong CS: Radiation-induced
apoptosis in the neonatal and adult rat spinal cord. Radiat Res.
154:268–276. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hopewell JW: Late radiation damage to the
central nervous system: a radiobiological interpretation.
Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 5:329–343. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ito M, Patronas NJ, Di Chiro G, Mansi L
and Kennedy C: Effect of moderate level X-radiation to brain on
cerebral glucose utilization. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 10:584–588.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Keyeux A: Late modifications of cephalic
circulation in head x-irradiated rats. Radiat Environ Biophys.
13:125–135. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kubota Y, Takahashi S, Sun XZ, Sato H,
Aizawa S and Yoshida K: Radiation-induced tissue abnormalities in
fetal brain are related to apoptosis immediately after irradiation.
Int J Radiat Biol. 76:649–659. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Fike JR, Gobbel GT, Chou D, Wijnhoven BP,
Bellinzona M, Nakagawa M and Seilhan TM: Cellular proliferation and
infiltration following interstitial irradiation of normal dog brain
is altered by an inhibitor of polyamine synthesis. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 32:1035–1045. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|